Janome Sewing Machine Parts Diagram Overview

Understanding how various elements connect and operate together can greatly enhance the efficiency and longevity of complex devices. A clear layout of internal components makes troubleshooting and maintenance more straightforward, empowering users to identify issues and address them independently.
Detailed visual references are essential for those seeking to grasp the internal structure of such devices. These references highlight the placement and role of individual components, offering insights into their interconnections and functionalities.
Whether performing upgrades or simple repairs, having a clear framework of the system’s inner workings ensures precision. Accurate illustrations minimize guesswork, allowing users to make informed decisions when working with intricate assemblies.
Janome Sewing Machine Parts Diagram
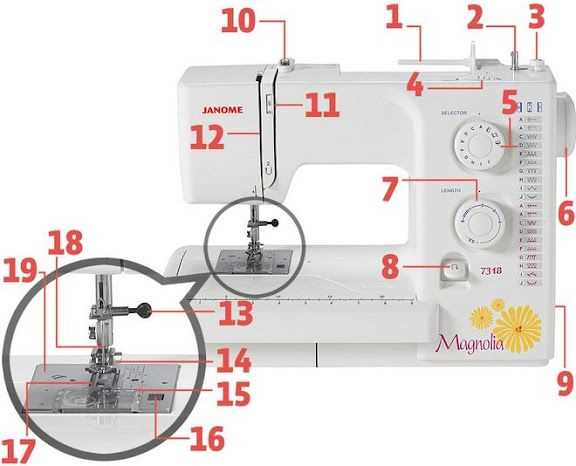
A well-structured layout of components ensures smooth operation and easy maintenance. Understanding the arrangement helps users quickly identify elements and address any performance issues. This overview provides clarity on how different sections work together to produce precise and consistent results.
Core Elements and Their Functions
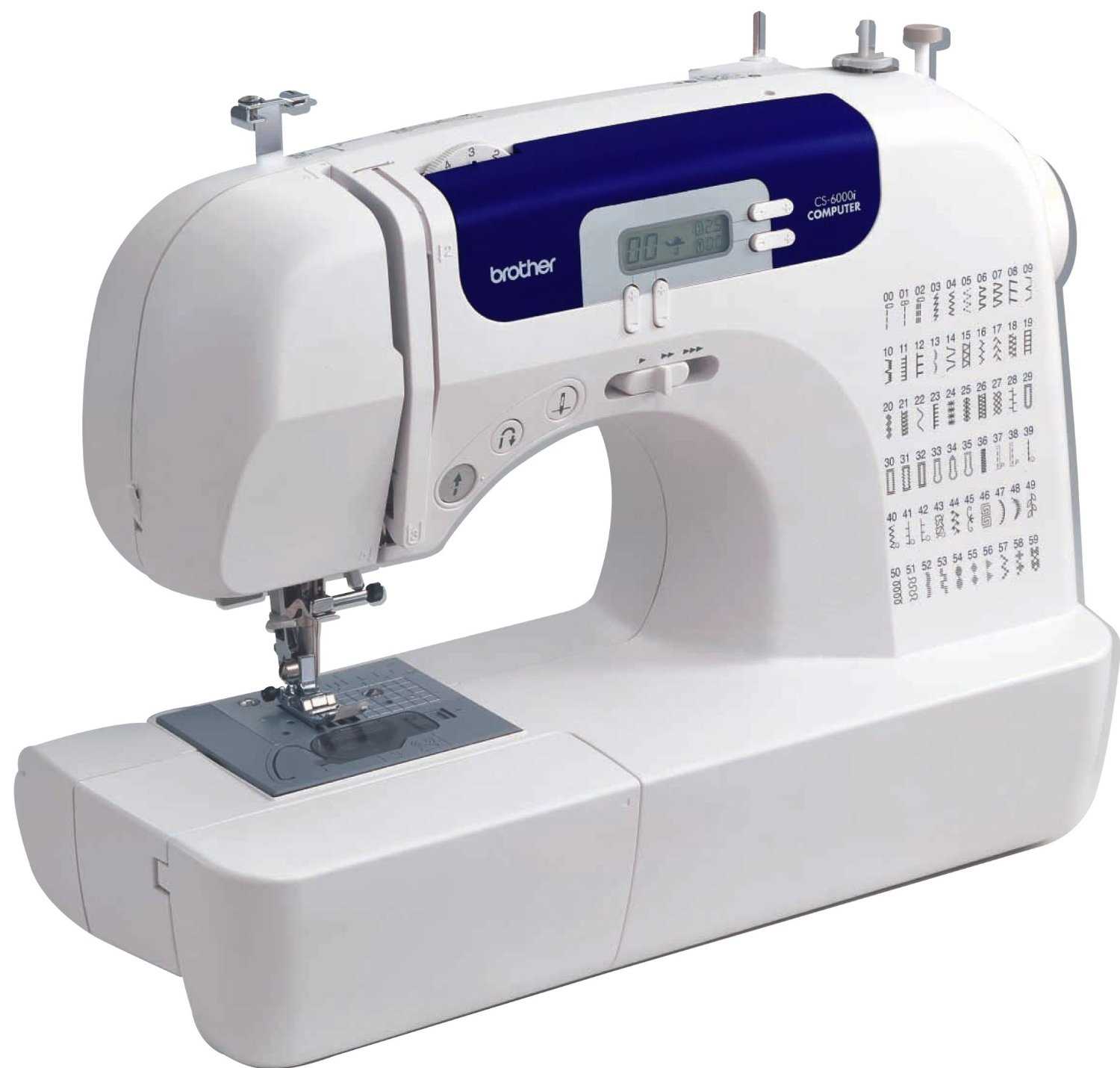

The internal framework contains essential components that control the movement and stitch formation. These elements operate in unison, ensuring accuracy across multiple layers of fabric. Proper alignment of these components reduces errors, enhancing reliability over time.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity

