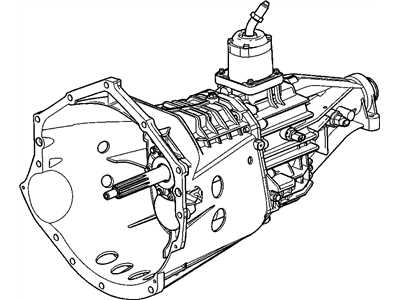
Driveshaft
Electrical System Connections and Wiring
The electrical system in a vehicle is crucial for ensuring that all components function properly and communicate effectively. Understanding the connections and wiring is essential for troubleshooting and maintenance. Properly configured wiring can prevent issues such as shorts, failures, and inefficiencies in the electrical system.
Connections in the electrical system involve various components, including the battery, alternator, and starter, along with multiple wiring harnesses that link these parts. Each connection point is designed to facilitate the flow of electricity, enabling features such as lighting, ignition, and entertainment systems. Proper installation and maintenance of these connections are vital for the overall performance and reliability of the vehicle.
Wiring diagrams serve as a guide to understanding how the electrical system is organized. They illustrate the routes taken by wires and the relationship between different components. Familiarity with these diagrams allows for more efficient diagnostics and repairs, ensuring that each electrical function operates as intended. Regular checks and upkeep of the wiring can enhance the longevity of the electrical system and contribute to a safer driving experience.
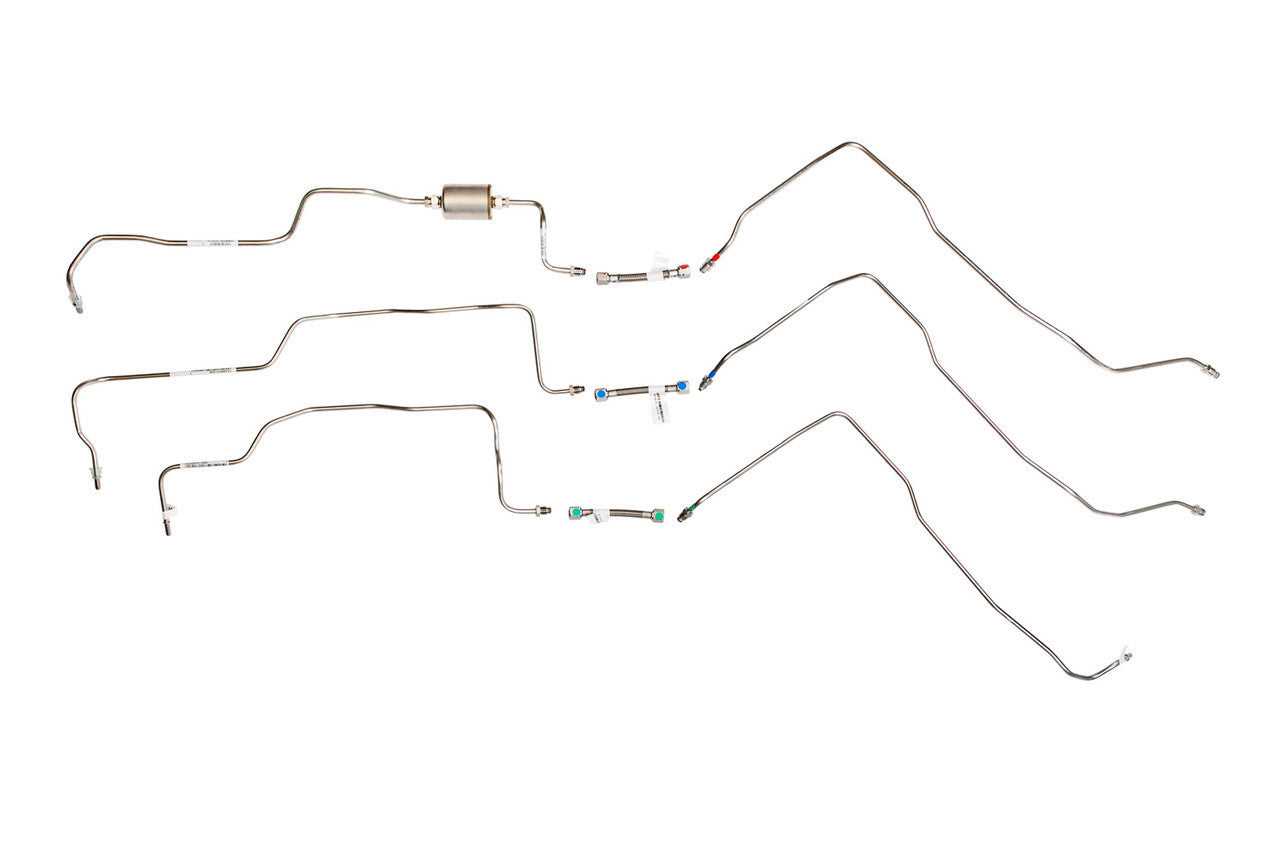
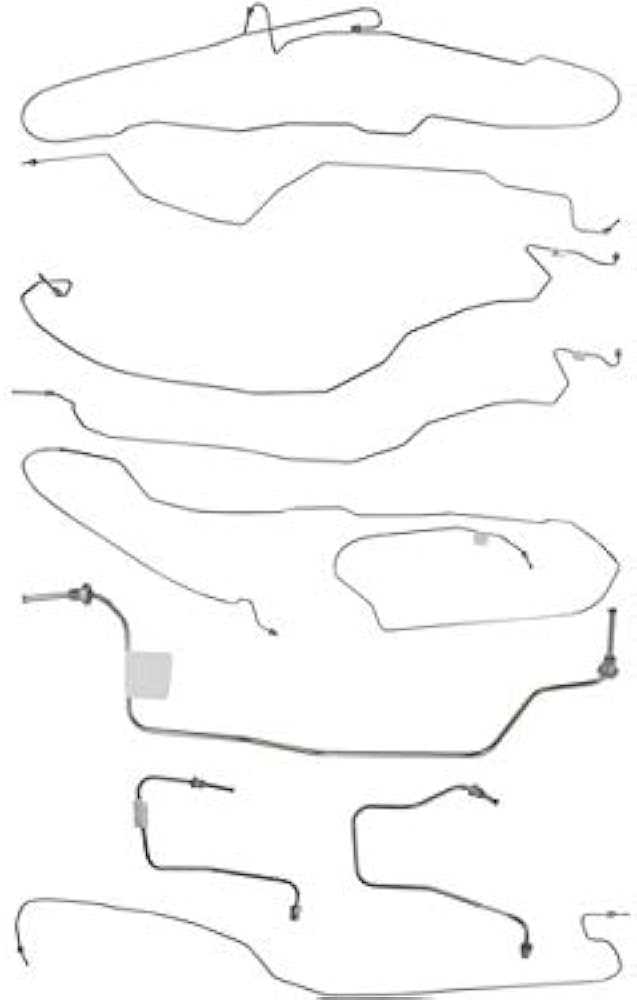
Fuel System Parts and Routing
