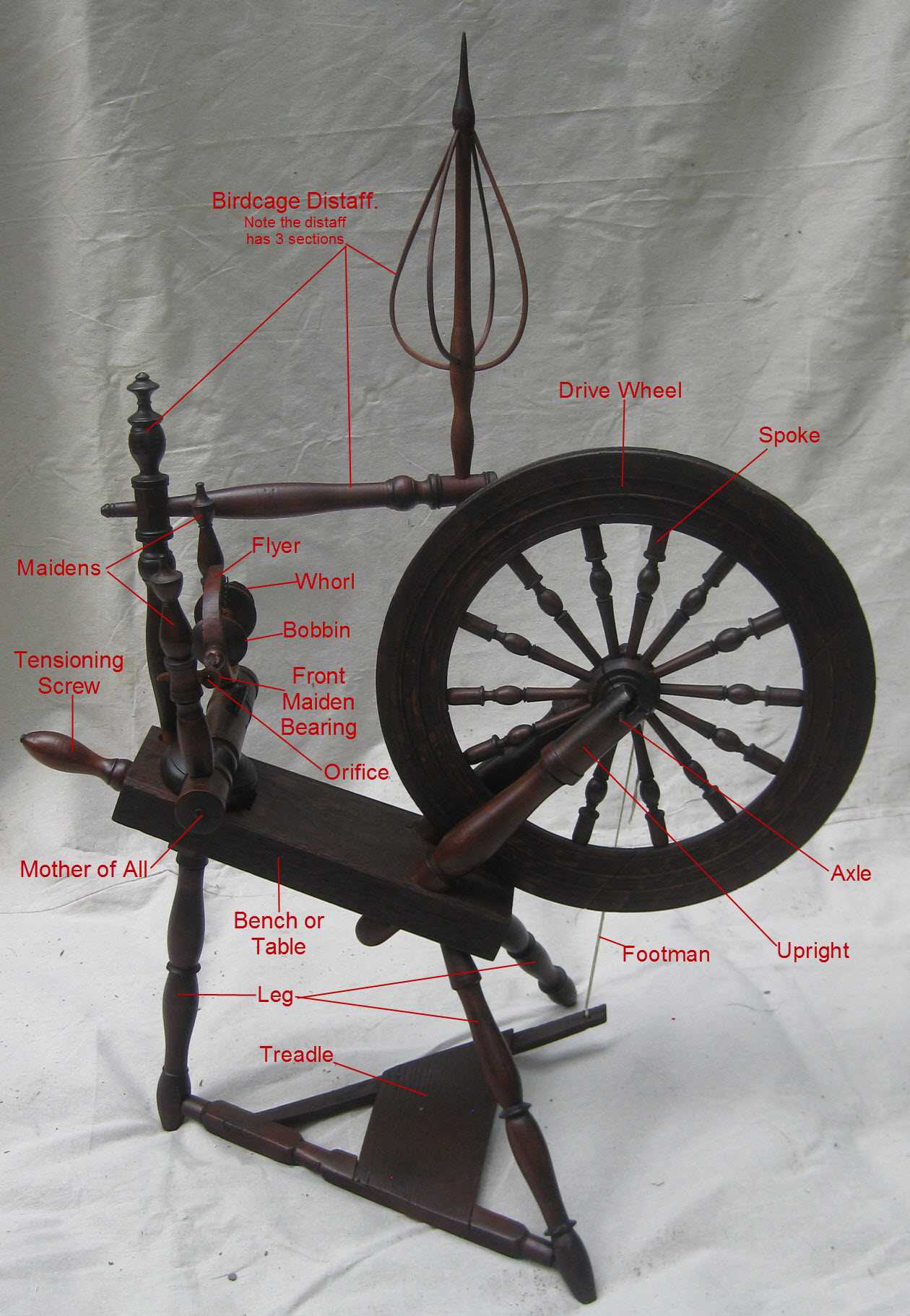
Understanding the Essential Components of Spinning Wheel Diagrams
Exploring the intricacies of a traditional crafting device reveals a rich tapestry of history and functionality. Each element plays a vital role, contributing to the overall efficiency and artistry of the process. Grasping these elements allows enthusiasts to appreciate the craftsmanship involved in creating textiles.
