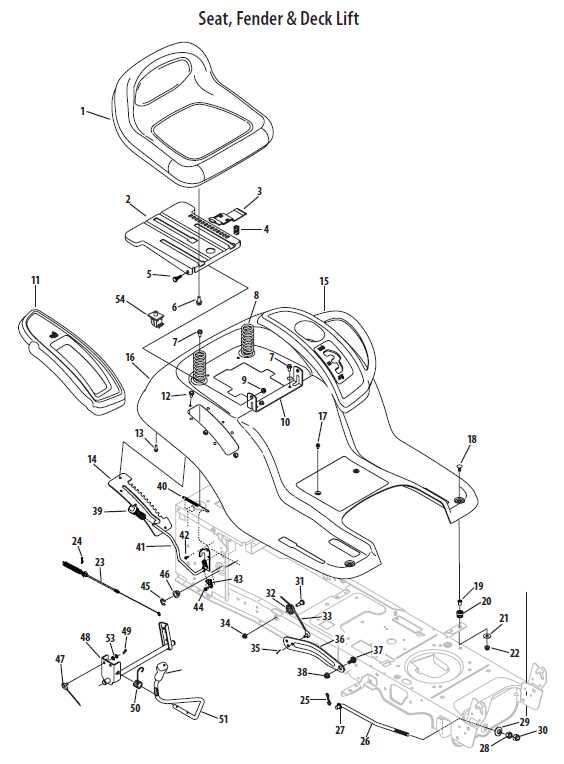
Overview of Ltx1040 Parts Diagram and Components
Understanding the internal structure and layout of various elements in a machine is crucial for ensuring smooth operation and timely maintenance. A detailed visual representation of these elements can significantly simplify the process of identifying the correct item for replacement or repair.
Efficient planning when it comes to upkeep can save both time and resources. By focusing on each component and its placement, users can better navigate the overall system, enabling faster solutions to technical issues.
Whether you are a professional mechanic or handling routine checks, having access to a structured and detailed overview of the system’s layout will improve your ability to address issues with precision.
Understanding the Mower Structure
The internal composition of the lawn tractor is designed to ensure efficient operation across various terrains. This section provides an overview of its key components and how they interact to deliver smooth performance during use. By examining the arrangement of its mechanical and functional systems, users can gain insight into the machine’s overall design.
Main Components of the Cutting System
The cutting mechanism plays a crucial role in maintaining lawns. It includes several key elements that work together to ensure precise trimming. Each part is strategically placed to contribute to the effectiveness of the machine, from the blades to the support elements. This system enables efficient grass cutting while maintaining durability.
Transmission and Movement
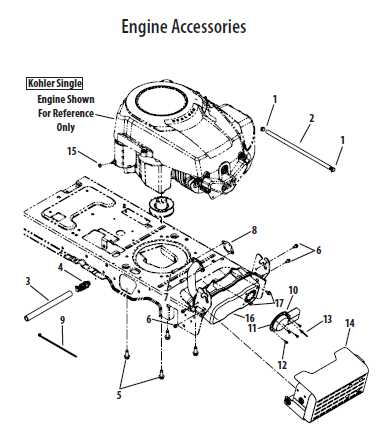
The propulsion system is another vital aspect, helping the machine move seamlessly over various surfaces. The connection between the engine and the drive system allows for a steady pace while minimizing strain on the motor. This ensures both stability and ease of control, making the equipment reliable for longer periods of operation.
| Component | Function |
|---|
| Component | Description | Specifications |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Tank | Reservoir for storing fuel. | Capacity: 10 gallons |
| Fuel Pump | Pumps fuel from the tank to the engine. | Flow Rate: 30 GPH |
| Fuel Filter | Removes impurities from the fuel. | Micron Rating: 10 microns |
| Fuel Injector | Atomizes fuel for efficient combustion. | Type: Electronic |
| Fuel Lines | Transport fuel between components. | Material: Reinforced rubber |
Understanding the layout and specifications of each element helps ensure the fuel system operates efficiently, providing optimal performance.
Tire and Wheel Assembly Details
The assembly of tires and wheels is a crucial component in ensuring optimal performance and safety in various machinery. Understanding the structure and characteristics of this assembly helps in maintaining and troubleshooting issues effectively.
Key components involved in the tire and wheel assembly include:
- Tires: The outer part that provides traction and supports the load.
- Rims: The metal framework that holds the tire in place.
- Valves: Essential for maintaining air pressure within the tire.
- Hub: The central part that connects the wheel to the axle.
- Bearings: Allow smooth rotation of the wheel.
Proper assembly ensures that all components fit securely and function together harmoniously. Regular inspections of the tire and wheel assembly can prevent performance issues and extend the lifespan of the machinery.
When addressing maintenance, consider the following aspects:
- Check for wear and tear on tires.
- Inspect rims for damage or corrosion.
- Ensure valves are functioning correctly to avoid air leaks.
- Verify the tightness of bolts connecting the wheel to the hub.
- Lubricate bearings to ensure smooth movement.
Understanding these details enhances the overall efficiency and reliability of the equipment, ensuring safe and effective operation.
Brake and Safety Mechanism Explained
The braking and safety systems play a vital role in ensuring the smooth and secure operation of machinery. These components work together to provide effective stopping power while minimizing the risk of accidents. Understanding how these mechanisms function can help users maintain and operate their equipment more safely.
There are several key elements involved in the braking and safety system:
- Braking System: This component is responsible for slowing down or stopping the machinery. It typically consists of a series of parts that work in tandem to create friction and bring the machine to a halt.
- Safety Features: Various safety measures are integrated to prevent unintended movement or accidents. These may include automatic shut-off switches and emergency brakes that activate in critical situations.
- Control Mechanisms: Operators can manage the braking system through various controls, ensuring precise handling and responsiveness during operation.
To ensure optimal performance, regular maintenance of the braking and safety systems is essential. Users should routinely check for wear and tear on components and address any issues promptly. This proactive approach not only enhances safety but also extends the lifespan of the machinery.
In summary, understanding the intricacies of the braking and safety systems is crucial for effective operation. By familiarizing oneself with these components, users can enhance their safety and the overall functionality of their equipment.
Chassis and Frame Structure Design
The design of the chassis and frame structure is fundamental to ensuring stability and durability in any vehicle. A well-engineered framework not only supports the overall weight but also influences handling and performance. Understanding the intricacies of these components is crucial for optimizing the vehicle’s functionality and safety.
Various elements contribute to the effectiveness of the chassis and frame structure, including materials used, design geometry, and load distribution. The integration of advanced engineering principles allows for the development of lightweight yet robust structures that can withstand various operational stresses.
| Component | Function | Material Used |
|---|---|---|
| Main Frame | Supports the vehicle’s body and components | Steel or Aluminum |
| Cross Members | Enhances rigidity and structural integrity | High-Strength Steel |
| Suspension Mounts | Connects suspension systems to the frame | Cast Iron or Steel |
| Chassis Brackets | Facilitates attachment of various components | Steel |