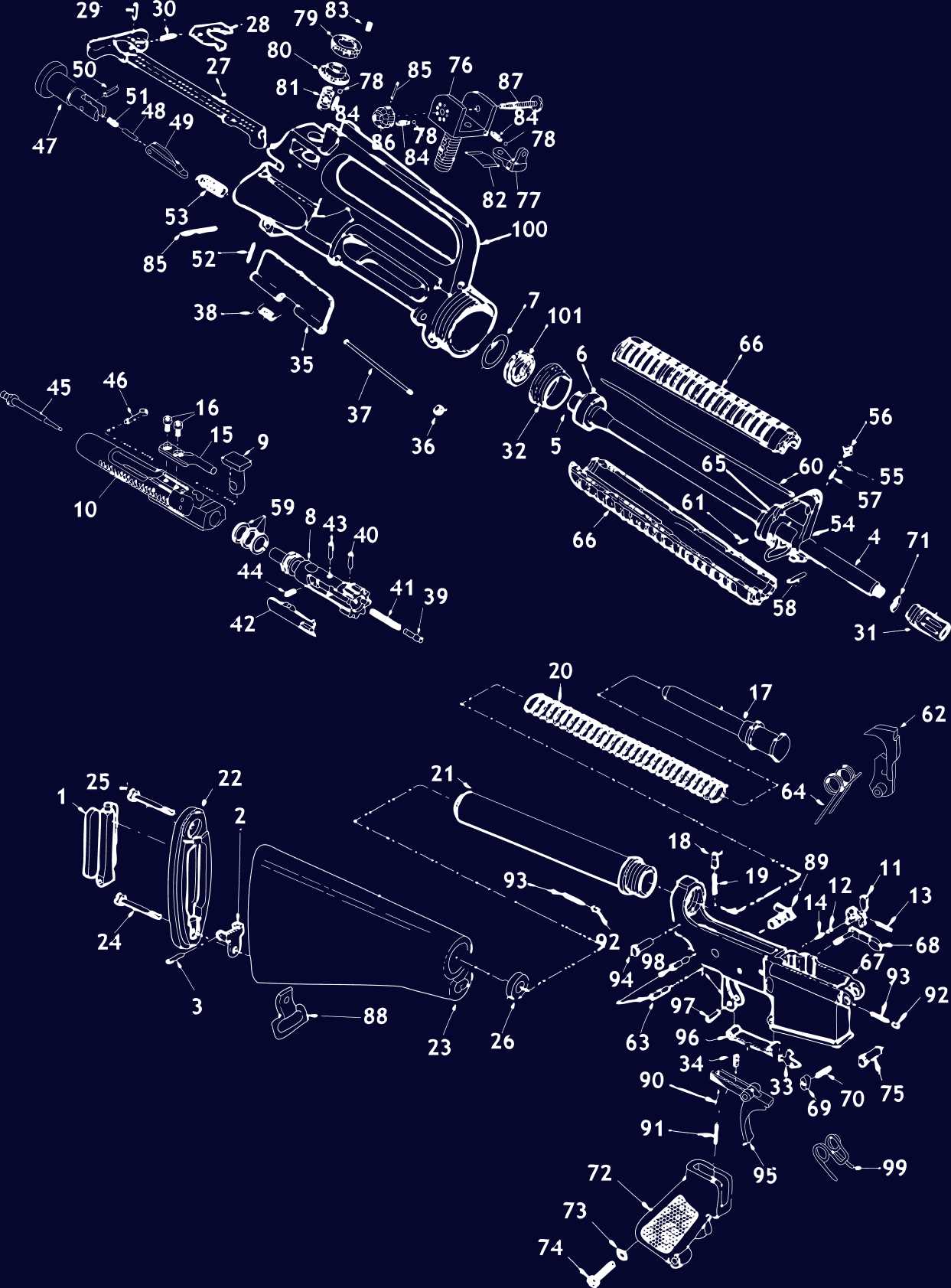
Savage 340 Parts Diagram and Components Overview

Understanding the internal structure and elements of a vintage firearm can provide enthusiasts and collectors with valuable insights into its functionality. The precise arrangement of each mechanism plays a crucial role in the overall performance and reliability of the weapon. By examining these elements closely, one can develop a deeper appreciation for the craftsmanship and engineering that went into its creation.