Regular care, such as cleaning and lubricating key areas, extends the lifespan of the device. Frequent inspections allow for early detection of wear, preventing breakdowns during use. Keeping each part in optimal condition ensures smooth functionality for all projects
Identifying Key Internal Components

Understanding the primary elements within a stitching device helps users maintain its performance and troubleshoot issues effectively. By knowing the function and placement of essential parts, it becomes easier to ensure smooth operation and extend the lifespan of the equipment.
Main Operational Elements
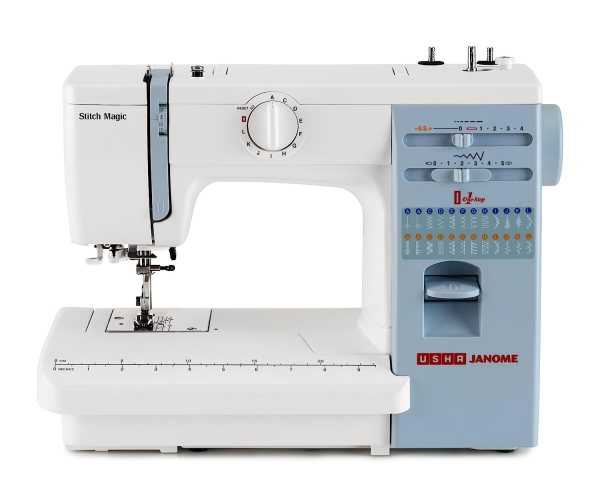

- Needle system: Facilitates the creation of fabric joins by moving up and down in coordination with other mechanisms.
- Bobbin mechanism: Holds a lower thread that interlocks with the upper thread to form stitches beneath the fabric surface.
- Thread tension control: Regulates the tightness of both upper and lower threads to prevent loops and uneven stitching.
- Feed mechanism: Moves material smoothly under the needle, ensuring even and consistent results with every
Understanding the Bobbin Mechanism
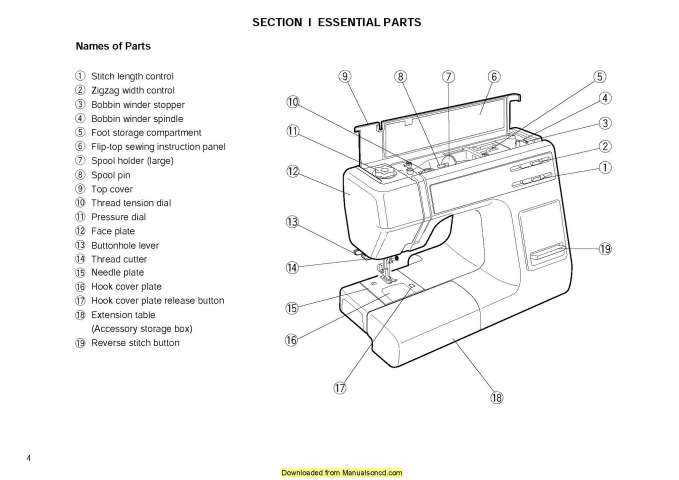
The bobbin mechanism plays a crucial role in maintaining smooth stitching by feeding the lower thread. It works in tandem with the top thread to create even and durable stitches, ensuring fabric layers are securely bound together.
