Understanding the Different Cuts of Beef from a Cow
The world of beef is rich and diverse, offering a variety of options for culinary enthusiasts and everyday cooks alike. Each cut comes from different regions of the animal, contributing to its unique flavor, texture, and suitability for various cooking methods. Exploring these selections not only enhances your cooking skills but also deepens your appreciation for this versatile ingredient.
When delving into the intricacies of beef, it’s essential to recognize how each section affects the final dish. From tender choices ideal for grilling to tougher cuts that benefit from slow cooking, understanding these distinctions allows for more informed decisions when selecting ingredients. This knowledge empowers chefs to create memorable meals tailored to specific tastes and occasions.
In addition, familiarizing oneself with the various selections promotes sustainability and ethical sourcing. Knowing where your meat comes from and how it’s processed can lead to better choices that align with personal values regarding animal welfare and environmental impact. As you embark on this journey through the world of beef, you’ll discover not only delicious options but also the stories behind them.
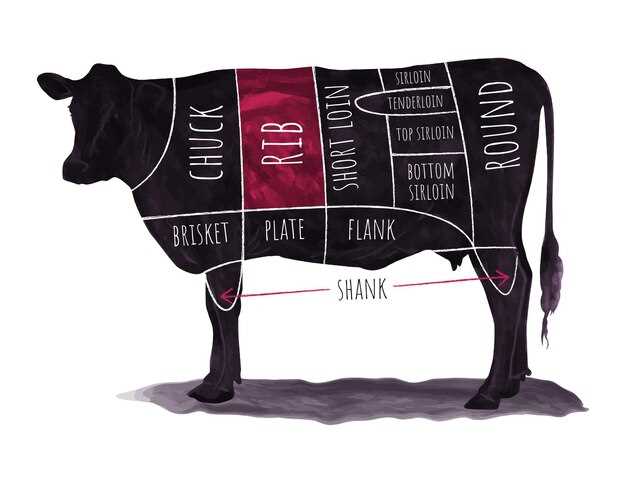
The Anatomy of a Cow
Understanding the structure of this domesticated animal is essential for various fields, including agriculture and culinary arts. This section explores the different sections of the animal, highlighting their significance and uses in food preparation. Each region contributes distinct flavors and textures, enriching the dining experience.
Overview of Sections
Each section of the creature has unique characteristics that influence its culinary applications. From tender cuts ideal for grilling to tougher areas suitable for slow cooking, the knowledge of these divisions helps in selecting the appropriate cooking methods and techniques.
Key Divisions

| Region | Description | Typical Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Chuck | This area is located near the neck and shoulder, known for its robust flavor. | Ideal for stews and pot roasts. |
| Rib | A rich section that offers a good balance of tenderness and taste. | Perfect for grilling and roasting. |
| Brisket | Situated at the chest, this cut is recognized for its rich marbling. | Commonly used in barbecue and smoked dishes. |
| Round | This area comes from the back leg, noted for its leanness. | Best suited for roasting or braising. |
| Flank | Located beneath the loin, it is known for its distinct flavor. | Often used for stir-frying or fajitas. |
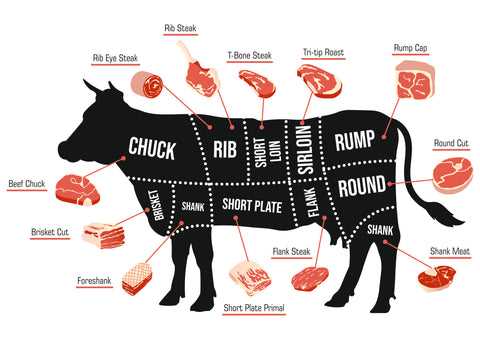
Popular Cuts of Steak Explained
When it comes to enjoying grilled meat, understanding the different selections can enhance your culinary experience. Each type of cut offers unique flavors and textures, making some more suitable for specific cooking methods than others. Here’s a closer look at some of the most favored varieties.
- Ribeye: Known for its marbling, this cut delivers a rich and buttery flavor. It’s often grilled or pan-seared for optimal taste.
- Filet Mignon: This tender choice comes from a less active muscle, making it exceptionally soft. It’s perfect for those who prefer a delicate texture.
- Sirloin: A versatile option, sirloin strikes a balance between flavor and tenderness. It can be enjoyed grilled, roasted, or stir-fried.
- T-bone: Featuring both strip and tenderloin, this cut offers a unique combination of textures. It’s ideal for those who want to savor multiple flavors in one bite.
- Porterhouse: Similar to the T-bone but larger, this cut provides generous portions of both strip and tenderloin, making it great for sharing.
