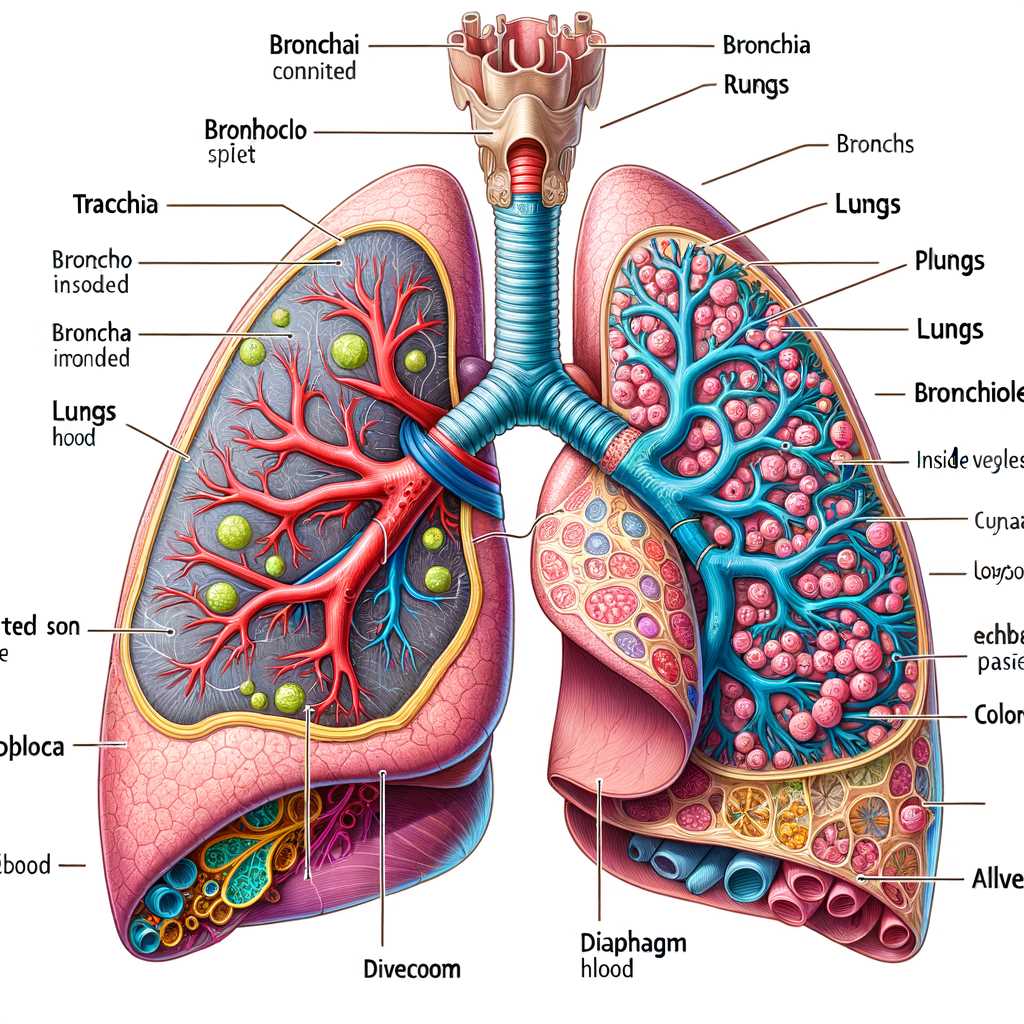
Understanding the Anatomy of the Lungs Through Detailed Diagrams

The intricate system responsible for facilitating gas exchange is vital to sustaining life. This complex arrangement consists of various elements that work harmoniously to ensure efficient respiration. By exploring the individual components, we can gain deeper insights into their specific functions and interconnections.
Each section of this system plays a crucial role in the overall functionality, contributing to the vital process of inhalation and exhalation. From the outer membranes that protect delicate tissues to the inner chambers responsible for transferring oxygen and carbon dioxide, every feature is designed for optimal performance. Understanding these elements enhances our appreciation for the remarkable efficiency of this biological mechanism.
Visual representations can greatly aid in comprehending the layout and relationships between these components. By examining such illustrations, one can visualize how each section integrates into the larger framework, ultimately facilitating the essential exchange of gases that keeps us alive. This knowledge not only serves academic purposes but also fosters a greater respect for the intricacies of our biological systems.
