Case 580L Parts Breakdown and Diagram Overview
When working with large industrial equipment, the ability to comprehend the layout of various mechanical elements is essential. Proper knowledge of how different systems interact can be invaluable for anyone involved in maintenance or repair work. The intricacies of such machines require a clear understanding of the structural arrangement.
Mechanical diagrams serve as crucial tools that illustrate how different sections are assembled. Each element plays a unique role, contributing to the machine’s overall function. These visual representations not only assist in troubleshooting but also help in ensuring that repairs are done efficiently.
In this section, we will explore the significance of technical blueprints that break down the individual units within a piece of machinery. These illustrations are an essential reference, guiding both experts and those new to heavy equipment.
Case 580L Parts Diagram Overview
An effective illustration of the mechanical components is essential for understanding the inner workings of heavy-duty machinery. Such schematics help users identify key elements, their arrangement, and connections. This layout is crucial for maintenance, repairs, and general familiarity with the equipment’s structure.
Mechanical breakdowns are minimized when operators have a clear visual representation of each component. From hydraulic systems to engine assemblies, these blueprints offer a detailed view of how various parts interact within the machine. By studying these diagrams, users can efficiently address issues and perform routine upkeep.
For professionals, exploded views of individual systems provide the necessary insight into proper disassembly and reassembly processes, ensuring that every element is in its right place.
Engine Components Layout
The arrangement of engine elements plays a crucial role in ensuring the smooth operation of the entire system. Understanding how various parts are organized and interact with each other can help maintain and troubleshoot the machinery more effectively. Key components like the fuel delivery system, cooling mechanisms, and exhaust systems are carefully placed to maximize efficiency and performance.
In the typical layout, you will find the intake manifold positioned near the top, with the exhaust manifold placed on the side. Below, the crankshaft and pistons form the heart of the engine, converting energy into motion. Other critical parts include the timing belt, oil pump, and alternator, each contributing to the overall functionality of the machine.
Hydraulic System Breakdown
The hydraulic system plays a crucial role in powering and controlling various functions in heavy machinery. It operates by converting mechanical energy into fluid power, allowing smooth and precise movements. Understanding the key components of this system is essential for proper maintenance and troubleshooting.
Main Components
The core elements of the hydraulic system include the pump, which generates the flow of fluid, and the valves, which regulate the pressure and direction of that flow. The cylinders then use this pressure to perform mechanical work. These parts work in harmony to ensure efficient operation of the equipment, enabling tasks like lifting, digging, or steering.
Common Issues and Maintenance
Regular inspection of hydraulic fluid levels and system components is important to prevent issues like leaks, blockages, or pressure loss. Ensuring proper maintenance helps to avoid system malfunctions, which could affect the overall performance of the machine. Proper care extends the lifespan of the hydraulic system and ensures
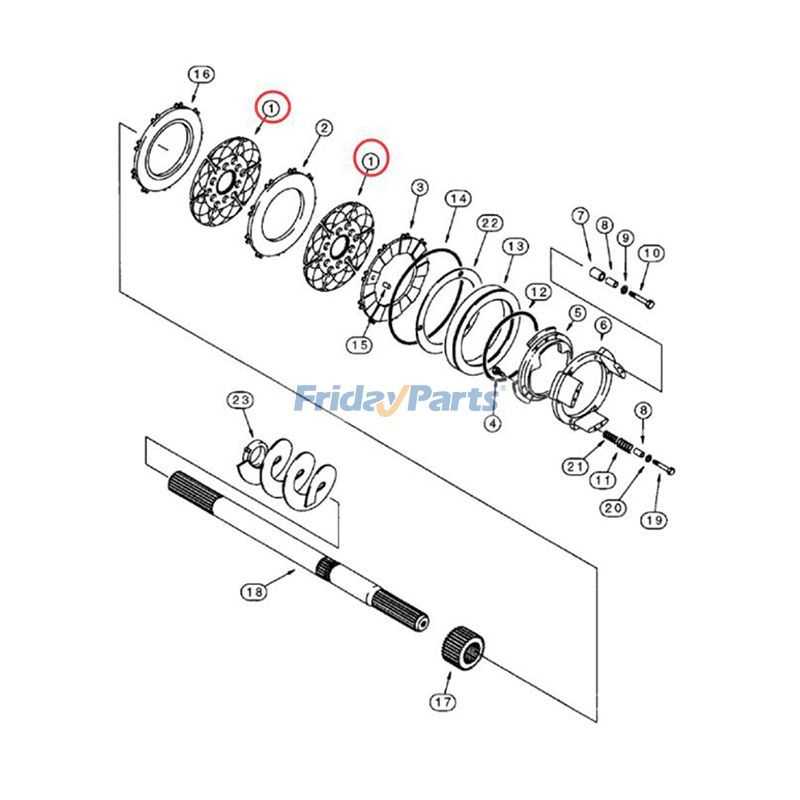
Transmission and Drive Assembly
The transmission and drive assembly is crucial for converting engine power into movement. This system ensures the machine can operate smoothly and effectively by managing power flow and torque. It plays a vital role in controlling the vehicle’s speed, maneuverability, and load-bearing capacity.
