Tig Welder Parts Diagram for Efficient Repairs and Maintenance
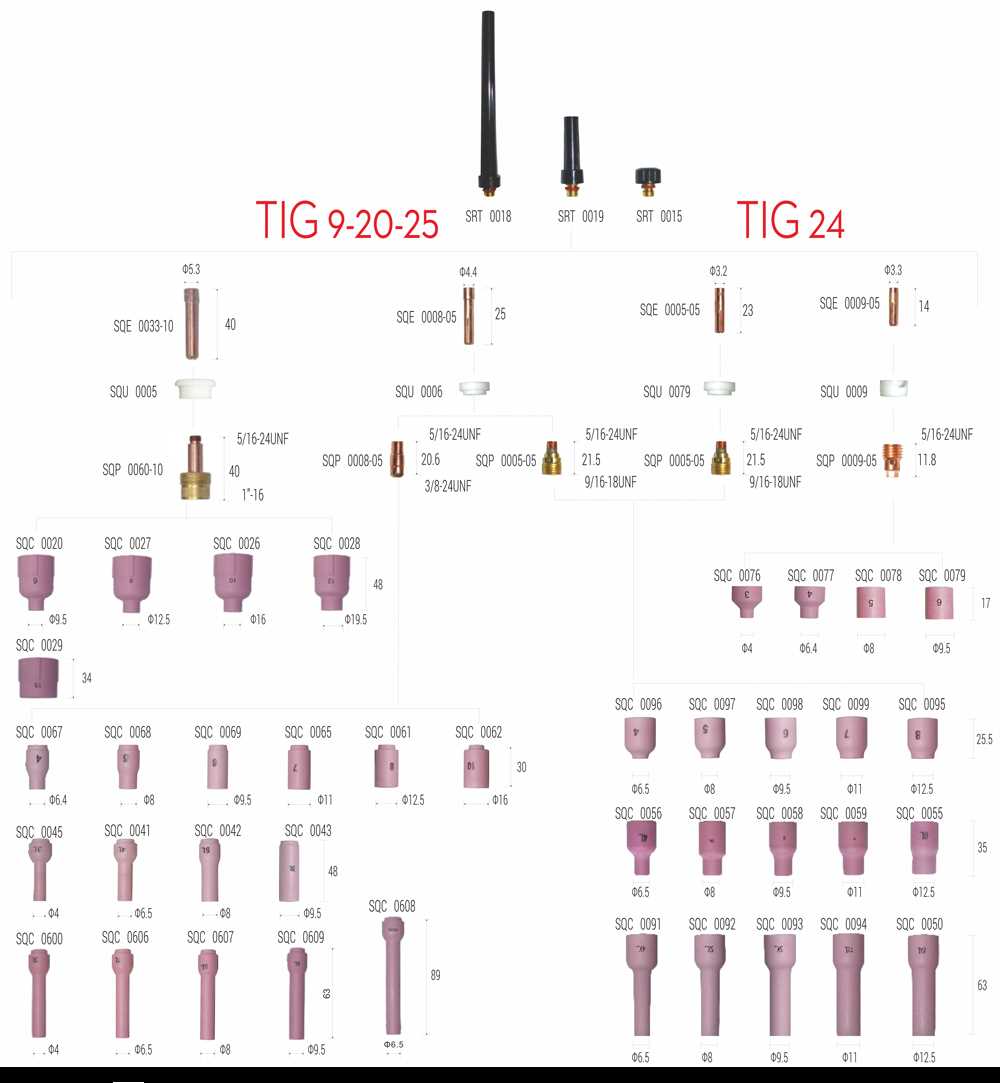
In the realm of metalworking, the effectiveness of your setup hinges on the intricate interplay of various components. Each element plays a pivotal role in ensuring a seamless and efficient operation, allowing artisans to achieve the desired outcomes in their projects. A clear comprehension of these pieces can greatly enhance both performance and precision.
Detailed insights into each segment not only facilitate better maintenance but also empower users to troubleshoot potential issues more effectively. By grasping how these elements interact, one can unlock the ultimate potential of their machinery. This knowledge is invaluable for both novices and seasoned professionals alike, providing a foundation for enhanced craftsmanship.
As we delve deeper into the structure and function of these essential components, it becomes evident how critical they are to the overall functionality. Understanding their design and arrangement can lead to improved results and a more enjoyable experience in any metalworking endeavor.
Tig Welder Components Overview
This section explores the essential elements that make up the advanced apparatus used for precision metal joining. Understanding these components is crucial for effective operation and maintenance.