A small spool holds the bottom thread, which is positioned in the bobbin case. The system rotates precisely to catch and intertwine with the upper thread, forming loops that lock each stitch in place. Proper alignment of these components ensures consistent tension and prevents skipped stitches or tangling.
Regular cleaning and thread tension adjustment help keep the mechanism running efficiently. Even minor debris can disrupt the flow of the lower thread, affecting the stitch quality. Routine maintenance ensures both precision and reliability over extended use.
Overview of the Needle Assembly
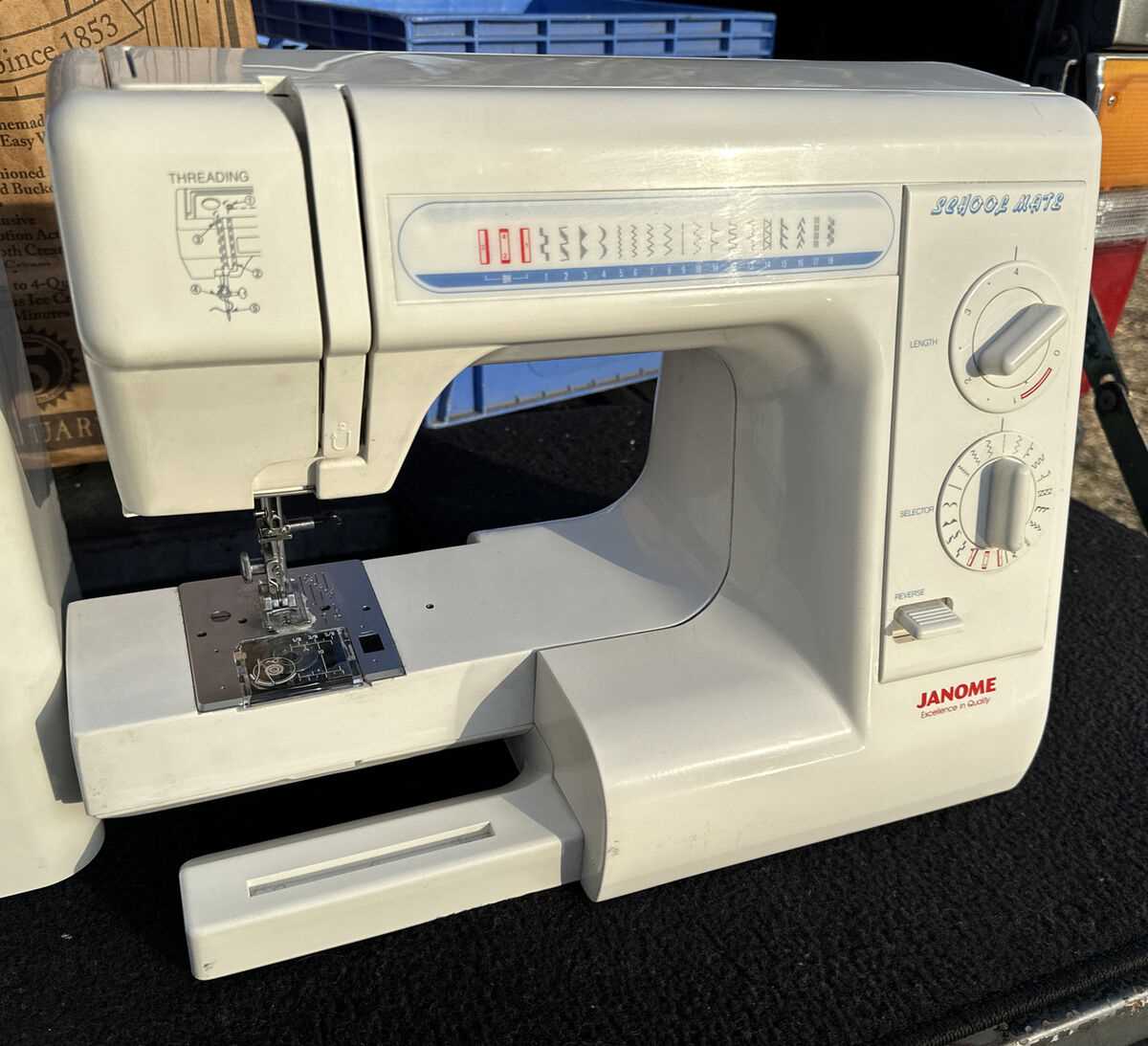

The needle assembly is an essential part of the system responsible for forming stitches with precision. It ensures smooth material penetration and consistent thread movement, playing a critical role in achieving high-quality results across different fabrics.
