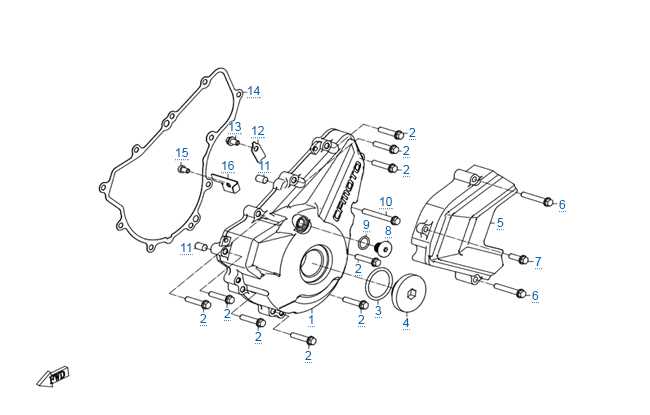
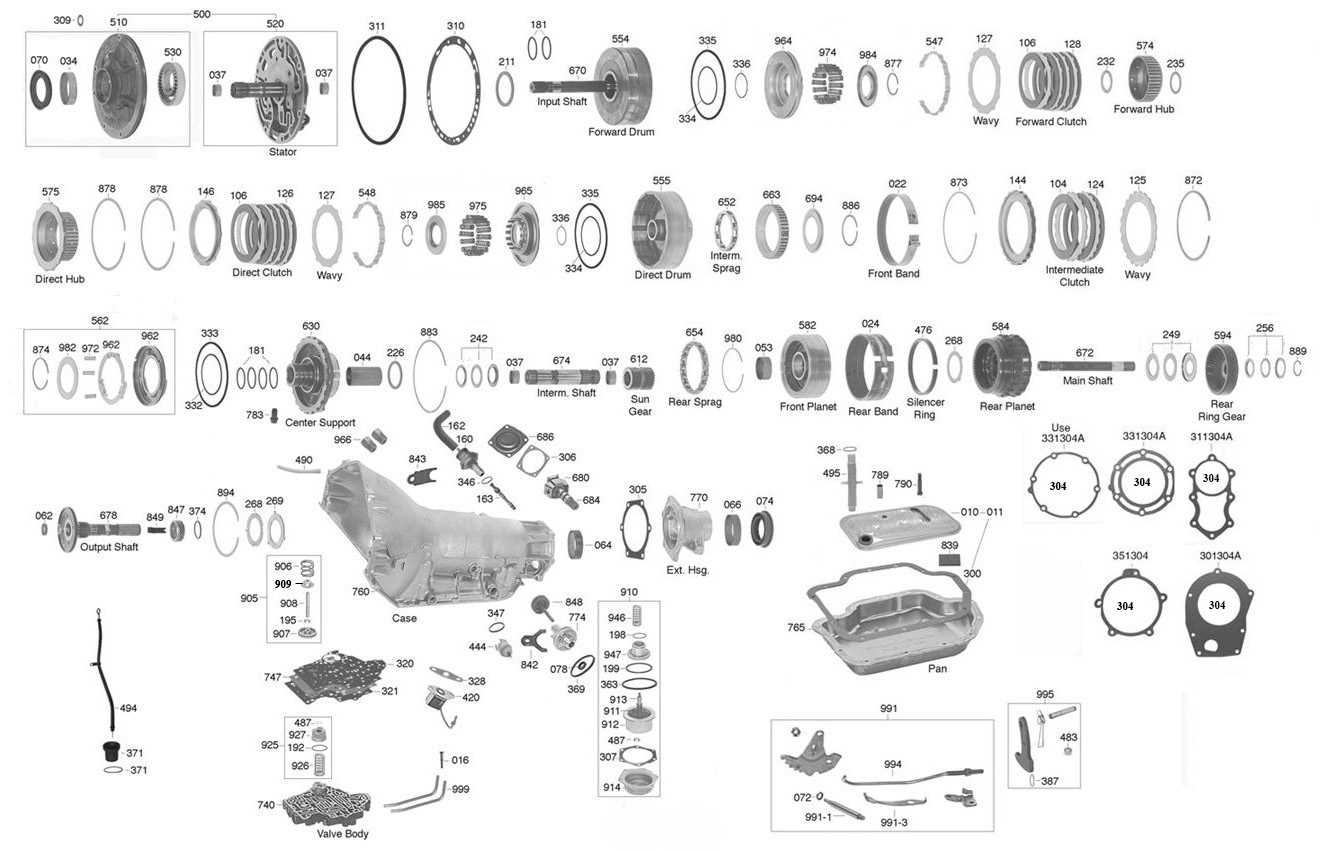
Understanding the 246 GM Transfer Case Parts Diagram
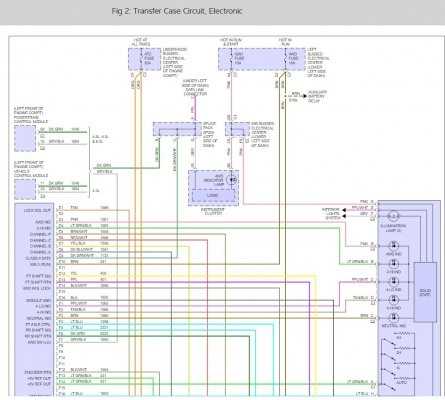
In the realm of automotive mechanics, a comprehensive understanding of the intricate elements that facilitate vehicle movement is essential. This section delves into the various components involved in the operation of a specific gear mechanism, highlighting their functions and interrelations. By exploring this intricate assembly, one gains valuable insights into how these mechanisms work seamlessly to enhance vehicle performance.
The interaction of these crucial elements not only ensures optimal functionality but also contributes to the overall reliability of the vehicle. Each component plays a vital role, and knowing their configurations can aid in troubleshooting issues that may arise. This knowledge is particularly beneficial for enthusiasts and professionals alike, as it fosters a deeper appreciation for the engineering that underpins modern vehicles.
As we explore the schematic representation of these components, the focus will be on understanding how they fit together and operate in harmony. This exploration serves as a guide for both novice mechanics and seasoned professionals, providing clarity on the complexities of automotive gear systems. With an emphasis on practical application, this section aims to illuminate the path toward effective maintenance and repair strategies.
Understanding the 246 GM Transfer Case
The intricate system responsible for delivering power to the wheels of a vehicle is crucial for ensuring optimal performance in various driving conditions. This component plays a pivotal role in managing torque distribution, allowing for seamless transitions between different drive modes. Familiarizing oneself with its structure and functionality can enhance maintenance practices and troubleshooting efforts.
At its core, this assembly comprises several essential elements that work in harmony to facilitate the transfer of energy from the engine to the drive axles. Each component has a specific function, contributing to the overall efficiency and reliability of the vehicle. Understanding these mechanisms can empower vehicle owners to recognize potential issues before they escalate.
Moreover, the operation of this system is influenced by various factors, including the vehicle’s design and intended use. Recognizing how these influences interact can aid in making informed decisions regarding upgrades or repairs. A comprehensive grasp of the system’s workings not only promotes better vehicle management but also enhances safety on the road.
In conclusion, delving into the details of this critical automotive element is not just beneficial for enthusiasts and mechanics alike; it can significantly improve one’s driving experience. Knowledge about its components and their interplay fosters a deeper appreciation for the engineering behind modern vehicles.
