Understanding the Components of a Grape Vine Diagram
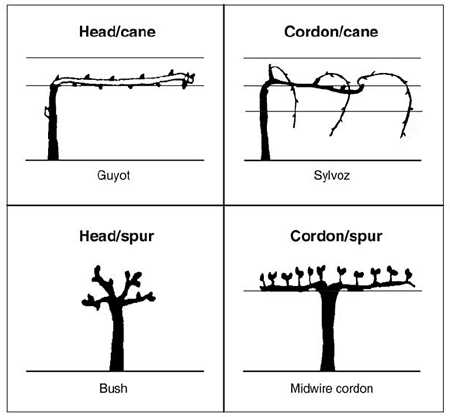
In the intricate world of horticulture, the anatomy of climbing flora offers a fascinating glimpse into their life cycle and growth patterns. Each component plays a crucial role in sustaining the organism, allowing it to thrive in various environments. A closer look reveals how these elements interconnect to support overall health and productivity.
From the foundational roots that anchor the organism to the soil, to the leaves that capture sunlight for energy, every section contributes to its vitality. Understanding these components not only enhances appreciation but also informs effective cultivation practices. This exploration will delve into the ultimate significance of each feature within this remarkable botanical structure.
Moreover, the intricate relationships between different sections foster resilience against environmental challenges. By examining these connections, one can uncover the strategies that enable such plants to adapt and flourish. Join us as we dissect the essential elements of this remarkable climbing entity, enriching your knowledge of its fascinating biology.
Understanding the Grape Vine Structure
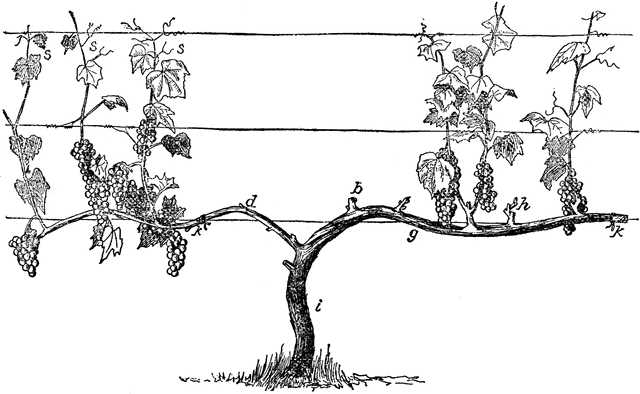
The intricate framework of this plant plays a crucial role in its overall growth and fruit production. Each component contributes to its ability to thrive in various environments, showcasing an amazing adaptation to different climates and soils.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Stem | Supports the plant and transports nutrients. |
| Leaves | Engage in photosynthesis, converting sunlight into energy. |
| Roots | Anchor the plant and absorb water and minerals. |
| Clusters | House the fruits, essential for reproduction. |
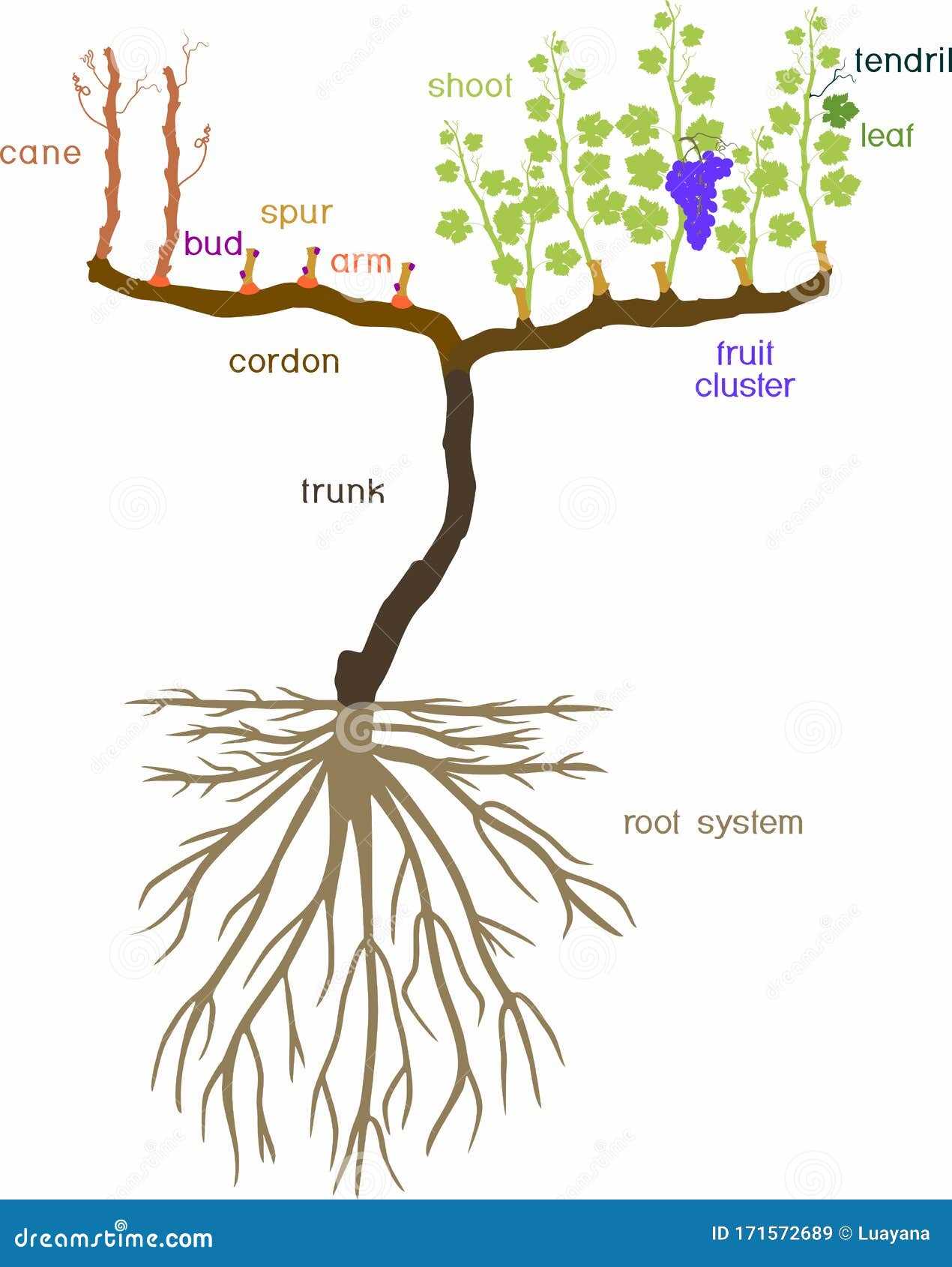
Key Components of a Grape Vine
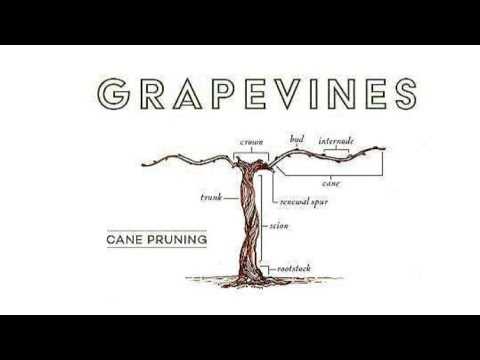