Lung Anatomy Overview
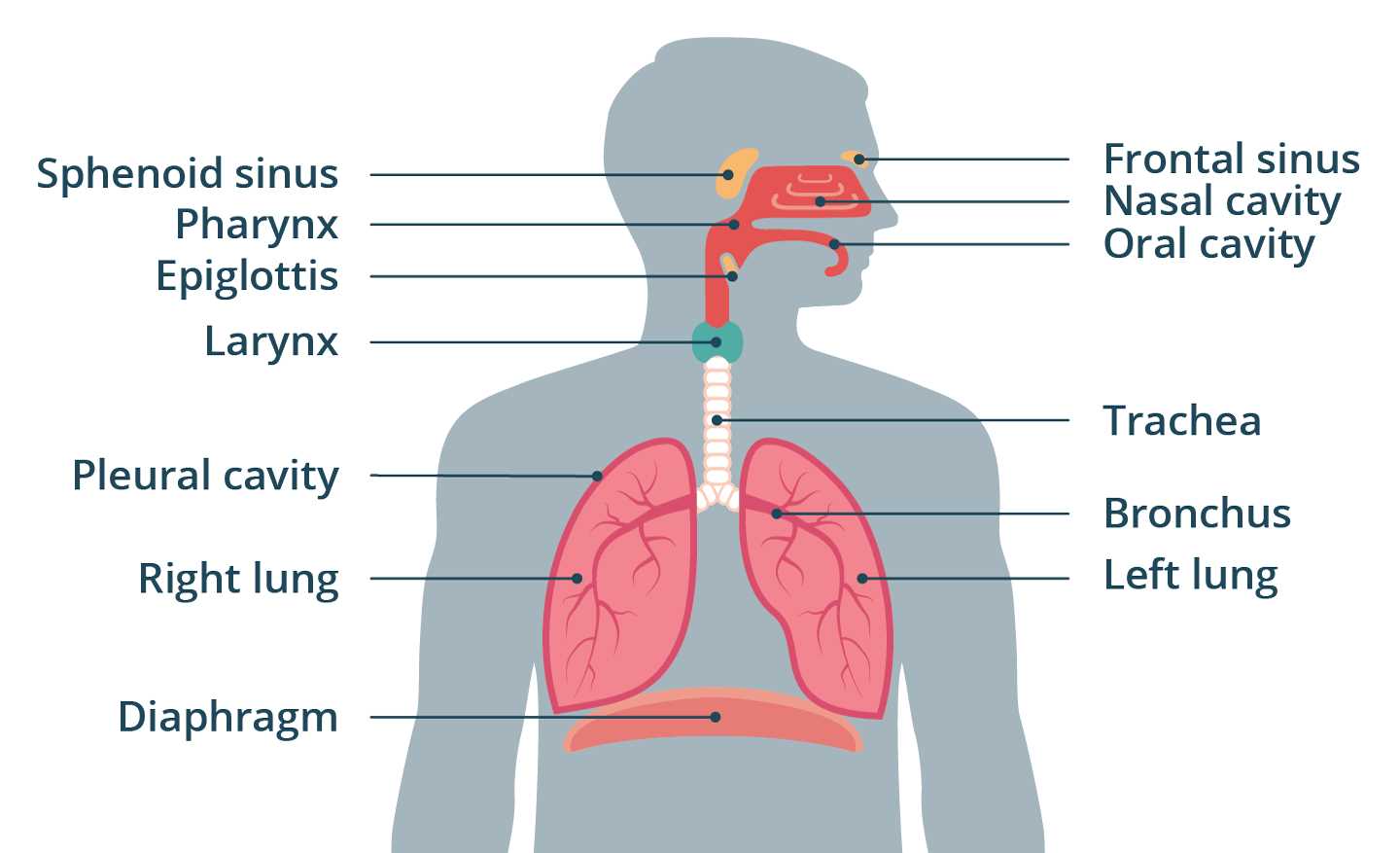
The respiratory system is a complex structure essential for gas exchange, enabling the body to take in oxygen and expel carbon dioxide. This intricate system comprises various components, each playing a critical role in maintaining respiratory efficiency and overall health.