The interrelation of various segments showcases not only their individual significance but also their collective impact on the crafting experience. Recognizing how these features work together enhances one’s understanding and mastery of the craft. The journey through this topic offers insights into both mechanical design and cultural heritage.
By examining detailed illustrations, one can gain a clearer picture of how each component interacts. This visual representation serves as a guide for beginners and experts alike, facilitating a deeper connection to the art of textile creation. Delve into the specifics to uncover the ultimate synergy that brings this timeless practice to life.
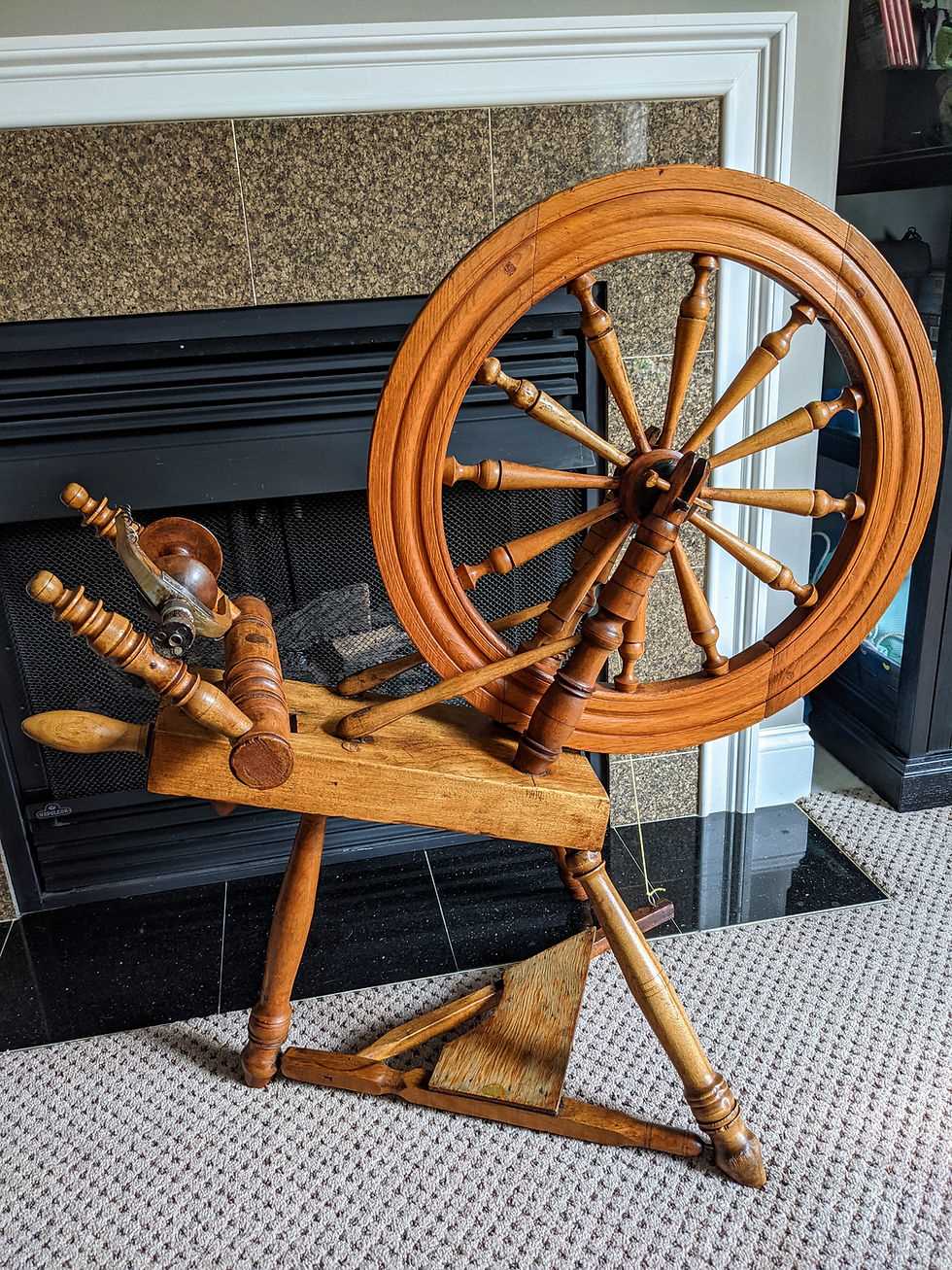
Understanding Spinning Wheel Mechanics

Exploring the intricacies of textile production reveals a fascinating interplay of components that work harmoniously to transform fibers into thread. Each element contributes to the overall functionality, ensuring efficiency and precision in the crafting process.