Main Components
The transmission and drive system consists of various interconnected elements, each performing specific tasks to maintain optimal performance. Below is a list of the primary parts involved in the assembly:
- Transmission gearbox for adjusting speed and power.
- Drive shafts responsible for transferring torque to the wheels.
- Differential mechanism ensuring smooth cornering by distributing torque between the wheels.
Operational Functions
The assembly’s design allows for smooth gear transitions, reducing strain on the engine. It also provides control over the machine’s acceleration and deceleration, ensuring it can adapt to different terrains and loads.
- Power is transmitted from the engine to the gearbox.
Cabin Controls and Interior Parts
The cabin of modern heavy-duty machines is equipped with a range of control systems and features designed to ensure both operator comfort and efficiency during work. These systems play a crucial role in providing easy access to vital functions while allowing the operator to remain focused and productive in various environments.
- Operator Controls: The essential levers and switches allow smooth handling of the machine, ensuring precise movements for various tasks. These controls are intuitively positioned for ease of use.
- Seating and Comfort: Adjustable seating with ergonomic design helps reduce operator fatigue, enhancing productivity during extended hours of use.
- Display Panels: Digital and analog displays provide real-time data regarding machine performance, fuel levels, and other important metrics, ensuring the operator remains informed at all times.
- Climate Control: Air conditioning and heating systems maintain a comfortable working environment inside the cabin, regardless of external weather conditions.
- Storage Compartments: Conveniently
Steering Mechanism Configuration
The steering system is a crucial component in the operation of machinery, providing the ability to control direction and maneuverability. Understanding its arrangement and functionality is essential for effective maintenance and repair. This section delves into the intricacies of the steering setup, exploring how various elements work together to achieve precise handling and responsiveness.
Key Components of the Steering System
The steering system comprises several integral parts that collaborate to facilitate smooth navigation. Major elements include the steering wheel, which acts as the primary control interface, and the steering column, which transmits the operator’s input to the mechanism. Additionally, linkages and gears convert rotational movement into directional changes, ensuring that the vehicle responds accurately to the operator’s commands.
Operational Principles
This mechanism operates on fundamental principles of mechanics, where the force applied by the operator translates through the system to affect wheel positioning. Proper adjustment and maintenance of these components are vital for optimal performance. Any misalignment or wear can lead to decreased responsiveness, highlighting the importance of regular inspections and timely replacements of worn parts.
