Comprehensive Guide to 2003 Toyota RAV4 Parts Diagram
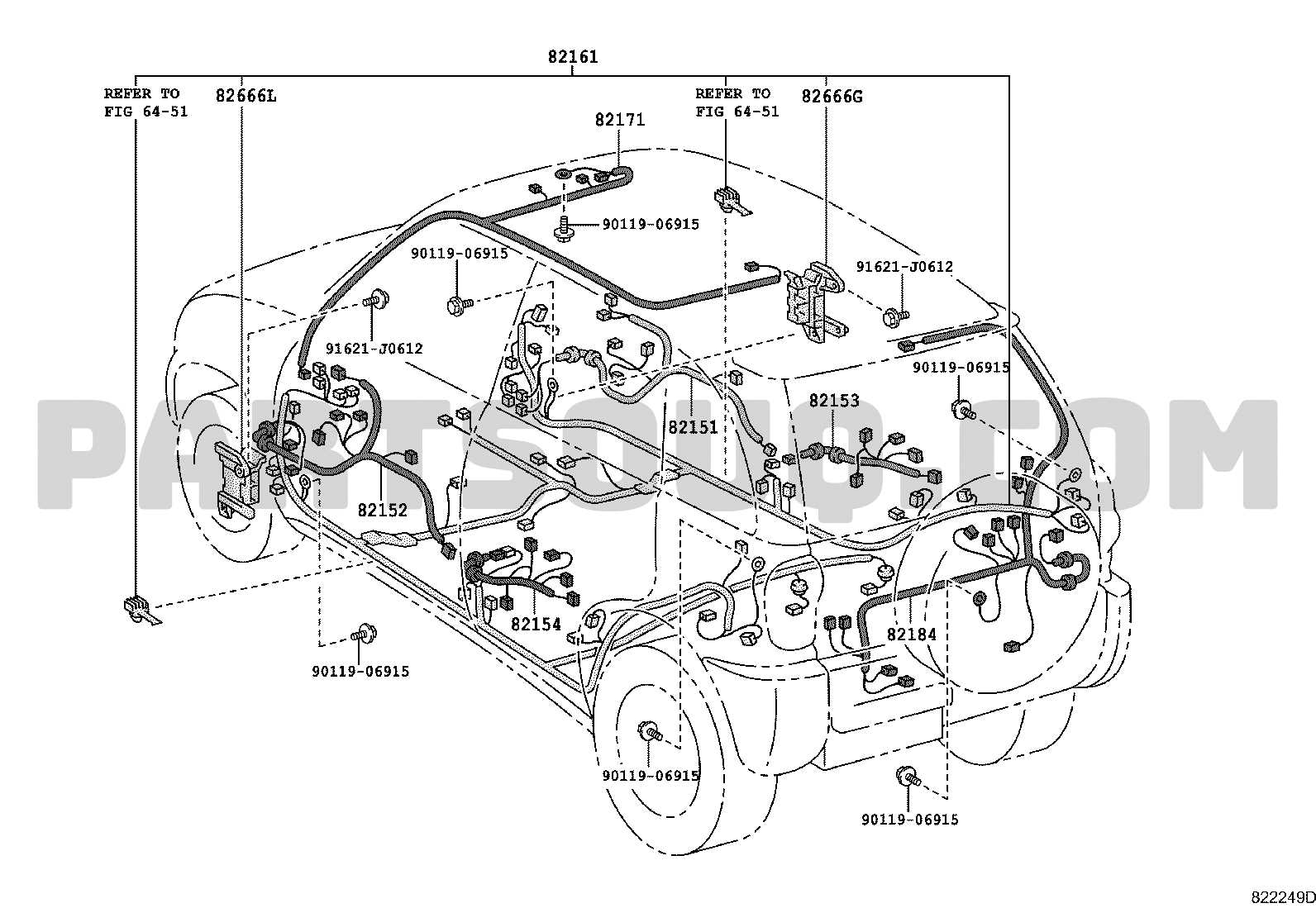
In understanding the structure and functionality of a vehicle, a clear and comprehensive overview of its various elements is essential. This guide delves into the configuration and layout of key elements in a widely recognized model from the early 2000s, aimed at helping enthusiasts and owners alike. By examining each section in detail, this resource serves as a valuable tool for identifying and understanding how individual elements contribute to the overall performance and longevity of the vehicle.
