Understanding the Key Components of a Fabric Diagram
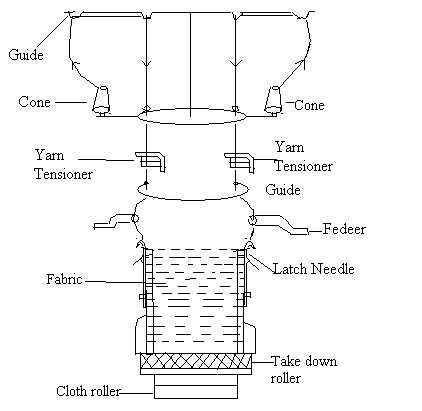
In the realm of textile design, comprehending the essential elements that contribute to the overall structure is crucial. Each individual piece plays a significant role in the final product, influencing not only the aesthetics but also the functionality and durability of the material. By dissecting these components, one can appreciate the intricate relationships that exist within the design process.
Various segments interact seamlessly, creating a cohesive unit that embodies both artistry and practicality. From the foundational layers to decorative accents, each segment serves a unique purpose while contributing to the harmony of the whole. Recognizing these elements empowers creators to make informed choices, enhancing their craft and the quality of their work.
Delving into this topic reveals the complexity and beauty of the textile world. Understanding the roles and characteristics of these segments allows for innovative approaches and more effective design solutions. Whether for fashion, upholstery, or industrial applications, a thorough grasp of these integral pieces fosters creativity and excellence in the field.
Understanding Fabric Diagrams
Visual representations are crucial for conveying intricate details of textile structures. They serve as a guide, illustrating various components and their interrelationships, facilitating a deeper comprehension of material properties and design techniques.
By analyzing these visuals, one can identify the essential elements that contribute to the overall composition. This understanding aids designers in making informed decisions about material selection and application, ultimately enhancing the quality and functionality of their creations.
Additionally, these illustrations often provide insights into manufacturing processes, allowing for a more comprehensive grasp of how different textiles are produced and utilized in various contexts. Engaging with these representations encourages a more thoughtful approach to textile design and innovation.
Types of Fabric Construction
This section explores the various methods utilized in creating textiles, highlighting their unique characteristics and applications. Understanding these techniques is essential for anyone interested in the intricacies of textile design and functionality.
- Woven: Crafted by interlacing threads at right angles, offering durability and structure.
- Knit: Formed by looping yarn together, providing stretch and comfort.
- Non-woven: Made by bonding fibers through mechanical, thermal, or chemical processes, ideal for specific applications.
Each method contributes to the ultimate performance and aesthetics of the material, influencing its use in various industries.
Key Components of Fabric Design
In the realm of textile creation, understanding the essential elements is crucial for achieving the desired aesthetic and functionality. Each aspect contributes to the overall identity and usability of the textile, allowing designers to craft unique and appealing materials that resonate with consumers.
Texture and Weave
The tactile quality and interlacing technique significantly influence the appearance and feel of the material. Variations in weave can create distinct patterns and durability, impacting both visual appeal and practical applications.
Color and Pattern
Color selection and pattern application play pivotal roles in evoking emotions and conveying messages. The interplay of hues and motifs can transform an ordinary piece into a striking statement, inviting deeper engagement from the viewer.
Importance of Accurate Measurements
Precision in sizing is crucial in various fields, as it directly influences the quality and functionality of the final product. Whether in design, manufacturing, or construction, accurate dimensions ensure that components fit together seamlessly, reducing waste and enhancing efficiency.
Impact on Quality
When measurements are exact, the overall standard of the work improves significantly. This meticulous attention to detail prevents errors that could lead to costly revisions and dissatisfaction among clients.
Efficiency and Cost-Effectiveness
By prioritizing precise sizing, organizations can streamline their processes. This not only saves time but also minimizes material waste, ultimately leading to more economical operations.
Fabric Weaves and Their Functions
Different weaving techniques create unique textures and properties that influence the performance and aesthetic appeal of textiles. Each method contributes distinct characteristics that cater to various applications, making it essential to understand how these techniques impact the final product.
Common Weaving Techniques
- Plain Weave: This basic structure consists of interlacing threads in a straightforward over-and-under pattern, offering durability and breathability.
- Twill Weave: Characterized by diagonal lines, this technique provides increased strength and a softer drape, commonly used in denim and chinos.
- Satin Weave: Featuring a smooth surface with a luxurious sheen, this method enhances light reflection and is often used in formal attire.
- Leno Weave: This unique style involves twisting adjacent threads, creating an airy and open fabric suitable for delicate applications.