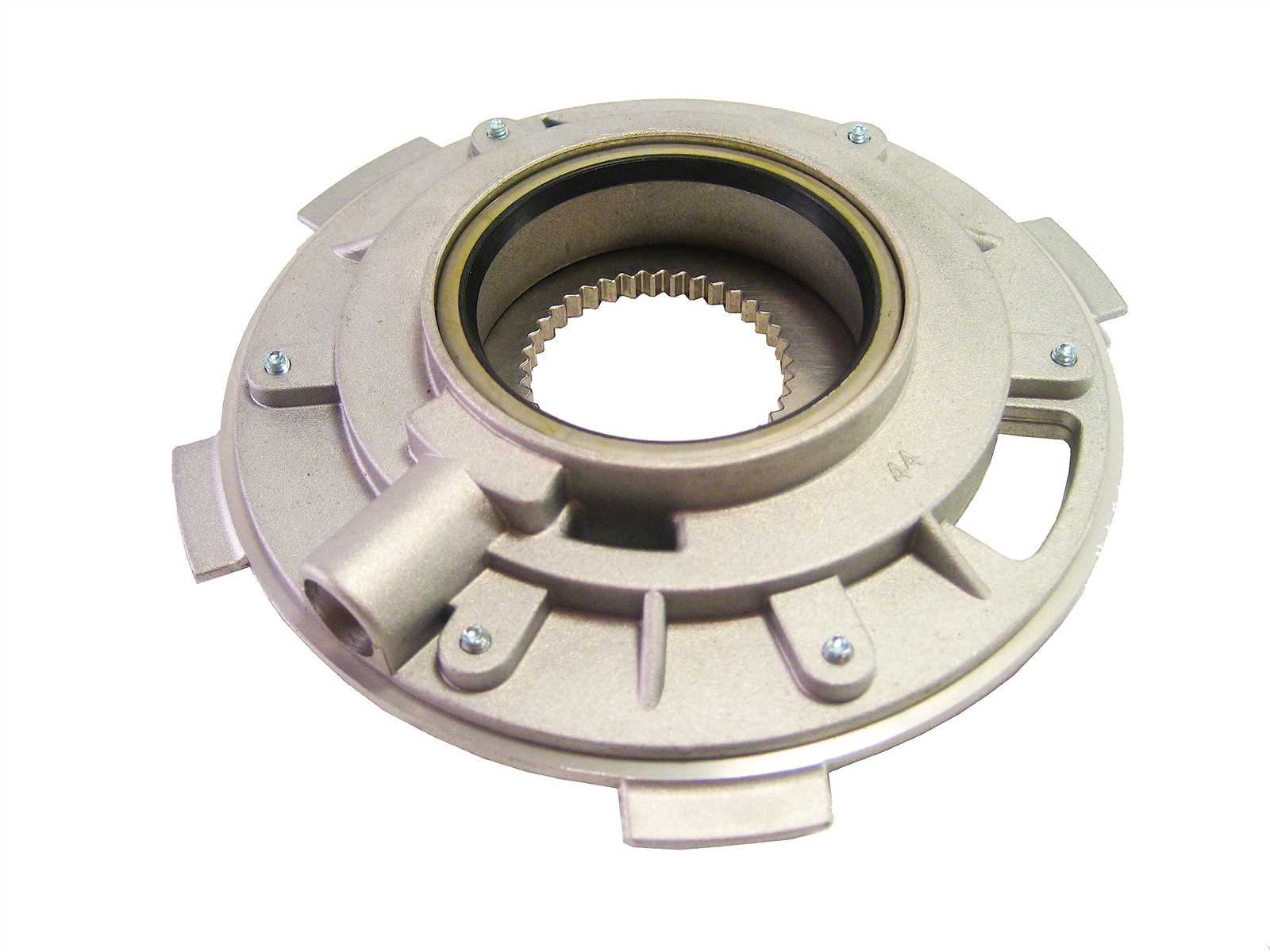
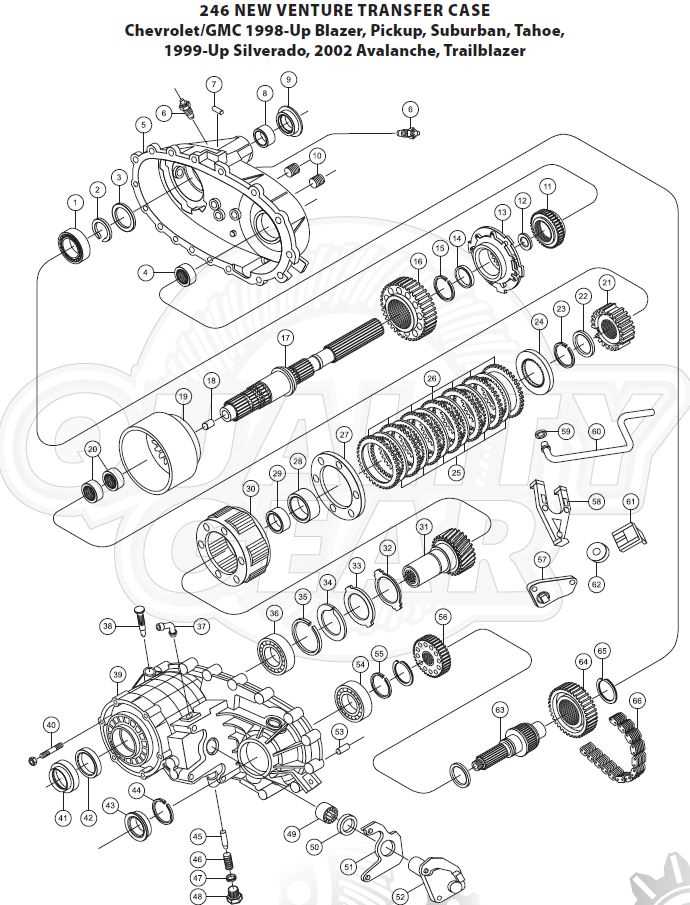
Components of the 246 GM System
The system in question consists of several integral elements that work harmoniously to facilitate optimal functionality and performance. Understanding each component’s role is essential for proper maintenance and troubleshooting, ensuring that the entire mechanism operates smoothly and efficiently.
