Understanding the Components of a Waterous Fire Hydrant
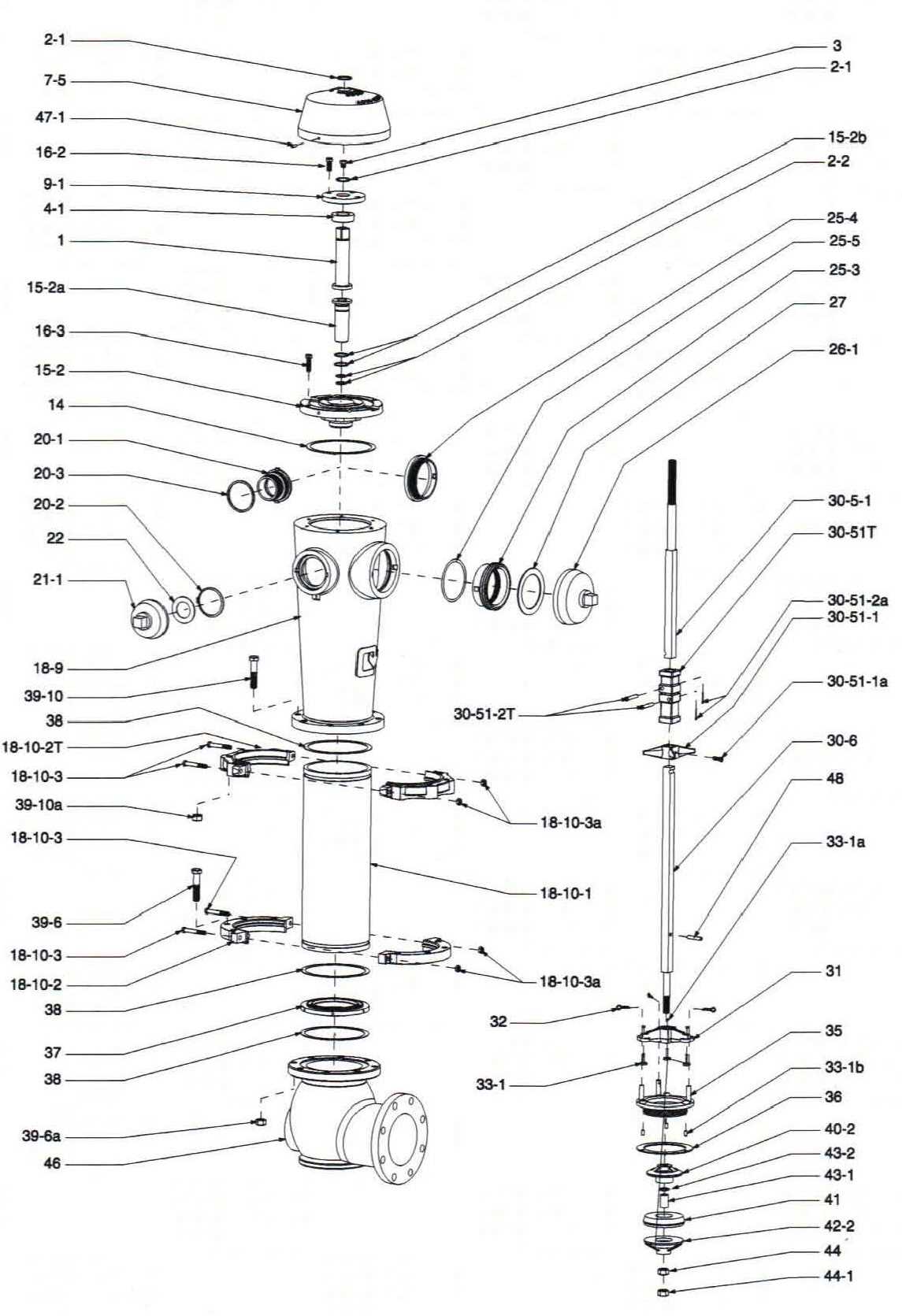
The functionality of a key element in water distribution systems relies heavily on the proper arrangement of various components. These systems are essential for ensuring a reliable flow of water when needed. The efficiency and durability of each part are crucial for maintaining the overall operation of the system.