Core Components and Their Functions

The central mechanism plays a crucial role, providing the necessary force to initiate the twisting of fibers. Coupled with various levers and belts, this system facilitates smooth operation and adaptability to different materials, enhancing versatility in usage.
Interplay of Forces
An understanding of the forces at play offers insight into how tension and speed affect the final output. Balancing these elements is key to achieving the desired quality and consistency, making mastery of these mechanics essential for artisans.
Basic Components of Spinning Wheels
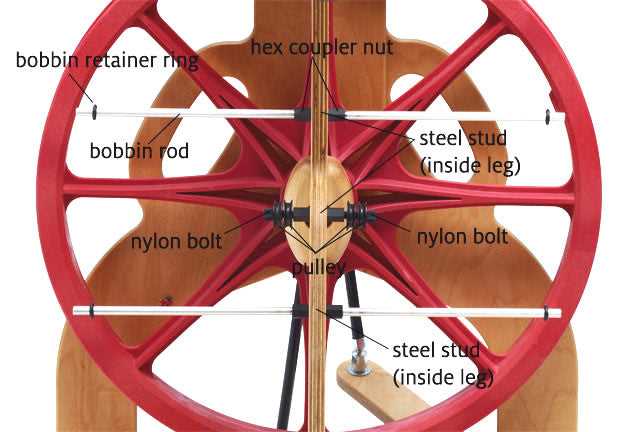
This section explores the essential elements that make up a traditional crafting apparatus used for fiber processing. Understanding these components enhances the user’s ability to operate and maintain the device effectively.
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Drive Band | A loop that connects the flyer to the treadle, enabling motion. |
| Bobbin | A cylindrical holder for the yarn, allowing for easy winding and storage. |
| Treadle | A foot-operated pedal that powers the mechanism when pressed. |
| Flyer | A rotating arm that twists the fiber into yarn while winding it onto the bobbin. |
| Orifice | A small opening where the fiber enters the flyer and is transformed into yarn. |
Types of Spinning Wheel Designs
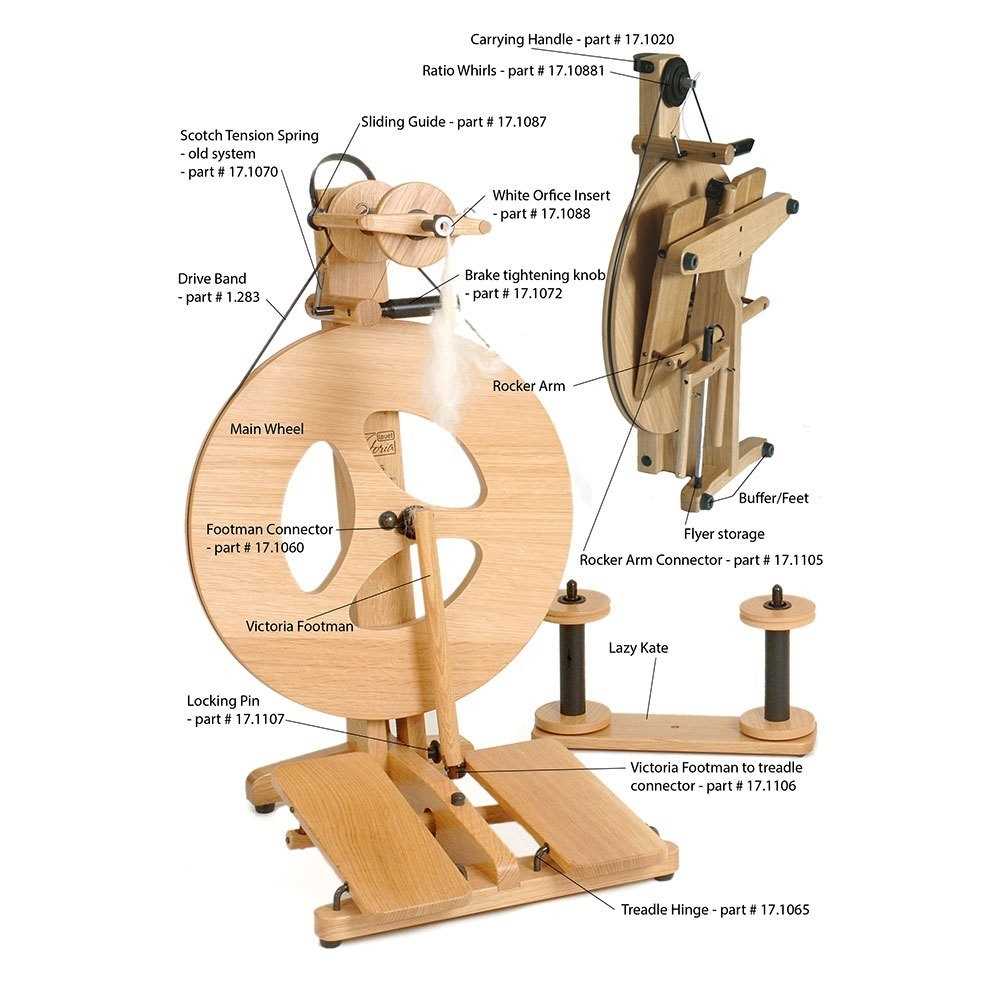
Throughout history, various designs have emerged, each reflecting unique cultural influences and practical needs. These creations not only serve functional purposes but also embody artistry and craftsmanship.