Main Components
- Power Source: Provides the necessary electricity for the process.
- Electrode Holder: Securely holds the consumable electrode during use.
- Gas Supply: Delivers shielding gas to protect the weld area.
- Cables: Transmit power and control signals to the system.
Auxiliary Features
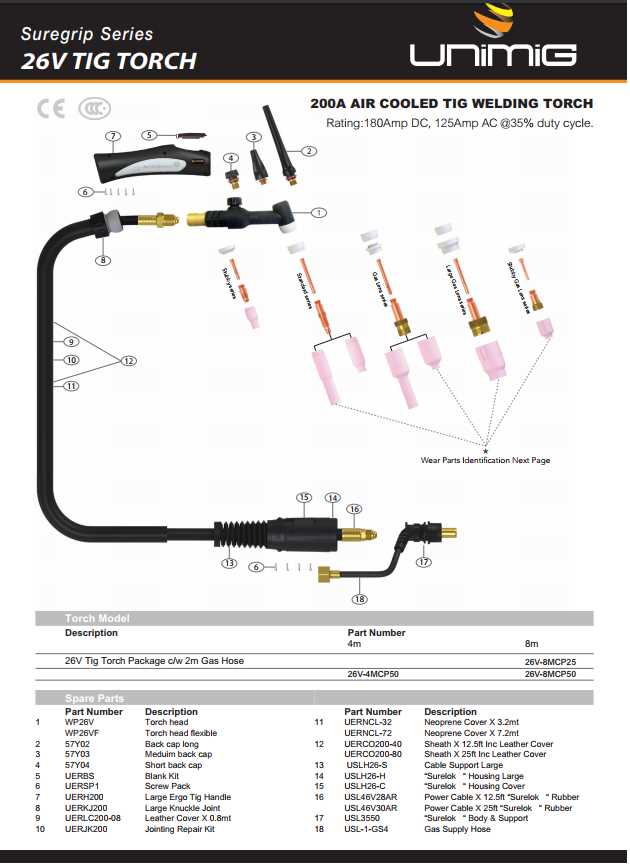
- Cooling System: Maintains optimal operating temperatures.
- Foot Pedal: Allows for precise control of the welding current.
- Fume Extraction: Removes hazardous fumes from the workspace.
Each component plays a vital role in achieving quality results and ensuring safety during operation.
Understanding TIG Welding Basics
This section provides a fundamental overview of a sophisticated metal joining technique that utilizes a non-consumable electrode and inert gas. The process allows for precise control, making it ideal for various applications, from automotive repairs to artistic projects.
Key Components
- Electrode: A crucial element that provides the arc.
- Inert Gas: Protects the weld pool from contamination.
- Power Source: Supplies the necessary current.
- Filler Material: Optional addition for enhancing joint strength.
Process Overview
- Prepare the materials by cleaning the surfaces.
- Set up the equipment, ensuring proper gas flow.
- Ignite the arc to start the process.
- Move the electrode in a controlled manner to create the weld.
- Cool the weld and inspect the joint for quality.
Key Parts of a TIG Welder
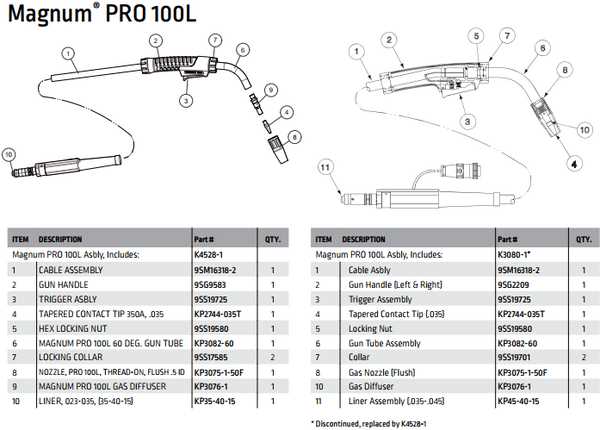
Understanding the essential components of a high-frequency arc tool is crucial for achieving optimal performance in various welding applications. Each element plays a vital role in the overall functionality, ensuring precision and control during the process. Below, we will explore the primary components that contribute to the effectiveness of this equipment.