When analyzing the construction and interaction of these individual elements, it’s important to recognize their specific roles. Each piece, from valves to nozzles, contributes to a smooth process, enabling rapid response in times of need. Understanding how these components are structured provides insight into how such systems work together seamlessly to serve their purpose effectively.
Detailed exploration of these parts offers a clearer view of their design, allowing for informed decisions regarding maintenance and upgrades. Breaking down each section of the system reveals the necessary relationships between all components, ensuring that each part performs optimally for its intended function.
Waterous Fire Hydrant Overview
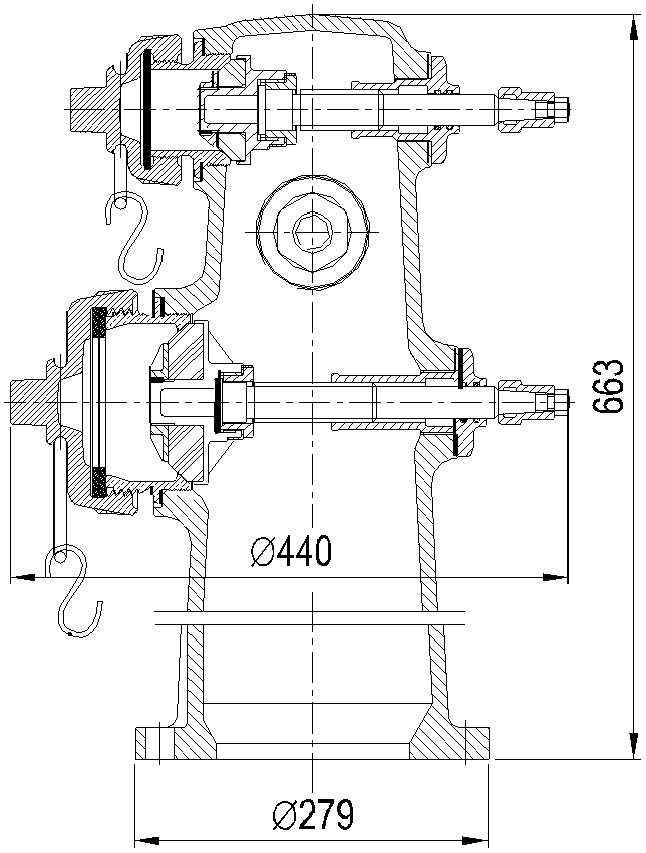
This section provides an introduction to the essential components and their roles in a water delivery system used for emergency purposes. The system consists of a robust assembly designed for quick access to a water source, ensuring effective response in critical situations. Each element is engineered for reliability, durability, and ease of use, providing a vital connection between the public water supply and firefighting operations.
Understanding the structure and functionality of this equipment is crucial for ensuring optimal performance during emergencies. The components work together to create a seamless operation, allowing for efficient water flow and distribution. Designed for simplicity yet effectiveness, the system facilitates swift deployment when every second counts.
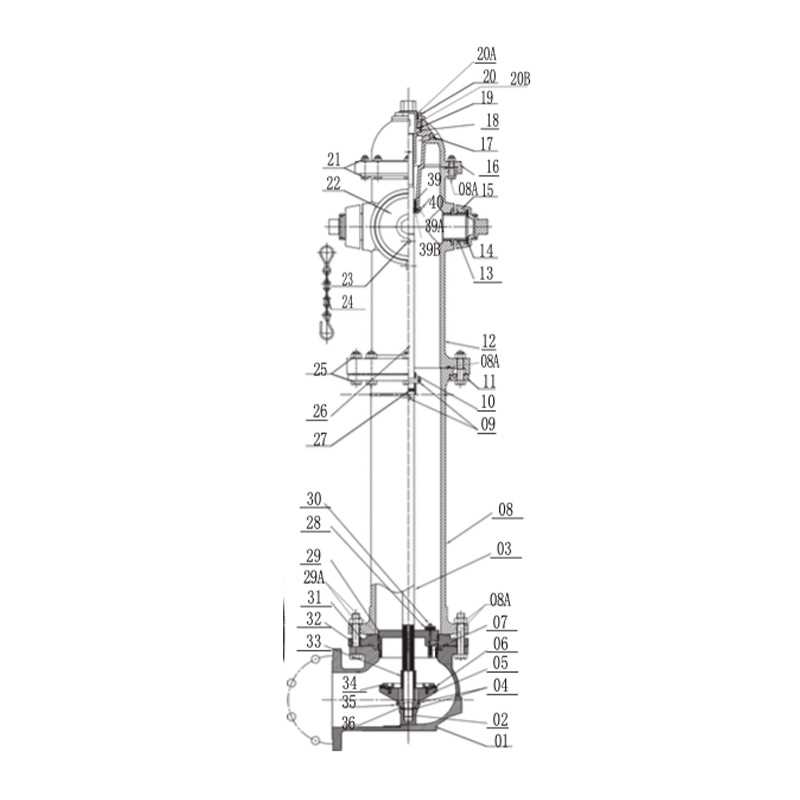
Components of a Waterous Hydrant
Every system designed to provide water under pressure consists of various essential elements that work together to ensure efficient operation. These components play a crucial role in maintaining the functionality and safety of the installation, allowing for smooth flow and reliable access when needed.
