Understanding the Essential Parts of a Roof Diagram
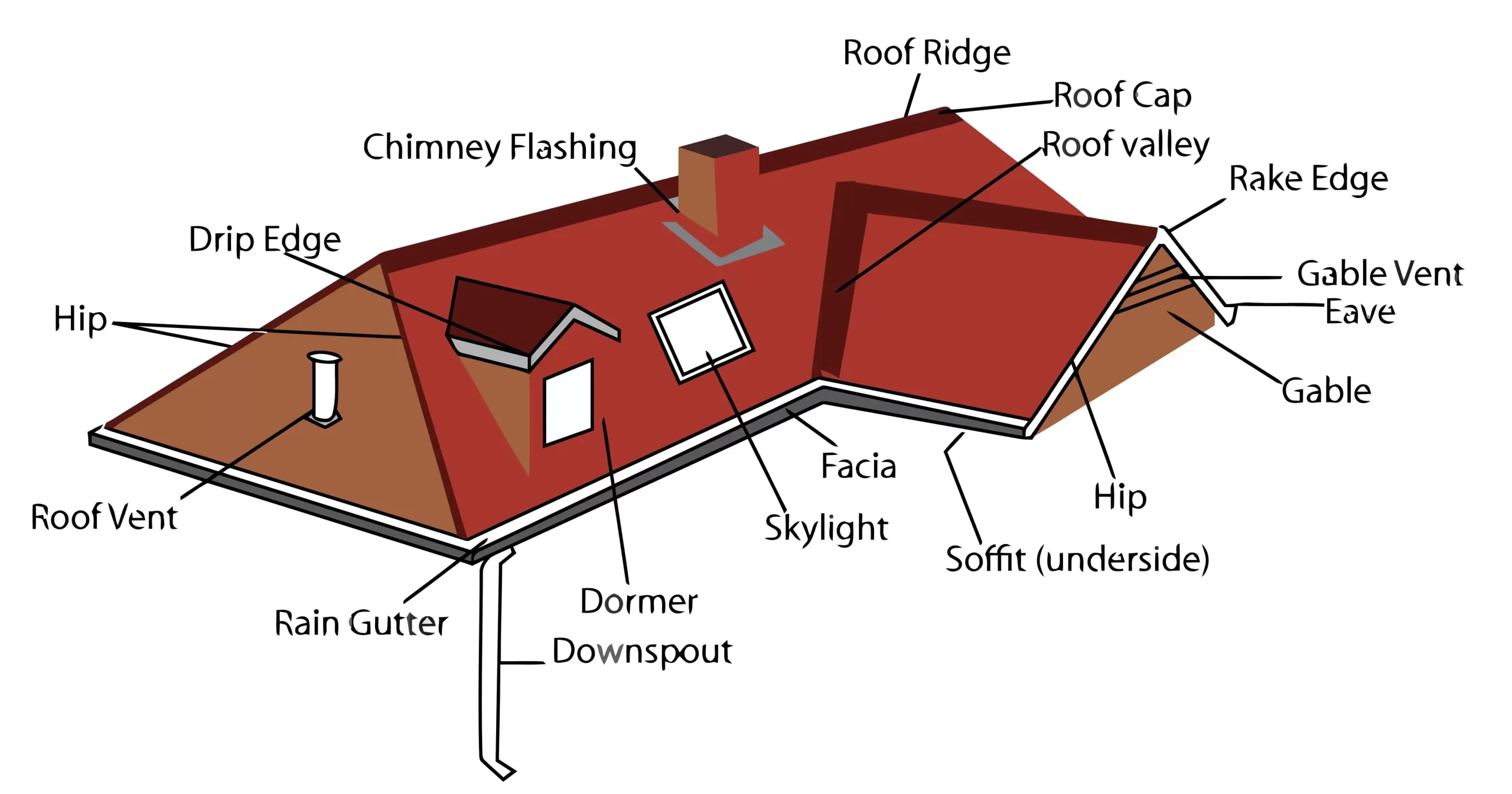
The essential framework that shelters a building plays a crucial role in its overall integrity and functionality. Comprehending its various elements is vital for both construction and maintenance. Each section contributes uniquely to the effectiveness of the entire assembly.
From the topmost layer that provides protection against the elements to the supporting structures beneath, every component has a specific purpose. This intricate system not only enhances aesthetic appeal but also ensures durability and safety. Exploring these elements will ultimately lead to a deeper appreciation of their significance.
In this exploration, we will delve into the various constituents that come together to form this vital covering. By examining their interconnections and functions, one can better understand how they collectively contribute to the stability and resilience of a building.
Understanding Roof Structure Components
The framework of any shelter is essential for ensuring stability, protection, and longevity. A comprehensive grasp of its elements is crucial for both construction and maintenance. Each component plays a specific role, contributing to the overall functionality and aesthetic appeal of the structure.