Understanding the essential elements of a climbing plant is crucial for both cultivation and appreciation. Each component plays a significant role in the overall health and productivity, contributing to the beauty and bounty of the harvest. These elements interact intricately, supporting growth and facilitating the production of fruit.
The trunk serves as the main support structure, allowing the plant to reach upward toward sunlight while also transporting vital nutrients and water. Branches extend from the trunk, spreading out to maximize exposure to sunlight and air. Foliage is critical, as it engages in photosynthesis, converting light energy into chemical energy to nourish the entire organism.
Clusters of flowers emerge from the branches, playing a vital role in reproduction. Successful pollination leads to the formation of fruit, which is not only the culmination of the plant’s efforts but also essential for the continuation of the species. Roots delve into the soil, anchoring the plant and absorbing moisture and minerals necessary for growth.
Understanding these core components allows for better care and management, ensuring a thriving organism that can yield abundant and high-quality produce.
Roles of Leaves in Photosynthesis
Foliage plays a crucial role in the process of converting sunlight into energy, enabling plants to thrive in their environments. Through a complex interaction of structures and functions, these green organs facilitate the essential chemical reactions that sustain life. Understanding their contributions provides insight into the vital nature of these organisms within ecosystems.
Key Functions of Foliage
- Light Absorption: Leaves contain chlorophyll, a pigment that captures sunlight, which is necessary for the photosynthetic process.
- Gas Exchange: Through small openings called stomata, foliage takes in carbon dioxide and releases oxygen, balancing atmospheric gases.