Main Structure
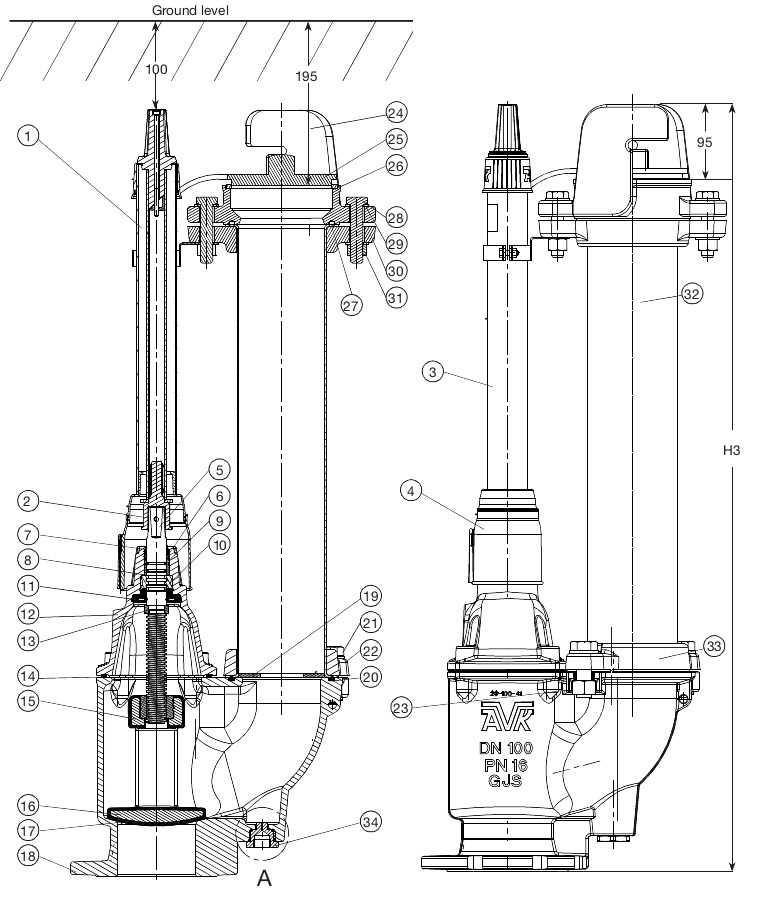
- Base Assembly: The foundation of the entire setup, typically made from durable materials, ensures stability and secure attachment to the ground.
- Valve Mechanism: A crucial part that controls the flow of water. It opens and closes to regulate pressure and volume.
- Nozzle System: Provides outlets for the release of water, offering different configurations to meet various operational needs.
Control Elements
- Cap Assembly: Protects the nozzles when not in use and provides access when water flow is required.
- Control Stem: A key part for regulating valve operation, it ensures the proper opening and closing of the flow channels.
- Drainage Mechanism: Facilitates the removal of residual water, preventing freezing and damage during off-seasons.
Understanding Hydrant Valve Mechanisms
The core function of these systems revolves around the control of water flow within a distribution network. Their role is to manage the release of water from a pressurized system, ensuring that it can be accessed and directed when necessary. These mechanisms typically involve various components that regulate water movement based on user input or operational requirements.
