Miller Furnace Parts Diagram Explained
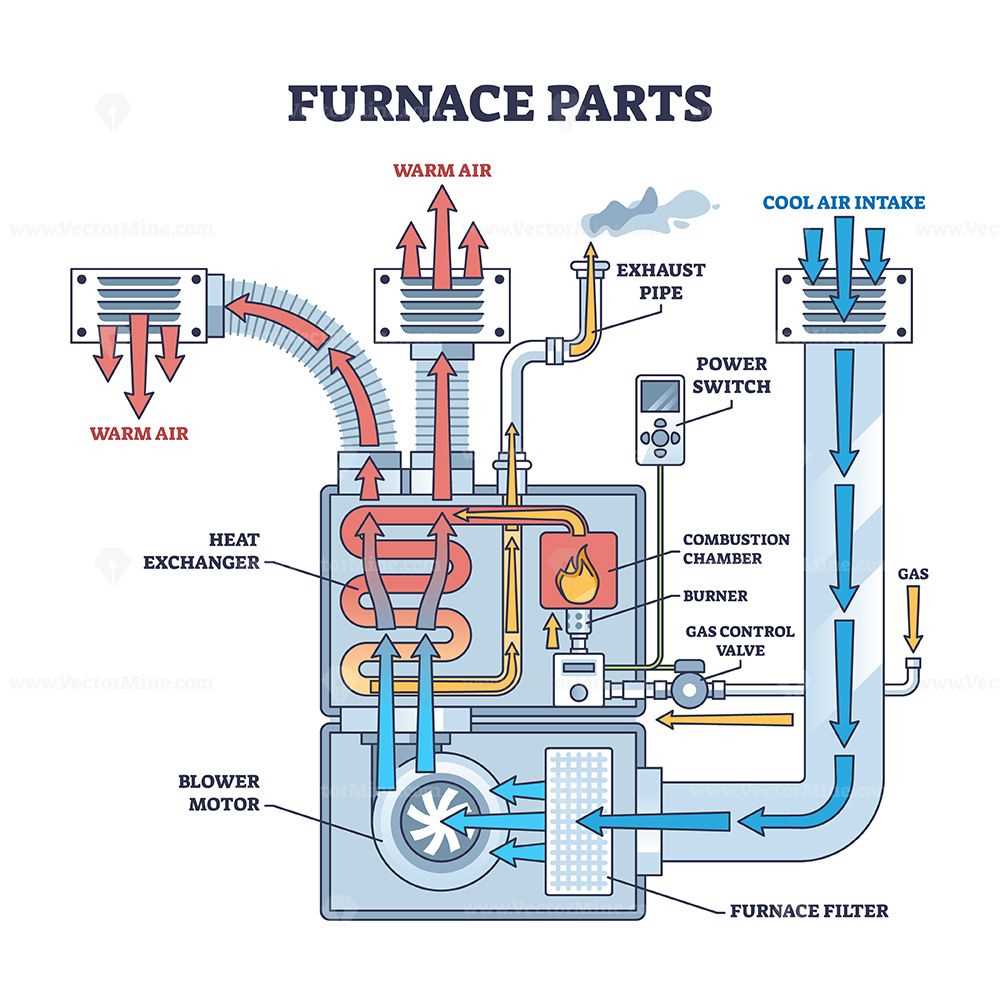
In the realm of heating technology, the intricacies of various systems can often be overwhelming. A comprehensive grasp of the individual elements that contribute to effective temperature regulation is essential for both maintenance and optimization. Each component plays a pivotal role in ensuring seamless functionality, and understanding their arrangement can significantly enhance performance.
Visual representations serve as invaluable tools in deciphering the layout and interconnections among these essential elements. By examining such illustrations, one can gain insights into how each section interacts with others, revealing the intricate dance of energy flow and mechanical operations. This knowledge not only aids in troubleshooting but also empowers users to make informed decisions regarding upgrades or repairs.
Whether you are a seasoned technician or a homeowner seeking to deepen your understanding, familiarizing yourself with the structure of these systems can lead to more effective management and longevity of your heating apparatus. Emphasizing the significance of each segment fosters a greater appreciation for the technology that keeps our environments comfortable.