Each component within the vehicle plays a unique role, from foundational structures to intricate systems supporting safety and efficiency. With a thoughtfully organized layout, this guide is designed to walk you through the principal sections, offering insights into the interconnections between parts and how they enhance the driving experience. Through this examination, users will gain a deeper appreciation for the engineering behind this popular model.
Whether for maintenance, upgrades, or general knowledge, gaining insight into the vehicle’s assembly and setup empowers owners with the information needed to maintain optimal performance. This overview provides a clear roadmap for exploring these essentials, highlighting features that make the model both reliable and versatile.
Complete Overview of 2003 Toyota RAV4 Parts
This section provides a detailed look into the essential mechanical and structural components of this well-loved vehicle model. Here, we explore key areas that contribute to its durability, performance, and safety, helping enthusiasts and owners understand the arrangement and role of each component under the hood, around the frame, and within the cabin. Our goal is to outline the significant elements that keep this model running smoothly, ensuring a dependable driving experience.
Engine and Transmission Elements
The heart of any vehicle, the engine, along with the transmission, is designed to deliver reliable power and efficiency. In this model, the engine’s structure includes a network of components working together to ensure smooth operation, such as belts, cylinders, and manifolds, while the transmission seamlessly transfers this energy to the wheels. Each of these elements requires specific maintenance to sustain long-term performance and efficiency, making knowledge of their layout beneficial for upkeep and repairs.
Suspension and Steering Systems
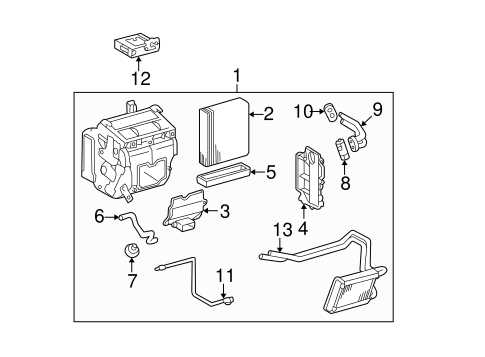
The suspension and steering systems play crucial roles in stability and handling. This vehicle’s suspension setup, with its complex arrangement of springs, struts, and shocks, is built to absorb impacts and provide a comfortable ride on various surfaces. Meanwhile, the steering components, including the rack and pinion and control arms, ensure precision in maneuvering. Proper understanding of these elements aids in maintaining the model’s characteristic responsiveness and safety.
Interior Components and Layout
The interior of this model offers a blend of comfort and functionality, designed to enhance both driver and passenger experiences. Each component is strategically placed to ensure ease of use and accessibility, contributing to a practical and inviting environment. From essential controls to storage solutions, the arrangement provides convenience and style.
Seating and Comfort Features are crafted to support various needs, offering adjustable options and ergonomic designs that prioritize comfort during short and long journeys alike. The layout ensures passengers enjoy ample legroom and a spacious feel throughout the cabin.
Dashboard and Control Panel contain essential functions organized for clear visibility and intuitive access. Key instruments are placed within easy reach, with displays and buttons that simplify monitoring and control, allowing drivers to focus on the road.
Storage Solutions and Compartments are distributed throughout the cabin, providing ample space for personal items, devices, and travel essentials. These compartments are seamlessly integrated into the design, ensuring that storage does not interfere with passenger space or comfort.
Additional Features such as climate controls, entertainment systems, and safety enhancements add to the comfort and utility of the interior, reflecting a thoughtful design that meets the needs of modern drivers and passengers.
Engine System Overview
The engine system is a complex network of components that work together to provide power and efficiency for the vehicle. This section will outline the main elements within the engine system, explaining how each component contributes to smooth performance and fuel management.
Main Components of the Engine System
- Combustion Chamber: The heart of the engine where fuel and air mix and ignite, generating the power that drives the vehicle.