Valves play a crucial role in maintaining control over water release. By opening or closing specific passages, they allow for adjustments in pressure and flow rates, which is essential for efficient use. These devices are designed with precision to withstand the pressures of the system, and their functionality is key to ensuring safety and performance during use.
When inspecting such systems, understanding the construction and operation of the controlling devices is critical. The valves’ ability to respond to external forces, like manual activation or automatic systems, determines how effectively the water can be accessed. Proper maintenance and comprehension of these control systems contribute significantly to overall reliability.
Design Features of Waterous Hydrants
The structure and function of modern water distribution units are influenced by several key elements that ensure reliability and efficiency. These systems are engineered with precision to meet the demands of urban and rural infrastructures, facilitating quick access to water during emergencies. Various components are strategically designed to enhance both the ease of use and durability under various conditions.
One of the defining aspects of these systems is the incorporation of robust materials, which help maintain high performance even in extreme climates. Each unit is designed to withstand both mechanical stress and exposure to environmental factors. The internal mechanics play a crucial role in controlling the flow and pressure, offering a steady and regulated distribution when needed.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Base Valve | Controls water flow, ensuring pressure stability. |
| Stem | Acts as the main connector for opening and closing the water flow. |
| Cap | Seals the unit to prevent contamination and protect the mechanism. |
| Nozzle | Provides the outlet for water, designed for different hose fittings. |
Additionally, the system’s design includes ergonomic features that allow for quick and efficient operation. The manual controls are strategically placed to ensure ease of access, while the shape of the exterior allows for better handling and reduces the risk of wear and tear.
Waterous Hydrant Operational System

