Connection
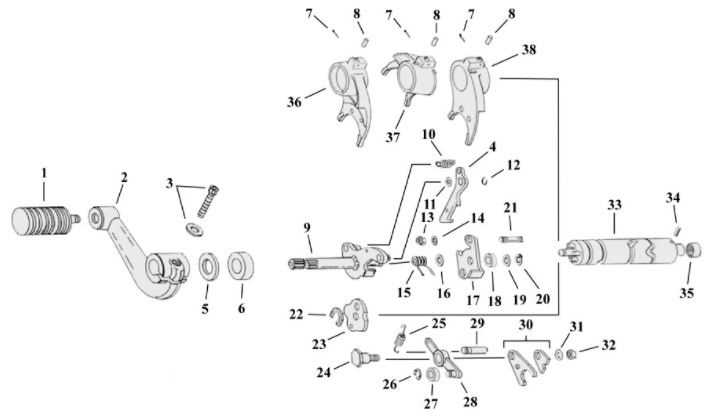
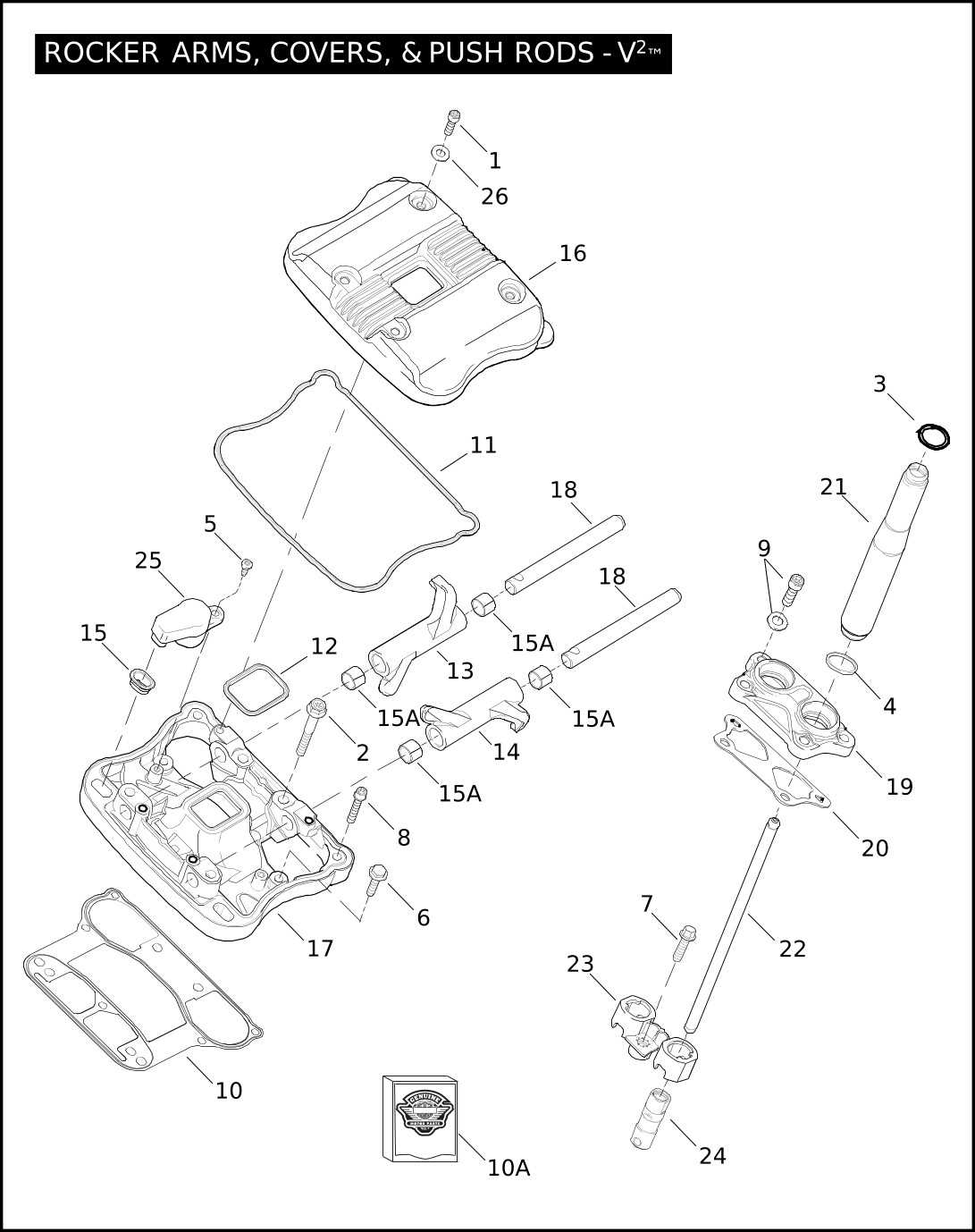
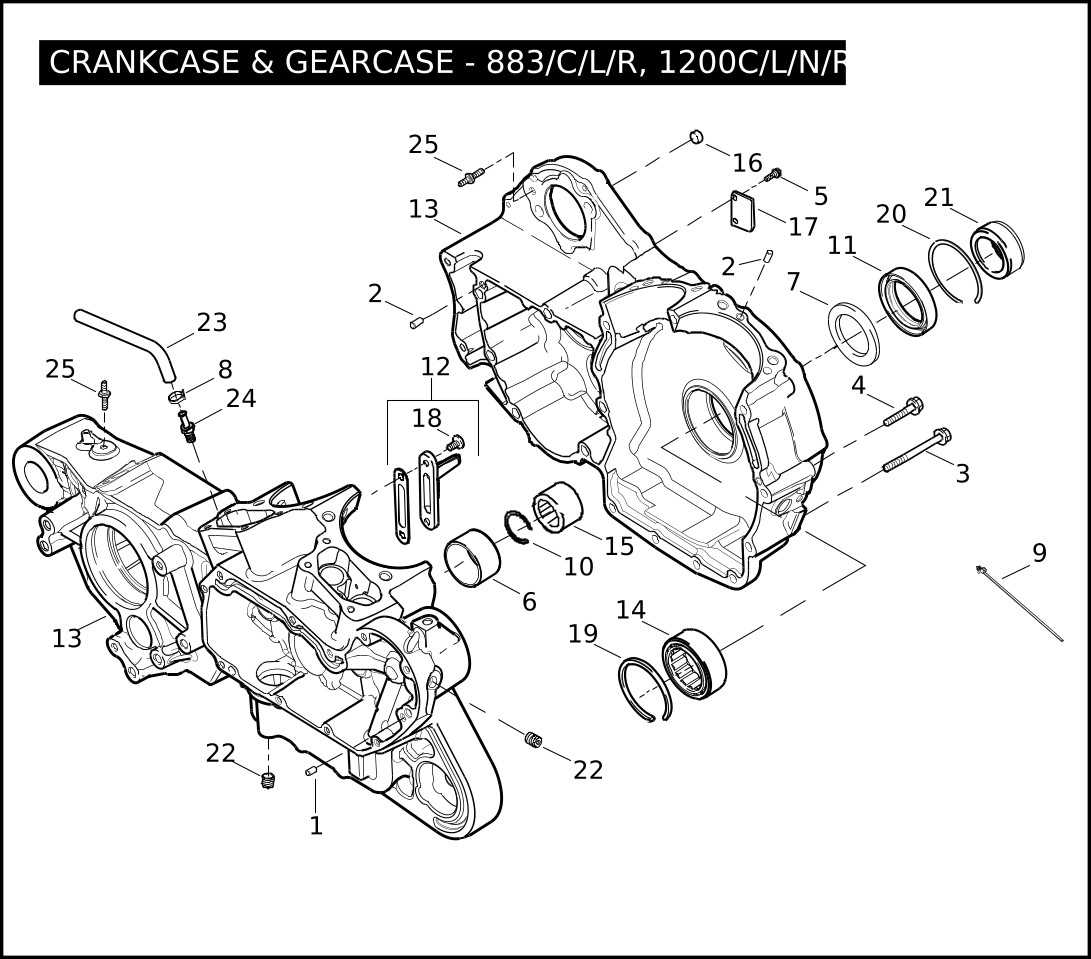
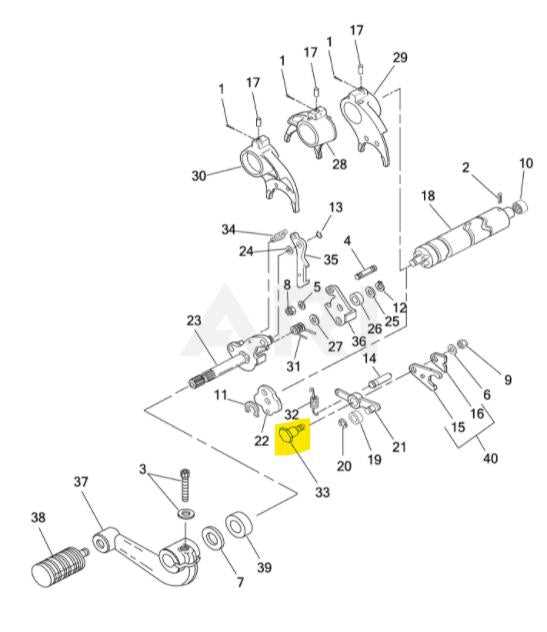
Transmission and Gearbox Breakdown
The heart of any two-wheeled vehicle’s performance lies in its ability to transfer power efficiently from the engine to the wheels. This section will delve into the mechanics of the transmission and gearbox system, focusing on the critical components that ensure smooth shifting and optimal torque delivery.
Key Components and Their Functions
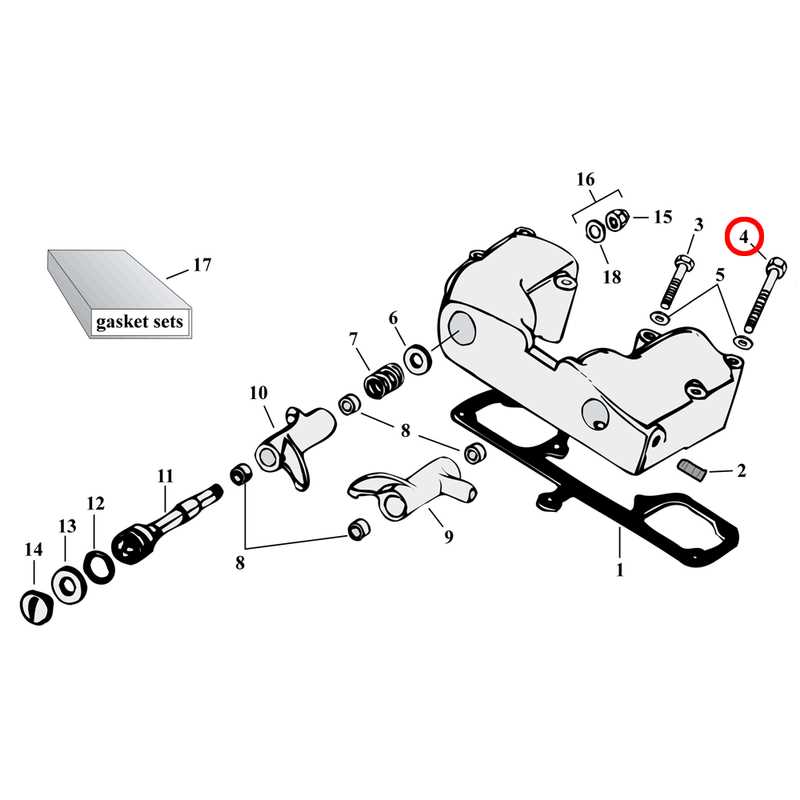
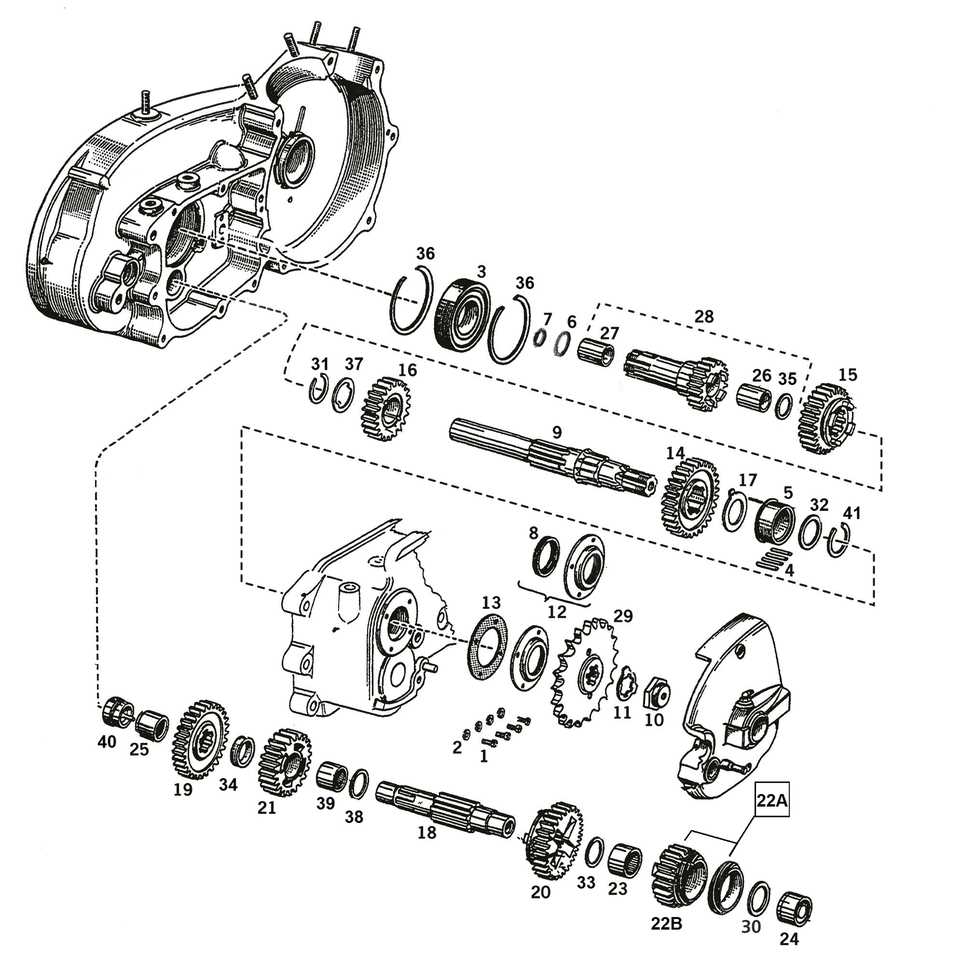