Miller Furnace Overview
This section provides a comprehensive understanding of the essential components and functionality of a specific heating system. Designed for efficiency and reliability, these systems play a crucial role in maintaining optimal indoor climate conditions. The interplay of various elements ensures smooth operation and longevity, making them vital for residential and commercial applications.
Key Features
One of the standout characteristics of this heating system is its innovative design, which promotes energy efficiency. With advanced technology integrated into its operation, users can expect reduced energy consumption while achieving effective temperature regulation. Additionally, maintenance requirements are minimized, allowing for a hassle-free user experience.
Common Applications

This heating solution is widely utilized in various settings, from homes to larger facilities. Its adaptability makes it suitable for both residential warmth and industrial processes, ensuring that users benefit from a reliable source of heat across different environments. Safety and performance are prioritized, ensuring peace of mind for all users.
Importance of Furnace Components
The functionality and efficiency of any heating system are deeply rooted in its various elements. Each component plays a pivotal role, ensuring the system operates smoothly and meets its intended purpose. Understanding the significance of these elements can lead to better maintenance and enhanced performance.
Critical Roles in Operation
Every individual element contributes to the overall effectiveness of the system. From regulating temperature to ensuring safety, these components work in harmony. For instance, sensors monitor conditions, while ignitors initiate the heating process. A malfunction in any of these parts can disrupt the entire system, leading to inefficiencies and potential hazards.