The operational system of a water supply mechanism is designed to ensure seamless access to essential water resources when required. This system employs a series of components that work together efficiently, providing control over the flow and pressure of the liquid to serve emergency needs or routine uses. Understanding how these parts function in tandem helps improve reliability and maintenance efforts, ensuring rapid and effective deployment when necessary.
Key Mechanisms in Operation
This system consists of various integral units that regulate the movement of water. It begins with the main valve that controls the water flow. When activated, the valve opens, allowing the flow to pass through to the designated output. The pressurization system ensures that there is a consistent force, enabling the water to reach its intended destination without any obstruction. The control valves and other safety features help prevent overflows or unwanted pressure issues, maintaining the system’s stability.
Maintenance and Performance Considerations
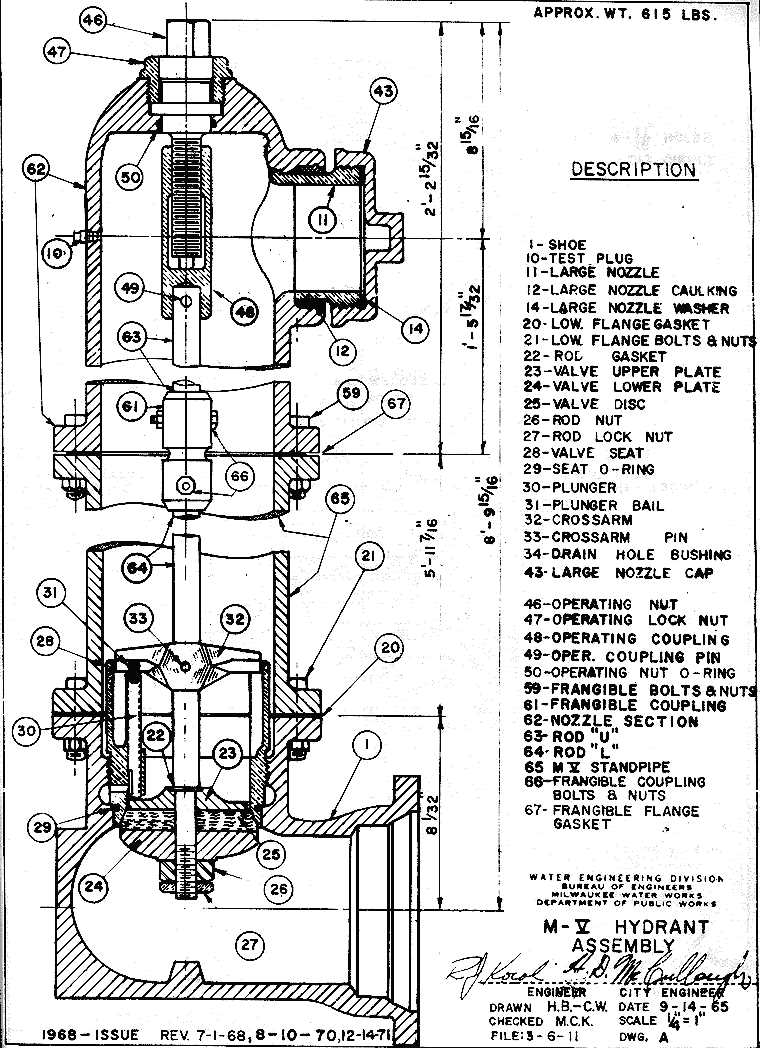
Proper upkeep is essential to avoid any operational failures. Regular inspection and testing of the individual components guarantee the system remains functional in critical situations. Ensuring that all seals, valves, and connectors are in good condition prevents leaks and inefficiencies, enhancing the longevity and reliability of the entire setup. By understanding these core operational aspects, users can ensure their system continues to perform optimally, day in and day out.
Maintenance Tips for Fire Hydrants
Regular upkeep is essential to ensure optimal performance of essential water control systems. Proper maintenance helps prevent malfunctions during emergencies, prolongs the life of equipment, and ensures they are ready when needed. By following a few key guidelines, you can ensure that these systems remain functional and efficient.
Inspection and Testing
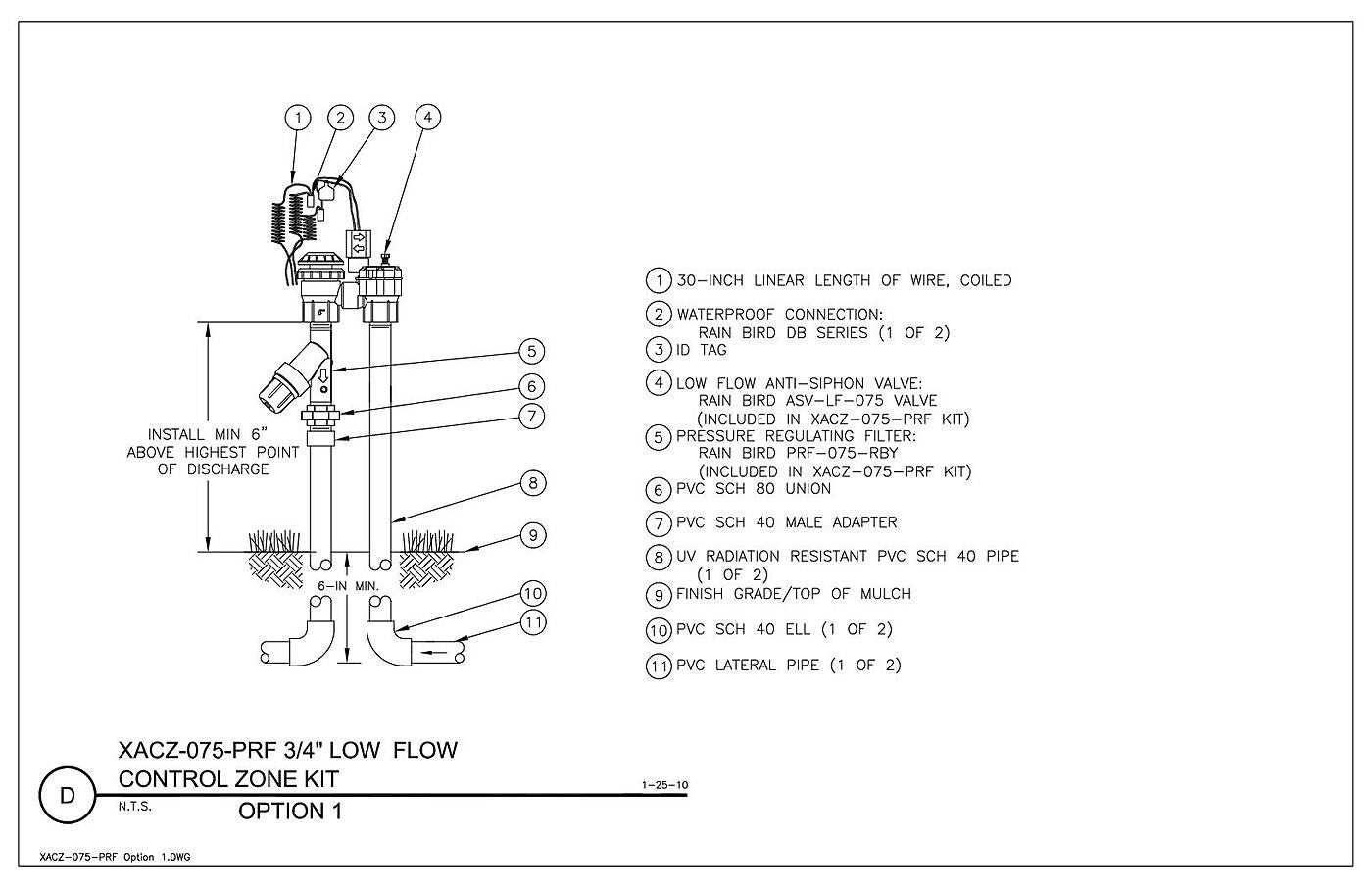
Routine inspections are vital to detect any wear or damage. Checking for leaks, corrosion, or dirt buildup around the valves and seals helps avoid potential failures. Testing the mechanisms under controlled conditions ensures the system operates smoothly when required. Perform these tests at regular intervals to stay ahead of possible issues.
Cleaning and Lubrication
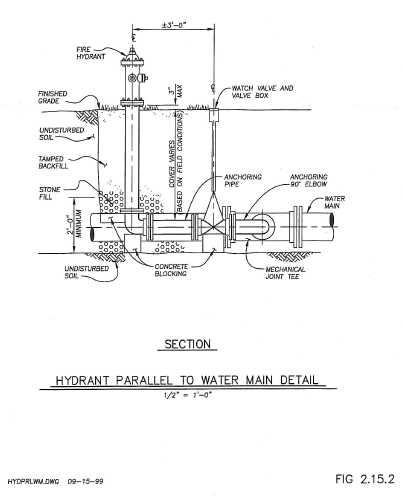
