Understanding the Parts of the Heart with a Blank Diagram
Exploring the complexities of a vital organ reveals an intricate network essential for sustaining life. A visual representation can significantly enhance comprehension of its components and functions. This section aims to provide clarity on each segment, illustrating their interconnections and roles within the circulatory system.
Familiarity with various sections can lead to a deeper appreciation for how blood flows and nourishes the body. By focusing on a simplified illustration, one can more easily identify significant areas and their respective contributions. Understanding these elements serves as an ultimate foundation for further study of physiology and health.
As we delve into this topic, we will uncover the distinctive characteristics that define each region, allowing readers to grasp the essence of this remarkable organ. Through a clear and structured format, the information presented here aims to illuminate the critical functions at play within the human body.
Understanding the Heart’s Structure
Exploring intricate components of this vital organ reveals its remarkable design and function. Each section plays a crucial role in maintaining circulation and ensuring efficient blood flow throughout the body.
Components of Circulatory System
Key elements include chambers that facilitate the movement of blood, valves that prevent backflow, and muscular layers that contract rhythmically. Understanding these structures enhances comprehension of their ultimate purpose.
Functionality and Coordination
Coordinated activity among different sections ensures optimal performance. Learning how these elements interact fosters appreciation for overall health and well-being.
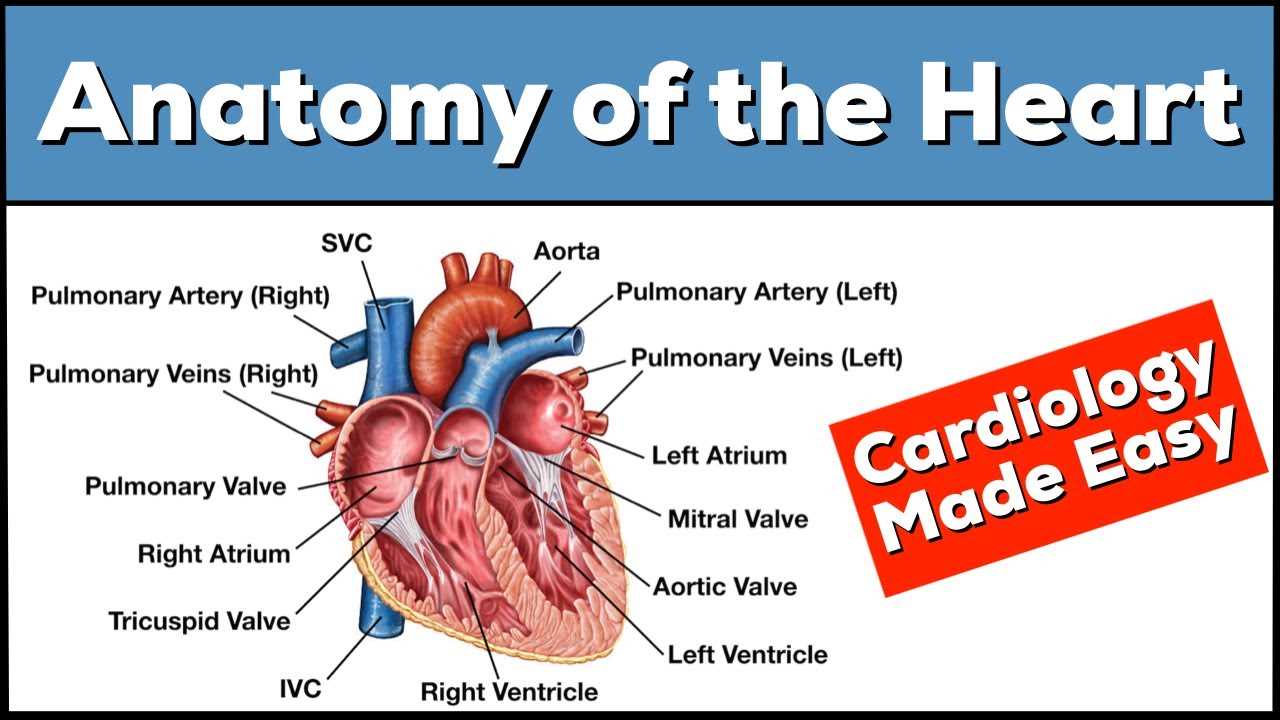
Overview of Heart Anatomy

This section presents a comprehensive exploration of cardiovascular structure, emphasizing its complexity and functionality. Understanding these components is crucial for grasping how blood circulates and sustains life.