The transmission consists of various gears and shafts that work in unison to control the speed and torque delivered to the wheels. The mainshaft and countershaft play essential roles in transferring power from the engine to the wheels. By shifting between different gears, the system adjusts the bike’s speed and acceleration according to rider input.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance of the gearbox is crucial for long-lasting performance. Over time, components like gears and clutch assemblies can wear down. Signs of issues include slipping gears, difficulty shifting, or strange noises. In such cases, a detailed inspection of the system, including checking for fluid levels and replacing worn-out components, is necessary to restore functionality.
Suspension Setup for a Smooth Ride
Achieving an optimal riding experience starts with proper suspension adjustment. Ensuring your vehicle’s suspension is fine-tuned can significantly enhance comfort and control on various terrains. The right setup helps absorb shocks and vibrations, providing stability while maintaining safety at higher speeds.
Key Elements of Suspension Adjustment
- Shock Absorber Tension: Adjust the spring preload to match your weight and riding style. This ensures the suspension responds appropriately to bumps and dips.
- Damping Settings: Fine-tune compression and rebound damping to control how fast the suspension absorbs impacts and returns to its original position.
- Fork and Rear Suspension Alignment: Proper alignment of the fork and rear suspension helps maintain balance, especially when cornering or navigating uneven surfaces.
Step-by-Step Setup Guide
- Start by checking the manufacturer’s recommended settings for your suspension system.
- Adjust the preload according to your weight, using a ruler or measuring tool to ensure precision.
- Next, set the compression and rebound damping to a medium range and test ride, making incremental adjustments for comfort.