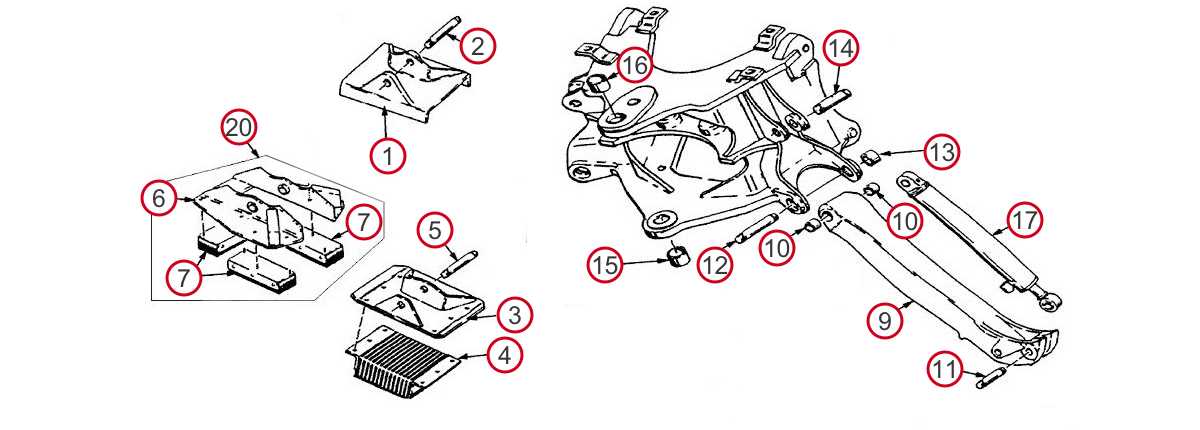
Axle and Suspension Structure
The axle and suspension system plays a crucial role in maintaining stability and handling while supporting the weight of the vehicle. This structural assembly is designed to absorb shocks and vibrations, providing a smoother ride and enhancing overall performance. Understanding its components is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
The axle is a vital element that connects the wheels and enables them to rotate. It is supported by bearings and is responsible for transferring power from the engine to the wheels. The suspension system, on the other hand, comprises various components that work together to provide support, flexibility, and control.
Component Description Axle Housing The outer casing that encases the axle, providing structural support and protection. Bearings Components that allow smooth rotation of the axle while minimizing friction. Leaf Springs Flat, elongated pieces of metal that provide support and absorb shocks from the road. Shock Absorbers Devices that dampen the impact of bumps and ensure a comfortable ride. Control Arms Links that connect the suspension system to the chassis, allowing for controlled movement. Proper inspection and maintenance of the axle and suspension components are essential for ensuring the vehicle’s safety and performance. Regular checks can prevent premature wear and enhance the lifespan of these crucial elements.
Electrical System Components
The electrical system is a crucial aspect of any heavy machinery, ensuring that all electrical functions operate smoothly and efficiently. Understanding the various elements that comprise this system is essential for maintenance and troubleshooting.
- Battery: The energy source that powers the electrical components of the machine.
- Alternator: Converts mechanical energy into electrical energy, recharging the battery while the engine is running.
- Starter Motor: Initiates the engine’s operation by turning it over.
- Wiring Harness: A network of wires that connects different electrical components, ensuring communication and power distribution.
- Fuses: Protect the electrical circuits by breaking the connection in case of overload, preventing damage to components.
- Relays: Act as switches, controlling the flow of electricity to various components based on signals from the system.
Understanding these elements helps operators and technicians diagnose issues effectively and maintain the electrical system’s reliability.
Brake Assembly Diagram
The brake assembly is a crucial component in any machinery that ensures effective stopping power and safety during operation. Understanding its structure and function can help in diagnosing issues and performing maintenance effectively. This section will explore the various elements involved in the brake assembly, highlighting their roles and interconnections.
Components of the Brake Assembly
- Brake Caliper: This part houses the brake pads and is responsible for applying pressure to the brake disc.
- Brake Pads: These friction materials come into contact with the brake disc to create the necessary friction for stopping.
- Brake Disc: Also known as the rotor, this circular metal piece is where the brake pads clamp down to slow or stop the vehicle.
- Master Cylinder: This component converts the force applied to the brake pedal into hydraulic pressure.
- Brake Lines: These tubes carry the hydraulic fluid from the master cylinder to the calipers.