The configuration of individual mechanisms reveals much about how different parts interact with each other to achieve a smooth operation. This exploration not only enhances technical knowledge but also aids in identifying possible wear points or areas requiring maintenance. It’s an essential guide for those looking to preserve or restore an
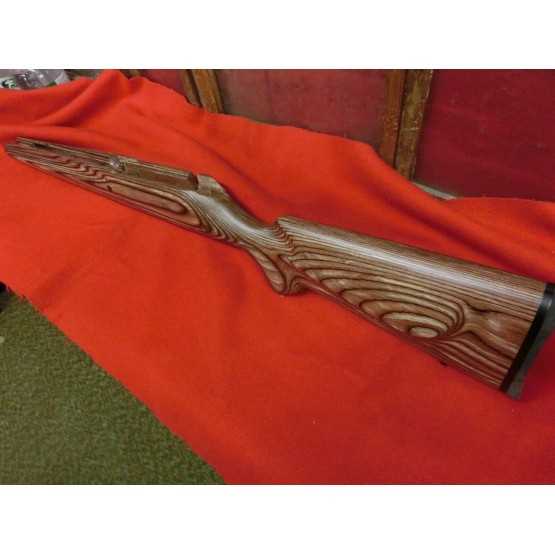
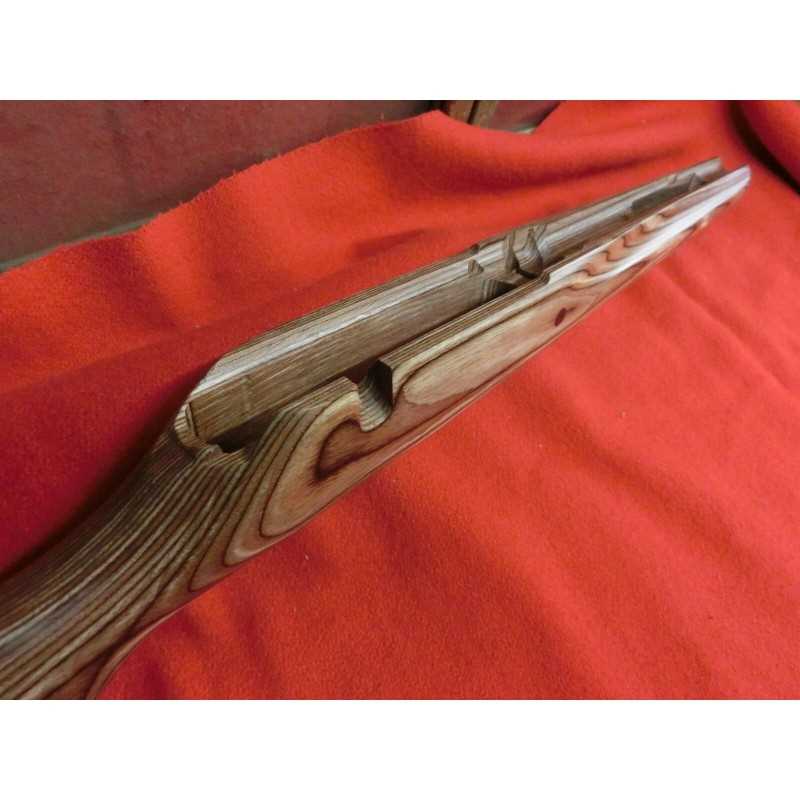
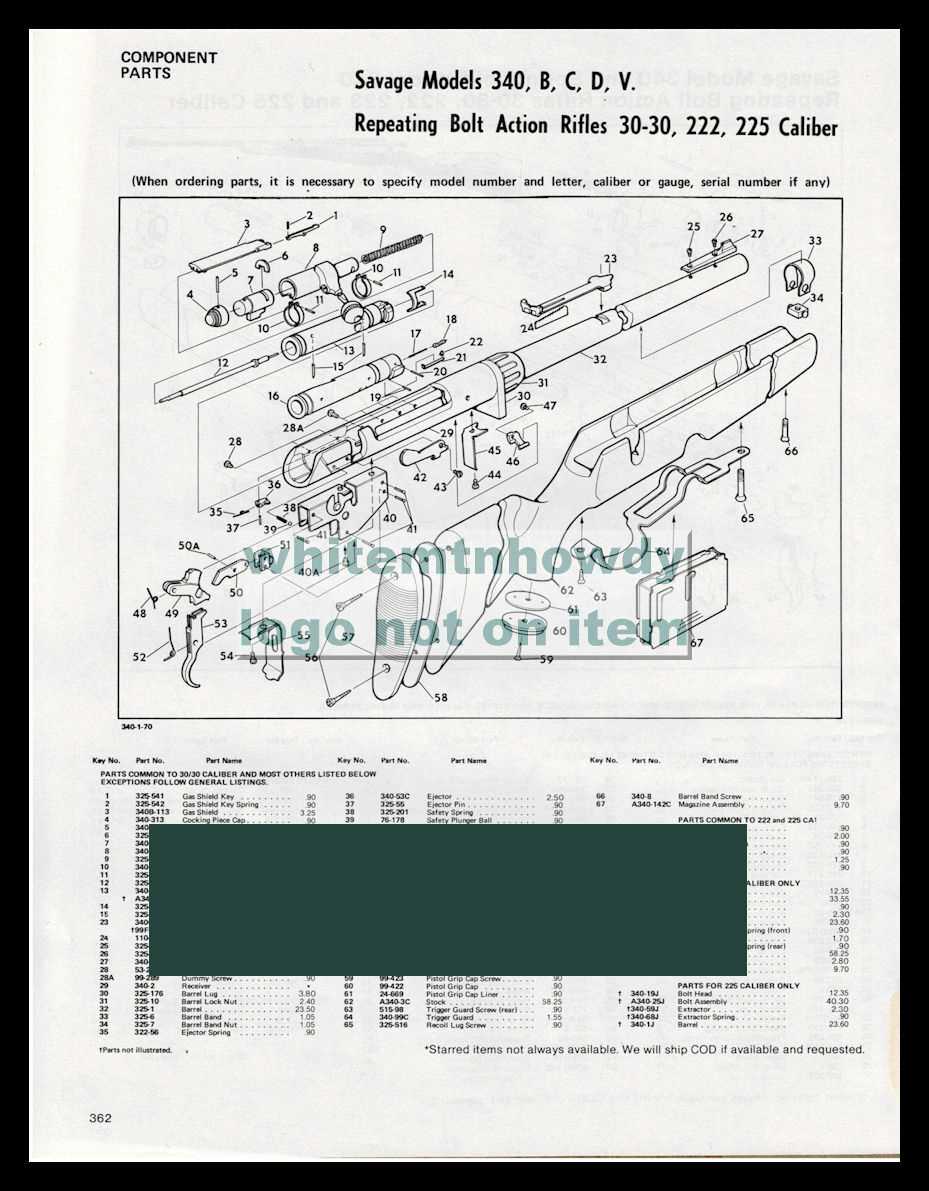
Exploring the Components of Savage 340
The intricate assembly of this iconic model showcases a careful blend of functionality and craftsmanship. Each piece, from the core mechanical structures to the smallest connectors, plays a vital role in ensuring smooth operation. By understanding how these individual elements work together, one can appreciate the precision behind its design and maintain its efficiency over time.