Framework serves as the backbone, providing support and shape. It consists of various beams and trusses, which distribute weight evenly and withstand external forces. These elements are critical for ensuring that the upper layer remains secure.
Covering acts as a shield against the elements, preventing water infiltration and protecting against temperature fluctuations. Materials used for this purpose can vary widely, influencing both durability and visual character.
Insulation plays a vital role in regulating internal temperatures, enhancing energy efficiency. By minimizing heat transfer, it contributes to a comfortable environment year-round.
Ventilation systems are essential for maintaining airflow, which prevents moisture buildup and prolongs the lifespan of the upper components. Proper air circulation also helps in regulating temperature, making it an integral aspect of the design.
Each of these elements works in harmony, ensuring that the entire system functions effectively. Understanding their interactions is key for anyone involved in construction, renovation, or simple maintenance tasks.
Main Elements of a Roof
The structure that shelters a building encompasses various critical components, each serving a specific function to ensure durability and protection. Understanding these fundamental aspects is essential for both construction and maintenance, as they contribute to the overall integrity and performance of the sheltering system.
At the forefront is the framework, which provides the necessary support and shape, typically constructed from timber or metal. This skeleton forms the base on which other elements rest. Covering this framework, the outer layer plays a vital role in shielding against the elements, with materials ranging from shingles to tiles, each offering distinct advantages.
Another significant component is the insulation layer, designed to regulate temperature and enhance energy efficiency within the space below. Ventilation features are equally important, allowing airflow to prevent moisture buildup and ensure a comfortable environment. Lastly, drainage systems are crucial for directing rainwater away, thereby safeguarding the structure from potential water damage.
Types of Roofs and Their Features
Various structures exhibit distinct designs, each with unique attributes that cater to specific aesthetic and functional needs. Understanding these variations can enhance both the appearance and performance of a building, ensuring it stands the test of time while meeting the demands of its environment.
| Design Type | Characteristics | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Flat | Horizontal surface with minimal slope | Easy to construct and maintain, ideal for urban settings |
| Gable | Two sloping sides that form a triangle | Excellent water drainage, provides additional attic space |
| Hip | Four slopes that meet at a ridge | Stable design, effective in windy areas |
| Gambrel | Two slopes on each side with a steeper lower slope | Maximizes overhead space, commonly seen in barns |
| Mansard | Two slopes on all sides, with the lower slope steeper | Provides extra living space, often used in historic architecture |
Importance of Roof Pitch
The angle at which a structure is designed plays a crucial role in its overall performance and longevity. This aspect affects not only aesthetics but also functionality and safety.
- Water Drainage: A steeper incline facilitates effective water runoff, reducing the risk of leaks and damage.
- Snow Management: Higher slopes prevent snow accumulation, minimizing the potential for collapse during winter months.
- Ventilation: The angle can enhance airflow, promoting a healthier environment within the building.
- Energy Efficiency: Certain pitches allow for better insulation, impacting heating and cooling costs.
Understanding the significance of this element is essential for making informed decisions about construction and maintenance.
Materials Used in Roofing Systems
The choice of materials plays a crucial role in the overall performance and longevity of a structure’s covering. Various options are available, each with distinct characteristics that affect durability, insulation, and aesthetic appeal. Understanding these materials is essential for making informed decisions in construction and renovation projects.