- Finally, perform a test ride on different road conditions to fine-tune the setup for maximum smoothness.
Fine-tuning these components ensures that your ride remains smooth, responsive, and enjoyable over long distances.
Fuel System Configuration and Flow
The fuel delivery process in a motorcycle engine plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal performance and efficiency. Understanding how fuel moves from the tank to the combustion chamber ensures proper tuning and maintenance of the system. This section outlines the basic layout and flow of fuel, from its entry into the system to its eventual combustion in the engine.
- Fuel Tank: The starting point where fuel is stored and pressurized for distribution.
- Fuel Lines: Tubing that directs the fuel from the tank to the carburetor or fuel injection system.
- Fuel Pump: The component responsible for moving fuel from the tank to the engine, ensuring a steady supply under pressure.
- Fuel Filter: Positioned along the fuel line to remove impurities and contaminants before reaching the carburetor or injectors.
- Carburetor or Fuel Injectors: The parts that mix the fuel with air to form the correct air-fuel ratio for combustion.
- Throttle Body: Controls the amount of air and fuel entering the engine, responding to the rider’s throttle input.
The fuel system operates in a closed loop, ensuring that fuel is delivered efficiently and consistently under varying riding conditions. Proper maintenance of each component in the system is essential for smooth operation and fuel efficiency.
Brake System Layout and Safety Features
The braking mechanism plays a critical role in ensuring the overall safety and performance of a two-wheeled vehicle. Proper design and integration of braking components allow for responsive control, especially during high-speed or emergency situations. This section outlines the essential layout of the braking system and highlights key safety features to prevent accidents and enhance rider confidence.
| Component |
Description |
| Brake Levers |
Handlebars are equipped with brake levers that control either front or rear braking. These levers are connected to hydraulic or mechanical systems. |
| Disc Brakes |
Rotating discs attached to the wheels are clamped by brake pads to reduce speed and provide efficient stopping power. |
| Brake Pads |
Friction material that contacts the brake discs, converting kinetic energy into heat for effective deceleration. |
| ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) |
A safety feature that prevents wheel lockup under hard braking, improving traction and reducing the risk of skidding. |
| Brake Fluid |
Hydraulic brake systems rely on brake fluid to transfer force from the lever to the braking mechanism, ensuring smooth and responsive braking. |
Each element in the braking system is designed with precision to optimize both control and safety. Features such as anti-lock braking and high-quality materials for discs and pads contribute to reliable stopping performance, even in challenging conditions. Regular maintenance of these components is essential to ensure that the braking system functions at its peak efficiency.
Handlebars, Controls, and Instrumentation

The steering mechanism, control elements, and display systems play a crucial role in the functionality and safety of a motorcycle. These components are designed to ensure smooth operation and provide the rider with necessary information at all times. Proper maintenance and understanding of these systems are essential for an optimized riding experience.
Handlebars and Control Layout
The handlebars are the central point of interaction between the rider and the motorcycle, offering control over direction and stability. Along with the handlebars, various control switches and levers are integrated to manage key functions such as braking, acceleration, and lighting.
- Throttle control for speed regulation
- Brake levers for front and rear braking systems
- Clutch lever for gear shifting
- Turn signal switches for signaling lane changes
Instrumentation and Gauges
Instrumentation provides the rider with essential data such as speed, fuel levels, and engine performance. Gauges and indicators are typically mounted on the dash or integrated into the handlebars for easy visibility. These components help the rider monitor the bike’s health and make informed decisions while riding.