Among the key elements are those responsible for the firing mechanism, stability, and user control. The interlocking sections ensure reliability, while the adjustable components allow for fine-tuning performance to suit various needs. Paying attention to these parts can greatly enhance both handling and accuracy.
For enthusiasts and professionals alike, examining these components offers valuable insights into both maintenance and customization. By delving into the specifics of
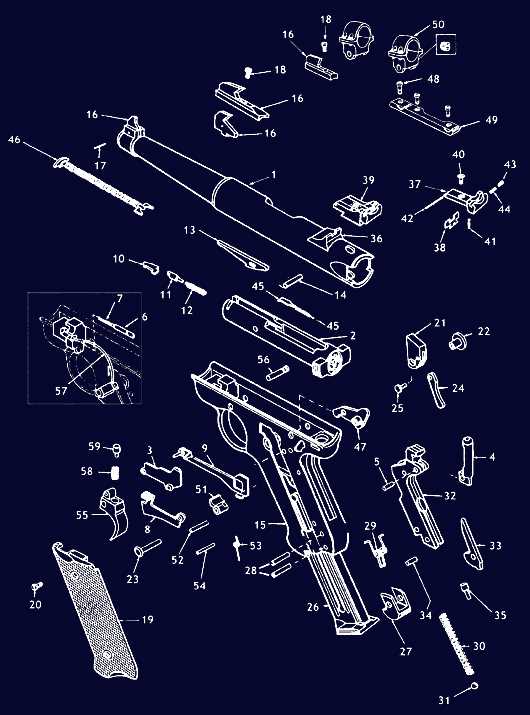
Understanding the Bolt Mechanism Assembly
The bolt mechanism is a crucial element in the operation of many devices, facilitating smooth and efficient interaction between components. It plays a key role in the overall functionality, ensuring proper alignment, secure engagement, and reliable performance. Understanding how the assembly works helps in maintaining and troubleshooting issues that may arise over time.