Traditional Models: Often crafted from wood, these designs emphasize simplicity and efficiency. They typically feature a single drive band and a foot pedal, allowing for smooth operation.
Modern Innovations: Contemporary versions incorporate advanced materials and ergonomic features. These often include adjustable settings for different fiber types, enhancing versatility for users.
Portable Variants: Compact and lightweight, these designs cater to artisans on the go. Their foldable structures and easy assembly make them ideal for travel.
Specialized Equipment: Some creations focus on specific fibers, like cotton or wool, incorporating tailored mechanisms for optimal results. These specialized tools often boast intricate designs to facilitate unique spinning techniques.
Exploring these diverse forms reveals the rich tapestry of tradition and innovation, making each design a reflection of both utility and aesthetic appeal.
The Role of the Flyer Assembly

The flyer assembly serves a crucial function in the process of transforming fiber into thread. It acts as the main component that facilitates the twisting and winding of the material, ensuring a consistent and balanced formation throughout the creation process.
Mechanics of the Flyer
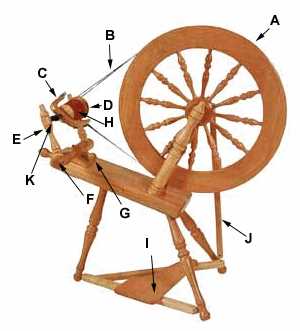
This assembly is designed to control the tension and twist applied to the fibers. By allowing for smooth rotation, it helps in maintaining an even thickness, which is essential for producing high-quality yarn. The efficiency of the flyer directly influences the final product’s strength and texture.