Essential Components
The following table outlines the main elements and their functions within the welding apparatus:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Power Source | Supplies electrical energy needed to create the arc. |
| Torch | Houses the electrode and directs the shielding gas. |
| Electrode | Conducts current to produce the arc and melt the material. |
| Shielding Gas | Protects the weld area from contamination and oxidation. |
| Filler Rod | Added material that helps create a stronger joint. |
Conclusion
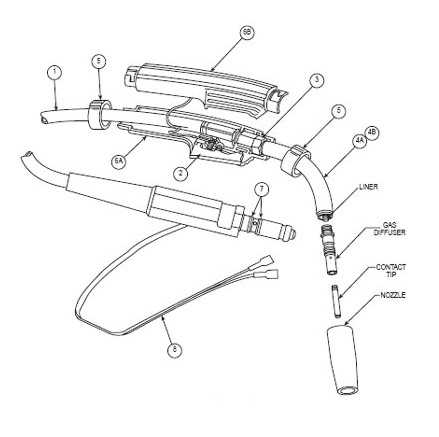
Each of these key elements is integral to the operation of the equipment, ensuring that welds are performed with accuracy and durability. Mastery of these components will greatly enhance the welding experience and results.
Importance of High-Frequency Start
The initiation of an arc plays a crucial role in achieving optimal results in various welding processes. A reliable and efficient method to commence this arc significantly enhances the overall performance and quality of the operation. Utilizing a high-frequency start mechanism ensures a stable and consistent arc formation, which is vital for successful welding applications.
Enhanced Arc Stability
One of the primary benefits of employing a high-frequency starting technique is the improved stability of the arc. This stability allows for precise control over the heat input and penetration, which is essential when working with thin materials. By minimizing fluctuations, the welder can achieve a cleaner and more uniform weld bead.
Reduced Contamination Risks
Another critical aspect is the reduction of contamination during the arc initiation phase. By establishing the arc without direct contact, this method prevents the tungsten electrode from touching the workpiece, which can lead to impurities and defects. This results in higher-quality welds and less rework, ultimately saving time and resources.
Choosing the Right Tungsten Electrode
Selecting the appropriate electrode is crucial for achieving optimal performance in your welding tasks. The choice can significantly impact the quality of your work and the efficiency of the process. Various factors come into play when determining which option best suits your needs.
- Electrode Type: Consider the different types available, such as pure tungsten, thoriated, or lanthanated.
- Diameter: The size of the electrode should match the thickness of the material you’re working with.
- Current Type: Determine whether you’ll be using alternating or direct current, as this influences electrode selection.
- Application: Identify the specific tasks–such as aluminum or stainless steel welding–to select the most effective option.
Ultimately, taking the time to evaluate these factors will enhance your welding results and ensure greater satisfaction with your projects.
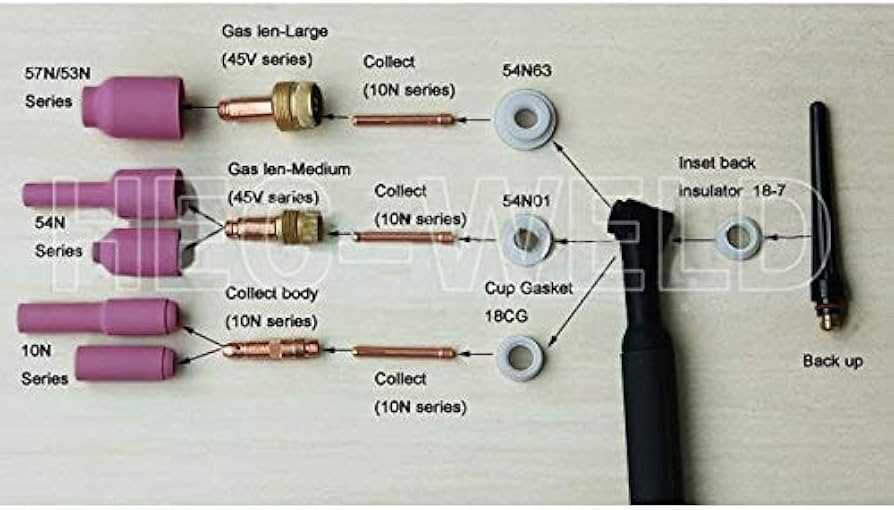
Role of the Gas Lens System
The gas lens system plays a crucial role in the overall effectiveness and quality of the welding process. It serves as a sophisticated mechanism designed to optimize shielding gas flow, thereby enhancing arc stability and minimizing contamination. This functionality is vital for achieving clean, strong welds that meet industry standards.