The fuel system in a vehicle plays a crucial role in delivering the necessary energy for optimal engine performance. This section outlines the essential components involved in fuel delivery and the pathways through which fuel travels from the tank to the engine.
- Fuel Tank: The reservoir that stores the fuel before it is sent to the engine.
- Fuel Pump: A device that moves fuel from the tank to the engine, ensuring proper pressure and flow.
- Fuel Filter: A component that removes impurities from the fuel, protecting the engine from potential damage.
- Fuel Lines: Tubes that transport fuel from the tank to the pump and then to the engine. These lines must be secure to prevent leaks.
- Fuel Injectors: Devices that atomize the fuel, allowing for efficient combustion within the engine’s cylinders.
- Pressure Regulator: A mechanism that maintains the appropriate fuel pressure in the system, ensuring consistent engine performance.
Understanding the layout and function of these components is vital for troubleshooting issues related to fuel delivery. Proper routing and maintenance of the fuel system ensure the longevity and efficiency of the engine.
Cooling System Diagram and Structure
The cooling system is a crucial component of any vehicle, designed to maintain optimal operating temperatures for the engine. It works by circulating a fluid that absorbs heat from the engine, ensuring that it runs efficiently while preventing overheating. Understanding the layout and components of this system can help in diagnosing issues and performing maintenance effectively.