Main Components
- Airways
- Alveoli
- Blood Vessels
- Supporting Tissues
Functionality
Each element works in harmony to facilitate breathing and ensure effective oxygen transfer. Key functionalities include:
- Transporting air to and from the external environment.
- Moistening and warming inhaled air.
- Filtering out particulates and pathogens.
- Exchanging gases at the cellular level.
Key Components of Lung Structure
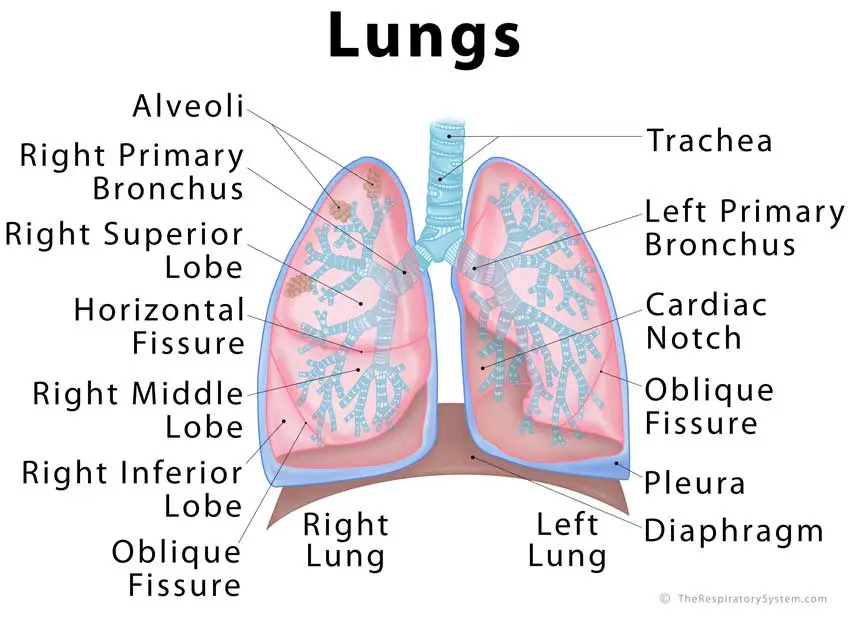
This section explores the fundamental elements that contribute to the overall function and efficiency of the respiratory system. Understanding these structures is essential for grasping how gases are exchanged and how air flows within the body.
Primary Structures
The essential components include various types of tissues and specialized formations that facilitate breathing and oxygen transfer. Each element plays a crucial role in maintaining respiratory health.
Functional Characteristics
These structures exhibit unique features that allow for optimal performance in gas exchange, highlighting their importance in the respiratory process.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Bronchi | Air passageways leading to the lungs. |
| Alveoli | Site of gas exchange with blood. |
| Pleura | Membranes providing protection and reducing friction. |
| Diaphragm | Muscle aiding in the inhalation process. |
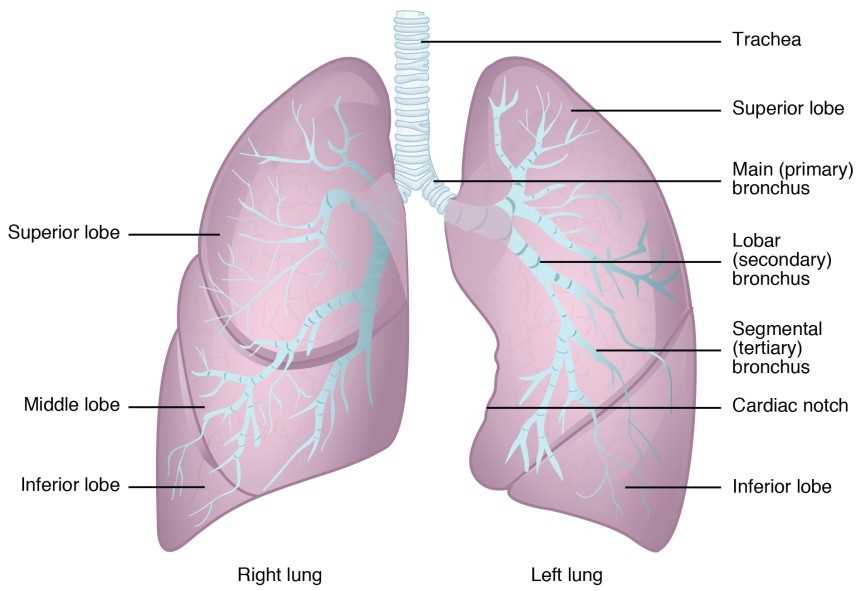
Functions of Different Lung Parts
The respiratory system comprises various components, each playing a vital role in the process of breathing and gas exchange. Understanding how these structures contribute to overall functionality provides insight into their significance in maintaining health.