Impact on Efficiency and Longevity
Regular maintenance of these essential components not only boosts operational efficiency but also extends the lifespan of the system. Keeping each element in optimal condition reduces energy consumption and minimizes wear and tear. Therefore, understanding their importance is crucial for both performance and sustainability.
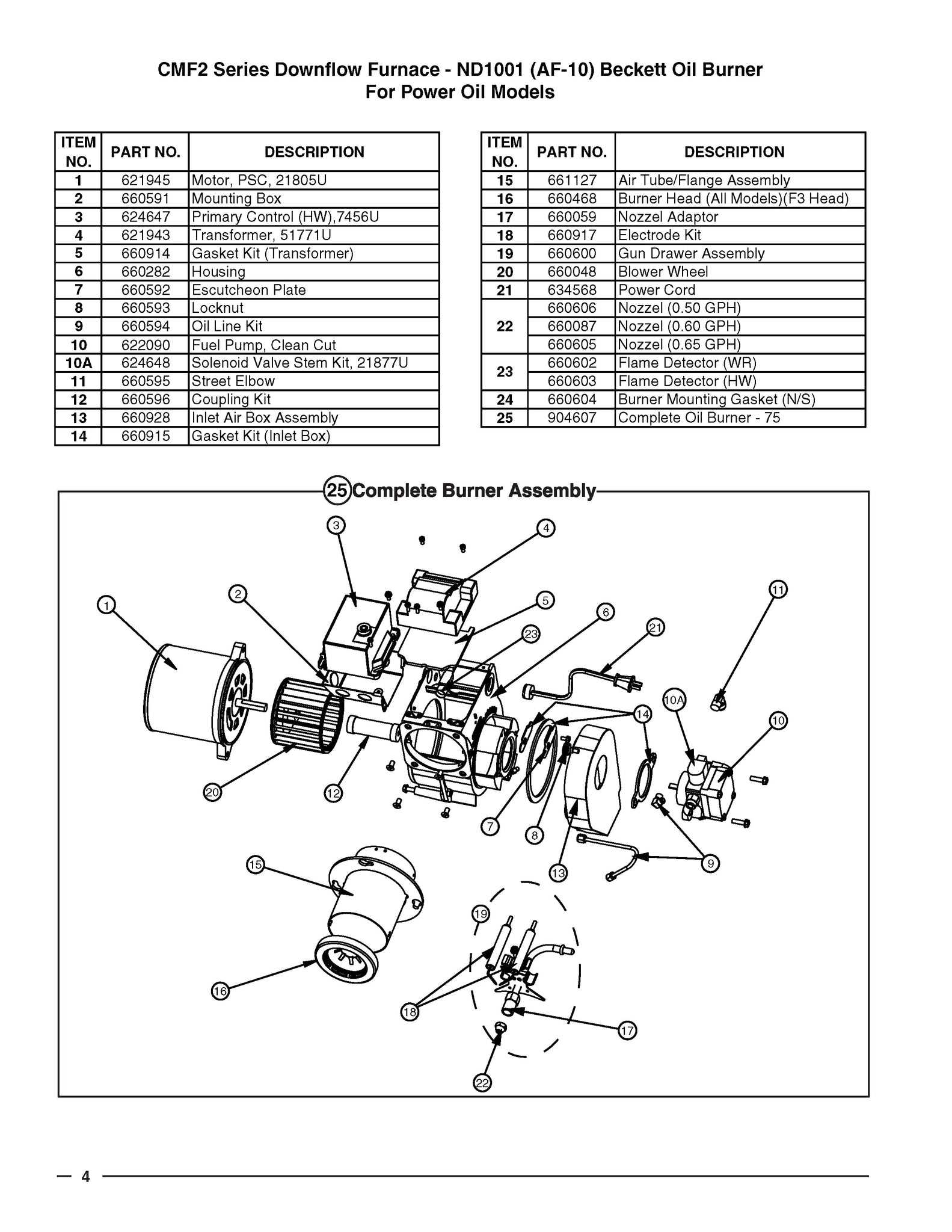
Common Parts in Miller Furnaces
Understanding the essential components of a heating system is crucial for effective operation and maintenance. Each element plays a vital role in ensuring efficiency and reliability. Below are some of the frequently encountered components in these heating units.
- Heat Exchanger: This is the primary element where heat transfer occurs, allowing warm air to circulate through the space.
- Burner Assembly: Responsible for igniting the fuel, this component ensures a consistent and controlled flame.
- Blower Motor: This part drives the airflow, distributing heated air throughout the environment.
- Thermostat: A crucial device for temperature regulation, it monitors and adjusts the heat output based on user settings.
- Control Board: This electronic component orchestrates the operation of various elements, responding to signals from the thermostat and safety devices.
- Safety Limit Switch: Designed to prevent overheating, this switch shuts down the system when temperatures exceed safe levels.
- Ignition System: This may include a pilot light or electronic ignition, initiating the combustion process safely and efficiently.