Main Components of the Needle Assembly
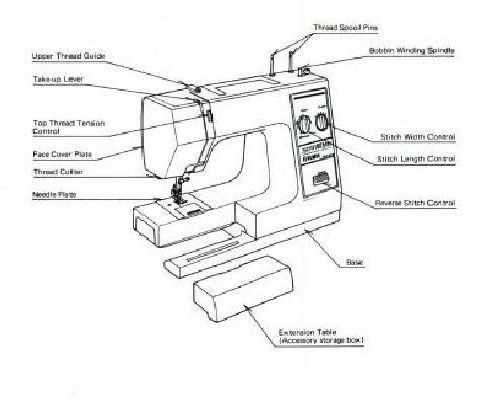
This section includes several interconnected elements that work in harmony. Together, these components guide the thread and stabilize the needle, allowing for efficient operation and reducing the risk of skipped stitches or fabric damage.
Component Description Needle Bar Holds the needle in place and moves vertically to create stitches. Needle Clamp Secures the needle tightly, preventing any unwanted movement during operation. Thread Guide Directs the thread towards the needle, ensuring smooth feeding and tension control. Function and
Thread Tension Control Explained

Proper adjustment of thread tension ensures smooth and even stitching on fabric layers. The balance between upper and lower threads prevents loops or tightness that could affect the quality of the final work.
- Upper Thread Regulation: Adjusting the top thread helps align it with the lower thread, preventing uneven stitches.
- Lower Thread Calibration: Fine-tuning the bobbin tension avoids loose or puckered seams.
- Impact of Fabric Type: Thicker materials may require tighter tension, while delicate ones benefit from lighter settings.
- Needle and Thread Choice: Matching the thickness of thread and needle optimizes tension control.
Regular testing on a fabric sample before starting a project ensures that the thread flows evenly, minimizing the risk of disruptions during work.
How the Presser Foot Operates
The presser foot plays a crucial role in the functioning of textile creation equipment, facilitating the manipulation of fabric during the stitching process. Its primary function is to hold the fabric in place, ensuring that it moves smoothly through the feed mechanism while the needle performs its task.
When the operator lowers the presser foot, it exerts downward pressure on the fabric, which helps maintain tension and stability. This action prevents the material from shifting, allowing for precise stitching. Additionally, the design of the presser foot can vary, enabling it to accommodate different types of stitches and fabric thicknesses. Some variants feature specialized designs to enhance the feeding of delicate fabrics or to create unique stitch patterns.
The operation of the presser foot is synchronized with the movement of the needle and the feed dogs. As the needle pierces the fabric, the feed dogs rise and fall to grip the material, pulling it through the machine. This harmonious interaction ensures that stitches are evenly spaced and consistent, contributing to the overall quality of the finished project.
Exploring the Feed Dog Function
The feed dog plays a crucial role in the operation of textile crafting equipment, serving as an essential component in the process of moving fabric through the work area. This part helps ensure that materials are properly advanced during stitching, allowing for precision and consistency in the final product.
Typically located beneath the needle plate, the feed dog comprises a set of metal teeth that can be raised or lowered. When activated, these teeth grip the fabric, pulling it forward in small increments. This action is vital for maintaining even tension and alignment, particularly when executing intricate patterns or designs.
Understanding the operation of the feed dog can enhance users’ abilities to manage different types of textiles. For example, adjusting the height or feed rate can significantly affect the outcome when working with lightweight versus heavier materials. Thus, familiarity with this feature contributes to more successful crafting experiences.
Overall, the feed dog is an indispensable element that facilitates smooth and accurate stitching, making it essential for both novice and experienced users alike. Mastering its function allows for greater creativity and efficiency in fabric manipulation.
Role of the Handwheel in Sewing
The handwheel is a vital component in the realm of textile crafting, serving as a manual control for various functions. Its design allows users to navigate the intricacies of their craft with precision, enhancing the overall experience and ensuring accuracy in every project.
This essential tool enables individuals to easily adjust the needle position, making it indispensable for intricate work. It empowers crafters to control the speed of the fabric feed, allowing for meticulous handling of delicate materials.
Function Description Needle Control Facilitates precise needle placement for various stitching techniques. Speed Regulation Allows users to manage the rate of fabric movement for enhanced control. Manual Adjustment Enables manual corrections and adjustments during the crafting process. In summary, the handwheel is not just a mechanical accessory; it embodies a crucial function that significantly influences the quality and finesse of every crafted piece.
Foot Pedal and Speed Regulation
The foot pedal serves as a crucial interface for controlling the speed of your fabric crafting tool. This component allows the user to modulate the pace of operation, providing flexibility in handling various materials and tasks. By pressing down on the pedal, one can effortlessly adjust the speed, making intricate work simpler and more precise.
