Sony Camera Parts Breakdown
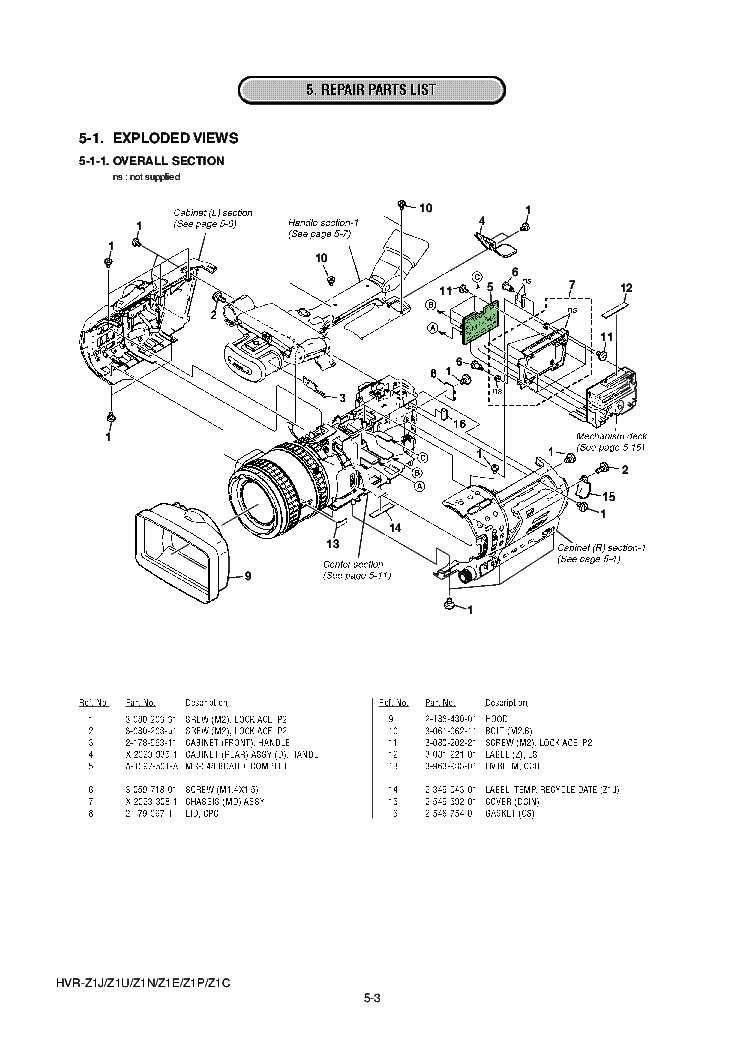
Exploring the internal structure of various gadgets can provide valuable insights into their functionality and design. By analyzing how different elements are organized and interact with one another, users can gain a deeper appreciation for the engineering behind these devices. This section delves into the arrangement of essential elements that make modern electronic equipment perform optimally.
Each device relies on a carefully planned configuration of elements, which are assembled to ensure smooth operation. Recognizing how these elements fit together allows for a better understanding of the repair and maintenance processes. In this section, we will examine how key components are strategically positioned within the structure to enhance performance and durability.
Whether you are curious about the internal workings or seeking to address technical issues, understanding the layout of individual elements can be crucial. By grasping the connections between different components, it becomes easier to troubleshoot problems and enhance your familiarity with the inner workings of modern technology.
Understanding the Internal Components of Sony Cameras
Exploring the intricate design of modern digital devices reveals the importance of each internal element. These components work together seamlessly to deliver high-quality performance and advanced functionality. Understanding how they are organized and function is essential for those interested in maintaining or enhancing their performance.
- Processor Unit: This section manages the data flow, allowing for quick processing of visual information and smooth operation.
- Lens Mechanism: Responsible for focusing and adjusting to various lighting conditions, it ensures clear and precise image capturing.
- Display Module: Provides real-time visual feedback, allowing users to monitor and adjust settings as needed.
- Sensor Assembly: Captures light and transforms it into digital signals, playing a critical role in the quality and detail of the final image.
- Control Interface: Includes buttons, dials, and other
Key Elements of the Lens Assembly
The lens system is a crucial component responsible for the clarity and focus of visual capture. It is designed to manipulate light effectively, ensuring the correct balance between sharpness, brightness, and detail. Understanding how the various elements work together helps to appreciate its complexity and importance.