- Flue System: Essential for venting combustion gases outside, it helps maintain indoor air quality.
Familiarity with these components can enhance understanding of the system’s functionality and aid in troubleshooting potential issues.
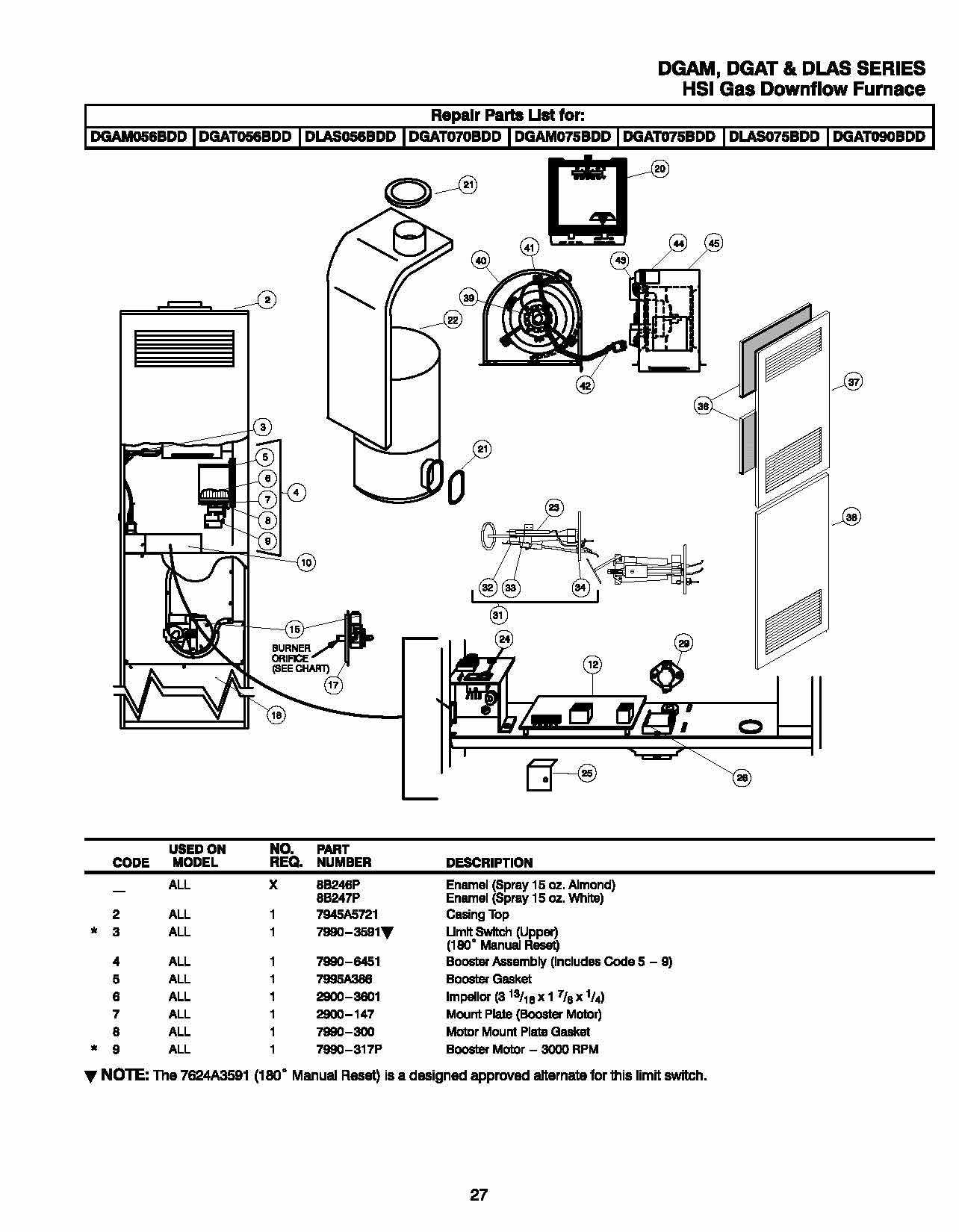
Understanding the Diagram Layout
The arrangement of components in a schematic representation is crucial for comprehending how different elements interact within a system. By analyzing the layout, one can identify key features and their relationships, facilitating a deeper understanding of operational mechanics.
Key Components of the Layout
- Symbols: Each element is represented by a specific symbol, denoting its function and type.
- Connections: Lines and arrows indicate how different components are linked, illustrating pathways for energy or signals.
- Labels: Annotations provide essential information, such as part numbers, specifications, or operational notes.
Interpreting Relationships
- Start by identifying the main units in the layout.
- Trace the connections to understand how energy flows through the system.
- Refer to the labels for additional context and specifications that may influence performance.
By systematically analyzing these aspects, one can develop a comprehensive grasp of how each element contributes to overall functionality.
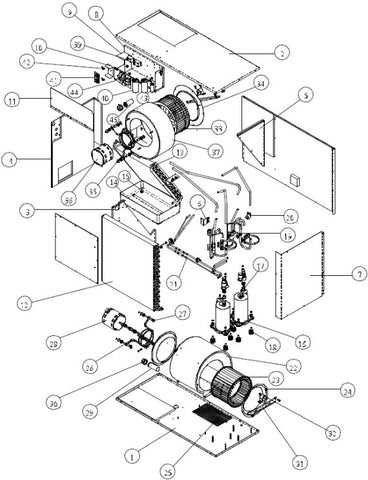
Functionality of Each Component
Understanding the role of each element within a heating system is essential for effective operation and maintenance. Each component plays a distinct part, contributing to the overall efficiency and safety of the unit. By exploring these functions, one can gain insight into the system’s performance and identify potential issues before they escalate.