Core Elements
At the heart of this system lies the central hub that distributes power to the wheels. This component is crucial for managing torque and ensuring that traction is maintained across various terrains. Additionally, there are gear sets that enable different drive ratios, allowing the vehicle to adapt to different driving conditions seamlessly.
Supporting Mechanisms
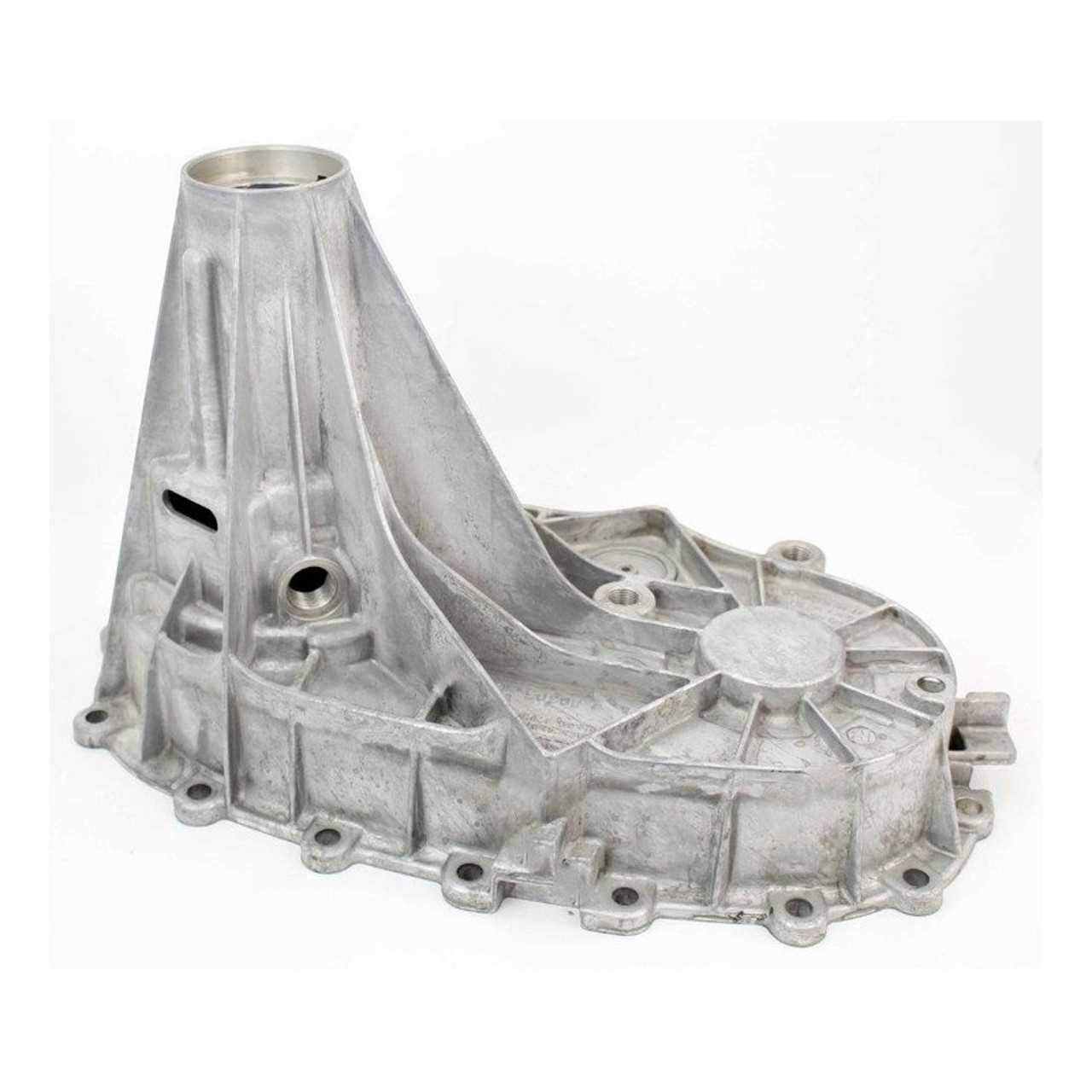

In conjunction with the core elements, various supporting mechanisms enhance the overall performance. Actuators play a vital role in engaging and disengaging different functions, while sensors monitor operational parameters, providing feedback for adjustments. The housing structure not only protects these components but also contributes to the system’s durability under challenging conditions.
Common Issues with Transfer Cases
The mechanisms that facilitate power distribution between axles can experience various problems over time. Understanding these issues can help vehicle owners recognize symptoms early and take appropriate action, ensuring longevity and performance.
Here are some prevalent challenges associated with these systems:
| Issue | Description | Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Fluid Leaks | Seals or gaskets may wear out, leading to fluid loss. | Puddles under the vehicle, low fluid levels. |
| Strange Noises | Worn gears or bearings can produce grinding or whining sounds. | Unusual noises during operation. |
| Difficulty Engaging | Issues with linkage or internal components can make shifting difficult. | Resistance when changing modes or no response. |
| Overheating | Excessive use or insufficient lubrication can cause overheating. | Warning lights, burnt smell, reduced performance. |
Regular maintenance and timely diagnostics can mitigate these issues, ensuring smoother operation and preventing costly repairs.
How to Diagnose Transfer Case Problems
Identifying issues within the driveline system can be crucial for maintaining vehicle performance. A range of symptoms can indicate underlying malfunctions, and early detection can prevent further damage. This section will guide you through recognizing these signs and understanding potential causes.