- Water Regulation: Leaves help control water loss through transpiration, maintaining moisture levels within the plant.
Photosynthesis Process Overview
- Light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll.
- Water is split into oxygen and hydrogen within the leaf cells.
- Carbon dioxide combines with hydrogen to form glucose, a form of sugar that serves as food for the plant.
This intricate mechanism illustrates the indispensable role foliage plays in not only supporting the life of the plant itself but also contributing to the broader ecological balance. Through these processes, leaves are essential to the survival of numerous organisms, including humans, by generating oxygen and forming the basis of the food chain.
Importance of Grapevine Roots
The foundational system of any plant plays a crucial role in its overall health and productivity. This underground network not only anchors the organism but also serves as a vital source of nourishment and hydration.
Nutrient Absorption
Roots are responsible for absorbing essential minerals and nutrients from the soil, which are critical for growth and development. Key functions include:
- Uptake of water
- Mineral acquisition
- Storage of carbohydrates
Soil Interaction
The interaction between the root system and soil has significant implications for sustainability and resilience. Consider the following:
- Enhancing soil structure
- Promoting microbial activity
- Preventing erosion
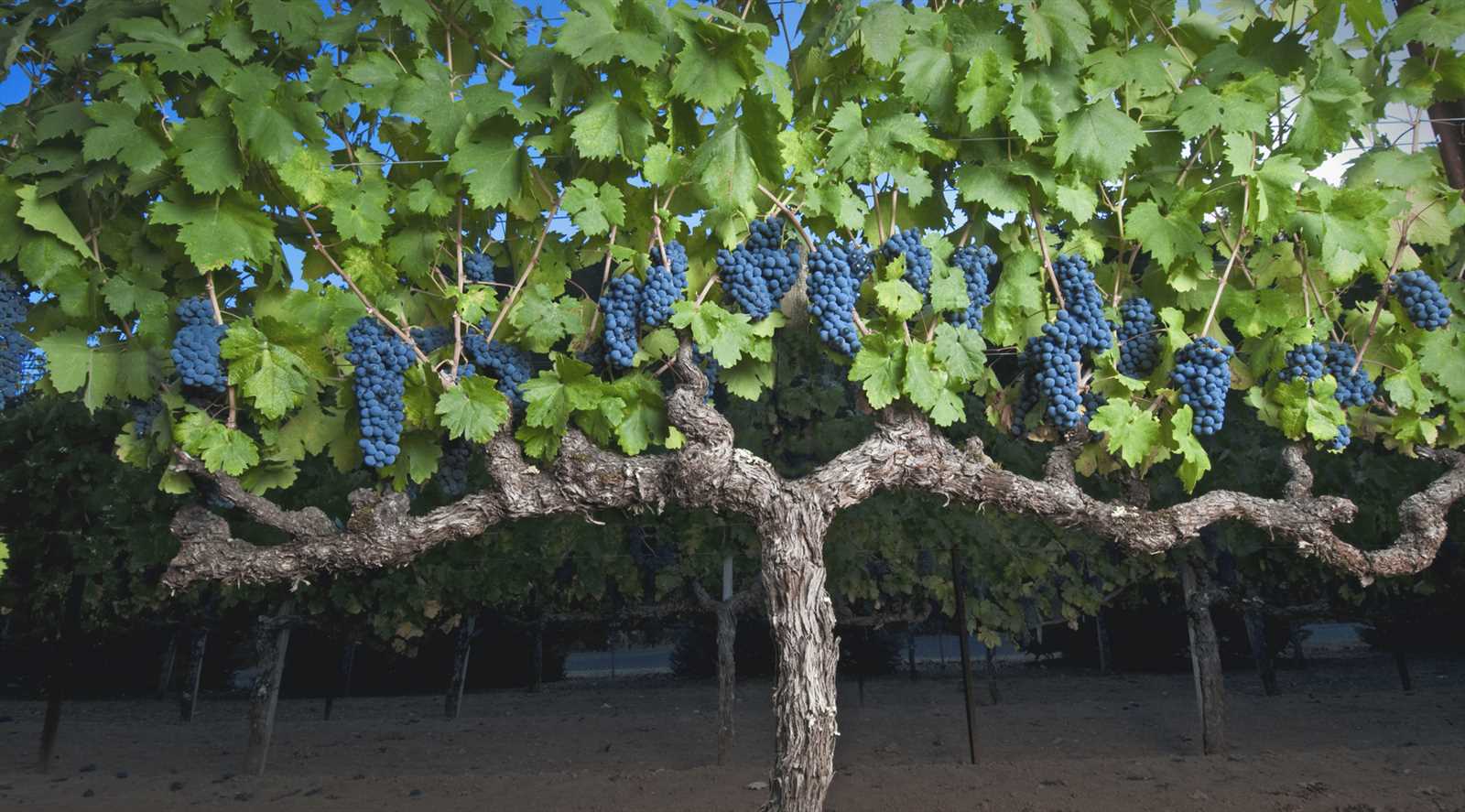
Function of the Stem in Growth
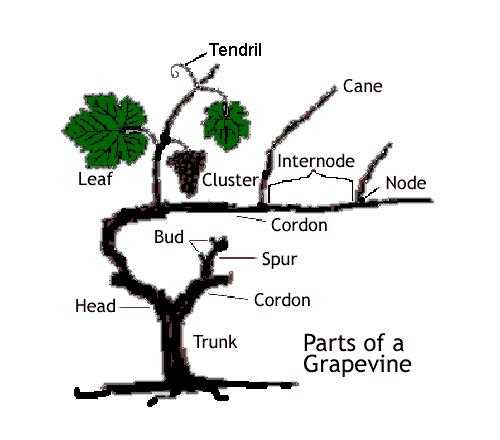