- Muscular organ responsible for pumping blood.
- Divided into four chambers, each with distinct roles.
- Comprises valves that regulate blood flow direction.
- Upper chambers: atria, receive blood.
- Lower chambers: ventricles, pump blood out.
- Major vessels connect this organ to lungs and body.
Knowledge of these elements provides insight into overall functionality and health of this vital system.
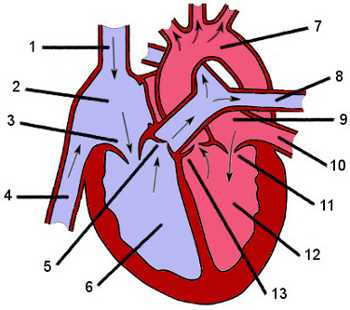
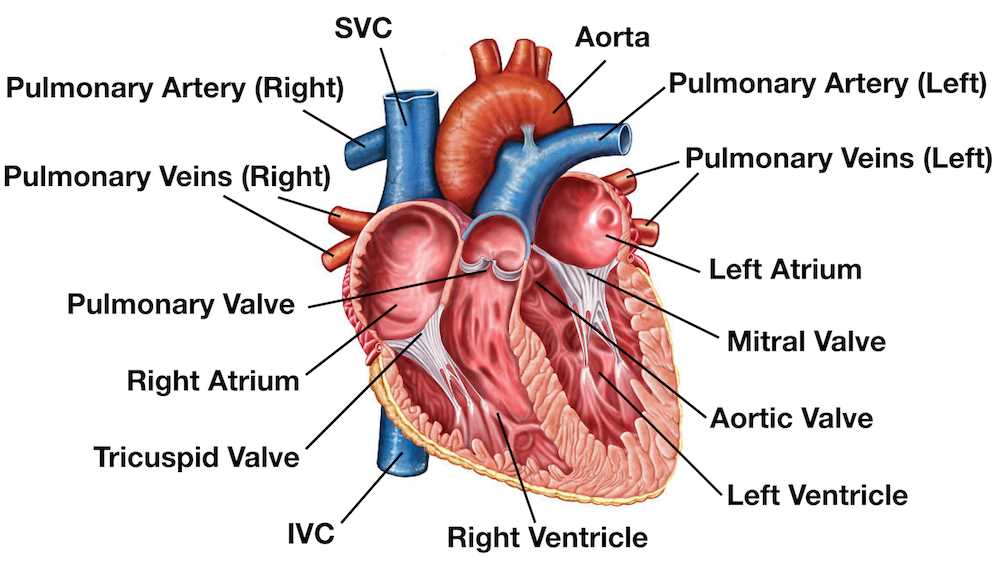
Major Chambers of the Heart
This section explores the primary compartments responsible for circulating blood throughout the organism. Each of these areas plays a critical role in maintaining efficient flow and ensuring vital functions are supported.
- Right Atrium: Receives deoxygenated blood from the body.
- Right Ventricle: Pumps blood to the lungs for oxygenation.
- Left Atrium: Collects oxygen-rich blood from the lungs.
- Left Ventricle: Distributes oxygenated blood to the entire body.
Understanding these chambers is essential for comprehending overall cardiovascular mechanics.
Function of Heart Valves
Valves play a crucial role in maintaining proper blood flow within the circulatory system. These structures ensure unidirectional movement of blood, preventing backflow and promoting efficiency in the overall functioning of the cardiovascular network.
Key Responsibilities
- Regulating blood flow: Valves open and close at specific intervals, allowing blood to move from one chamber to another or into major vessels.
- Preventing regurgitation: By closing tightly, they eliminate the possibility of blood flowing backward, thus maintaining optimal pressure levels.
- Facilitating coordinated contractions: Valves work in harmony with the muscular walls, ensuring synchronized contractions and optimal circulation.