Accumulation of debris can obstruct the operation of these systems. Cleaning moving parts and components ensures smooth operation, while lubrication helps prevent rust and friction. Always use recommended lubricants for the specific type of mechanism to avoid any compatibility issues.
Note: Pay special attention to the seal integrity. Proper sealing prevents unnecessary water loss and maintains pressure during use. Regularly replace worn seals to maintain efficiency and performance.
Common Issues with Hydrant Components
Over time, various components of outdoor water systems may experience wear and tear, leading to malfunction or complete failure. These issues can be caused by a variety of factors such as improper maintenance, harsh environmental conditions, or simply age. Identifying common problems is crucial to ensure the system’s reliability when needed most.
Corrosion and Wear
One of the most prevalent issues affecting system components is corrosion. Exposure to moisture and air, along with constant use, can cause parts to deteriorate, particularly metal ones. Rust and corrosion can weaken the integrity of the components, affecting their function and longevity.
Leaks and Seal Failures
Another common issue involves the failure of seals and gaskets, leading to leaks. These parts are designed to maintain a tight seal, but they can degrade over time due to wear or extreme temperatures. Leaks not only reduce efficiency but can also result in water loss, making the system unreliable when it is required to operate effectively.
How to Troubleshoot Fire Hydrants
Ensuring that emergency water supply systems are functioning properly is crucial for safety. When issues arise, it’s important to identify the root cause and address it quickly. Troubleshooting these systems requires an understanding of their components and potential failure points. Regular inspection and maintenance can prevent major malfunctions and ensure the system operates smoothly when needed.
Start by checking for any visible signs of damage or wear on the exterior. Leaks, rust, or broken components can prevent proper operation. Next, test the pressure to confirm that it meets the required standards for effective use. If there is low pressure, the issue could be related to the valve mechanism or internal blockages. Inspecting seals and moving parts will help identify any areas that may require lubrication or repair.