The central structure plays a crucial role in the overall development and stability of the organism. It serves as a supportive framework that facilitates essential processes necessary for thriving and reaching maturity.
Support and Stability
This structure provides the necessary support for leaves and clusters, ensuring they receive adequate sunlight. Its strength allows the organism to withstand environmental challenges.
- Anchors the plant in the soil
- Distributes weight from above
- Resists external pressures
Nutrient Transport

Another vital function involves the movement of nutrients and water from the roots to various parts. This transportation system is essential for sustaining growth and vitality.
- Transports water from the roots
- Delivers essential nutrients
- Facilitates photosynthesis through leaf support
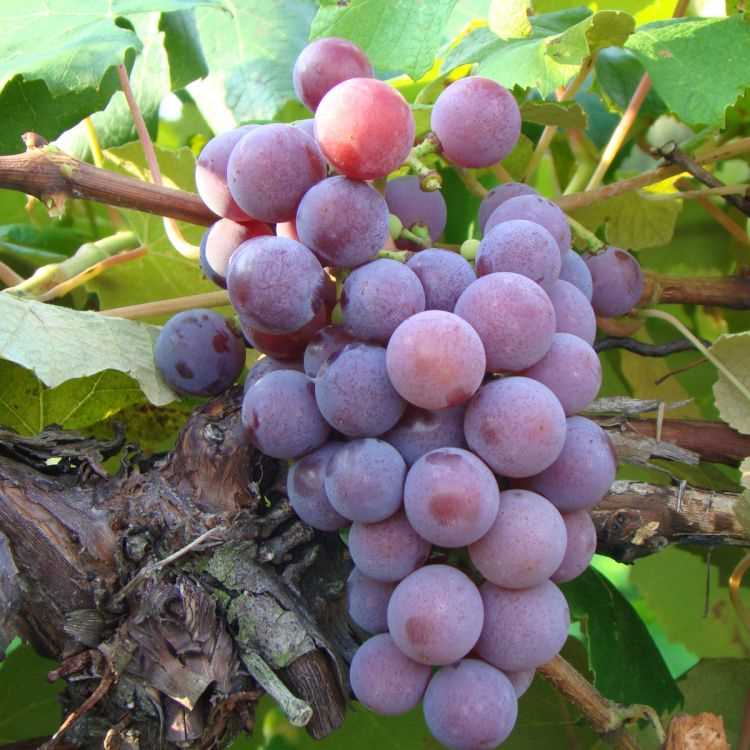
Types of Grape Bunches Explained
The formation of clusters in this beloved fruit is diverse, each exhibiting unique characteristics that influence both appearance and flavor. Understanding these varieties can enhance appreciation for the agricultural art of cultivation and the nuances they bring to winemaking and table consumption.
Common Cluster Varieties
- Loose Clusters: These formations consist of berries spaced apart, allowing for better airflow and reducing the risk of disease.
- Compact Clusters: Dense arrangements where berries are tightly packed together, often leading to higher yields but potentially greater disease susceptibility.
- Conical Clusters: Shaped like a cone, these structures are typical for many popular cultivars and contribute to uniform ripening.