Common Symptoms to Look For
- Unusual noises during operation
- Difficulties engaging or disengaging specific modes
- Unexplained vibrations while driving
- Fluid leaks around the housing
- Warning lights on the dashboard
Steps for Diagnosing Issues
- Conduct a visual inspection for leaks or damage.
- Check the fluid level and condition; contaminated or low fluid can signal problems.
- Listen for abnormal sounds while the vehicle is in motion.
- Test the engagement of various driving modes to ensure they function smoothly.
- Use diagnostic tools to read error codes, if applicable.
By following these steps and remaining vigilant about symptoms, you can effectively diagnose and address issues within the driveline system, ensuring a smoother and safer driving experience.
Maintenance Tips for Optimal Performance

Ensuring the longevity and efficiency of your vehicle’s drivetrain requires regular upkeep and attention to detail. By following a few essential practices, you can enhance functionality and prevent potential issues, leading to a smoother driving experience.
Regular Inspections
Conducting routine checks on your system can help identify wear and tear before it escalates into a major problem. Look for signs of leaks, unusual noises, or any irregularities in operation. Early detection is key to maintaining reliability.
Fluid Maintenance
Maintaining the right fluid levels is critical for optimal operation. Changing the lubricant at recommended intervals not only helps reduce friction but also prevents overheating. Ensure you use high-quality products suited for your specific setup, as this can significantly impact performance.
Repair vs. Replacement: Making the Choice
When faced with a malfunction in a critical component of your vehicle, the decision to repair or replace can significantly impact both performance and finances. Understanding the nuances of each option is essential for making an informed choice that aligns with your long-term goals.