Common Materials
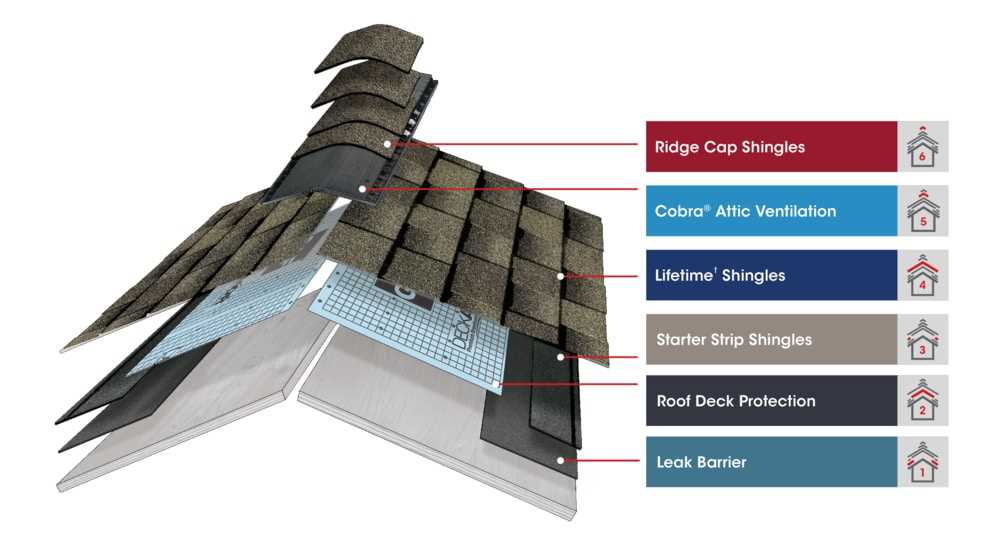
Different substances are utilized for their unique properties and advantages. Below is a table summarizing some of the most commonly used materials, along with their key features:
| Material | Durability | Insulation | Aesthetic Appeal |
|---|---|---|---|
| Asphalt Shingles | Moderate | Good | Variety of colors |
| Metal | High | Excellent | Modern look |
| Clay Tiles | Very High | Good | Classic aesthetic |
| Wood Shakes | Moderate | Fair | Natural appearance |
Considerations for Selection
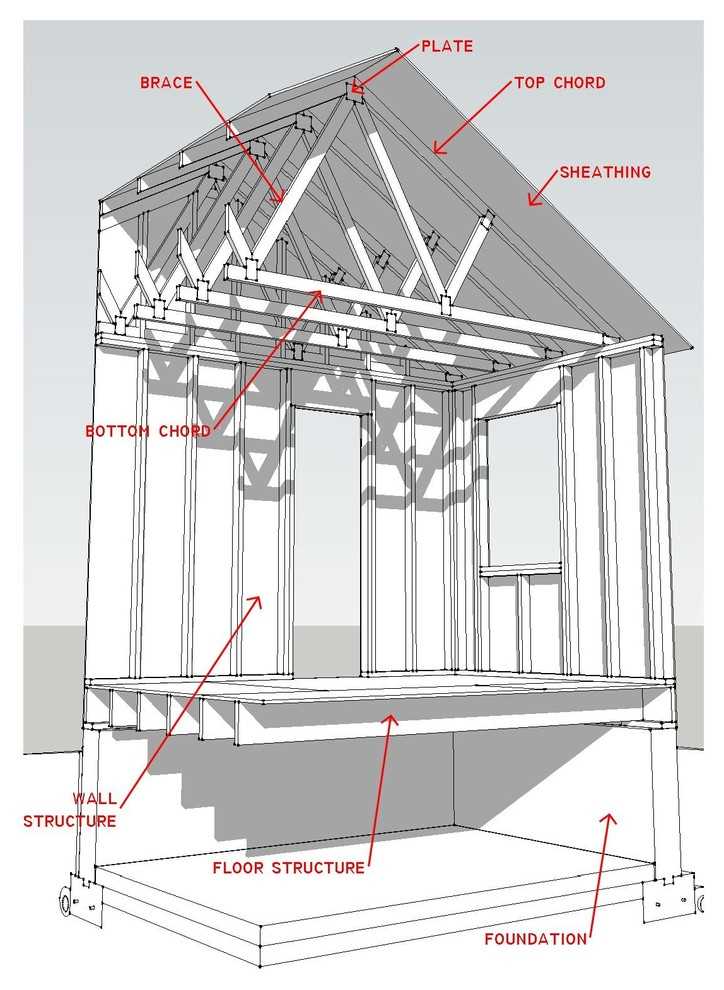
When selecting materials for a structure’s covering, factors such as climate, budget, and desired aesthetic must be taken into account. Each option has its advantages and disadvantages, making it important to evaluate the specific needs of the project to ensure optimal performance and visual appeal.
Roof Insulation and Energy Efficiency
Effective thermal barriers play a crucial role in enhancing the energy performance of a structure. By minimizing heat transfer, they contribute significantly to maintaining comfortable indoor temperatures, reducing reliance on heating and cooling systems. This not only lowers energy consumption but also leads to substantial cost savings over time.
Choosing the right materials is essential for maximizing energy efficiency. Various options, such as fiberglass, foam boards, and reflective barriers, offer unique benefits that cater to different climates and building styles. Proper installation further ensures that these materials perform at their best, preventing air leaks and enhancing overall effectiveness.
Additionally, a well-insulated enclosure can have a positive impact on sustainability. By decreasing energy demand, it helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions, aligning with modern eco-friendly practices. Overall, investing in effective thermal barriers is a key strategy for achieving ultimate energy efficiency and environmental responsibility.
Flashing and Its Protective Role
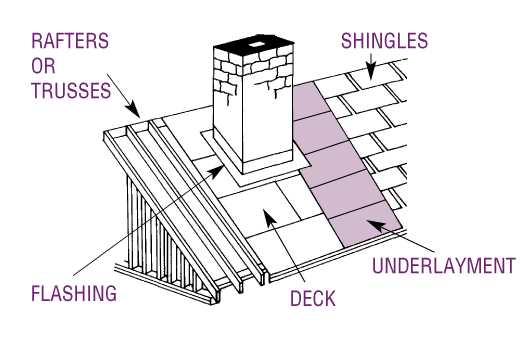
Flashing serves as a crucial element in safeguarding structures from water infiltration and weather-related damage. Its strategic placement ensures that vulnerable areas remain sealed, providing a barrier against the elements.