- Crankshaft and Pistons: These parts convert the energy from combustion into motion, transferring power through the engine to other parts of the vehicle.
- Fuel Injection System: Responsible for delivering the correct amount of fuel into the combustion chamber, enhancing fuel efficiency and power output.
- Cooling System: This system maintains optimal engine temperature, preventing overheating and ensuring long-term durability.
Supporting Systems for Optimal Performance
Beyond the core components, various support systems help the engine maintain efficiency and reduce emissions.
- Air Intake System: Supplies the combustion chamber with fresh air, which is essential for efficient combustion.
- Exhaust System: Channels gases safely out of the vehicle, minimizing pollution and maintaining performance.
- Lubrication System: Keeps the engine’s moving parts well-lubricated, reducing friction and preventing wear.
Each part of the engine system plays a vital role, ensuring reliability, performance, and environmental sustainability.
Brake System Breakdown

The braking system is a critical component of any vehicle, designed to ensure safe and efficient stopping power. Each part within this system plays an essential role in controlling speed and providing stability during various driving conditions. By understanding the unique functions of these elements, drivers can better appreciate how the entire mechanism contributes to safe driving.
Brake Pads and Rotors: The pads and rotors work together to create the necessary friction for stopping the wheels. When the pedal is pressed, these components engage, slowing down wheel rotation and bringing the vehicle to a halt. High-quality materials and correct fitment are crucial to ensure these parts wear evenly and perform effectively.
Hydraulic Lines and Calipers: The hydraulic lines deliver fluid pressure to the calipers, which press the brake pads against the rotors. This system relies on precisely balanced pressure, and even a small leak or air bubble can disrupt the process, affecting braking performance. Regular inspection of these lines helps maintain optimal braking efficiency.
Brake Fluid Reservoir and Master Cylinder: The reservoir holds the fluid that powers the entire braking process. As the pedal is pushed, the master cylinder generates pressure, pushing fluid through the lines. Monitoring fluid levels and replacing the fluid periodically can prevent potential issues with response time and pressure balance.
Parking Brake: The parking brake is a secondary system designed to secure the vehicle when stationary. Engaging this brake bypasses the hydraulic system, relying instead on a mechanical linkage to hold the vehicle in place, especially on inclines or rough terrain.
With these interconnected parts working seamlessly together, the braking system ensures a stable and reliable driving experience. Proper maintenance and regular checks are key to preserving the safety and functionality of these essential components.
Suspension and Steering Components
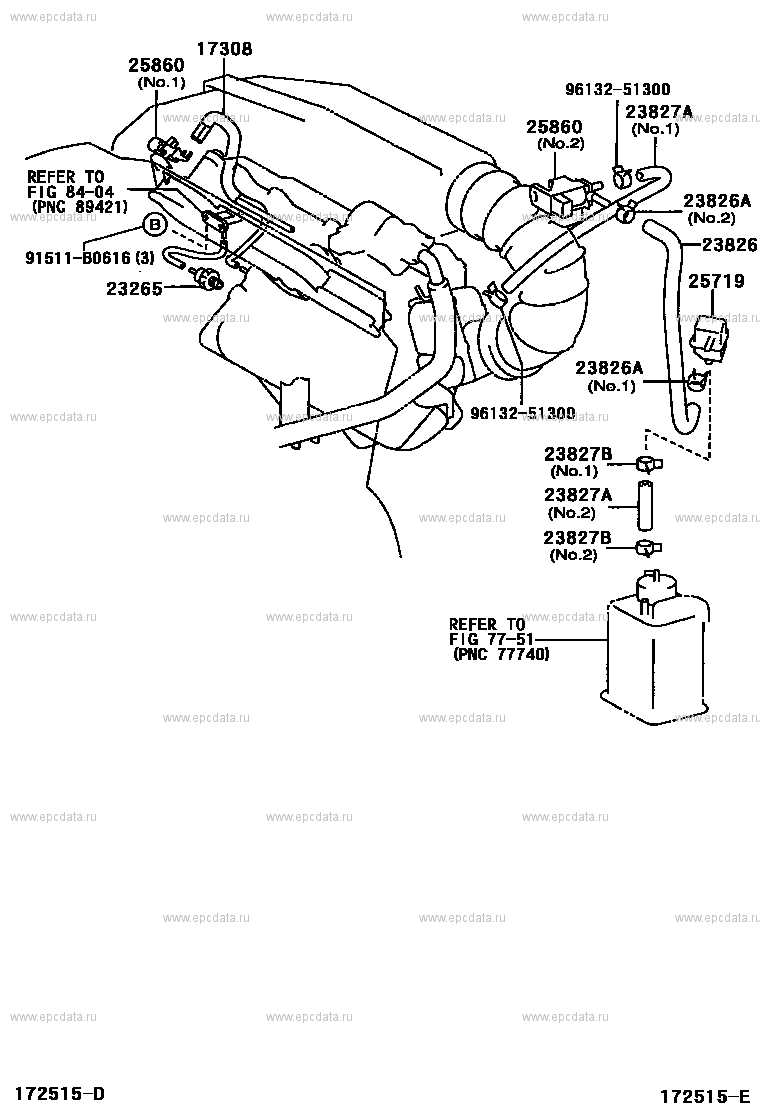