Key Elements and Their Roles
Every system consists of several key elements, each designed to fulfill specific tasks. Below is a breakdown of these components along with their respective functionalities.
| Component | Functionality |
|---|---|
| Burner | Ignites and maintains the combustion process for heat generation. |
| Heat Exchanger | Transfers heat from the combustion gases to the air or water being heated. |
| Blower | Circulates air throughout the system and into the living spaces. |
| Thermostat | Monitors and regulates the temperature settings within the environment. |
| Control Panel | Central hub for managing system operations and settings. |
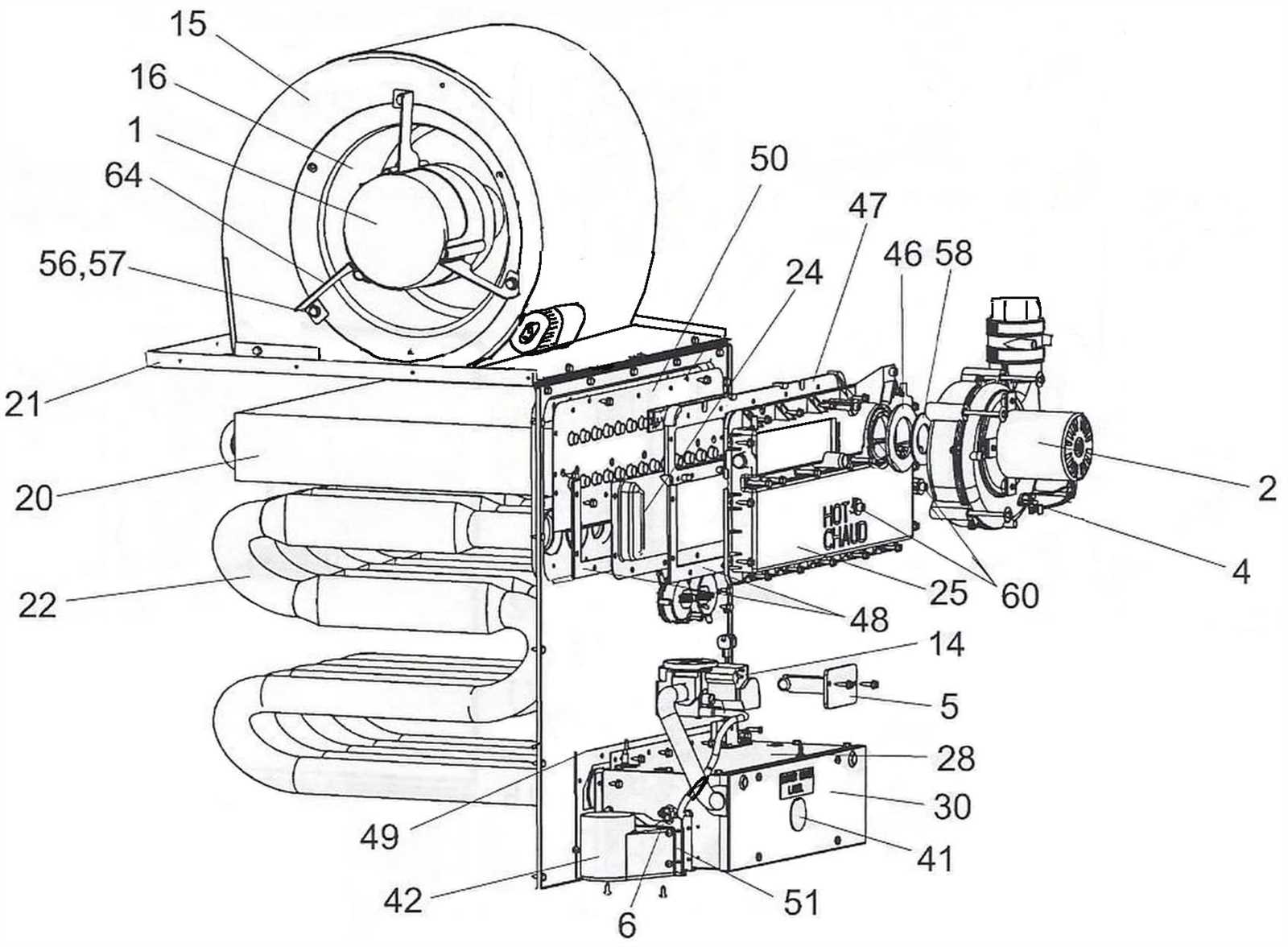
Additional Components
In addition to the primary elements, various auxiliary components enhance the system’s reliability and safety. Recognizing their contributions can further improve understanding and troubleshooting.