Choosing the right selection can make a significant difference in your meal. Each cut has its characteristics, making them more suitable for certain dishes or cooking methods.
How to Choose Quality Beef
Selecting high-grade meat requires attention to various factors that indicate freshness and flavor. It is essential to understand the qualities that make meat not only appetizing but also nutritious. The following guidelines can help in making informed choices when purchasing.
Look for vibrant coloration; fresh meat should display a rich, deep hue without any dullness. The texture also plays a significant role; it should be firm yet slightly springy to the touch, indicating proper handling and storage. Additionally, examining the marbling is crucial; fine flecks of fat within the muscle contribute to tenderness and enhanced taste.
When purchasing, consider the source. Meat from reputable suppliers who adhere to quality standards ensures a more satisfying culinary experience. Always inquire about the origin and rearing practices, as these aspects can greatly influence the quality of the product.
Finally, pay attention to packaging. The absence of excessive liquid and the integrity of the wrapping are indicators of freshness. Choosing well-preserved cuts is vital for both safety and flavor. By following these tips, you can confidently select premium meat for your meals.
Cooking Techniques for Different Cuts

Each type of meat cut has unique characteristics that influence the most suitable cooking methods. Understanding these techniques can enhance flavor and tenderness, allowing for a delightful culinary experience. This section explores various approaches tailored to specific meat selections.
- Grilling: Ideal for thinner cuts, this method imparts a smoky flavor while sealing in juices. Ensure the grill is preheated to achieve a perfect sear.
- Roasting: Best for larger sections, roasting in the oven allows for even cooking and the development of a flavorful crust. Use a meat thermometer to achieve the desired doneness.
- Slow Cooking: Perfect for tougher cuts, this technique involves cooking at low temperatures for extended periods. The result is tender meat that falls apart easily, rich in flavor.
- Pan-Searing: Suitable for medium-thickness cuts, this method involves cooking in a hot pan with a little oil. It creates a delicious crust while keeping the interior moist.
- Braising: A combination of dry and wet cooking, braising is excellent for tougher sections. Start with browning the meat, then simmer it in liquid until tender.
Choosing the right technique based on the meat cut ensures optimal results. Experimenting with different methods can lead to discovering new flavors and textures.
Flavor Profiles of Various Steaks
The taste experience of different cuts of meat can vary significantly, influenced by factors such as the animal’s diet, muscle composition, and cooking methods. Understanding these nuances enhances the enjoyment of each type and guides culinary choices.
Filet Mignon is renowned for its tenderness and subtle flavor. This cut, taken from the tenderloin, is often praised for its buttery texture, making it a favorite among those who prefer a mild taste. Its delicate profile pairs beautifully with rich sauces and complementary spices.
Ribeye offers a robust and juicy flavor, characterized by its marbling. The fat content in this cut not only adds moisture but also intensifies the meaty taste. When grilled or roasted, the rich, savory notes are enhanced, making it a go-to option for those seeking a bold experience.
Sirloin strikes a balance between flavor and tenderness. This cut presents a hearty taste that is often described as beefy yet not overpowering. It is versatile and can be seasoned in various ways, making it suitable for grilling, broiling, or sautéing.
T-bone combines two different textures and flavors in one cut, featuring both the tenderloin and strip steak. The contrast between the two enhances the overall dining experience, as each bite offers a unique taste sensation. The T-bone is ideal for those who appreciate variety.
By exploring the diverse flavor profiles of these cuts, culinary enthusiasts can elevate their meals, making informed choices that cater to their preferences and enhance their dining experiences.
Regional Variations in Beef Cuts
Beef selections vary significantly across different geographical areas, influenced by local culinary traditions, cultural preferences, and butchering techniques. Each region showcases unique offerings, emphasizing distinct textures and flavors that cater to diverse tastes.
In the United States, the emphasis is often on well-known cuts like the ribeye and brisket, celebrated for their tenderness and flavor. Meanwhile, in European countries, such as France and Italy, cuts may be less familiar to those outside the region but are equally valued, with specialties like onglet and bavette taking center stage.
| Region | Popular Cuts | Description |
|---|---|---|
| United States | Ribeye, Brisket | Known for rich marbling and flavor, ideal for grilling and smoking. |
| France | Onglet, Bavette | Flank cuts that are flavorful and often used in traditional dishes. |
| Argentina | Asado, Vacío | Popular for barbecues, focusing on a communal dining experience. |
| Japan | Wagyu, Chuck | Renowned for its marbling and tenderness, offering a luxurious experience. |
Nutrition Facts of Different Steaks
When it comes to choosing premium cuts of beef, understanding the nutritional content is essential for making informed dietary choices. Each type of cut offers unique flavors and textures, along with varying nutritional profiles that can impact health and well-being. This section will explore the nutritional values associated with various cuts of meat, providing insight into their benefits.