One of the primary benefits of a gas lens system is its ability to provide a more focused and uniform shielding gas coverage. Unlike traditional setups, the gas lens allows for greater control over the gas delivery, which is essential for protecting the weld pool from atmospheric elements. This improved gas distribution results in better arc characteristics, leading to a smoother and more efficient welding operation.
Moreover, the incorporation of a gas lens can significantly extend the reach of the shielding gas. This is particularly advantageous in applications where accessibility is limited or where intricate work is required. By maintaining optimal gas flow even in challenging positions, the system contributes to enhanced overall performance.
In summary, the gas lens system is an integral component that not only improves the quality of the welding process but also increases the versatility and effectiveness of the operation. Its ability to refine gas distribution and protect the weld area underscores its importance in modern welding applications.
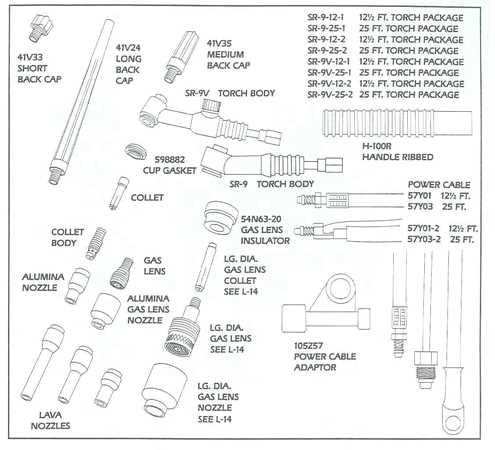
Types of TIG Welding Torches

In the world of precise metal joining, the choice of torch plays a crucial role in achieving optimal results. Various designs cater to different needs, ensuring that welders can select the right tool for their specific applications and preferences.
Air-Cooled Torches are commonly used for light to medium-duty tasks. They rely on ambient air to dissipate heat and are ideal for portability and ease of use. These tools are generally lighter and more convenient for smaller projects, though they have limitations in terms of duty cycle.
Water-Cooled Torches, on the other hand, are designed for heavy-duty applications. They utilize a cooling system that circulates water through the torch, allowing for extended use without overheating. This makes them suitable for more demanding jobs where performance and durability are critical.
Adjustable Nozzle Torches offer versatility in the size and shape of the welding arc. Welders can modify the nozzle to suit different materials and thicknesses, enhancing control over the welding process. This adaptability is particularly useful for projects requiring precision and finesse.
Push-Pull Torches provide a unique design that facilitates the feeding of filler material directly into the weld pool. This feature is especially advantageous when working with softer metals or in situations where a consistent feed rate is necessary. The design enhances the efficiency and quality of the weld.
Ultimately, selecting the right torch involves considering the specific demands of the task at hand. Each type offers distinct advantages, making it essential for welders to understand their options to achieve the best results in their work.
Function of the Flowmeter and Regulator
The components responsible for controlling gas flow and pressure are essential in any gas-related application. Their primary role is to ensure that the right amount of gas is delivered to the process, maintaining efficiency and safety. Understanding how these elements function is crucial for optimal operation and performance.
Flowmeter Overview
A flowmeter measures the volume or mass of gas that passes through it, providing real-time data that allows users to monitor usage and adjust settings as needed. This ensures that the right flow rate is maintained, which is vital for achieving the desired results in various tasks.
Regulator Role
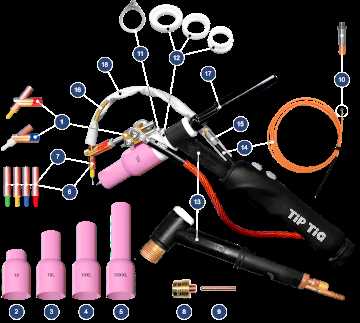
The regulator controls the pressure of the gas entering the system, ensuring that it remains within specified limits. By adjusting the pressure to match the requirements of the application, the regulator helps prevent fluctuations that could affect performance or safety.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Flowmeter | Measures the flow rate of gas |
| Regulator | Controls the gas pressure |
Common Accessories for TIG Welding
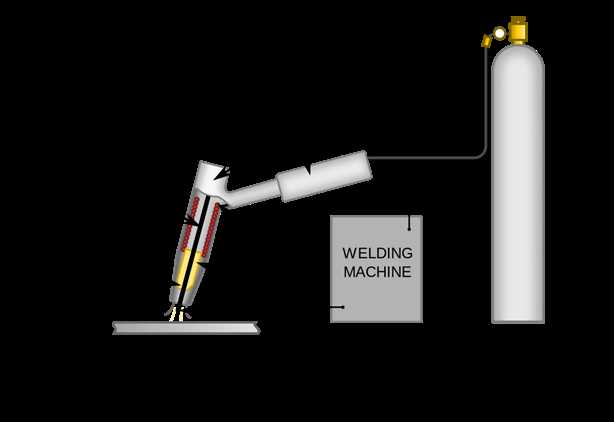
In the realm of precise metal joining, a variety of supplementary tools and components play a vital role in enhancing performance and efficiency. These essentials not only contribute to achieving superior results but also ensure a seamless experience during operations.