The mechanism typically consists of several interconnected elements that work together to allow controlled movement and secure locking. When assembled correctly, each piece fits seamlessly into the next, allowing for smooth operation. Proper understanding of this system can enhance maintenance efforts and ensure long-lasting performance.
At the core of this system are components responsible for rotational and linear motion. These parts must interact with precision, ensuring that forces applied during operation are evenly distributed and do not cause wear or damage over time
Barrel and Receiver: Key Features
The connection between the barrel and receiver plays a crucial role in the overall performance and accuracy of the firearm. These two components form the foundation of the entire system, ensuring stability and precision during operation. Proper alignment and interaction between these parts directly affect reliability and functionality.
| Component | Main Functions | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Barrel | Directs the projectile, providing stability and improving accuracy with its length and internal structure. | ||||||||||||||
| Receiver | Acts as the core housing for the firing mechanism,
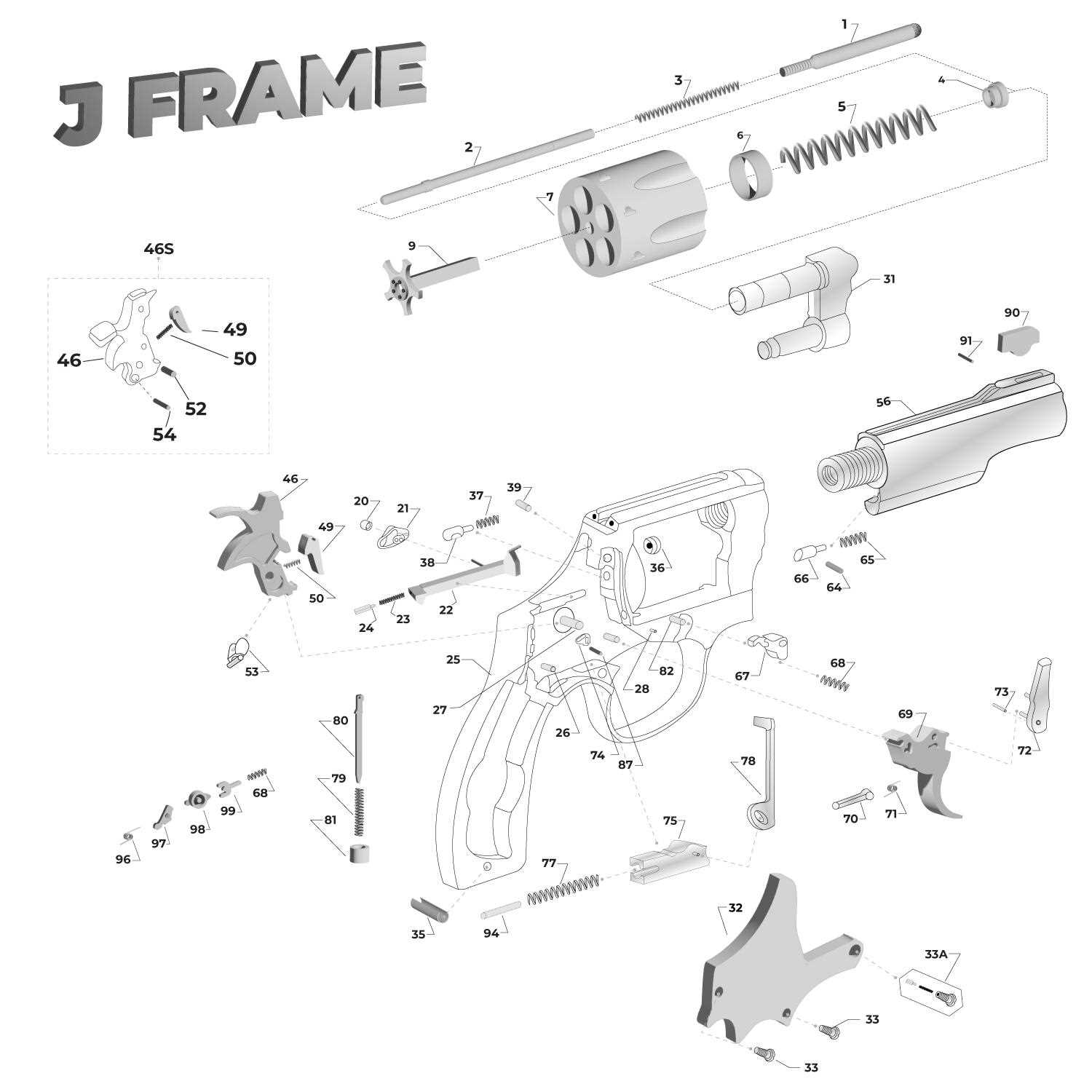
Trigger System Breakdown
The trigger mechanism is a crucial component responsible for initiating the firing sequence. By pressing the trigger, the user controls the release of stored energy, allowing the system to operate efficiently and reliably. Understanding the components within this mechanism is key to maintaining functionality and ensuring safety during operation. Key Components of the Trigger MechanismThe trigger assembly consists of several interconnected parts that work together to perform the release action. These include the sear, which holds back the spring-loaded firing pin, and the trigger itself, which releases the sear when pulled. Each component is designed to ensure smooth operation, minimizing the effort required from the user. Magazine Design and Capacity
|
| Safety Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Manual Safety | A lever or switch that must be engaged to prevent the trigger from being pulled unintentionally. |
| Drop Safety | Prevents firing if the firearm is dropped, ensuring it will not discharge under unexpected impacts. |
| Decocking Mechanism | Allows the hammer to be safely lowered without firing the weapon, reducing the risk during storage. |
Additional Protective Features
Alongside primary safety mechanisms, additional protective features further enhance user safety. These innovations reflect advancements in technology and design, aiming to minimize risks while ensuring effective operation.