| Component | Functionality |
|---|---|
| Flame Sensor | Detects the presence of a flame and ensures safe operation. |
| Draft Inducer | Facilitates proper venting of exhaust gases, promoting safety and efficiency. |
| Safety Valve | Prevents overpressure by releasing excess pressure within the system. |
| Ignition System | Initiates the combustion process to begin heating. |
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
Ensuring the extended lifespan of your heating system requires regular attention and care. By adopting a proactive approach to maintenance, you can enhance efficiency, minimize the risk of breakdowns, and save on energy costs. Here are essential practices to keep your unit operating smoothly.
| Tip | Description |
|---|---|
| Regular Cleaning | Dust and debris can accumulate, leading to inefficiency. Clean the unit and surrounding areas periodically. |
| Check Filters | Replace or clean filters every few months to ensure optimal airflow and system performance. |
| Inspect Vents | Ensure that all vents are unobstructed to allow for proper air circulation throughout your space. |
| Schedule Professional Inspections | Have a qualified technician inspect the system at least once a year to catch potential issues early. |
| Monitor Performance | Pay attention to unusual sounds or fluctuations in temperature, as these can indicate underlying problems. |
Common Issues and Solutions
When dealing with heating systems, various challenges can arise that affect efficiency and performance. Identifying these common problems is crucial for maintaining optimal operation and ensuring longevity. Here, we explore frequent complications and their practical remedies.
1. Inconsistent Heating: A common issue is uneven warmth throughout the space. This can often be resolved by checking for blocked vents or ducts. Ensuring that air passages are clear will promote better circulation.
2. Unusual Noises: If you hear rattling or banging sounds, this could indicate loose components. Tightening any loose screws or fittings can often eliminate these disturbances, improving overall functionality.
3. Increased Energy Bills: Unexpected spikes in energy costs may signal inefficiencies. Regular maintenance, such as cleaning filters and inspecting insulation, can help restore efficiency and lower expenses.
4. Short Cycling: If the system frequently turns on and off, it could be a sign of a malfunctioning thermostat or an oversized unit. Adjusting the thermostat settings or consulting with a professional to assess sizing may be necessary.
5. Odors: Strange smells can indicate various issues, from dust accumulation to potential gas leaks. If unusual odors persist, it’s essential to conduct a thorough inspection and, if needed, contact a technician immediately.
By recognizing these common complications and implementing effective solutions, users can enhance the performance and reliability of their heating systems.
Replacement Parts Availability
Ensuring the functionality of heating equipment often relies on the availability of essential components. A robust supply chain for these items is crucial for maintaining operational efficiency and extending the lifespan of the equipment.
Finding reliable sources for necessary replacements can significantly affect maintenance strategies. Here are some key factors to consider when looking for suitable alternatives:
| Source Type | Description |
|---|---|
| OEM Suppliers | Original manufacturers offer components specifically designed for optimal compatibility and performance. |
| Aftermarket Vendors | Third-party companies provide alternatives that may be more cost-effective while still meeting industry standards. |
| Local Distributors | Regional suppliers often carry a selection of components for quick access, reducing downtime. |
| Online Marketplaces | Web-based platforms provide a vast array of choices and often include user reviews to guide purchasing decisions. |
When seeking replacements, it’s important to evaluate the quality and compatibility of the components to ensure seamless integration and performance. Making informed decisions can lead to significant benefits in both efficiency and cost savings.
How to Read the Diagram
Understanding a schematic representation is crucial for effective troubleshooting and maintenance. By familiarizing yourself with the various symbols and connections, you can gain insights into the operational flow and identify potential issues.
Here are some essential steps to effectively interpret the representation:
- Familiarize with Symbols:
- Identify common symbols used for different components.
- Refer to a legend if available, which explains each symbol in detail.
- Trace the Flow:
- Start from the power source or entry point.
- Follow the connections to see how energy or signals move through the system.
- Note the Connections:
- Look for lines that indicate electrical or fluid pathways.
- Check for junctions or nodes where multiple paths meet.
- Identify Key Components:
- Locate vital elements that play a significant role in operation.
- Understand their functions within the overall system.
- Analyze Annotations:
- Pay attention to any notes or labels that provide additional context.
- These may indicate specifications or operational parameters.
By following these steps, you can effectively decode the schematic and enhance your understanding of the entire system. This knowledge will empower you to perform maintenance tasks with greater confidence and accuracy.