Key Components of the Cooling System

The main elements of the cooling system include the radiator, water pump, thermostat, and various hoses and connections. Each part plays a significant role in regulating temperature and facilitating the flow of coolant. A well-maintained system ensures reliable performance and extends the lifespan of the engine.
Structure Overview
| Component |
Function |
| Radiator |
Dissipates heat from the coolant |
| Water Pump |
Circulates coolant throughout the system |
| Thermostat |
Regulates coolant flow based on temperature |
| Coolant Hoses |
Transport coolant between components |
Exhaust System Arrangement and Flow
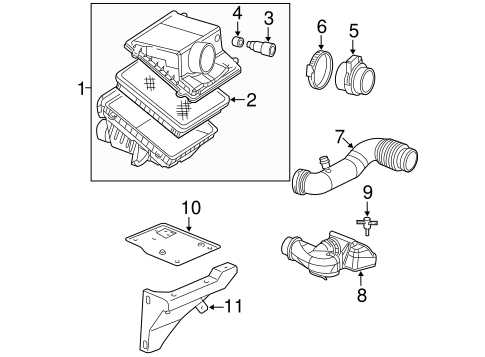
The arrangement and flow of the exhaust system are crucial for the efficient performance of any vehicle. Proper design ensures that gases are expelled from the engine effectively, minimizing back pressure and maximizing horsepower. An optimized exhaust configuration not only enhances performance but also contributes to better fuel efficiency and reduced emissions.
Key components of the exhaust system include:
- Exhaust Manifold: Collects exhaust gases from the engine cylinders.
- Catalytic Converter: Reduces harmful emissions by converting gases into less harmful substances.
- Muffler: Reduces noise produced by the engine’s exhaust gases.
- Tailpipe: Directs exhaust gases away from the vehicle.
The flow of exhaust gases through these components follows a specific path:
- Gases exit the engine through the exhaust manifold.
- They pass through the catalytic converter for emission control.
- Next, the gases flow into the muffler, where sound is dampened.
- Finally, the cleaned and quieted gases exit through the tailpipe.
Efficient exhaust flow is essential for maintaining optimal engine performance and longevity. Regular inspection and maintenance of the exhaust system can prevent potential issues and ensure that the vehicle operates smoothly.
Body Frame and Mounting Points
The structure of a vehicle’s body is crucial for its overall stability and performance. Understanding the various components and their connections allows for better maintenance and repair. This section focuses on the framework that supports the vehicle’s exterior and the key locations where it is secured to the chassis.
| Component |
Description |
| Frame Rails |
Longitudinal beams that provide strength and rigidity to the body structure. |
| Crossmembers |
Horizontal supports that connect the frame rails, enhancing structural integrity. |
| Body Mounts |
Rubber or polyurethane components that absorb vibrations and secure the body to the frame. |
| Firewall |
A partition between the engine compartment and the passenger area, providing safety and insulation. |
| Cab Supports |
Vertical elements that support the cabin, ensuring proper alignment and stability. |
Interior Controls and Dashboard Layout
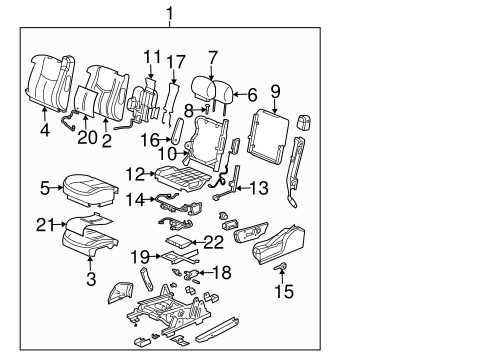
The arrangement of controls and instruments within a vehicle’s cabin plays a crucial role in enhancing user experience and functionality. A well-designed dashboard not only provides essential information but also ensures that drivers can access controls with ease. This section delves into the features and layout of interior controls, emphasizing their significance in daily operation.
Control Placement and Accessibility
Strategic positioning of controls is vital for safety and convenience. Key elements such as the climate control system, audio settings, and navigation interfaces should be within easy reach. This thoughtful arrangement allows drivers to adjust settings quickly without diverting attention from the road.