Key Functions
- Gas Exchange: The primary function involves transferring oxygen into the bloodstream and removing carbon dioxide.
- Air Filtration: Specific structures filter out dust, allergens, and pathogens, ensuring cleaner air reaches deeper tissues.
- Regulation of pH: By controlling carbon dioxide levels, these components help maintain acid-base balance in the body.
Supporting Roles
- Sound Production: Certain regions are essential for vocalization and communication.
- Temperature Control: Structures help warm or cool incoming air, protecting delicate internal tissues.
- Moisture Regulation: These components add moisture to inhaled air, preventing dryness in the respiratory tract.
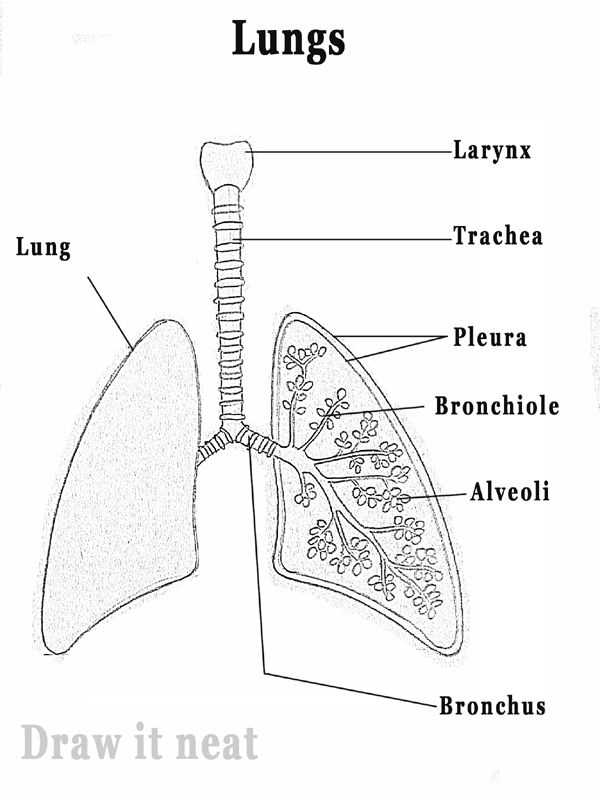
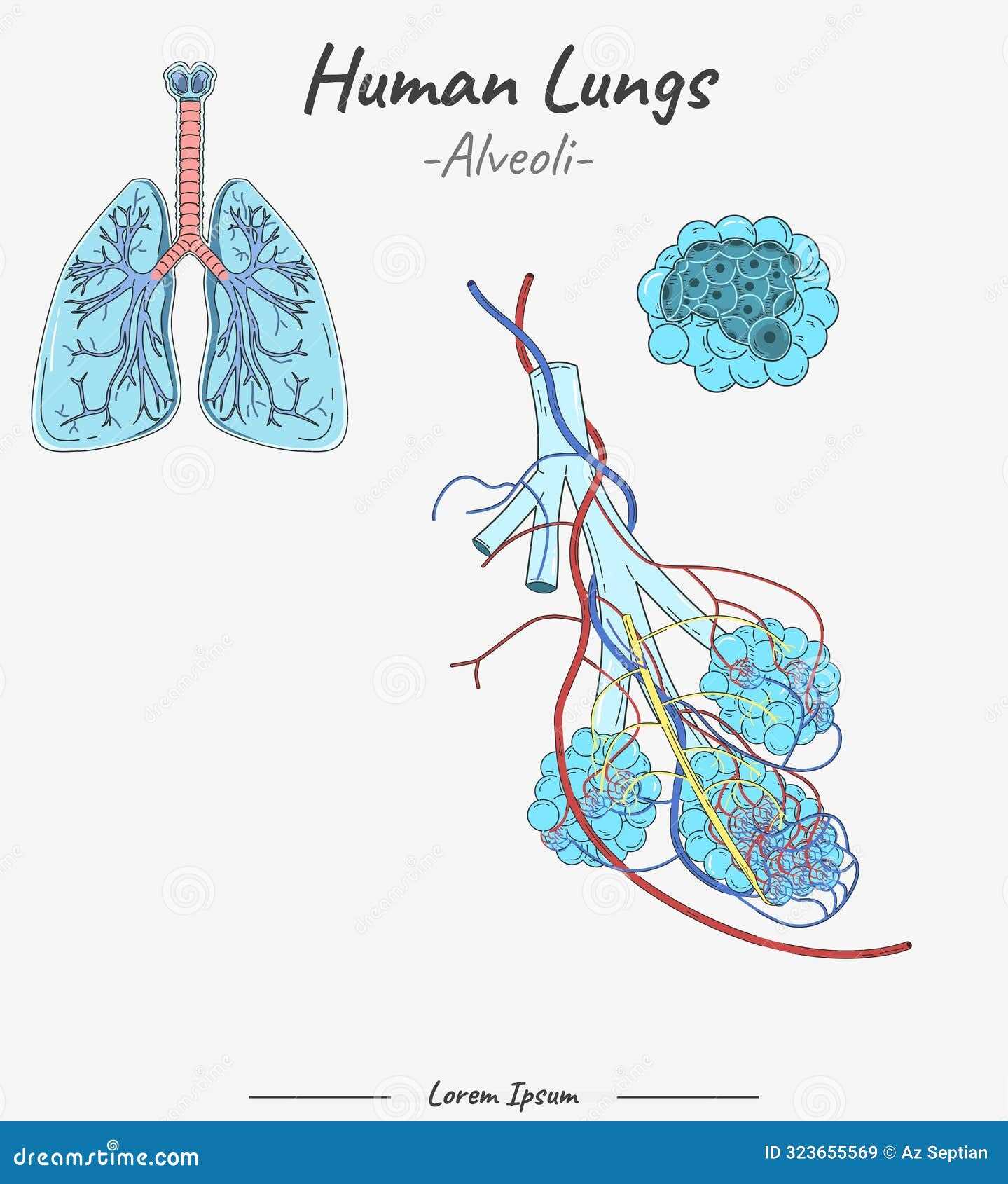
How Alveoli Facilitate Gas Exchange
The tiny air sacs in the respiratory system play a crucial role in the process of exchanging gases between the body and the environment. This intricate mechanism ensures that oxygen enters the bloodstream while carbon dioxide is expelled, supporting vital functions within the body.
The Structure of Alveoli
These microscopic structures have unique characteristics that enhance their efficiency:
- Thin Walls: The walls are extremely thin, allowing for rapid diffusion of gases.
- Large Surface Area: A vast network increases the area available for gas exchange.
- Moist Lining: A thin layer of moisture facilitates the movement of gases.
The Process of Gas Exchange
Gas exchange occurs through a series of steps:
- Inhalation brings oxygen-rich air into the sacs.
- Oxygen diffuses across the thin walls into the surrounding capillaries.
- Simultaneously, carbon dioxide moves from the blood into the sacs.
- Exhalation expels carbon dioxide-laden air from the body.
This continuous cycle is essential for maintaining healthy bodily functions, ensuring that cells receive the oxygen they need while removing waste products efficiently.
The Role of Bronchi and Bronchioles
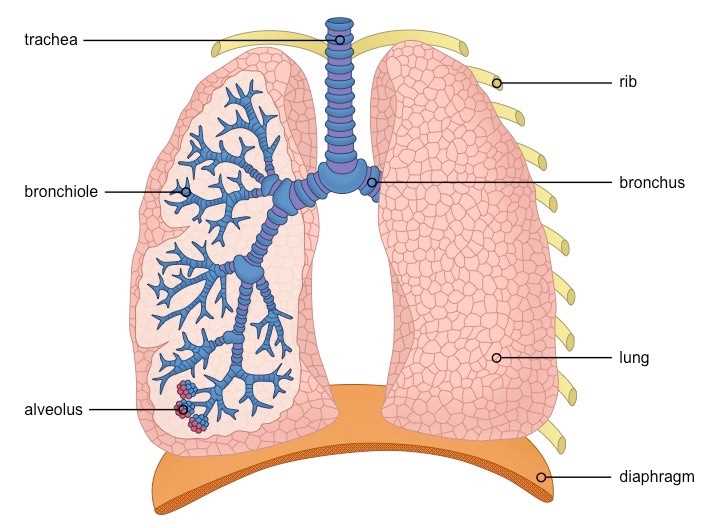
The intricate network of air passageways plays a crucial role in facilitating the movement of air to and from the regions responsible for gas exchange. These structures ensure that oxygen reaches the alveoli while allowing for the efficient removal of carbon dioxide. Their architecture and functionality are vital for maintaining respiratory health and optimizing the exchange process.