Types of Valves
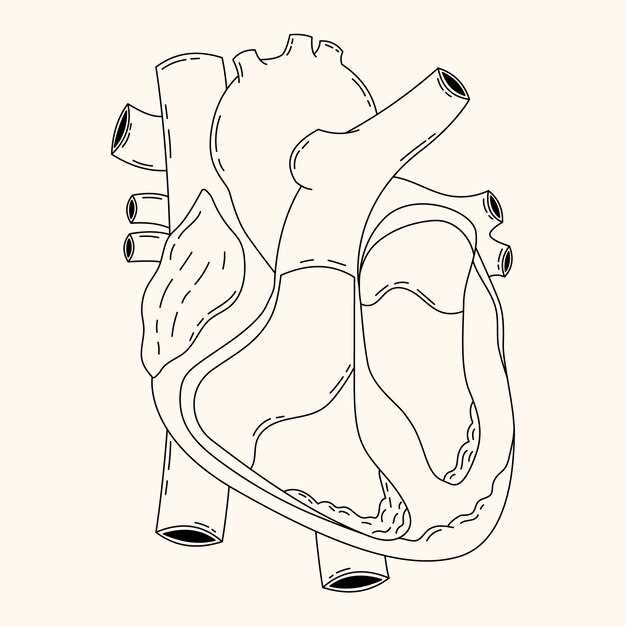
- Atrioventricular valves: Located between the atria and ventricles, these structures manage blood flow from upper chambers to lower ones.
- Semilunar valves: Positioned at the exits of ventricles, they control blood flow into major arteries, such as the aorta and pulmonary artery.
Understanding the functions of these essential components underscores their importance in sustaining life and maintaining cardiovascular health.
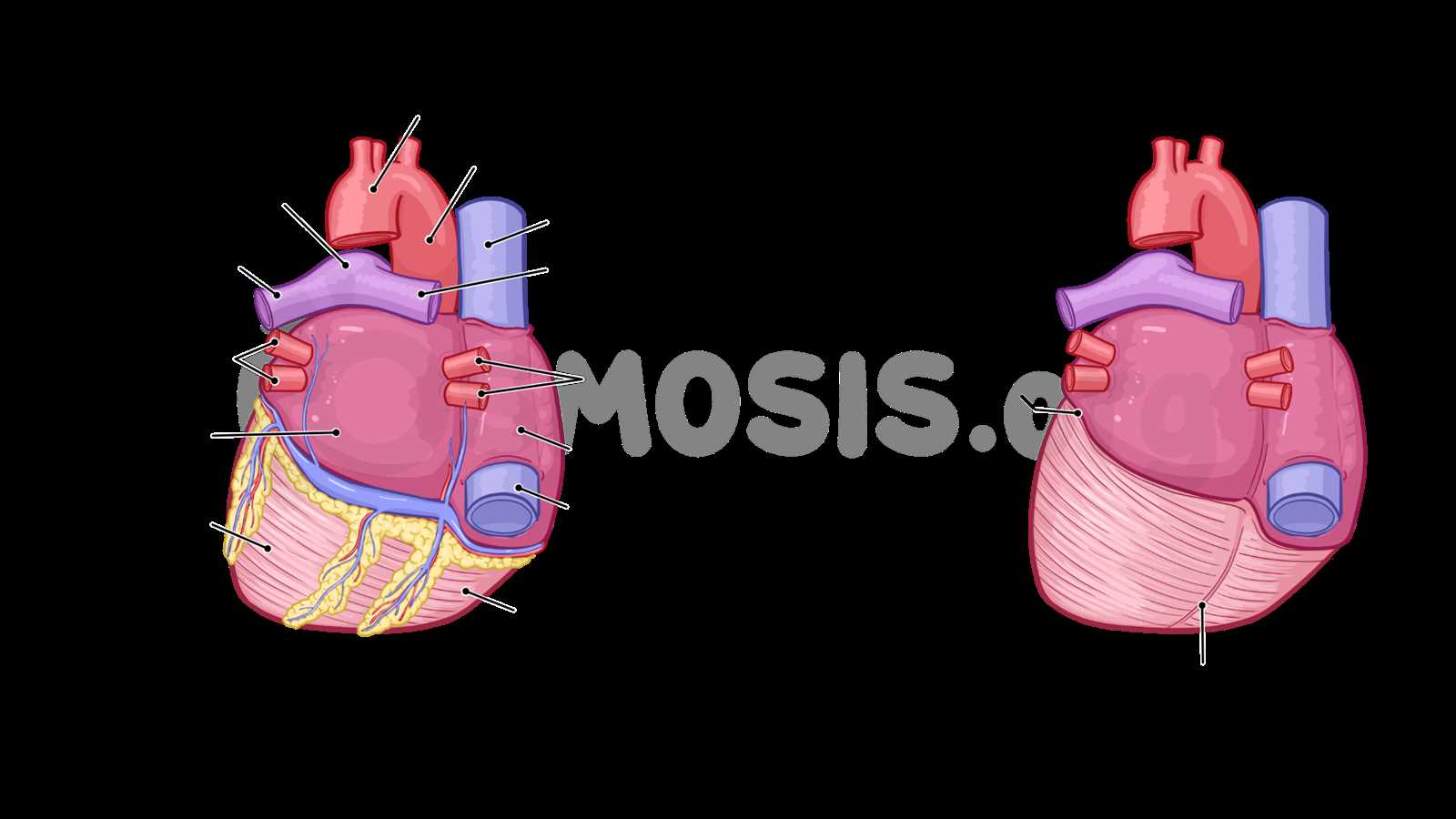
Coronary Circulation Explained
Understanding how blood nourishes a vital organ is essential for grasping its function and health. This system ensures that every part receives adequate oxygen and nutrients, which are crucial for sustaining overall activity. A complex network of vessels plays a key role in this process, maintaining balance and efficiency.
Key Components of Circulation
Two main arteries branch off from the aorta, supplying blood to various regions. Their roles are pivotal, as they dictate how effectively this organ operates.
| Artery | Function |
|---|---|
| Left Coronary Artery | Supplies blood to left side and front |
| Right Coronary Artery | Supplies blood to right side and back |
Significance of Proper Functioning
When circulation is compromised, it can lead to severe consequences, impacting overall well-being. Monitoring and maintaining health of these vessels is crucial for longevity and vitality.
Role of the Aorta
The aorta serves as a vital conduit in the circulatory system, ensuring efficient distribution of oxygen-rich blood throughout the body. Its significance extends beyond mere transportation; it plays a crucial role in maintaining hemodynamic stability and overall physiological function.