- Oval Clusters: Characterized by a more rounded appearance, these can affect harvesting methods and grape quality.
Factors Influencing Cluster Development
- Climate: Temperature and humidity levels significantly impact cluster formation and health.
- Soil Composition: Nutrient availability affects growth patterns and berry quality.
- Varietal Differences: Each cultivar has distinct genetic traits that determine cluster type and growth behavior.
- Pruning Practices: Careful management of growth can enhance or modify cluster structure and yield.
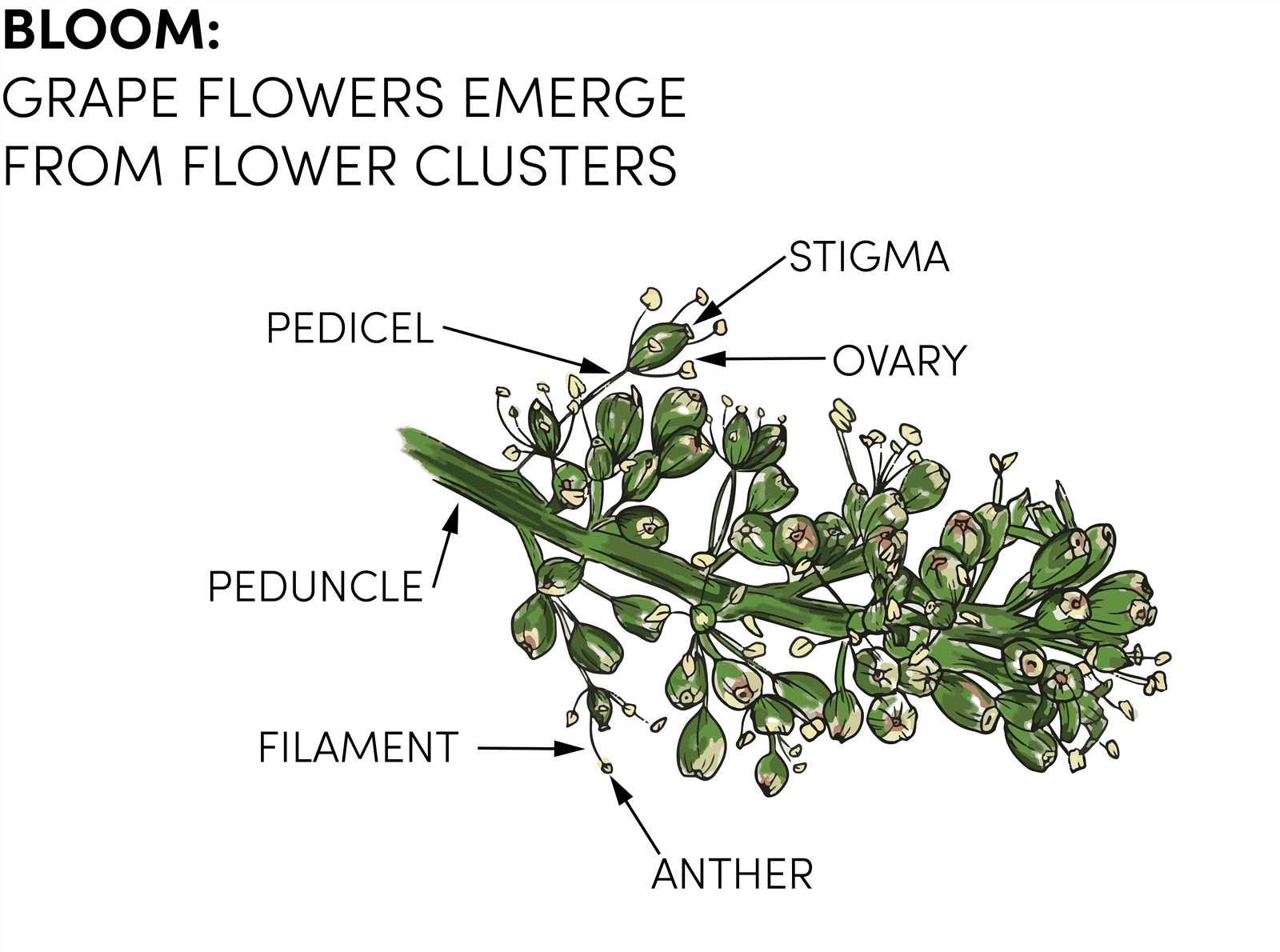
How Flowers Develop into Grapes
The transformation from blooms to fruit is a fascinating process that showcases the intricate relationships within nature. This journey begins with pollination, leading to the development of seeds and the eventual formation of clusters.