Functions and Applications
- Durability: Techniques like twill and plain weaves are preferred for workwear and upholstery due to their robust nature.
- Comfort: Lightweight weaves provide breathability, making them ideal for summer clothing.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Satin and intricate patterns are favored in fashion and home décor for their visual impact.
- Specialty Uses: Unique weaves like leno are utilized in products requiring ventilation, such as bags and curtains.
Common Fabric Patterns Explained
Understanding various textile designs is essential for anyone looking to enhance their wardrobe or interior spaces. These unique motifs add character and depth, transforming simple materials into captivating statements. Below, we explore some of the most popular styles found in the world of textiles.
Geometric Designs
Geometric patterns often feature shapes like squares, triangles, and circles. They can create a modern, structured look. Here are a few common types:
- Stripes
- Polka Dots
- Checks
Floral Motifs
Floral themes bring a touch of nature indoors, adding elegance and vibrancy. These designs can range from delicate to bold:
- Small, dainty blossoms
- Large, dramatic flowers
- Botanical illustrations
Each of these styles offers distinct advantages, making them versatile choices for different occasions and settings.
Role of Color in Fabric Selection
Choosing the right hue is crucial in the process of textile selection, as it significantly influences the overall aesthetic and emotional impact of a piece. Colors can evoke feelings, set moods, and even define cultural significance, making them an essential consideration in design.
Color psychology plays a pivotal role, as different shades can inspire various reactions. For instance, warm tones often convey energy and warmth, while cool tones tend to evoke calmness and serenity. Understanding these associations helps designers create harmonious compositions that resonate with their intended audience.
Moreover, trends in color can shift, affecting consumer preferences and market dynamics. Staying attuned to these changes ensures that selections remain relevant and appealing. Ultimately, the thoughtful integration of color not only enhances visual appeal but also aligns with the functional purpose of the textile.
Textile Finishes and Their Benefits
Finishing processes play a crucial role in enhancing the qualities of materials used in various applications. These treatments not only improve the appearance but also modify the performance characteristics, ensuring that the end products meet specific requirements. From aesthetic appeal to functional enhancements, the benefits of these techniques are numerous and significant.
The following are some common types of treatments and their respective advantages:
- Water Resistance: Provides protection against moisture, making items suitable for outdoor use.
- Wrinkle Resistance: Reduces the need for ironing, maintaining a neat appearance over time.
- Stain Resistance: Helps in repelling spills and dirt, making maintenance easier.
- Flame Retardancy: Enhances safety by reducing the flammability of materials.
- UV Protection: Shields against harmful ultraviolet rays, prolonging the lifespan of products.
Additionally, these treatments can significantly impact comfort and usability:
- Softening: Improves tactile quality, making materials more pleasant to touch.
- Breathability: Enhances airflow, ensuring comfort during wear.
- Thermal Regulation: Helps maintain an optimal temperature for the user, contributing to overall comfort.
In summary, the application of various finishing techniques is essential in the textile industry, leading to improved functionality and satisfaction for consumers. The ongoing development of innovative treatments promises to further enhance the versatility and performance of materials in the future.
How to Read Fabric Diagrams
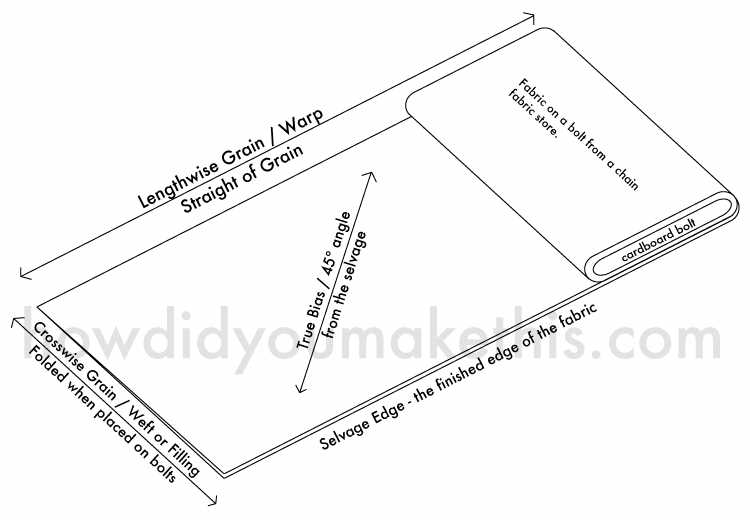
Understanding the visual representation of textile designs is essential for anyone working with textiles, whether for crafting, fashion, or interior design. These representations serve as a blueprint, conveying intricate details about the layout, materials, and techniques needed for successful execution. By familiarizing yourself with the symbols and conventions used, you can unlock the potential of any textile project.