Functionally, this large vessel originates from the left ventricle, where it receives blood pumped from the chamber. The aorta then branches into smaller arteries, delivering life-sustaining oxygen and nutrients to various tissues and organs. Its elasticity allows it to absorb pressure during ventricular contractions, regulating blood flow effectively.
Additionally, the aorta’s structure is designed to adapt to varying pressure levels, safeguarding against potential damage. This adaptability is essential for preventing complications such as aneurysms or ruptures, which can lead to serious health issues. Overall, the aorta’s functionality underscores its importance in maintaining the body’s homeostasis and supporting daily activities.
Pulmonary Circulation Basics
Pulmonary circulation is a vital component of the cardiovascular system, ensuring efficient oxygenation of blood. This process involves movement of blood between lungs and a central organ, facilitating exchange of gases necessary for sustaining life.
In this circuit, deoxygenated blood is transported to lungs, where it releases carbon dioxide and absorbs oxygen. This occurs in specialized structures that maximize contact with air, promoting optimal gas exchange. Once enriched with oxygen, blood returns to its original source, ready to be distributed throughout the body.
Understanding this cycle is essential for grasping how our bodies maintain proper oxygen levels, which are crucial for overall health and functioning. Each phase plays a significant role, contributing to the efficiency and effectiveness of our circulatory system.
Furthermore, recognizing abnormalities in this circulation can help in diagnosing various medical conditions, highlighting its importance in both health and disease management.