The suspension and steering system is essential for ensuring a smooth and controlled ride. It combines various elements that work together to absorb road impact, provide stability, and allow precise maneuvering. These parts are interconnected, playing a crucial role in the vehicle’s overall handling and driving comfort.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Shock Absorbers | These parts help dampen vibrations and control the movement of the springs, providing a comfortable ride on uneven surfaces. |
| Struts | Combining a shock absorber with a spring, struts support the vehicle’s weight and impact resistance, especially in the front wheels. |
| Control Arms | These connect the wheels to the frame, allowing smooth upward and downward movement, aiding in proper wheel alignment and stability. |
| Steering Rack | The steering rack transmits the driver’s input to the wheels, enabling responsive control and accurate turning. |
| Ball Joints | Located at the ends of the control arms, these joints facilitate flexibility, allowing the wheels to pivot with minimal friction. |
| Tie Rods | These connect the steering rack to the wheels, helping to maintain alignment and stability during steering movements. |
Transmission and Drivetrain Details
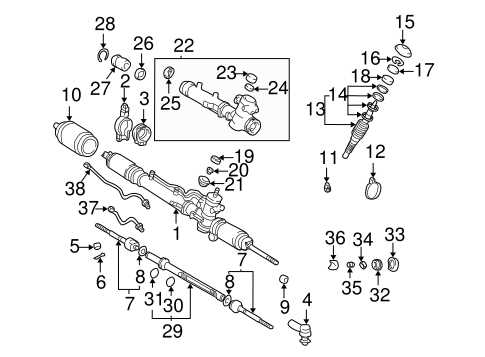
This section focuses on the components that play a crucial role in the movement and control of a vehicle. Understanding these elements is essential for maintenance and ensuring optimal performance.
The transmission is a vital mechanism that transfers power from the engine to the wheels, allowing for smooth acceleration and deceleration. It adjusts the gear ratios according to speed and driving conditions, enhancing fuel efficiency and driving experience.
The drivetrain encompasses various parts, including the driveshaft, axles, and differential. These elements work together to transmit power to the wheels, enabling the vehicle to navigate different terrains effectively. Regular inspection and servicing of these components can prevent potential issues and extend the lifespan of the vehicle.
In summary, understanding the intricacies of the transmission and drivetrain is essential for any vehicle owner. It not only aids in troubleshooting but also helps in making informed decisions regarding repairs and upgrades.
Cooling System Parts Overview
The cooling mechanism of a vehicle plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal engine temperature, preventing overheating, and ensuring efficient operation. Understanding the components involved in this system is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
Key elements of a typical cooling setup include:
- Radiator: This component dissipates heat from the coolant, facilitating temperature regulation.
- Water Pump: It circulates coolant through the engine and radiator, ensuring consistent flow and temperature control.
- Thermostat: This valve regulates the coolant flow, opening and closing based on the engine’s temperature to maintain an ideal operating range.