Functionality of the Brake Assembly
The brake assembly operates through hydraulic pressure generated by the master cylinder when the brake pedal is pressed. This pressure travels through the brake lines, activating the calipers, which then clamp the brake pads against the brake disc. The friction generated slows down the machinery, ensuring safe operation. Regular inspection and maintenance of each component are essential for optimal performance.
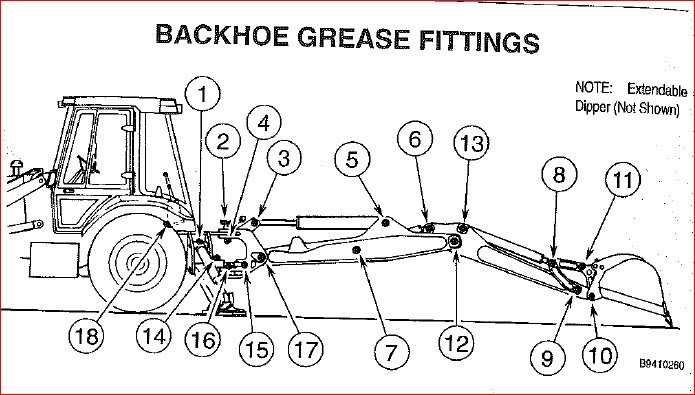
Loader and Backhoe Components
The functionality of a construction machine relies heavily on its various components, each designed to perform specific tasks that contribute to the overall efficiency of the equipment. Understanding these elements is crucial for optimal operation and maintenance.
At the forefront, the loading mechanism plays a pivotal role in lifting and transporting materials. It consists of a bucket attached to arms that allow for vertical movement. The hydraulic system is essential here, providing the necessary force to maneuver the bucket with precision. In tandem with this is the digging apparatus, which features a sturdy arm that extends backward, equipped with a digging tool. This assembly allows for effective excavation of soil and other materials.
Additionally, the powertrain is vital for the mobility of the machine. It encompasses the engine, transmission, and drive components that work together to propel the unit across various terrains. The cab houses the operator’s controls, ensuring ease of use and comfort during operation. Regular maintenance of these components ensures longevity and reliability, allowing the equipment to perform efficiently on job sites.
Cooling System Layout
The cooling system is a crucial component in maintaining optimal operating temperatures for machinery. It ensures that the engine and other vital parts function efficiently, preventing overheating and prolonging the lifespan of the equipment. Understanding the layout of this system can help in effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
Typically, the cooling system consists of several key components, each playing a significant role:
- Radiator: The primary unit for dissipating heat from the coolant.
- Water Pump: Circulates the coolant through the engine and radiator.
- Thermostat: Regulates the coolant flow based on temperature.
- Cooling Hoses: Transport coolant between components.
- Coolant Reservoir: Holds excess coolant and provides a buffer for the system.
The layout typically follows a closed-loop design, where the coolant is continuously cycled through the engine and radiator. The water pump draws the coolant from the reservoir, sending it through the engine block, where it absorbs heat. This heated coolant then flows to the radiator, where air circulation helps to lower its temperature before it returns to the reservoir.
Maintaining the integrity of each component is essential for the overall efficiency of the cooling system. Regular inspections can help identify issues such as leaks or blockages that could impede performance.
Fuel System Diagram
The fuel system is essential for the efficient operation of any machinery. It encompasses various components that work together to ensure the proper delivery and management of fuel to the engine. Understanding this system is crucial for maintaining performance and preventing potential issues.
Key elements of the fuel system include:
- Fuel tank: Stores the fuel required for the engine’s operation.
- Fuel pump: Delivers fuel from the tank to the engine at the required pressure.
- Fuel filter: Removes impurities and contaminants from the fuel before it reaches the engine.
- Fuel injectors: Spray the correct amount of fuel into the combustion chamber for optimal mixing with air.
- Fuel lines: Transport fuel between the tank, pump, filter, and injectors.
Each component plays a vital role in ensuring the engine receives a clean and sufficient supply of fuel, which is essential for efficient combustion and overall performance.