Understanding the Essential Components of a Kite Diagram
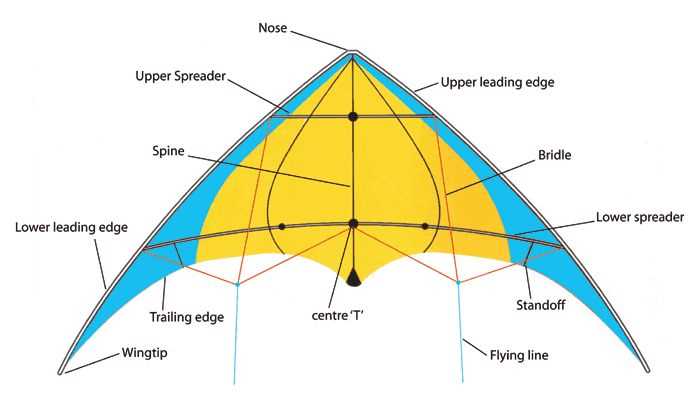
In the realm of data visualization, certain graphical forms serve as essential tools for illustrating relationships and hierarchies. These representations, characterized by their unique shapes and elements, enable viewers to grasp complex information at a glance. Each segment within these forms plays a vital role in conveying specific insights and fostering comprehension.
Every element contributes to the overall narrative, guiding the observer through layers of meaning. From the apex to the base, each section reveals different facets of the information being presented. By analyzing the arrangement and interplay of these components, one can uncover deeper interpretations and trends that might otherwise remain hidden.
The interplay of various sections creates a dynamic visual experience, allowing for an engaging exploration of data. Understanding how each piece fits into the larger picture empowers analysts and audiences alike to draw informed conclusions and make decisions based on the presented findings.
Understanding Kite Diagrams
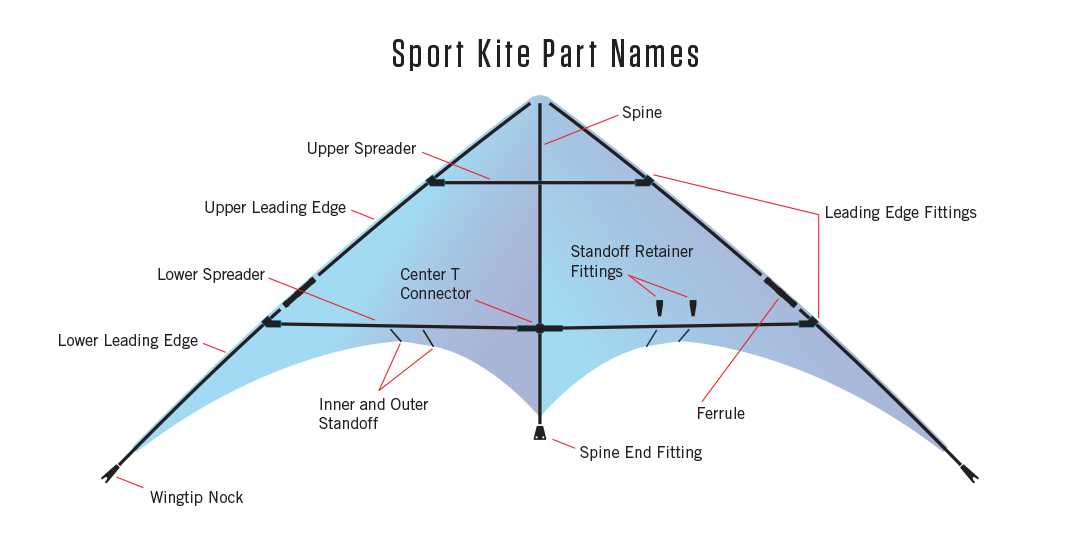
Visual representations can effectively illustrate relationships between different sets of data, providing insights into their interconnections. This particular structure is designed to help analyze distributions and reveal patterns that might otherwise remain hidden. By examining these visual constructs, one can glean important information about the characteristics and behaviors of various elements.