- Cooling Hoses: Flexible tubes that transport coolant between the engine, radiator, and other components, preventing leaks and blockages.
- Cooling Fan: An electric or mechanical fan that enhances airflow through the radiator, especially during idle or low-speed conditions.
- Coolant Reservoir: A storage tank for excess coolant, allowing for expansion and contraction as the temperature fluctuates.
Each of these components works in harmony to ensure the engine operates within its designated temperature range, thereby enhancing performance and longevity.
Electrical System Components

The electrical framework of a vehicle is crucial for its functionality and performance. This system encompasses a variety of elements that work together to ensure efficient energy distribution and control over various features. Understanding these components can enhance maintenance practices and improve overall reliability.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Battery | Stores electrical energy and provides power to start the engine and operate electrical systems. |
| Alternator | Generates electricity while the engine is running, recharging the battery and powering electrical components. |
| Fuses | Protect circuits by breaking the connection if an overload occurs, preventing damage to the electrical system. |
| Relays | Act as switches to control high-power circuits using low-power signals, allowing for efficient operation of various components. |
| Wiring Harness | A collection of wires that connect all electrical components, facilitating communication and power distribution throughout the vehicle. |
| Ignition System | Includes components like spark plugs and coils, responsible for igniting the fuel-air mixture in the engine. |
Exhaust System Layout
The exhaust system is a critical component of any vehicle, responsible for directing harmful gases away from the engine and reducing emissions. A well-designed exhaust layout ensures optimal performance, efficiency, and sound quality. Understanding its configuration is essential for maintenance and troubleshooting purposes.
Key Components
- Exhaust Manifold: Collects gases from the engine’s cylinders and directs them to the exhaust system.
- Catalytic Converter: Reduces harmful emissions by converting them into less harmful substances.
- Resonator: Helps to reduce noise and fine-tune the sound of the exhaust.
- Muffler: Diminishes sound produced by the exhaust gases before they exit the vehicle.
- Tailpipe: The final section that expels gases outside the vehicle.
Layout Considerations
- Ensure proper alignment of all components to prevent leaks.
- Regularly check for rust or damage, especially in the muffler and tailpipe sections.
- Consider upgrades or modifications for enhanced performance and sound quality.
Fuel System Diagram
The fuel system in a vehicle plays a crucial role in delivering the necessary energy to the engine. Understanding its layout helps in diagnosing issues, ensuring efficient operation, and maintaining overall performance. This section outlines the components involved and their interactions, facilitating a clearer comprehension of how the system functions.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Fuel Tank | Stores the fuel until it is needed by the engine. |
| Fuel Pump | Moves fuel from the tank to the engine under pressure. |
| Fuel Filter | Cleans the fuel of impurities before it reaches the engine. |
| Fuel Injectors | Atomize fuel and deliver it into the combustion chamber. |
| Fuel Lines | Transport fuel between the tank, pump, filter, and engine. |
Each component is essential for optimal fuel delivery and performance. Regular inspection and maintenance of these elements can prevent issues that may arise from fuel system malfunctions.
Exterior Body Parts Structure
The outer shell of a vehicle plays a crucial role in both aesthetics and functionality. This assembly not only contributes to the overall appearance but also protects internal components and occupants from external elements. A well-designed exterior enhances the vehicle’s performance, safety, and longevity.
Panel Arrangement: The configuration of panels creates a cohesive form that defines the vehicle’s silhouette. Each segment, from the hood to the fenders, works harmoniously to ensure aerodynamic efficiency and structural integrity.
Protective Features: Various components, such as bumpers and side skirts, are strategically placed to absorb impact and mitigate damage during minor collisions. These features are essential for maintaining safety standards while adding a distinctive style.
Access Points: Doors and windows serve as crucial access points, allowing entry to the cabin while ensuring security. Their design incorporates both functionality and aesthetic appeal, contributing to the vehicle’s character.
Finishing Elements: Exterior trim elements, such as moldings and decals, enhance visual interest and provide additional protection against wear. These details can be tailored to suit personal preferences, adding a unique touch to the overall design.