Importance in Fiber Artistry
Exploring the Drive Band Function

The drive band plays a crucial role in the operation of various textile machinery, facilitating the transmission of motion and energy between components. Its design and functionality are integral to achieving efficient performance, impacting the overall effectiveness of the device. Understanding how this element works can enhance both the quality of output and the ease of operation.
Mechanics of the Drive Band
This component serves as a connector, transmitting power from one rotating part to another. The tension and material composition of the band significantly influence its effectiveness. A well-maintained drive band ensures smooth operation and minimizes energy loss during the transfer of movement.
Key Characteristics
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Tension | Proper tension ensures efficient energy transfer. |
| Material | Different materials affect durability and flexibility. |
| Width | Affects the amount of friction and grip on the surfaces. |
| Length | Must be appropriate for the distances between components. |
Ultimately, a thorough understanding of the drive band function leads to better maintenance practices and improved machine efficiency, contributing to higher productivity in textile production.
Importance of the Wheel Hub

The hub serves as a crucial component in the functionality of rotational mechanisms, playing a vital role in ensuring stability and performance. Its design significantly impacts the overall efficiency of movement, influencing both speed and safety during operation.
A well-constructed hub facilitates smooth rotation, minimizing friction and wear. This aspect is essential for extending the lifespan of the entire assembly, reducing the need for frequent maintenance or replacements.
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Durability | Increases the longevity of the assembly |
| Stability | Enhances control during movement |
| Weight Distribution | Improves overall balance and performance |
| Friction Reduction | Allows for smoother and faster rotation |
In summary, the hub is indispensable for optimal operation, directly affecting performance and efficiency. Its proper design and maintenance are essential for any system relying on rotational movement.
How Tension Affects Yarn Quality
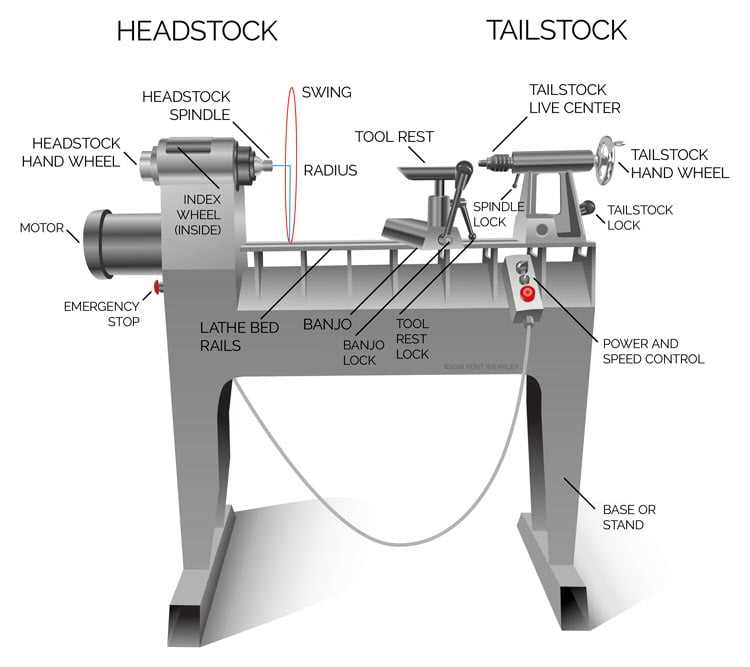
The degree of strain applied during the process of creating thread significantly influences its characteristics and overall quality. Proper management of this force is essential for achieving the desired attributes in the finished product, affecting everything from texture to durability.
The Role of Consistency
Uniform pressure during the formation of the strand ensures that each fiber is aligned and integrated cohesively. Inconsistent tension can lead to irregularities, resulting in weak spots or overly tight sections that compromise the integrity of the yarn. Maintaining steady tension is crucial for producing reliable and high-quality threads.
Impact on Fiber Properties
The physical properties of the fibers used also interact with the level of tension. Different materials respond uniquely under strain, which can affect elasticity and flexibility. Understanding how various fibers react to different levels of tension allows artisans to optimize their techniques for better outcomes, enhancing the overall functionality and aesthetic of the yarn.