Glass and Optical Elements
At the core of the system, several glass components work in harmony to manage the incoming light. These parts are crafted with high precision to minimize distortions and enhance image quality. Each element plays a role in directing and focusing light rays onto the sensor, ensuring a high level of accuracy.
Focus and Aperture Mechanism
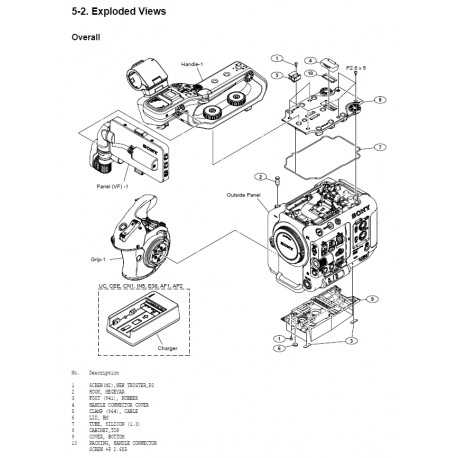
The focus mechanism allows for adjustment of the distance at which objects appear sharp. Paired with this is the aperture, a set of blades that control the amount of light entering the system. Together, these mechanisms ensure that the exposure and focus meet the desired visual outcome.
Main Circuit Board Layout and Function
The central structure of the main control unit is essential for understanding how various components interconnect and operate. It is the foundation that links key elements and ensures smooth communication between different sections. This arrangement determines the overall performance and efficiency of the system.
Key Sections of the Board
- Power Regulation: This section manages the voltage and power distribution across all modules.
- Data Processing Unit: Here, information is processed and instructions are relayed to various peripherals.
- Input/Output Management: Handles communication between the external controls and the internal modules.
Functional Importance
Each part of the layout serves a critical role in maintaining optimal operation. From power management to data handling, every section is carefully designed to balance efficiency and reliability. The arrangement of these sections influences how well the system responds to user inputs and
Battery Compartment Structure and Design
The layout and configuration of the battery housing play a crucial role in ensuring efficient power management and secure placement. This section delves into the intricate details behind the arrangement and structure of the compartment, providing insights into how it contributes to the overall performance and ease of use. Understanding the design choices helps users appreciate the seamless integration of functionality and accessibility.
Key Elements of the Housing
The compartment typically includes various components that ensure both protection and accessibility. The locking mechanism, for instance, is designed to prevent accidental disconnection, while the internal layout optimizes space for power cells. These elements work together to deliver a secure and convenient power solution.
Design Considerations for Durability
Durability is a primary focus in the construction of the power cell housing. It is built to withstand daily wear and tear, with materials chosen for their resilience and strength. The external casing is often reinforced
Shutter Mechanism Overview and Maintenance
The shutter mechanism plays a crucial role in controlling the exposure time, which impacts the quality of captured images. Its precise function is to regulate the amount of light that reaches the internal sensor, ensuring balanced exposure. However, due to its intricate design and frequent use, this component may require regular upkeep to maintain optimal performance.
Key Elements of the Mechanism
The assembly consists of various moving parts that work together to open and close at specific intervals. These elements, though small, are finely calibrated to function seamlessly, providing consistent performance. With time and usage, some components may wear out, causing delays or improper function.
Basic Maintenance Tips
Regular maintenance can help extend the lifespan of the system. Dust and debris can accumulate, affecting its smooth operation. Gentle cleaning using air blowers can remove particles that could obstruct
Viewfinder System Breakdown
The viewfinder system is a crucial component that enhances the user’s experience by providing a direct line of sight for composing images. This system plays a vital role in allowing individuals to frame their subjects accurately and monitor the exposure settings effectively. Understanding its elements can greatly improve the overall functionality and usability of the device.
This system typically comprises several key components:
- Optical Element: This allows light to enter, providing a clear view of the scene.
- Prism: A reflective surface that directs light toward the user’s eye, often crucial for achieving a correct orientation of the image.
- Diopter Adjustment: A feature that enables users to customize the focus according to their vision needs.
- Display Overlay: In electronic models, this displays vital information such as exposure settings, focus points, and grid lines.
- Eyecup: A comfortable component that helps to block stray light and improve viewing clarity.
Each of these elements contributes to the functionality of the viewfinder system, enhancing the overall imaging experience. Knowing how these components work together can help users optimize their creative process and achieve better results.