Bronchi, the larger conduits branching from the trachea, serve as the primary channels directing air into each side of the thoracic cavity. Their rigid structure, supported by cartilage, prevents collapse during inhalation and exhalation. This durability is essential for withstanding the pressure changes that occur with each breath.
As the bronchi divide into smaller branches, they transition into bronchioles, which are narrower and more flexible. These smaller airways lack cartilage and instead rely on smooth muscle to regulate airflow. This adaptability allows bronchioles to constrict or dilate in response to various stimuli, such as allergens or irritants, thereby controlling the volume of air reaching the alveolar sacs.
Furthermore, the inner lining of these passageways is equipped with cilia and mucus-producing cells. The cilia help trap and expel particles and pathogens, safeguarding the delicate tissues involved in gas exchange. This defense mechanism is essential for preventing infections and maintaining optimal respiratory function.
In summary, the bronchi and bronchioles are indispensable components of the respiratory system, playing a multifaceted role in airflow management and protection against harmful agents. Their proper functioning is essential for sustaining the body’s oxygen supply and overall health.
Understanding Pleura and Its Importance
The pleura is a vital structure that plays a significant role in respiratory health. This double-layered membrane surrounds and protects the organs responsible for breathing, providing a critical interface between the chest cavity and the organs themselves.
Key functions of the pleura include:
- Protection: It serves as a shield, minimizing the risk of injury to the organs during movement.
- Fluid Secretion: The pleura produces a lubricating fluid that facilitates smooth expansion and contraction during inhalation and exhalation.
- Pressure Regulation: It helps maintain the pressure necessary for optimal respiratory function, ensuring efficient gas exchange.
Understanding the significance of this membrane is crucial for recognizing various medical conditions that may arise, such as:
- Pleurisy, an inflammation that can cause sharp chest pain.
- Pneumothorax, which occurs when air leaks into the space between the pleura layers.
- Hydrothorax, characterized by excess fluid accumulation in the pleural space.
In summary, the pleura is not merely a protective layer; it is integral to the overall functionality of the respiratory system, making awareness of its role essential for both health professionals and the general public.
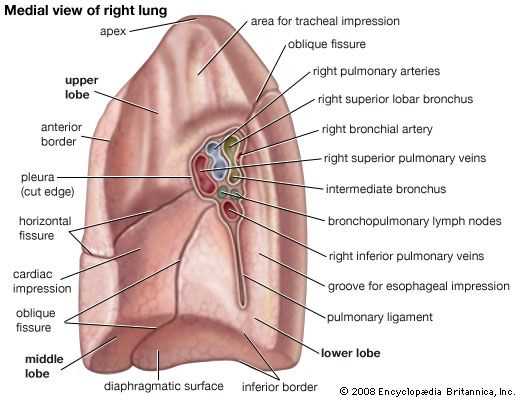
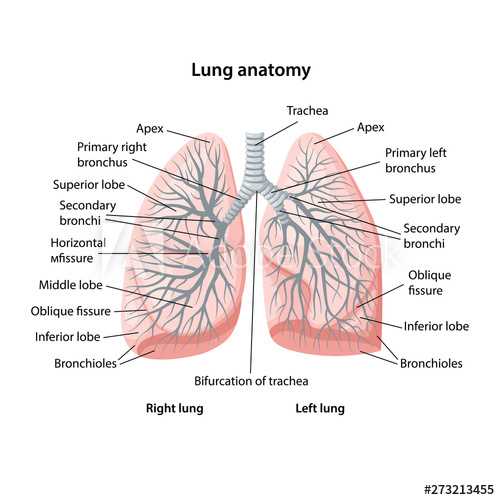
Lung Lobes: Their Unique Functions
The respiratory system consists of distinct regions, each playing a vital role in the overall process of gas exchange. Understanding these areas enhances our knowledge of their individual contributions to respiratory health and efficiency.