This protective component is typically made from materials like metal, plastic, or rubber, which are designed to withstand various environmental conditions. Proper installation is essential for maximizing effectiveness and longevity.
| Material | Durability | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | High | Chimneys, skylights |
| Copper | Very High | Roofs, dormers |
| Vinyl | Moderate | Wall junctions |
Incorporating effective flashing not only enhances structural integrity but also contributes to the overall longevity of the building. Neglecting this vital aspect can lead to costly repairs and significant damage over time.
Gutters and Drainage Systems Explained
Effective management of water flow is crucial for maintaining the integrity of any structure. A well-designed system not only directs precipitation away from the building but also protects the foundation and surrounding landscape. Understanding how these components work together can prevent costly damages and enhance the longevity of the property.
Gutters serve as the primary channel for capturing rainwater, guiding it along the edges and directing it toward downspouts. These elements are typically installed along the eaves and must be constructed from durable materials to withstand various weather conditions. Regular maintenance is essential to ensure they remain free of debris and function properly.
Drainage systems, on the other hand, encompass a broader network that includes not only the channels for directing water but also the pathways that lead it away from the structure. This may involve underground pipes, soakaways, or retention basins. An efficient setup is vital for preventing water pooling, which can lead to erosion or flooding.
Proper installation and maintenance of these systems can significantly mitigate risks associated with water damage. Homeowners should consider factors such as slope, soil type, and vegetation when planning for effective water management. By addressing these aspects, one can create a robust framework that safeguards both the property and its surroundings.
Ventilation for Roof Longevity
Effective air circulation is essential for enhancing the lifespan of a shelter’s upper structure. When warm air is allowed to escape and cool air is drawn in, it helps to maintain a balanced environment that minimizes moisture buildup and temperature extremes. This balance not only preserves the materials but also prevents potential damage caused by prolonged exposure to adverse conditions.
Proper ventilation systems play a crucial role in mitigating issues such as mold growth and structural degradation. By ensuring that the air can flow freely, homeowners can significantly reduce the risks associated with trapped heat and humidity. This proactive approach not only protects the integrity of the materials used but also contributes to energy efficiency.
In addition, strategically placed vents can enhance the overall comfort within the living space. By regulating temperatures and allowing for better air quality, these systems can create a more pleasant atmosphere throughout the year. Investing in a well-designed ventilation strategy is a key step toward ensuring longevity and durability.
Common Roof Styles and Designs
This section explores various architectural forms and their unique characteristics, highlighting how each contributes to the overall aesthetics and functionality of a structure. From classic designs to modern interpretations, these styles reflect cultural influences and practical considerations.
| Style | Description |
|---|---|
| Gable | Features two sloping sides that meet at a ridge, offering a classic look and effective water drainage. |
| Hip | Characterized by slopes on all four sides, providing stability and resistance against wind. |
| Mansard | Includes a double-pitched design, maximizing living space in the upper levels while adding a touch of elegance. |
| Flat | Offers a sleek, minimalistic appearance, often used in urban settings for modern architecture. |
| Gambrel | Similar to a mansard, but typically found in barns, with two slopes on each side that create a distinctive silhouette. |
How Roofs Handle Weather Conditions
Structures designed to shield buildings are essential for withstanding various environmental factors. These protective layers are engineered to deal with rain, snow, wind, and extreme temperatures, ensuring durability and safety for occupants.
Resistance to Moisture
Effective water drainage systems prevent accumulation, minimizing the risk of leaks and structural damage. Materials chosen for their hydrophobic properties play a crucial role in repelling precipitation.
Wind Protection
Strong, aerodynamic shapes reduce wind resistance, while secure fastening methods keep the coverings intact during storms. This combination ensures stability and longevity against harsh breezes.
Maintenance Tips for Roof Durability
Ensuring the longevity of your overhead structure requires consistent care and attention. By following a few essential practices, you can enhance its resilience against various environmental factors.
- Regular Inspections: Conduct thorough checks at least twice a year to identify potential issues early.
- Clean Gutters: Remove debris to prevent water accumulation, which can lead to damage over time.
- Check for Damage: Look for missing or damaged shingles and replace them promptly.
- Trim Overhanging Branches: Prevent unnecessary wear from branches that may fall or scrape against the surface.
- Sealant Application: Use quality sealants to protect vulnerable areas from moisture penetration.
By implementing these practices, you can significantly extend the lifespan of your structure and maintain its integrity.