Exploring the Sensor Placement and Types
Understanding the arrangement and variety of image capture components is crucial for grasping how visual devices function. These elements play a vital role in determining the quality and characteristics of the images produced. Different types of sensors can influence the overall performance, providing various capabilities based on their design and placement within the system.
Types of Image Capture Devices
There are several categories of image capture devices, each offering distinct features and benefits. Here are some common types:
- CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) – Known for its low power consumption and high-speed performance.
- CCD (Charge-Coupled Device) – Renowned for its exceptional image quality and sensitivity in low light.
- Foveon X3 – Utilizes a unique three-layer approach to capture color information in a single shot.
- Live MOS – Combines the advantages of both CMOS and CCD technologies.
Placement Considerations
The positioning of these image capture components within the device is critical. Factors influencing their arrangement include:
- Size of the device – Smaller models may require compact sensor designs.
- Intended use – Different applications may necessitate specialized sensor placements for optimal results.
- Optical design – The lens system’s characteristics can dictate sensor positioning to ensure effective light capture.
By exploring these aspects, one can gain insight into how sensor design and arrangement contribute to the overall effectiveness of visual devices.
Button Layout and External Control Parts
This section explores the arrangement of controls and the various elements that facilitate interaction with the device. Understanding the configuration of these components enhances usability and helps users optimize their experience.
Control Arrangement Overview
The control arrangement plays a crucial role in how effectively users can navigate and operate the device. Thoughtful placement of buttons and switches allows for intuitive access, ensuring that essential functions are within easy reach. Users can quickly familiarize themselves with the layout, contributing to a smoother operation.
Functional Components and Accessibility
Each control element serves a specific function, from adjusting settings to initiating actions. The strategic positioning of these components ensures that users can access them comfortably. Features like tactile feedback and responsive designs enhance user interaction, making the overall experience more engaging.
Flash Unit Components and Wiring
The functionality of a flash unit relies on a variety of integral elements and their interconnections. Understanding these components and their arrangement is crucial for anyone seeking to maintain or enhance their equipment’s performance.
At the heart of the flash unit lies the ignition source, which generates the necessary light. This component works in tandem with capacitors that store energy, releasing it rapidly to create a bright flash. A transformer is often included to step up the voltage, ensuring sufficient power for the ignition process.
Additionally, various resistors and diodes play vital roles in regulating electrical flow and protecting sensitive parts from potential damage. Proper wiring is essential to connect these components effectively, forming a cohesive system that operates smoothly under various conditions. By carefully analyzing the layout and function of each element, one can gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate design that makes these units effective lighting tools.
Body Frame and Exterior Shell Design
The structure and outer casing of a photographic device play a crucial role in its functionality and aesthetic appeal. These components are meticulously crafted to ensure durability while providing a lightweight experience for users. The design of the frame not only influences the overall look but also enhances the performance of internal mechanisms.
Manufacturers often utilize high-quality materials that resist wear and tear, which helps in maintaining the integrity of the device over time. Additionally, ergonomic shapes are considered to improve handling and user comfort. The exterior shell may also incorporate various textures and finishes, contributing to both style and grip.
In summary, the combination of a robust body frame and a thoughtfully designed outer shell significantly affects the usability and visual appeal of a photographic instrument. This interplay between design and functionality is essential for both casual users and professionals who rely on such devices for their creative pursuits.
Connector Ports and Their Functions
Understanding the various interface points found on devices is crucial for users who wish to maximize functionality. Each connector serves a unique role, allowing different accessories and peripherals to communicate effectively with the main unit. This section will delve into the common types of interfaces and their specific purposes.
Types of Connectors
- USB Ports: Widely used for data transfer and charging. They enable connections to computers, power adapters, and external storage devices.
- HDMI Connectors: These ports facilitate high-definition video and audio output to external displays, enhancing viewing experiences.
- Audio Jacks: Typically used for headphones or external microphones, these ports improve sound quality and input options.
- SD Card Slots: Allow for expandable storage by enabling the insertion of memory cards for additional data storage.
- Ethernet Ports: Used for wired network connections, providing reliable internet access and faster data transfer rates compared to wireless options.
Functions of Each Connector
- USB Ports enable quick data synchronization and device charging.
- HDMI Connectors deliver superior audio-visual output for a rich multimedia experience.
- Audio Jacks allow users to connect audio equipment, enhancing sound quality.
- SD Card Slots provide convenient means for expanding storage capacity, essential for media-heavy tasks.
- Ethernet Ports ensure stable internet connectivity, especially in environments where wireless signals may be weak.