Key Features of the Visual Representation
At the heart of this model are several essential components that work together to convey information clearly and concisely. Each element serves a distinct purpose, allowing for a comprehensive understanding of the data being presented.
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Axes | Horizontal and vertical lines that define the framework for the visual. |
| Regions | Distinct areas that represent different categories or ranges of values. |
| Points | Markers indicating specific data points within the framework. |
| Lines | Connections that illustrate relationships between the points and regions. |
Applications and Benefits
Utilizing this type of representation can enhance the analysis of data in various fields, from education to business analytics. It allows for quick comprehension of complex information, making it easier to identify trends, compare different datasets, and support informed decision-making.
Basic Structure of a Kite Diagram
The foundational layout of this visual representation serves to illustrate relationships and categorizations effectively. By employing a specific configuration, it allows for clear interpretation of data, facilitating a better understanding of the underlying concepts.
At its core, this structure consists of several key components. Each section is designed to represent different categories or attributes, often arranged symmetrically to enhance visual appeal and comprehension. The connections between these sections highlight the relationships among the various elements, ensuring that viewers can easily grasp the overall message being conveyed.
In addition, the use of labels is crucial for clarity. Each segment typically includes descriptive text, which guides the audience through the information presented. This not only aids in immediate understanding but also reinforces the connections and distinctions among the various categories.
Furthermore, the arrangement often follows a hierarchical model, with broader concepts placed prominently and more specific details cascading beneath. This organization allows for a seamless flow of information, leading to a coherent narrative that is both engaging and informative.
Key Components Explained
Understanding the essential elements of this graphical representation is crucial for effective analysis and communication of data. Each component plays a significant role in conveying relationships and insights, helping to illustrate the structure and interconnectivity of various attributes.
At the core, the primary elements are designed to categorize and differentiate information, allowing for easy interpretation of trends and patterns. These sections can be viewed as distinct entities that contribute to a comprehensive overview, enabling users to grasp complex relationships at a glance.
Additionally, the connections between these entities serve to highlight the interactions and dependencies that exist within the data set. By emphasizing these links, the visual tool aids in identifying correlations, enhancing the overall understanding of the subject matter.
In summary, the individual elements and their interrelations form a cohesive visual narrative, guiding viewers through the intricacies of the presented information. Mastery of these components ultimately empowers users to draw meaningful conclusions and make informed decisions based on the depicted data.
Types of Data Represented
The visual representation of data can convey various forms of information, allowing for a deeper understanding of relationships and distributions. Different categories of data can be illustrated effectively, each serving a distinct purpose in analysis and interpretation.
- Categorical Data: This type includes distinct groups or categories, such as:
- Colors
- Types of animals
- Brands of products
- Numerical Data: This encompasses measurable quantities, which can be divided into:
- Discrete values (e.g., number of students)
- Continuous values (e.g., height, weight)
- Ordinal Data: This consists of ordered categories, where the sequence matters but the differences between values are not uniform. Examples include:
- Survey ratings (e.g., poor, fair, good, excellent)
- Class rankings
- Temporal Data: This type relates to time, showcasing trends and changes over specific periods. It can include:
- Sales over the months
- Population growth over decades
lessCopy code
Understanding these various forms of data is essential for effective analysis, enabling the identification of patterns and insights that inform decision-making processes.
Creating a Kite Diagram
Crafting a visual representation to illustrate relationships and data can significantly enhance understanding. This method effectively conveys complex information in a structured format, allowing viewers to grasp insights quickly. In this section, we will explore the steps to construct such a visual tool effectively.
Planning Your Visual Representation
Begin by determining the key themes or categories you want to display. Identifying these elements is crucial as they form the foundation of your visual. Once you have outlined the main concepts, consider how they interconnect and the hierarchy among them. This planning phase will guide the overall structure of your illustration.
Design and Construction
After establishing your concepts, proceed to sketch a rough outline. Utilize shapes to represent different elements, ensuring clarity and simplicity. As you build your visual, focus on balancing the design; use contrasting colors and distinct shapes to differentiate categories while maintaining coherence. Label each section clearly to enhance understanding, and consider incorporating data points or examples to support the visual narrative.