Factors to Consider
- Cost: Evaluate the immediate and long-term expenses associated with each option.
- Condition: Assess the current state of the component and its potential for future reliability.
- Time: Consider how quickly you need the issue resolved and how long each option will take.
- Warranty: Check if a new part comes with a guarantee, which may influence your decision.
Pros and Cons

- Repair:
- Cost-effective for minor issues.
- Can extend the life of the component.
- Potentially quicker turnaround time.
- Replacement:
- Provides peace of mind with a new, reliable unit.
- Often backed by a warranty.
- Eliminates the risk of recurring problems.
Ultimately, the decision hinges on a careful evaluation of these factors. Taking the time to analyze your specific situation will lead to a choice that enhances your vehicle’s performance and durability.
Tools Needed for Transfer Case Work
When tackling maintenance or repairs related to drivetrain components, having the right tools is essential for efficiency and effectiveness. A well-equipped workspace ensures that you can address any issue that arises without unnecessary delays or complications. Below are key instruments that will help facilitate your project.
Essential Hand Tools

- Socket Set: A variety of sizes is necessary to accommodate different fasteners.
- Wrenches: Both open-end and box-end wrenches are crucial for loosening and tightening bolts.
- Screwdrivers: A selection of flathead and Phillips screwdrivers will be useful for various screws.
- Pliers: Needle-nose and standard pliers assist with gripping and manipulating components.
Specialized Equipment
- Torque Wrench: Ensures fasteners are tightened to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Oil Catch Pan: Useful for collecting fluids during maintenance procedures.
- Gear Puller: Helps in removing gears or bearings without damaging them.
- Work Light: Proper lighting is vital for detailed inspections and repairs.
Having these tools on hand will not only streamline your work process but also enhance the overall outcome of your repairs and maintenance tasks.
Step-by-Step Disassembly Guide
This section provides a comprehensive approach to the careful separation of the components within a specific mechanical assembly. By following these detailed instructions, you can ensure that each element is removed systematically, reducing the risk of damage and facilitating effective reassembly.
Preparation for Disassembly
Before starting the process, gather all necessary tools, including wrenches, screwdrivers, and pliers. Ensure that your workspace is clean and organized, allowing for easy access to components as they are removed. Additionally, consult any relevant manuals or guides to familiarize yourself with the assembly’s layout and structure.
Step-by-Step Removal Process
Begin by disconnecting any electrical connections and fluid lines to prevent spills and ensure safety. Next, remove any outer coverings or shields that may obstruct access to the inner components. Carefully detach each part in the designated order, using appropriate tools to avoid stripping screws or damaging connections. As you progress, label each component and fastener to simplify the reassembly process later on.
Reassembly Procedures Explained
The process of putting components back together requires careful attention to detail and a systematic approach. Proper reassembly ensures the functionality and longevity of the entire assembly. Each element must be aligned correctly, and all fasteners should be tightened to specified torque levels.
Step 1: Preparation
Before beginning, gather all necessary tools and components. Ensure the workspace is clean and organized to avoid misplacing any pieces. Review any diagrams or manuals to familiarize yourself with the order of reassembly.
Step 2: Initial Assembly
Start by placing the largest components together. Ensure that all seals and gaskets are in good condition and properly positioned to prevent leaks. Align all holes and insert fasteners loosely, allowing for adjustment.
Step 3: Tightening Fasteners
Once initial alignment is confirmed, gradually tighten fasteners in a crisscross pattern. This technique helps distribute pressure evenly and minimizes the risk of warping. Follow the manufacturer’s specifications for torque values.
Step 4: Final Checks
After everything is securely in place, conduct a thorough inspection. Verify that all connections are tight and no tools or foreign objects are left inside the assembly. This step is crucial for preventing future issues.
Step 5: Testing
After reassembly, perform a series of tests to ensure proper operation. Monitor for any unusual sounds or vibrations during initial use. If any issues arise, revisit the assembly process to identify and rectify the problem.
Upgrading Parts for Enhanced Performance
Improving the components of your vehicle can significantly enhance its overall functionality and driving experience. By focusing on key upgrades, you can boost power delivery, enhance durability, and improve handling. This section will explore various enhancements that can transform your machine into a high-performing powerhouse.