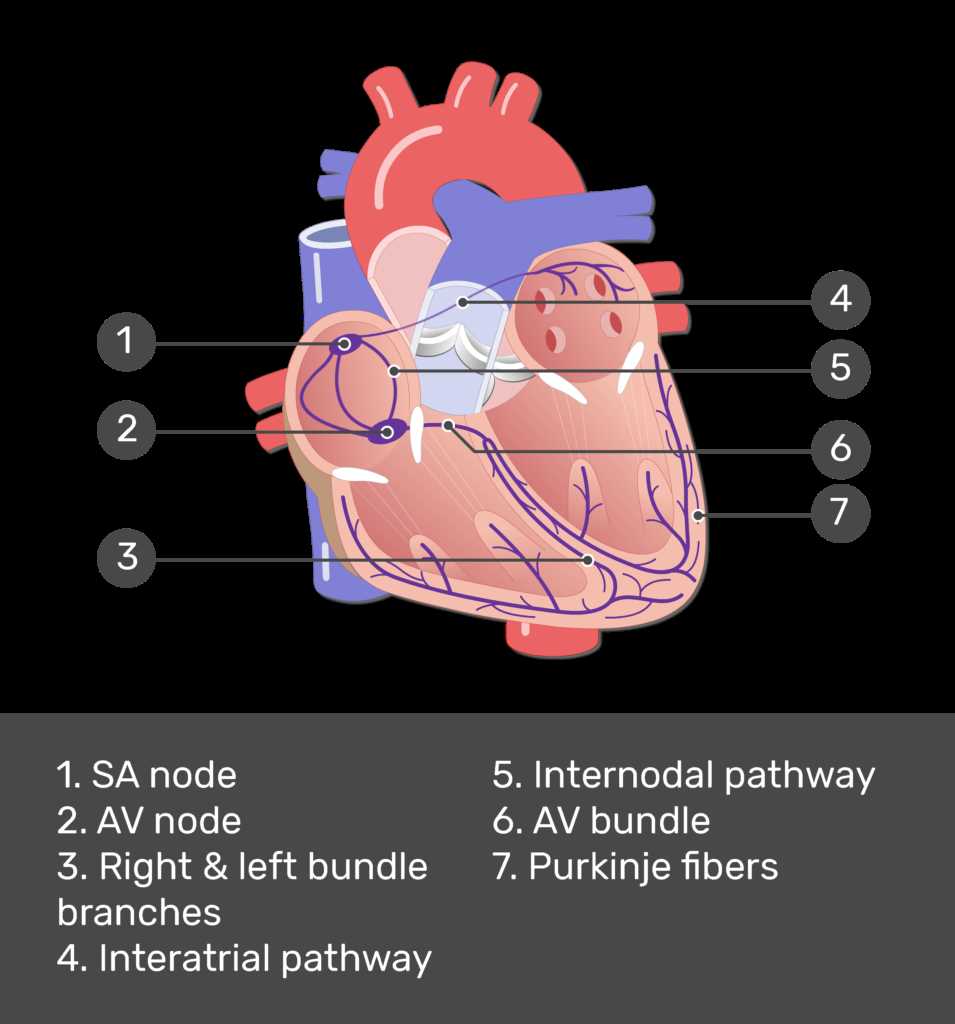
Heart’s Electrical System
This intricate network serves as a vital communication channel, ensuring coordinated contractions and efficient blood flow throughout the body. By generating and transmitting electrical impulses, it orchestrates rhythmic beats that maintain optimal circulation, adapting to varying physical demands.
Components of Electrical Conduction
At the core of this system lies a specialized group of cells, known for their ability to initiate impulses autonomously. These cells not only set the pace but also relay signals to neighboring tissues, enabling synchronized contraction. Understanding this hierarchy is essential for appreciating how each segment contributes to overall functionality.
Significance of Rhythm Regulation
Maintaining a consistent rhythm is crucial for health. Disruptions can lead to arrhythmias, impacting efficiency and potentially causing serious conditions. Monitoring and managing these irregularities is essential for preventing complications and ensuring that the system operates smoothly, allowing for sustained vitality.