By following these steps, you will create an engaging and informative representation that effectively communicates your ideas.
Common Applications in Research
Visual representations play a crucial role in various research disciplines, enabling scholars to convey complex relationships and insights in a clear and concise manner. These tools facilitate the exploration of data, helping to identify patterns and trends that might not be immediately evident through traditional analysis.
Social Sciences
In social sciences, these visual aids are employed to illustrate connections between variables such as demographics, behavior, and societal trends. Researchers utilize them to demonstrate how factors like education level and income can influence social mobility. By presenting information visually, they enhance comprehension and foster engaging discussions.
Natural Sciences
Within the realm of natural sciences, these visual frameworks are essential for depicting relationships among biological, chemical, or physical elements. They assist in the formulation of hypotheses and the interpretation of experimental results. For instance, scientists might use them to represent the interactions within an ecosystem or the reaction pathways in a chemical process, highlighting the dynamic nature of their studies.
In both fields, the ability to visualize data not only aids in effective communication but also supports collaborative efforts, driving advancements in research and understanding across disciplines.
Interpreting Data from Diagrams
Understanding visual representations of information is crucial for effective analysis. These illustrations offer a structured way to convey complex data, allowing for quick insights and comparisons. By examining various elements within these visuals, one can draw meaningful conclusions and make informed decisions based on the presented figures.
To accurately interpret such visuals, it’s essential to consider key components like the axes, scales, and any labels or legends that accompany the visuals. Each element contributes to a comprehensive understanding of the data, guiding the viewer through the relationships and patterns that may not be immediately obvious.
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Axes | Provide the framework for measurement, indicating the variables being compared. |
| Scales | Represent the intervals or units of measurement, allowing for precise reading of values. |
| Legends | Clarify the meaning of symbols or colors used, essential for understanding different data categories. |
| Data Points | Highlight specific values or observations, which can reveal trends or outliers. |
By paying close attention to these aspects, one can better grasp the narrative woven through the visual data. This understanding enhances the ability to extract insights and apply them in real-world contexts, making data interpretation a valuable skill across various fields.
Visualizing Relationships with Kites
Understanding complex relationships and hierarchies can be challenging, but using a graphical representation can simplify this process. By employing specific shapes and structures, one can effectively illustrate how different elements interact and connect with one another. This visual method enhances comprehension and allows for a clearer analysis of data.
Connecting Elements

Each shape in the visualization serves a distinct purpose, helping to categorize and link various components. The broader sections signify general concepts, while the narrower ones indicate specific details or subcategories. This design allows viewers to quickly grasp the overall structure and discern connections at a glance.
Enhancing Clarity
Utilizing these visual tools not only facilitates better understanding but also encourages deeper engagement with the material. By representing relationships in a visually appealing way, complex information becomes more accessible. This method aids in retention and encourages thoughtful exploration of the data presented.
Comparative Analysis Techniques
In various fields of research and data interpretation, the ability to draw comparisons between different elements is essential. These methods enable researchers to identify similarities and differences, providing deeper insights into patterns and relationships. By employing structured approaches, analysts can enhance their understanding of complex data sets and facilitate informed decision-making.
Qualitative Comparison Methods
Qualitative techniques focus on non-numerical data, emphasizing themes and patterns within qualitative information. These approaches allow researchers to explore contextual factors and subjective experiences, enabling a rich understanding of the data. Techniques such as case studies, interviews, and content analysis facilitate a nuanced exploration of similarities and differences in diverse contexts.
Quantitative Comparison Techniques
Quantitative methods, on the other hand, rely on numerical data to conduct comparisons. Statistical analysis, including t-tests and ANOVA, enables researchers to ascertain significant differences between groups. These techniques provide a robust framework for evaluating hypotheses and drawing conclusions based on empirical evidence, making them essential for data-driven decision-making.