- Speedometer for tracking speed
- Odometer for recording distance traveled
- Fuel gauge for monitoring fuel levels
- Indicator lights for signals, warnings, and notifications
Wheel and Tire Assemblies
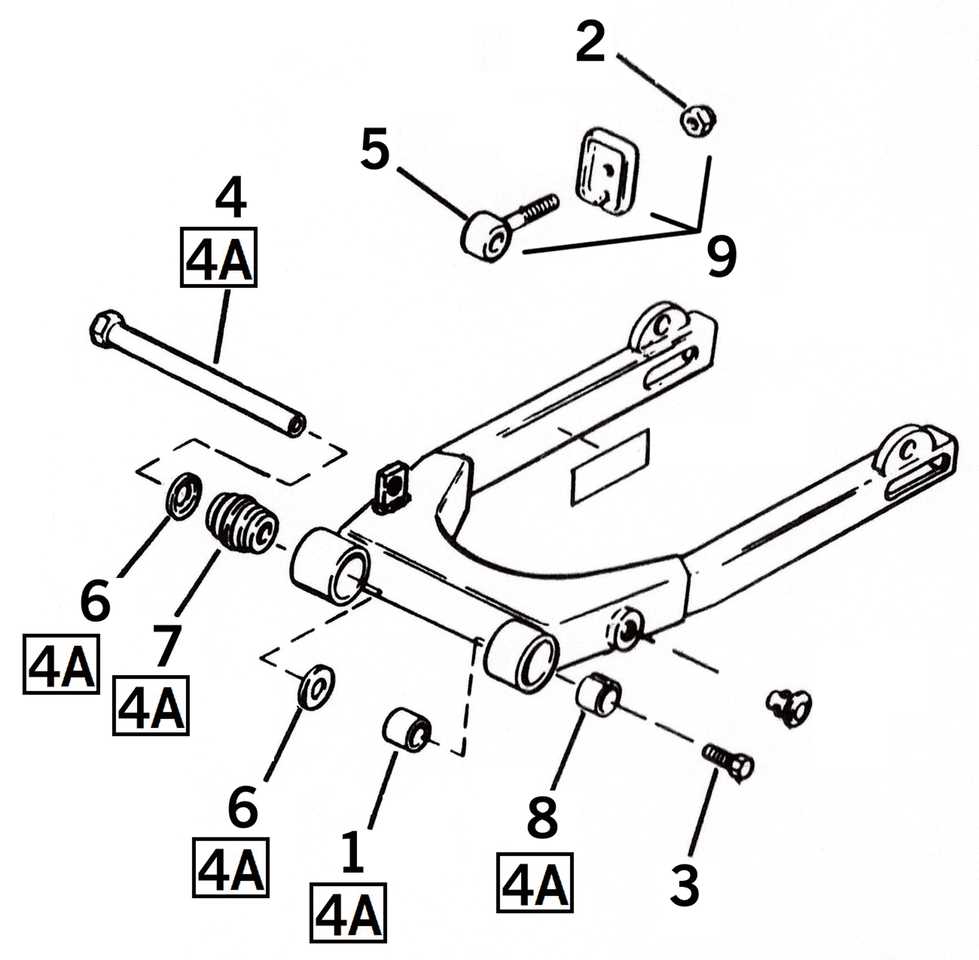
In any two-wheeled vehicle, the combination of the wheel and tire plays a critical role in both performance and safety. These components work together to ensure smooth handling, proper traction, and optimal stability. The assembly includes several parts that interact to form a reliable system that withstands road conditions and delivers the best riding experience.
Key Components
- Rim
- Tire
- Hub
- Spokes (if applicable)
- Valve
Assembly Considerations
- Ensure the correct size and fit for both rim and tire.
- Proper balancing of the wheel assembly to reduce vibrations.
- Inspection of tire tread and sidewalls for wear or damage.
Maintenance Tips for Key Parts
Proper upkeep of vital components is essential for ensuring the longevity and smooth performance of your motorcycle. Regular inspections and maintenance can prevent unnecessary wear and costly repairs. Focus on key areas to maximize efficiency and safety.
- Engine Care: Regular oil changes and filter replacements are crucial for maintaining engine health. Check for leaks and ensure that all connections are tight.
- Brakes: Inspect brake pads frequently and replace them when they show signs of wear. Keep the brake fluid at optimal levels to maintain braking performance.
- Suspension: Keep an eye on shock absorbers and fork seals. Lubricate and replace worn-out parts to maintain stability and comfort during rides.
- Battery: Clean battery terminals to prevent corrosion and ensure a proper charge. Replace the battery if it shows signs of reduced power.
- Chain and Sprockets: Regularly check and lubricate the chain. Ensure sprockets are free from damage and adjust the chain tension for smooth operation.
By keeping these critical areas in top condition, you’ll enjoy a smoother ride and extend the lifespan of your vehicle.
|