Initially, the flowers emerge and go through several stages:
- Pollination: The transfer of pollen from the male parts to the female structures, which is essential for fertilization.
- Fertilization: Once pollen reaches the ovule, fertilization occurs, initiating the development of seeds.
- Ovule Development: After fertilization, the ovule matures into seeds, laying the groundwork for future growth.
Following these stages, the ovary of the flower begins to swell:
- Cell Division: The cells within the ovary multiply, causing it to enlarge.
- Growth Hormones: Hormones play a critical role in stimulating growth, ensuring the developing fruit expands properly.
- Ripening: As time progresses, the fruit continues to mature, accumulating sugars and flavors that enhance its appeal.
This remarkable process emphasizes the interconnectedness of life, transforming simple blossoms into the flavorful produce enjoyed by many. Understanding these stages provides insight into agricultural practices and the importance of nurturing each phase for a successful harvest.
Effects of Climate on Vine Parts
Climate plays a crucial role in shaping the development and health of various components of these plants. Factors such as temperature, precipitation, and sunlight directly influence growth patterns, productivity, and resistance to diseases. Understanding these relationships can provide insights into optimal cultivation practices.
Temperature variations impact the maturation processes of fruit and foliage, affecting sugar accumulation and flavor profiles. Warmer conditions often lead to earlier harvests, while cooler climates can prolong the growing season, enhancing complexity in flavor.
Precipitation levels are essential for hydration, but excessive moisture can lead to root rot and fungal infections. Conversely, drought conditions may stress the organism, resulting in smaller yields and concentrated flavors.
Sunlight exposure is vital for photosynthesis, influencing leaf development and overall vigor. Regions with ample sunlight typically produce healthier specimens with richer characteristics, while shaded areas may yield less robust growth.
Ultimately, the interplay between these climatic elements defines the health and productivity of the organism, guiding growers in their practices and decisions for optimal outcomes.
Grapevine Pruning Techniques Revealed

Understanding the art of trimming is essential for achieving optimal growth and fruit quality in these climbing plants. Effective methods enhance both yield and health by promoting better air circulation and sunlight exposure. This section explores various techniques that can transform the way these plants are cultivated.
One widely recognized approach is the cane pruning technique, which involves selecting a few strong canes from the previous year’s growth. This method focuses on maintaining a balanced structure while encouraging fruitful shoots to develop. It is particularly beneficial for established plants that require rejuvenation.
Another method is spur pruning, where short stubs are left after cutting back the previous season’s growth. This technique fosters new growth from the base of each spur, leading to an abundant harvest in the following year. It is often favored for its simplicity and effectiveness in producing high-quality clusters.
Additionally, the method of trellising plays a crucial role in maximizing sunlight exposure and ease of maintenance. By training the plants along a structured framework, growers can optimize space and promote a healthier environment for fruit development. This strategic approach allows for better management of both pests and diseases.
In summary, mastering these trimming techniques not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of the garden but also significantly improves productivity and plant vitality. By implementing the right strategies, cultivators can ensure their climbing plants thrive for years to come.
Pests and Diseases in Vine Anatomy
Understanding the threats that affect the structure of these plants is crucial for maintaining their health and productivity. Various organisms and conditions can significantly impact growth, leading to reduced yield and quality.
Common Pests
- Leafhoppers: These insects feed on sap and can transmit harmful viruses.
- Mealybugs: They cause damage by sucking juices and can lead to mold growth.
- Spider Mites: These tiny arachnids weaken plants by removing essential fluids.
Diseases to Watch For
- Powdery Mildew: A fungal infection that appears as a white powdery substance.
- Downy Mildew: Another fungal disease, characterized by yellow spots and a downy growth.
- Phomopsis: A disease causing cankers and fruit rot, affecting overall vigor.
Effective management strategies are essential to mitigate these risks and ensure robust growth.
Ultimate Guide to Grape Varieties
This section explores the diverse selection of fruits used in winemaking, highlighting the characteristics that make each unique. Understanding these varieties can enhance appreciation and enjoyment of different wines.
Key Characteristics
- Flavor profiles
- Aromatic qualities
- Growing conditions
- Color variations
Popular Varieties
- Chardonnay
- Merlot
- Sauvignon Blanc
- Cabernet Sauvignon