Understanding the Bobbin’s Purpose

The bobbin plays a crucial role in the textile creation process, serving as a fundamental component that facilitates the efficient management of fibers. Its design and function ensure that the material is properly stored and utilized during crafting, allowing artisans to produce intricate patterns and textures with ease.
Functionality of the Bobbin
At its core, the bobbin acts as a reservoir, holding the thread that will ultimately be woven or stitched into the final product. This allows for continuous work without frequent interruptions for reloading. The mechanism by which the thread is released is both simple and effective, ensuring that the tension remains consistent throughout the crafting process.
Importance in Crafting
Beyond its basic function, the bobbin also contributes to the overall quality of the finished item. A well-designed bobbin helps maintain the right amount of tension, which is essential for producing a uniform appearance. Additionally, it enables artisans to easily switch between different threads, enhancing creativity and versatility in their work. Understanding this component’s significance can greatly improve one’s crafting techniques and outcomes.
The Spindle: A Key Element
The spindle serves as a fundamental component in the art of fiber transformation, playing a crucial role in the production of thread. Its design is both simple and effective, allowing for the efficient twisting and elongation of fibers. Understanding this element is essential for anyone interested in the craft, as it directly influences the quality and consistency of the final product.
Functionality is at the heart of the spindle’s design. It typically consists of a rod, often tapered, which is complemented by a weight that aids in the spinning process. As the user rotates the spindle, the fibers are drawn out and twisted together, creating a continuous strand. This motion not only enhances the strength of the thread but also determines its texture and thickness.
In addition to its basic function, the spindle offers a variety of techniques and styles that can affect the outcome of the spun material. Different weights and shapes can lead to diverse results, catering to various spinning methods and personal preferences. Exploring these variations allows artisans to achieve unique characteristics in their yarn, enriching their craft.
Overall, the spindle is more than just a tool; it embodies the creativity and skill involved in transforming raw fibers into usable material. Its significance in the crafting process cannot be overstated, as it remains an indispensable element for artisans dedicated to their trade.
Distinguishing Single vs. Double Drive
When exploring the mechanisms that enable rotation, one often encounters two distinct approaches: the single and double drive systems. Each method presents unique characteristics and functionalities that cater to different needs and preferences in the realm of textile crafting. Understanding the nuances between these configurations can greatly enhance the efficiency and experience of the user.
Single drive systems typically feature a more straightforward design, where a single source of power drives the entire mechanism. This simplicity can lead to a lighter and more portable option, making it appealing for those who prioritize ease of use and mobility. However, this design might limit the control and versatility during operation, particularly when handling various fiber types.
In contrast, double drive mechanisms offer a more complex interplay between components, allowing for greater adaptability. By utilizing two independent sources of motion, these systems provide enhanced control over the spinning process, enabling the user to achieve finer results and manage different materials with greater finesse. While this configuration may require a more intricate understanding, the rewards in terms of craftsmanship can be significant.
Ultimately, the choice between these two systems depends on the individual’s goals, experience level, and the specific requirements of the project at hand. Weighing the advantages and disadvantages of each can guide users toward a more fulfilling creative journey.
Parts Involved in Plying Techniques

The process of combining multiple strands into a cohesive yarn is an art that requires an understanding of the essential components and their functions. Each element plays a crucial role in achieving the desired texture, strength, and appearance of the final product. Familiarity with these components enhances both the efficiency and quality of the plying experience.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Fibers | The raw materials used, which can vary in type, length, and texture. |
| Tension Adjuster | A mechanism that regulates the tightness of the strands during the process. |
| Twist Mechanism | The device that introduces twist to bind the fibers together. |
| Take-up Spindle | The part where the finished yarn is wound for storage or further processing. |
| Guide Hook | A tool that directs the fibers into the twisting area for optimal alignment. |
Common Issues with Wheel Parts
When engaging with components that facilitate motion, users often encounter a variety of challenges that can affect performance and longevity. Recognizing these common obstacles is essential for maintaining optimal functionality and ensuring a smooth operation.