Functionality of the Foot Pedal
The primary function of the foot pedal is to enable seamless acceleration and deceleration. When pressure is applied, it activates the device, initiating movement. Conversely, releasing the pedal stops the operation, giving users complete control over their workflow. This responsiveness is essential for achieving desired results, especially during complex techniques.
Speed Adjustment Features
Many foot pedals come equipped with features that enhance speed control. Variable speed settings allow for tailored adjustments, accommodating different tasks such as delicate stitching or heavy-duty applications. Ergonomic design also contributes to comfort, enabling longer crafting sessions without fatigue. Understanding how to utilize these features can significantly improve efficiency and outcomes.
Maintenance of the Spool Pin
The proper upkeep of the thread holder is essential for ensuring smooth operation and consistent results in any textile creation process. Regular attention to this component can help prevent issues such as thread tangling and breakage, leading to more efficient crafting sessions.
Cleaning the Spool Holder
To maintain optimal performance, it is important to keep the thread holder clean. Dust and lint can accumulate over time, affecting its functionality. Here are steps to effectively clean this component:
- Remove the thread and any attachments from the holder.
- Use a soft brush or cloth to gently wipe away any dust or debris.
- Check for any damage or wear, and replace if necessary.
Regular Inspection
Conducting periodic inspections of the thread holder is crucial. This ensures that any potential issues are identified early, preventing larger complications down the line. Consider the following during your inspection:
- Ensure that the holder is securely attached and free from cracks.
- Verify that the thread unwinds smoothly without resistance.
- Look for any signs of corrosion or other damage that may affect performance.
Replacing Belts and Drive Systems
Maintaining the functionality of any textile device is crucial for optimal performance. One of the key components that may require attention over time is the system responsible for power transmission. Properly functioning belts and drive mechanisms ensure that the entire setup operates smoothly, preventing interruptions during use.
Identifying When to Replace Components

It is essential to recognize signs that indicate a need for component replacement. Common indicators include:
- Unusual noises during operation
- Slipping or erratic movement
- Visible wear or damage on belts
- Decreased efficiency or performance
Steps for Replacement
When the need arises to replace the power transmission elements, follow these guidelines to ensure a smooth process:
- Gather Necessary Tools: Prepare the required tools and new components before starting.
- Power Down: Ensure the entire setup is unplugged to avoid accidents.
- Remove Covers: Detach any protective covers to access the internal mechanisms.
- Take Notes: Document the arrangement of the current setup for reference during reassembly.
- Install New Components: Carefully replace the old belts and drive systems with the new ones, ensuring correct alignment.
- Reassemble: Replace all covers and secure them properly.
- Test: Power on the unit to verify that everything operates correctly.
Electrical Components and Wiring Layout
This section delves into the essential elements that govern the functionality of textile equipment, focusing on the electrical components and their respective wiring arrangements. Understanding these elements is crucial for efficient operation and maintenance.
Proper wiring and arrangement of electrical components ensure seamless connectivity and optimal performance. Below are key components typically found in such equipment:
- Power Supply Unit: Converts electrical energy from the outlet to a usable form for the device.
- Control Board: Serves as the central hub for managing operations and settings.
- Motors: Responsible for driving the various functionalities, including movement and adjustments.
- Switches: Allow users to control power flow and functionality, enhancing user experience.
- Connectors: Facilitate secure connections between various components, ensuring stability and safety.
The wiring layout plays a pivotal role in the efficiency of the overall system. Here are some important aspects to consider:
- Organization: Clear pathways for wires prevent tangling and damage.
- Insulation: Proper insulation reduces the risk of shorts and electrical failures.
- Accessibility: Easy access to wiring allows for simpler maintenance and troubleshooting.
Adhering to these principles can enhance the longevity and performance of the device.
Troubleshooting Common Mechanical Issues
When engaging with a fabric crafting device, it’s common to encounter various mechanical challenges that can hinder performance. Understanding how to identify and address these issues is essential for maintaining optimal functionality and ensuring a smooth crafting experience.
Here are some frequent mechanical problems you might face along with potential solutions:
Issue Possible Causes Solutions Stitch skipping Incorrect needle type, dirty bobbin area, or improper threading. Use the correct needle, clean the bobbin area, and rethread the device. Thread bunching Poor tension settings or tangled threads. Adjust the tension settings and check for knots in the thread. Noise during operation Insufficient lubrication or foreign objects in the mechanism. Lubricate moving parts and remove any debris. Fabric not feeding Worn feed dogs or incorrect presser foot pressure. Replace feed dogs and adjust the presser foot pressure accordingly.