If the issue persists, consider the functionality of the valve system. Ensure that the mechanisms responsible for opening and closing are operating smoothly and not obstructed. Sometimes, debris or corrosion can cause the system to malfunction. Addressing these issues early on can prevent unnecessary delays during an emergency response.
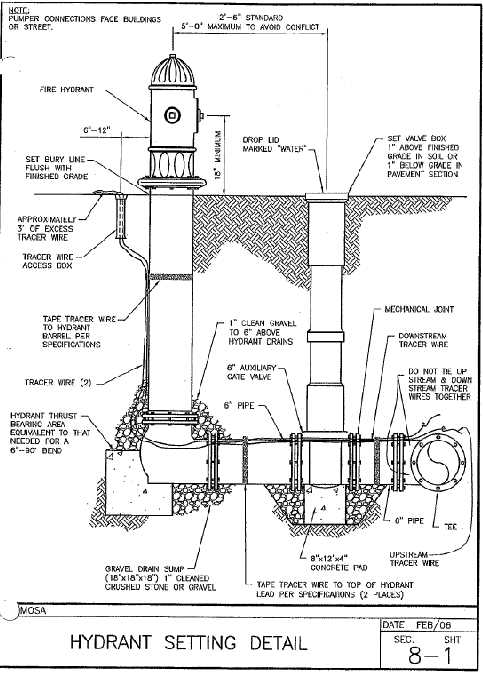
Waterous Hydrant Installation Guide
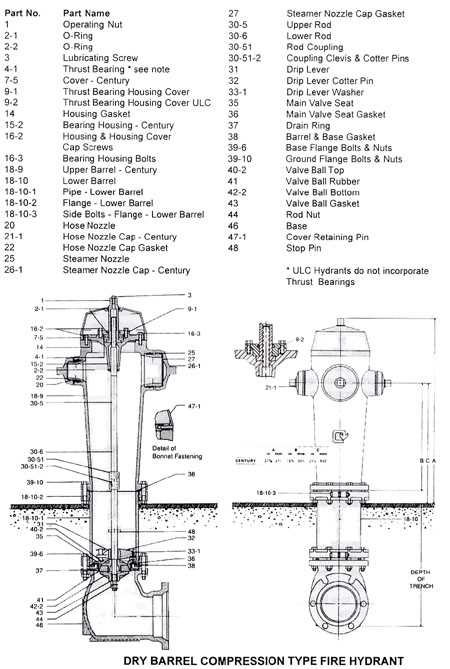
Installing a crucial water access point requires careful planning and execution to ensure functionality and durability. The process involves preparing the ground, placing the unit in the correct position, and connecting it to the necessary plumbing system. Proper alignment and secure mounting are key to maintaining efficiency over time. This guide outlines the essential steps for installing this vital apparatus, focusing on best practices for setup and safety.
Before starting the installation, ensure the location is accessible and complies with local regulations. The installation site should allow for proper water flow and minimize the risk of damage from external elements. Clear the area of debris and prepare the surface for the installation base to ensure stability. Additionally, check for any underground utilities to avoid potential hazards.
The next step is setting the apparatus in place. Carefully lower it into the prepared foundation, ensuring the alignment matches the planned layout. Once positioned, secure it using the appropriate fasteners to prevent movement or shifting. Make sure all components are properly connected and sealed to avoid leaks.
After the main structure is in place, the connection to the water source should be made. Double-check all fittings and tighten them securely to ensure there is no risk of water leakage. It’s also important to test the unit to ensure it performs as expected, checking for any irregularities or malfunctions. Finally, restore the area surrounding the installation site, making sure that it is safe and accessible for future maintenance or emergency use.
Key Parts of Hydrant Assembly
The assembly of a water control system involves several critical components that work together to ensure effective operation. Each element has a specific role, contributing to the overall performance and reliability of the system. Understanding the function of each of these components is essential for proper maintenance and troubleshooting.