Electrodes are fundamental to the process, allowing for effective heat generation and metal fusion. Selecting the appropriate type can significantly impact the quality of the weld. Common options include tungsten varieties, each suited for specific applications and materials.
Filler materials are another crucial accessory, enabling the addition of metal to joints where necessary. The choice of filler depends on the base materials and the desired strength of the final product, making it essential to understand compatibility.
Gas flow equipment ensures that the shielding gas is delivered effectively to protect the weld area from contamination. Regulators, hoses, and nozzles are key components in this setup, allowing for precise control of gas flow and coverage.
Welding helmets equipped with appropriate lenses provide the necessary protection for the operator’s eyes from harmful UV rays and bright arcs. Modern models often feature auto-darkening capabilities, enhancing convenience and safety.
Gloves designed for welding protect the hands from heat and sparks, ensuring a secure grip while maintaining dexterity. Investing in high-quality gloves can prevent injuries and improve overall comfort during prolonged tasks.
Clamps and fixtures help secure workpieces in place, allowing for better stability and alignment. This ensures consistent results, particularly in complex setups where precision is crucial.
By integrating these accessories into your workflow, you can greatly enhance both the quality and efficiency of your metal joining tasks, leading to professional-grade outcomes.
Maintenance Tips for TIG Parts
Regular upkeep of your welding equipment is essential for optimal performance and longevity. By following some straightforward guidelines, you can ensure that all components remain in excellent condition, enhancing both safety and efficiency during your work.
1. Cleanliness is Key: Always keep the equipment free from contaminants such as dust, oil, and debris. Regular cleaning of the torch, electrodes, and collets will prevent malfunctions and improve the quality of your welds.
2. Inspect Regularly: Conduct routine checks for wear and tear. Look for any signs of damage on the electrode, nozzle, and other components. Replacing worn items promptly will prevent further issues and maintain consistent results.
3. Proper Storage: When not in use, store your equipment in a dry and safe environment. Using protective cases or covers can shield sensitive components from damage and environmental factors.
4. Ensure Correct Settings: Always use the appropriate settings for your specific tasks. Incorrect voltage or amperage can lead to premature wear and affect the quality of your work.
5. Utilize Quality Consumables: Investing in high-quality electrodes and nozzles will provide better performance and reduce the frequency of replacements, ultimately saving time and costs in the long run.
By incorporating these practices into your routine, you can significantly extend the life of your equipment and ensure consistent, high-quality results in your projects.
Troubleshooting Common Welding Issues
When engaging in metal joining processes, encountering challenges is not uncommon. Understanding the various factors that can affect the quality of the joint is essential for achieving optimal results. This section delves into common problems that practitioners may face and offers insights for effective resolution.
Poor Arc Stability
Inconsistent arcs can lead to weak connections and material defects. Check for proper gas flow, ensure that the electrode is clean, and verify that the power settings are appropriate for the material thickness. Adjusting these elements often enhances arc performance significantly.
Inadequate Penetration

Shallow fusion may occur if settings are incorrect or if the materials are not prepared adequately. Ensure that the surfaces are clean and free from contaminants. Additionally, increasing the amperage or adjusting the travel speed can improve penetration depth, leading to stronger joints.