Wear and Tear
Continuous usage can lead to deterioration of various elements, impacting efficiency. Friction and exposure to environmental factors contribute to the gradual breakdown of materials, necessitating regular inspection and timely replacement to avoid further complications.
Misalignment Problems
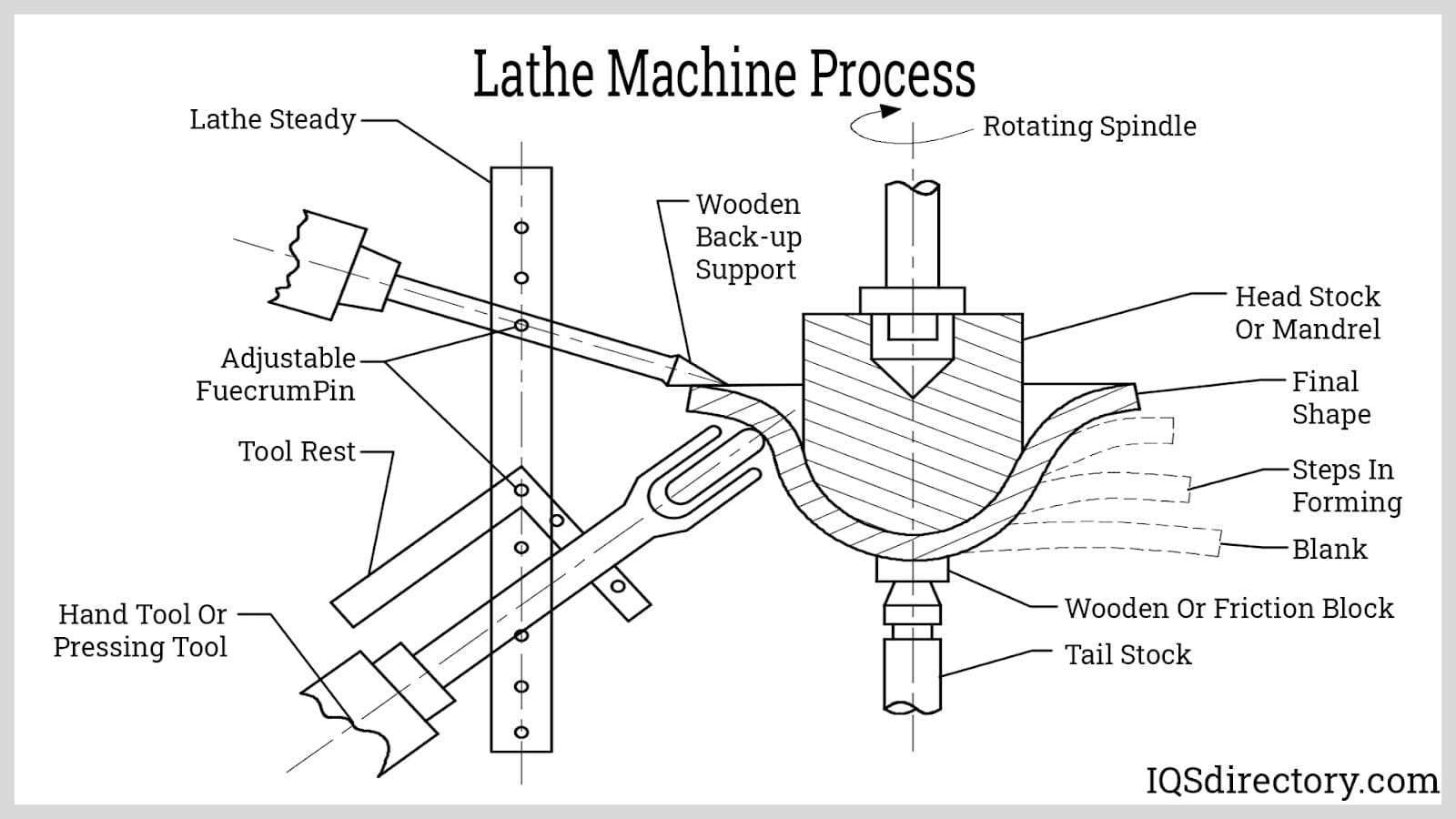
Misalignment can result in uneven wear and unpredictable handling. Proper alignment is crucial for balance and stability, and any deviations can lead to increased strain on the components. Regular adjustments and maintenance can mitigate these issues and enhance overall performance.