Key Elements to Observe
- Symbols: Different shapes and icons represent various components, such as stitches, textures, and colors. Take time to familiarize yourself with these symbols.
- Color Codes: Color often indicates specific materials or sections. Ensure you note any color legends provided.
- Measurements: Accurate dimensions are critical. Pay attention to any scale markings that help translate the design into reality.
Steps to Interpret the Visuals
- Start by identifying the key symbols and their meanings.
- Refer to any accompanying legends for clarification on colors and patterns.
- Examine the layout carefully, noting the arrangement and flow of elements.
- Consider any additional notes that provide context or instructions.
- Practice by following a simple project before tackling more complex designs.
With patience and practice, reading these visual guides will become second nature, empowering you to bring your creative visions to life with confidence.
Applications in Fashion Industry
The integration of various components in the textile realm has revolutionized the fashion industry, enabling designers to explore innovative ways to create unique garments and accessories. By understanding the structure and interplay of different elements, fashion professionals can push boundaries and enhance their creative processes.
Innovative Design Techniques
Fashion designers leverage intricate layouts to experiment with new styles and silhouettes. By analyzing how diverse elements interact, they can develop fresh concepts that resonate with contemporary trends. This analytical approach allows for the exploration of unconventional materials and patterns, ultimately leading to groundbreaking collections.
Sustainable Practices
As the industry shifts towards sustainability, the thoughtful combination of materials plays a crucial role in minimizing waste. By strategically selecting and arranging components, brands can optimize production processes, reduce environmental impact, and offer eco-friendly options to consumers.
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Custom Tailoring | Utilizing detailed layouts for personalized garment creation, ensuring perfect fit and style. |
| Textile Innovation | Experimenting with combinations of materials to develop new textures and functionalities. |
| Trend Analysis | Studying the interplay of elements to forecast upcoming fashion movements and consumer preferences. |
Influence of Fabric on Garment Fit

The choice of material significantly impacts how a piece of clothing conforms to the body. Different textures and compositions interact with body shapes in unique ways, affecting overall comfort and aesthetic appeal. Understanding these interactions can lead to better design choices and improved wearability.
- Stretchability: Materials with elastic properties can enhance fit, allowing garments to hug the body while providing freedom of movement.
- Weight: Heavier substances tend to drape differently, which can affect how a design hangs on the figure, while lighter options may create a more flowing silhouette.
- Breathability: The permeability of a substance influences comfort, especially in warmer climates, where airflow is essential for wearability.
- Structure: Stiff materials can create defined shapes, while softer options allow for a more relaxed, casual look.
When selecting materials, designers must consider how each option will interact with the body’s movement and shape. This decision is crucial in achieving both functional and aesthetic goals.
- Identify the intended use of the garment.
- Evaluate the properties of potential materials.
- Test various combinations to observe fit and feel.
A thoughtful approach to material selection can elevate the quality and desirability of a garment, ensuring it not only looks good but also feels good to wear.
Innovations in Textile Technology
Recent advancements in the realm of material development have transformed the industry, enabling new possibilities in design, functionality, and sustainability. These innovations are not only enhancing aesthetic appeal but also improving durability and performance across various applications.
| Innovation | Description |
|---|---|
| Smart Fabrics | Integrate technology to respond to environmental stimuli, offering dynamic properties. |
| Biodegradable Materials | Developed to reduce environmental impact and promote sustainability in production. |
| 3D Knitting | Allows for complex structures and custom designs, minimizing waste during creation. |
| Moisture-Wicking Textiles | Enhance comfort by drawing moisture away from the body, suitable for athletic wear. |
| UV-Blocking Materials | Provide protection against harmful UV rays, catering to outdoor and health-conscious consumers. |
Future Trends in Fabric Design
The evolution of material creation is poised to undergo significant transformations, driven by innovation and sustainability. As technology advances, new methodologies and materials will redefine how textiles are designed and utilized, catering to the needs of a conscious consumer base.
Innovative Techniques
- 3D Printing: This technology enables the production of intricate structures and customizable designs.
- Smart Textiles: Integrating electronics into materials offers functionalities like temperature regulation and health monitoring.
- Biodegradable Materials: Emphasizing eco-friendliness, these options minimize environmental impact.
Consumer-Centric Approaches
- Personalization: Tailored designs allow for individual expression and unique aesthetics.
- Ethical Production: Increased demand for transparency and fair labor practices shapes sourcing strategies.
- Enhanced Comfort: Focus on performance and usability meets the evolving lifestyle of users.