Key Nutritional Components
- Protein: Essential for muscle growth and repair, high-quality meat cuts typically contain a significant amount of protein.
- Fats: The fat content varies widely among different cuts, influencing both flavor and calorie density.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Many cuts are rich in essential nutrients such as iron, zinc, and B vitamins.
Comparative Nutritional Values
- Ribeye: Known for its marbling, this cut is higher in fat but offers a rich flavor.
- Filet Mignon: A leaner option, it provides a tender texture with lower fat content.
- Sirloin: A versatile cut that balances flavor and leanness, making it a popular choice.
- Flank: Often lean and flavorful, this cut is a great source of protein with moderate fat.
Understanding the nutritional values associated with various meat options allows consumers to select cuts that align with their dietary preferences and health goals.
Storage Tips for Fresh Beef
Ensuring the freshness of high-quality meat is essential for maintaining its flavor and texture. Proper storage methods play a crucial role in prolonging the shelf life and preventing spoilage. Here are some effective strategies to keep your meat fresh.
1. Refrigeration: Always store fresh meat in the refrigerator at a temperature of 32°F to 36°F (0°C to 2°C). This range is optimal for slowing bacterial growth. Place the meat in its original packaging or in an airtight container to minimize exposure to air.
2. Freezing: If you don’t plan to use the meat within a few days, freezing is a great option. Wrap it tightly in plastic wrap, aluminum foil, or freezer paper to protect it from freezer burn. Label each package with the date to track its freshness.
3. Thawing: When ready to use frozen meat, thaw it in the refrigerator rather than at room temperature. This method helps maintain a safe temperature and reduces the risk of bacterial growth.
4. Avoiding Cross-Contamination: Keep raw meat separate from other foods in your refrigerator. Use separate cutting boards and utensils to prevent the spread of bacteria from raw to cooked foods.
5. Regular Checks: Periodically check the freshness of stored meat. Look for any signs of spoilage, such as discoloration or off odors. If in doubt, it’s safer to discard the meat.
By following these storage guidelines, you can enjoy the full flavor and quality of your meat while minimizing waste.
Pairing Steaks with Sides and Wines
Creating a harmonious dining experience involves carefully selecting complementary accompaniments and beverages to enhance the main dish. By considering flavor profiles and textures, one can elevate a meal, making it truly memorable. This section explores how to pair grilled cuts with ideal sides and wines.
Choosing the Right Accompaniments
When selecting sides to accompany grilled cuts, aim for a balance between richness and freshness. Classic choices include roasted vegetables, creamy mashed potatoes, or a crisp salad. These options provide contrasting flavors that highlight the main dish while adding variety to the plate.
Wine Selection
The right wine can elevate the dining experience, complementing the flavors of the main dish. A full-bodied red wine typically pairs well with heartier cuts, while lighter options may be suitable for more delicate flavors. Consider the characteristics of both the wine and the dish to ensure a harmonious pairing.
| Type of Dish | Recommended Side | Suggested Wine |
|---|---|---|
| Rich and Flavorful | Garlic Mashed Potatoes | Cabernet Sauvignon |
| Grilled | Roasted Asparagus | Pinot Noir |
| Light and Tender | Mixed Green Salad | Sauvignon Blanc |
Understanding Meat Grading Systems
Meat grading systems play a crucial role in determining the quality and value of various cuts derived from livestock. These classifications help consumers, retailers, and producers make informed choices by providing a standardized way to assess attributes such as tenderness, flavor, and overall texture. Understanding these grading systems is essential for both culinary professionals and home cooks aiming to select the best options for their needs.
Key Criteria for Grading
- Marbling: This refers to the small flecks of fat within the muscle tissue, which can enhance flavor and tenderness.
- Color: The hue of the meat can indicate freshness and quality, with brighter colors generally preferred.
- Age: The age of the animal can influence the meat’s tenderness, with younger animals typically producing more tender cuts.
- Fat Cover: A certain level of fat on the exterior can help retain moisture and flavor during cooking.
Common Grading Systems
- USDA Grading: In the United States, the United States Department of Agriculture categorizes meat into various grades such as Prime, Choice, and Select.
- European Grading: In Europe, a similar system exists, with classifications such as A, B, and C, which reflect the quality and type of meat.
- Japanese Beef Grading: This system focuses heavily on marbling and includes rankings from A to C, with additional numerical scores.