Main Components
The system includes a range of parts that are responsible for controlling the flow of water and maintaining pressure levels. These components are designed to withstand high pressures and frequent use, ensuring safety and functionality when needed.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Valve Assembly | Regulates water flow and pressure within the system, controlling access to the water supply. |
| Connection Nozzle | Allows the attachment of hoses or other equipment for the distribution of water during emergencies. |
| Upper Stem | Facilitates the opening and closing of the system, allowing operators to control the water release. |
| Cap and Nut | Secures the nozzle or other parts of the assembly, preventing leaks and ensuring tight connections. |
Supportive Components
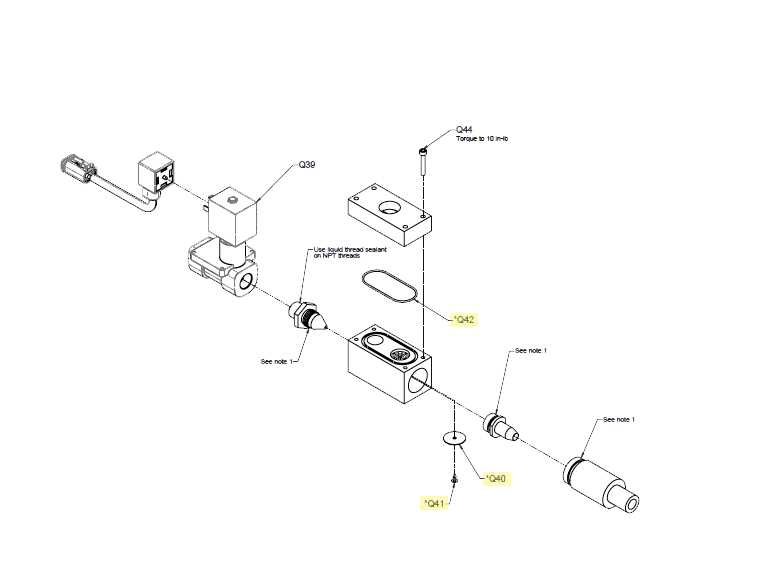
In addition to the main components, there are several other elements that provide stability and enhance the durability of the system. These supportive parts help maintain the integrity of the structure and ensure smooth operation over time.
Pressure Regulation Mechanisms
Controlling the pressure within a water distribution system is essential to ensure the safe and efficient operation of water outlets. Proper regulation prevents excessive flow or insufficient pressure that could impair functionality. Various components work together to maintain a stable pressure, preventing system damage and ensuring reliable performance during critical moments.
- Pressure Reducing Valve: This device plays a pivotal role by adjusting the pressure coming from the main supply line, reducing it to levels that are suitable for the connected system.
- Flow Control Mechanism: By managing the flow rate, this mechanism ensures that pressure remains within a safe range during both low and high demand conditions.
- Pressure Relief Valve: This safety feature releases excess pressure to avoid overloading the system, helping to prevent damage or failure of critical components.
Effective pressure regulation depends on maintaining balance between these devices, ensuring a consistent and safe water flow for all applications requiring high-pressure distribution.
Waterous Hydrant Seal Functions
The seals within a water distribution system serve an essential role in ensuring efficient operation and preventing leakage. These components are integral to maintaining the integrity of water flow, especially in systems exposed to external elements and high pressures. Understanding their functionality helps in preserving long-term system reliability.
Role of Seals in Fluid Control
Seals are primarily responsible for controlling the flow of liquids and ensuring that unwanted leakage is minimized. They are designed to create a tight barrier between different sections of the system, preventing any fluid from escaping under pressure. This is crucial for maintaining the desired water pressure levels and avoiding wastage.
- Prevent leakage around critical connections.
- Maintain system pressure for optimal performance.
- Ensure smooth operation of moving components.
- Protect against contamination from external elements.
Types of Seals and Their Applications
Various types of seals are used depending on the specific needs of the system. These seals are made from different materials, each suited to withstand specific environmental conditions such as temperature extremes and exposure to chemicals. Common types include O-rings, gaskets, and lip seals, each serving distinct functions.
- O-rings: These are circular seals designed to fit into grooves, providing a secure and tight fit to prevent leakage.
- Gaskets: These are flat seals that create a seal between two surfaces, often used in larger systems to maintain pressure integrity.
- Lip seals: These seals are typically used where there is a rotating component, preventing leakage along shafts or other moving parts.