| Additional Feature | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Chamber Indicator | Visually or physically indicates whether a round is chambered, providing clear feedback to the user. |
| Trigger Safety | Prevents the trigger from being pulled unless it is depressed in a specific manner, reducing the chance of unintentional firing. |
Scope Mounting Compatibility
When considering the attachment of optical devices to firearms, it’s crucial to understand the variations in mounting systems. The compatibility of different mounts with specific models can significantly influence performance and usability. This section will explore the essential factors that contribute to successful optics installation.
Factors to Consider
- Mounting Style: Various mounting systems, such as ring-style and base systems, offer different levels of stability and alignment.
- Height and Length: The height of the scope mount should align with the shooter’s line of sight, while the length must accommodate the overall design of the firearm.
- Material Quality: The durability of the mount affects its longevity and performance, particularly under heavy recoil.
Types of Mounts
- One-Piece Mounts: These provide a solid platform and are often preferred for their ease of installation.
- Two-Piece Mounts: This style allows for more customization and adjustment options, making them suitable for varied applications.
- Quick-Release Mounts: Designed for easy removal and reattachment, these mounts offer convenience without sacrificing stability.
Ultimately, selecting the right mounting system is vital for optimizing accuracy and functionality. Evaluating compatibility ensures a smooth integration of optical devices with the firearm.
Extractor and Ejector Overview
The components responsible for the removal of spent cartridges from the chamber play a crucial role in the functionality of a firearm. These elements ensure that the firing process is smooth and reliable, contributing to the overall efficiency and performance of the weapon. Understanding their mechanisms and functions is essential for proper maintenance and operation.
Functionality of Extractors

Extractors are designed to grasp the rim of a cartridge, pulling it from the chamber after firing. This action is vital for preventing malfunctions during operation. The quality of the extractor significantly affects the reliability of the ejection process, and a well-functioning extractor ensures that the firearm operates without interruption.
The Role of Ejectors
Ejectors work in conjunction with extractors to expel the spent cartridge from the firearm. Once the cartridge is released from the chamber, the ejector swiftly forces it out, allowing for a quick reload. The design and positioning of the ejector can vary, influencing how efficiently spent casings are expelled and affecting the overall shooting experience.
Rear and Front Sight Differences
The sighting mechanisms on firearms play a crucial role in ensuring accuracy and precision during shooting. Understanding the distinctions between the rear and front sights is essential for optimizing performance and achieving desired results. Each component serves a unique purpose in the sighting system, contributing to the overall effectiveness of aiming and targeting.
Functionality and Design
The primary function of the front sight is to provide a clear point of aim, guiding the shooter’s line of sight towards the target. Typically located at the muzzle end, this component is often smaller and more streamlined, allowing for quick target acquisition. In contrast, the rear sight is designed to align with the front sight, offering a reference point that enhances overall accuracy. It usually features adjustable elements, enabling users to fine-tune their aim based on various conditions.
Types and Adjustability
Front sights can vary widely in design, from simple post configurations to more elaborate bead or blade styles, depending on the intended use and shooting preferences. Rear sights also come in various forms, including notch, aperture, and ghost ring types, each providing different levels of precision and user experience. Adjustability is a key feature of many rear sights, allowing shooters to make necessary corrections for windage and elevation, which is less common with front sights.
In summary, while both sight types are integral to the aiming process, their specific designs and functionalities cater to different aspects of shooting, making it essential for users to understand their unique contributions to marksmanship.