Visual Diagrams of Spinning Wheels
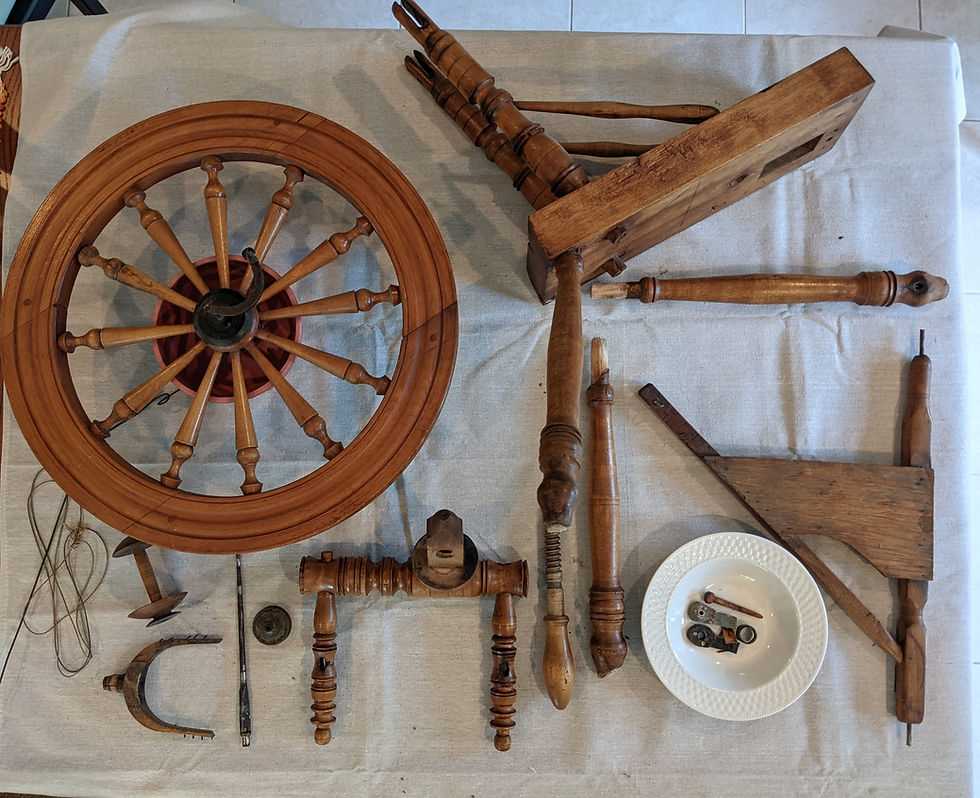

Visual representations play a crucial role in understanding the components and mechanisms of traditional textile creation tools. These illustrations simplify complex concepts, making it easier for enthusiasts and learners to grasp how various elements interact during the crafting process. By providing clarity, they enhance both educational and practical experiences in fiber arts.
Each visual aid highlights different aspects of the equipment, showcasing its structure and functionality. From the central spindle to the supporting framework, these images serve to demystify the intricacies involved in transforming raw fibers into thread. The detailed visuals also facilitate better comprehension of operational techniques, ensuring users can effectively engage with their chosen crafts.
Moreover, the use of color coding and labeling in these illustrations allows for quick identification of each element, fostering a deeper appreciation for the artistry involved. For both novices and seasoned artisans, such resources offer invaluable insights that promote skill development and creativity in textile production.