Dashboard Features and Indicators
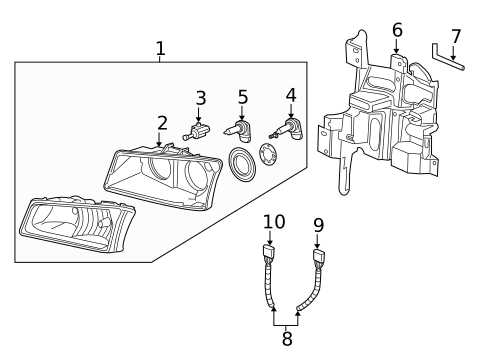
The dashboard serves as the primary interface for monitoring vehicle performance. It typically includes various indicators such as speedometer, fuel gauge, and warning lights. Modern designs often incorporate digital displays that enhance clarity and allow for customization, providing drivers with real-time data at a glance. Ergonomic designs and intuitive layouts significantly improve the overall driving experience.
Rear Axle and Differential Parts Setup
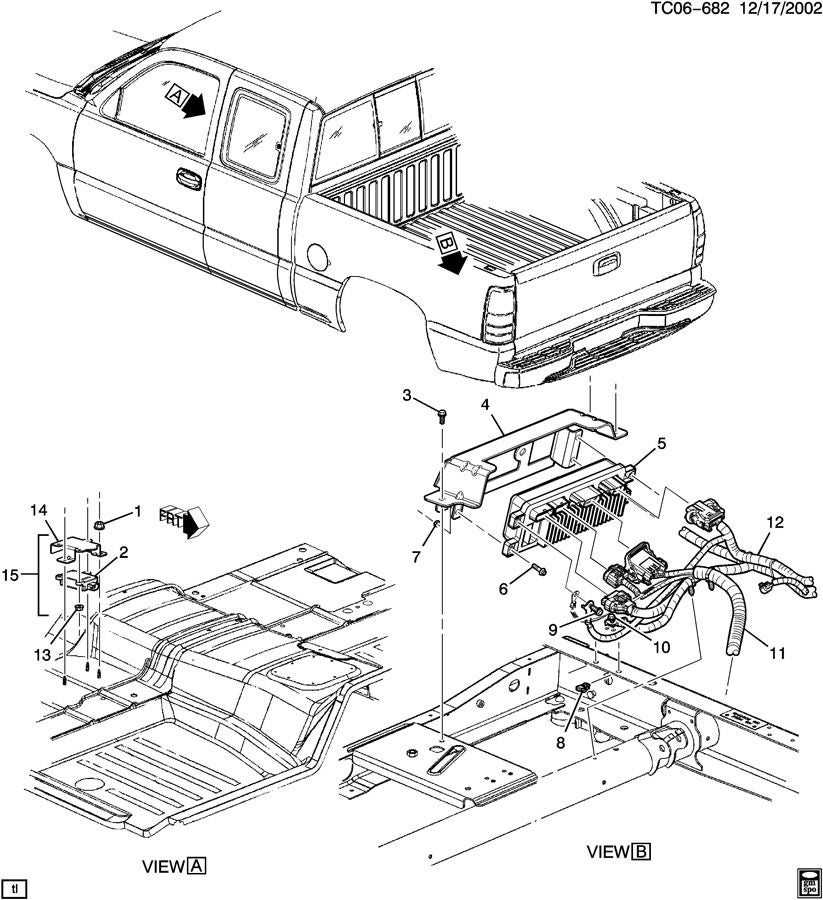
The configuration of the rear axle and differential is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and stability in vehicles. This assembly plays a significant role in transmitting power from the engine to the wheels, enabling smooth and controlled movement. Understanding the components involved and their arrangement can enhance maintenance and repair processes.
The rear axle consists of several key elements, including the housing, which encases the differential and gear assembly. The housing provides structural support and helps maintain the proper alignment of all components. Inside, the differential gears facilitate the distribution of torque to the wheels, allowing for smooth turns and varied wheel speeds during cornering.
Additional components such as bearings and seals are essential for ensuring a tight fit and preventing fluid leakage, which can lead to significant damage if left unaddressed. Proper lubrication is also vital for minimizing friction and heat, prolonging the life of the axle assembly.
In summary, a thorough understanding of the rear axle and differential setup is fundamental for effective vehicle maintenance. Familiarity with each component’s role can aid in troubleshooting issues and ensuring the longevity of the system.
|