Each region has specific responsibilities:
- Right Superior Region: Primarily involved in oxygen intake and carbon dioxide expulsion.
- Right Middle Region: Plays a crucial role in air filtration and humidification.
- Right Inferior Region: Essential for nutrient absorption from the air.
- Left Superior Region: Aids in optimizing oxygen saturation in the bloodstream.
- Left Inferior Region: Functions to maintain balance in gas concentrations within the body.
Exploring these unique functions reveals the intricate design of the respiratory system and its adaptability to various demands.
Visual Representation of Lung Parts
This section aims to provide an illustrative overview of the essential components responsible for respiration. A clear visual layout enhances understanding of the intricate structures involved in the process of breathing, showcasing their organization and interconnections.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Bronchi | The main air passages that branch from the trachea into each lung, facilitating airflow. |
| Alveoli | Microscopic sacs where gas exchange occurs, crucial for oxygen uptake and carbon dioxide removal. |
| Diaphragm | A muscular structure that plays a vital role in inhalation and exhalation by contracting and relaxing. |
| Bronchioles | Smaller branches of the bronchi leading to the alveoli, regulating airflow and gas exchange. |
| Pleura | A double-layered membrane surrounding the lungs, providing lubrication and protection. |
Common Lung Diseases Explained
Understanding the various conditions that affect our respiratory system is crucial for maintaining health. Many ailments can impact breathing efficiency, leading to discomfort and serious health issues. Below are some prevalent disorders that individuals may encounter.
- Asthma: A chronic condition characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways, causing wheezing, shortness of breath, and chest tightness.
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): A progressive disease that includes emphysema and chronic bronchitis, resulting in airflow obstruction and difficulty in breathing.
- Pneumonia: An infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs, which may fill with fluid or pus, causing cough, fever, and difficulty breathing.
- Interstitial Lung Disease: A group of disorders that cause scarring of lung tissue, leading to stiffness and reduced ability to take in air.
- Tuberculosis: A serious infectious disease that primarily affects the respiratory system, causing severe cough, weight loss, and night sweats.
Awareness of these conditions can aid in early detection and treatment. Regular check-ups and being attentive to symptoms are vital for optimal respiratory health.
Impact of Lifestyle on Lung Health
The way we live significantly influences our respiratory well-being. Daily habits, from diet to physical activity, play a crucial role in maintaining optimal function of the respiratory system. Understanding these connections can help individuals make informed choices to promote better health.
Factors Affecting Respiratory Function
Several lifestyle factors can adversely affect the efficiency of the respiratory system. Smoking remains one of the most detrimental habits, while pollution and a sedentary lifestyle also contribute to declining respiratory health. On the other hand, nutritious diets and regular exercise can enhance overall vitality.
Healthy Practices for Better Respiratory Health
Incorporating specific practices can lead to improved respiratory function. Strategies such as avoiding tobacco, engaging in aerobic exercises, and consuming a balanced diet rich in antioxidants can make a significant difference.
| Practice | Impact |
|---|---|
| Avoiding Smoking | Reduces risk of respiratory diseases |
| Regular Exercise | Enhances lung capacity and efficiency |
| Healthy Diet | Boosts immune function and reduces inflammation |
Advancements in Lung Research Techniques
Recent innovations in the field of respiratory studies have significantly transformed our understanding of the respiratory system. These advancements enable researchers to explore intricate mechanisms, improving diagnostic capabilities and therapeutic approaches. By employing cutting-edge technologies, scientists are uncovering new insights that were previously beyond reach.
Novel Imaging Techniques
One of the most notable developments is the use of advanced imaging methods, such as high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). These techniques provide unprecedented detail, allowing for a more thorough examination of the structure and function of the respiratory tissues. As a result, conditions can be identified at much earlier stages, leading to timely and effective interventions.
Genomic and Molecular Insights
Furthermore, the integration of genomic technologies into research practices has opened new avenues for understanding respiratory disorders at a molecular level. Techniques like next-generation sequencing facilitate the identification of genetic markers associated with various diseases, enhancing personalized medicine approaches. This shift towards a more tailored strategy promises to improve outcomes for individuals affected by respiratory ailments.