Safety Precautions During Repair
Ensuring safety during maintenance tasks is paramount to preventing accidents and injuries. Proper precautions should always be taken to create a secure working environment, especially when dealing with complex machinery. Awareness of potential hazards and adherence to safety protocols can significantly reduce risks associated with repairs.
First and foremost, always disconnect the power source before initiating any repair work. This simple step can prevent electric shocks and other dangerous situations. Additionally, using personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, goggles, and masks is crucial to safeguard against harmful substances and debris.
Furthermore, familiarize yourself with the specific equipment and its components before beginning repairs. Understanding the functionality and potential risks associated with each part can help in identifying safe handling practices. It’s also advisable to have a detailed manual or guide on hand for reference during the process.
Maintaining a clean and organized workspace can minimize hazards as well. Ensure that tools and materials are readily accessible and free from clutter. This will help maintain focus and reduce the likelihood of accidents occurring due to distractions.
Lastly, if you are unsure about any aspect of the repair, do not hesitate to seek assistance from a qualified professional. Knowledge and experience can make a significant difference in ensuring a safe and successful repair.
DIY vs. Professional Repairs
When it comes to fixing equipment at home, individuals often face a choice between tackling the task themselves or hiring a professional. Each approach has its own set of advantages and challenges that can impact the outcome and efficiency of the repair process.
DIY repairs can be appealing for several reasons:
- Cost savings, as labor fees are eliminated.
- Flexibility in scheduling, allowing repairs to be done at one’s convenience.
- A sense of accomplishment and skill-building through hands-on experience.
However, there are also potential drawbacks to consider:
- Risk of improper repairs, which can lead to further damage.
- Lack of specialized knowledge, making troubleshooting more difficult.
- Time investment that may exceed initial expectations.
On the other hand, professional assistance offers distinct benefits:
- Expertise and experience, ensuring the job is done correctly.
- Access to specialized tools and equipment that may not be available at home.
- Warranties on work performed, providing peace of mind.
Nonetheless, opting for a professional may come with its own challenges:
- Higher costs due to labor and service fees.
- Scheduling conflicts, which may delay repairs.
- Less personal involvement in the repair process, which some may find unsatisfying.
Ultimately, the decision between DIY repairs and hiring a professional depends on factors such as the complexity of the issue, personal skills, and the urgency of the repair needed.
Upgrading Components for Efficiency
Enhancing the effectiveness of your heating system involves a thoughtful examination and replacement of outdated elements. By investing in modern components, you can significantly improve energy consumption, reduce operational costs, and increase overall performance. This process not only boosts efficiency but also extends the lifespan of the entire unit.
Benefits of Modernization

Upgrading individual elements can lead to numerous advantages. For instance, newer designs often incorporate advanced technologies that enhance heat transfer and minimize energy losses. Additionally, improved materials can resist wear and tear, ensuring long-lasting reliability.
Key Components to Consider
When contemplating upgrades, focus on these essential elements:
| Component | Upgrade Options | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Exchanger | High-efficiency models | Improved heat transfer, lower emissions |
| Blower Motor | Variable speed motors | Energy savings, quieter operation |
| Thermostat | Smart thermostats | Enhanced control, remote accessibility |
| Burner Assembly | High-efficiency burners | Increased combustion efficiency, reduced fuel usage |
By prioritizing these upgrades, you can transform your heating system into a more efficient and sustainable solution, ultimately benefiting both your wallet and the environment.
Resources for Further Information
To enhance your understanding of heating systems and their components, a variety of resources are available. These materials can provide valuable insights into the functionality, maintenance, and troubleshooting of these essential appliances. Below are some recommended types of sources to explore.
Online Resources
The internet is rich with websites dedicated to home improvement and HVAC systems. You can find tutorials, forums, and expert articles that cover a range of topics from installation to repair.
Books and Manuals
Consider consulting instructional books or user manuals that offer comprehensive information on heating equipment. These texts often include detailed illustrations and step-by-step guidance.
| Type of Resource | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Websites | Informative platforms with articles and forums. | Home improvement blogs, HVAC forums |
| Books | In-depth guides covering installation and maintenance. | HVAC for Dummies, manuals by manufacturers |
| Videos | Tutorials demonstrating repairs and setup. | YouTube channels focused on home repairs |