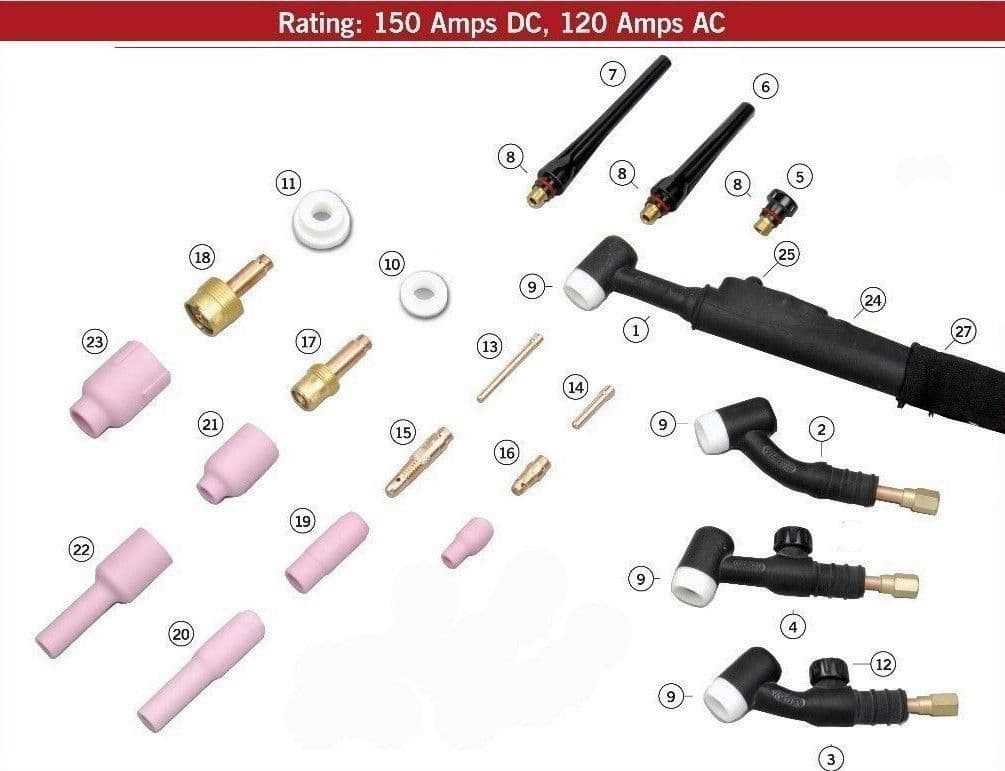
Upgrading Your TIG Welder Components
Enhancing the efficiency and performance of your welding equipment can significantly impact your projects. By integrating higher-quality components, you can achieve better results, improved longevity, and a more enjoyable experience. This section delves into the various upgrades available for your machine, highlighting the benefits and considerations for each.
Key Components to Consider
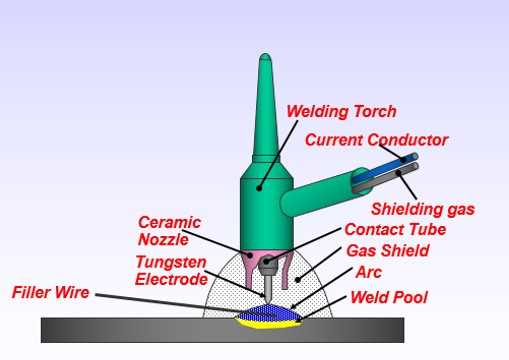
- Electrode Holder: Upgrading to a more robust holder can improve the stability and ease of use.
- Gas Lens: A high-quality lens ensures better gas coverage, reducing contamination and improving the weld appearance.
- Cables: Investing in premium cables enhances conductivity and minimizes heat buildup during operation.
- Torch Upgrade: A lightweight and ergonomic torch can improve maneuverability and reduce fatigue.
Benefits of Upgrading
- Enhanced precision and control during the welding process.
- Reduced downtime and maintenance with more durable components.
- Increased versatility for handling various materials and thicknesses.
- Improved overall performance, leading to higher-quality results.
By strategically upgrading specific components, you can unlock the full potential of your welding equipment, ensuring that each project is executed with precision and efficiency.
Safety Precautions in TIG Welding
Ensuring a safe working environment is paramount when engaging in metal joining processes. This section outlines essential guidelines to protect both the operator and the surrounding area from potential hazards. Adhering to these precautions can significantly reduce the risk of accidents and injuries during the operation.
| Hazard | Precaution |
|---|---|
| Electric Shock | Use insulated gloves and ensure all equipment is properly grounded. |
| Fume Inhalation | Work in a well-ventilated area or use appropriate respiratory protection. |
| Fire Risks | Keep flammable materials away from the work area and have a fire extinguisher nearby. |
| Eye Injury | Wear appropriate eye protection, such as welding goggles or a face shield. |
| Heat Burns | Use protective clothing and ensure that skin is covered to prevent burns. |
By understanding and implementing these safety measures, operators can minimize risks and create a safer workspace, ultimately leading to more effective and responsible practices in metal joining activities.