Limitations of Kite Diagrams
While visual representations are invaluable for illustrating data relationships, they also come with certain constraints that can impact their effectiveness. Understanding these limitations is crucial for accurate interpretation and application in various contexts.
One significant drawback is the potential for oversimplification. Complex relationships may be reduced to basic forms, leading to misinterpretations. When nuanced details are lost, the overall understanding of the subject matter can be compromised.
Additionally, such visuals may not effectively convey quantitative information. While they excel in showing patterns and classifications, precise numerical data can be obscured, making it challenging to draw conclusions based on statistical significance.
Moreover, audience familiarity plays a pivotal role. If viewers are not well-versed in interpreting these visualizations, they might struggle to grasp the intended message. This reliance on prior knowledge can limit their accessibility to a broader audience.
Lastly, the design itself can pose issues. Poorly constructed visuals may lead to confusion or misrepresentation of the data. A lack of standardization in the way these visuals are presented can result in varied interpretations, further complicating communication.
In summary, while these visual tools can enhance data presentation, it is essential to be aware of their inherent limitations to ensure accurate and effective communication.
Alternative Diagramming Methods
When exploring visual representation techniques, it’s important to consider various approaches that can effectively convey information and relationships. These methods provide different perspectives and can enhance understanding, depending on the context and audience.
Here are some popular alternatives:
- Flowcharts: Ideal for illustrating processes and workflows. They use shapes and arrows to depict the sequence of actions and decisions.
- Mind Maps: Great for brainstorming and organizing thoughts. They center around a main idea and branch out into related concepts, fostering creativity.
- Venn Diagrams: Useful for comparing and contrasting ideas or groups. Overlapping circles visually demonstrate relationships and shared characteristics.
- Network Graphs: Effective for showing connections between various elements. Nodes represent entities, while edges illustrate their relationships.
Choosing the right method depends on the specific goals and the nature of the information being presented. Each technique has its own strengths and can greatly enhance clarity and engagement.
Enhancing Clarity in Presentations
Effective communication is essential in conveying ideas clearly and engaging the audience. By focusing on the structure and organization of information, presenters can significantly improve understanding and retention. This section explores various strategies to enhance the clarity of visual representations in presentations.
Strategies for Clear Communication
- Simplify Content: Use straightforward language and avoid jargon to ensure your message is accessible.
- Organize Information: Structure your content logically, grouping related ideas together for better flow.
- Visual Aids: Incorporate charts, graphs, or illustrations that complement the spoken word and reinforce key points.
- Consistent Design: Maintain uniform colors, fonts, and layouts to create a cohesive look that enhances readability.
Engaging the Audience
- Encourage Interaction: Invite questions or discussions to make the audience feel involved and clarify any uncertainties.
- Use Examples: Provide real-life scenarios or case studies to illustrate complex concepts effectively.
- Practice Delivery: Rehearse your presentation multiple times to improve confidence and ensure smooth transitions between topics.
By implementing these techniques, presenters can create a more engaging and understandable experience for their audience, fostering better communication and learning outcomes.
Best Practices for Effective Use
To maximize the benefits of visual representations in data analysis, it is crucial to employ specific strategies that enhance clarity and comprehension. These approaches ensure that the audience can easily interpret the information presented and draw meaningful conclusions.
- Maintain Clarity: Use clear labels and legends to avoid confusion. Each section should be easily distinguishable.
- Limit Complexity: Simplify the visual by focusing on key elements. Overloading with information can obscure important insights.
- Choose Appropriate Scales: Ensure that the scales used for measurement are suitable for the data, facilitating accurate comparisons.
- Incorporate Color Wisely: Utilize color to differentiate categories, but avoid excessive hues that may distract from the main message.
- Utilize Annotations: Add notes or callouts to highlight significant data points or trends, guiding the viewer’s understanding.
- Test with the Audience: Gather feedback from potential users to identify areas of improvement and ensure the representation meets their needs.
By following these guidelines, one can create an effective visual tool that communicates data clearly and efficiently, fostering better understanding and decision-making.