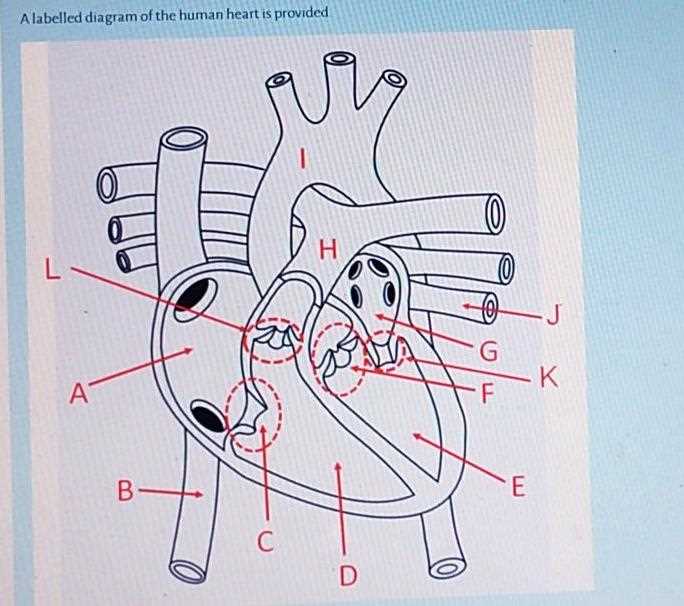
Visualizing Heart Diagrams
Understanding anatomical structures requires clear representations that enhance comprehension. Visual aids play a crucial role in grasping complex systems and their interconnections.
- Diagrams provide a simplified view of intricate networks.
- Color coding helps distinguish between various elements.
- Labels guide viewers to key components and their functions.
Utilizing different types of illustrations can aid in deeper understanding:
- 3D models offer a dynamic perspective.
- Cross-sectional views highlight internal arrangements.
- Interactive graphics engage users for a hands-on experience.
Ultimately, employing diverse visualization techniques enhances knowledge retention and encourages exploration of cardiovascular anatomy.
Common Heart Conditions
Numerous ailments affect this vital organ, leading to various health complications. Understanding these issues is essential for prevention and treatment, as they can significantly impact overall well-being.
Coronary Artery Disease occurs when arteries become narrowed, restricting blood flow and potentially causing chest pain or heart attacks. Early detection and lifestyle changes are crucial for management.
Heart Failure is a condition where the organ struggles to pump blood effectively. Symptoms include fatigue, shortness of breath, and fluid retention, necessitating medical intervention.
Arrhythmias refer to irregular heartbeats, which can lead to dizziness, palpitations, or even stroke. Monitoring and treatment can help manage these conditions effectively.
Valvular Disease affects the valves that control blood flow, leading to potential complications such as heart enlargement or heart failure. Regular check-ups are important for those at risk.
Cardiomyopathy is a disease that affects the heart muscle itself, reducing its ability to pump blood. This condition requires thorough evaluation and tailored treatment plans.
Importance of Heart Health
Maintaining well-being of this vital organ is crucial for overall physical condition and longevity. When it functions optimally, it supports various systems, ensuring efficient circulation and nutrient delivery throughout the body.
Prevention of diseases associated with this organ significantly impacts quality of life. By adopting a balanced diet, engaging in regular exercise, and managing stress, individuals can enhance their well-being.
Moreover, understanding risk factors, such as high blood pressure and cholesterol levels, allows for proactive measures. Regular check-ups can facilitate early detection, making it easier to address potential issues before they escalate.
Ultimately, prioritizing the well-being of this essential organ fosters a healthier lifestyle and can lead to a more fulfilling life.
Resources for Further Learning
Understanding complex systems requires access to various educational materials. Whether you are a student, educator, or simply an enthusiast, a multitude of resources can enhance your knowledge and comprehension of anatomy and physiology.
Books: Numerous texts provide in-depth exploration of circulatory systems. Consider titles that focus on human anatomy, physiology, or medical sciences for detailed insights.
Online Courses: Platforms like Coursera, edX, and Khan Academy offer courses that cover essential concepts and advanced topics. These courses often include video lectures, interactive quizzes, and community forums.
Videos: YouTube channels dedicated to science and medicine provide visual explanations, animations, and real-life applications, making complex ideas more accessible.
Websites: Educational websites such as Khan Academy, MedlinePlus, and AnatomyZone offer comprehensive articles, illustrations, and interactive tools for self-paced learning.
Podcasts: Listening to health-related podcasts can provide valuable insights and keep you updated on recent developments in the field of anatomy and medicine.
Exploring these resources can greatly enhance your understanding and foster a deeper appreciation for the intricacies of biological systems.