- High-Quality Gears: Upgrading to premium gears can lead to smoother operation and increased torque.
- Reinforced Housing: A sturdier housing can provide better protection and longevity for internal components.
- Improved Seals: Enhanced sealing solutions help prevent leaks and ensure optimal performance in all conditions.
Investing in advanced technologies can also provide significant benefits. Consider these options:
- Electronic Controls: Integrating smart controls can enhance responsiveness and efficiency.
- Performance Fluids: Using specialized lubricants can reduce friction and improve component lifespan.
- Lightweight Materials: Employing advanced materials reduces weight and boosts agility.
When upgrading, always prioritize compatibility and quality. These enhancements not only elevate performance but also contribute to a more enjoyable and reliable driving experience.
Understanding Fluid Requirements and Types
The significance of selecting the right lubricants for mechanical systems cannot be overstated. These substances play a crucial role in ensuring optimal performance, longevity, and efficiency. Each system has its unique specifications, requiring a careful assessment of the fluid’s properties to ensure compatibility and effectiveness.
When considering lubricants, it’s essential to recognize the various types available. Conventional oils are often derived from petroleum and provide basic protection, while synthesized options offer enhanced performance under extreme conditions. Biodegradable fluids are increasingly popular due to their environmental benefits, making them a favorable choice for those prioritizing sustainability.
Additionally, the viscosity of the fluid is a critical factor. It determines how easily the lubricant flows and its ability to create a protective film. Low-viscosity fluids excel in colder environments, whereas high-viscosity options provide superior protection under high temperatures and heavy loads. Understanding these characteristics is vital for maintaining the health of mechanical systems.
Ultimately, proper fluid selection not only affects performance but also influences maintenance schedules and overall system reliability. Knowledge of the appropriate types and their specific requirements will contribute to informed decisions, ensuring optimal functionality over time.
Aftermarket Parts vs. OEM Options
When considering vehicle components, enthusiasts often face a choice between aftermarket alternatives and original equipment manufacturer offerings. Each option presents its own set of benefits and drawbacks, impacting both performance and budget. Understanding these differences is essential for making informed decisions that align with your needs.
Benefits of Aftermarket Alternatives
- Cost-Effectiveness: Generally, aftermarket solutions are priced more competitively, making them an attractive option for budget-conscious individuals.
- Diverse Selection: The aftermarket offers a vast array of choices, allowing for customization and upgrades that enhance functionality and appearance.
- Performance Enhancements: Many aftermarket products are designed to improve vehicle performance beyond factory specifications.
Advantages of OEM Offerings
- Quality Assurance: OEM products are manufactured to meet the exact standards set by the original manufacturer, ensuring compatibility and reliability.
- Warranty Coverage: Using OEM options often comes with warranty protection, providing peace of mind against potential issues.
- Resale Value: Vehicles equipped with OEM components may retain a higher resale value, appealing to future buyers.
Ultimately, the choice between aftermarket and OEM solutions will depend on personal preferences, specific requirements, and budget considerations. Evaluating both options thoroughly can lead to a more satisfying ownership experience.
Real-Life Case Studies of Repairs
This section delves into practical examples of successful repairs undertaken in various vehicles. By analyzing specific instances, we can gain valuable insights into common issues and effective solutions. Each case provides a unique perspective on the challenges faced and the strategies employed to resolve them.
Case Study 1: Overheating Issue
A popular SUV experienced persistent overheating, causing concern among its owners. The investigation revealed several contributing factors:
- Faulty thermostat
- Blocked radiator
- Low coolant levels
After replacing the thermostat and flushing the cooling system, the vehicle’s temperature returned to normal during operation. This case highlights the importance of regular maintenance to prevent such problems.
Case Study 2: Gear Shifting Difficulties
Another vehicle presented challenges with gear engagement, causing frustration for the driver. The diagnosis uncovered issues related to:
- Worn linkage components
- Improper fluid levels
- Contaminated transmission fluid
By replacing the worn components and performing a fluid change, the vehicle regained smooth shifting capabilities. This example underscores the significance of timely inspections to ensure optimal performance.