Understanding the Components of a Rowing Boat Diagram
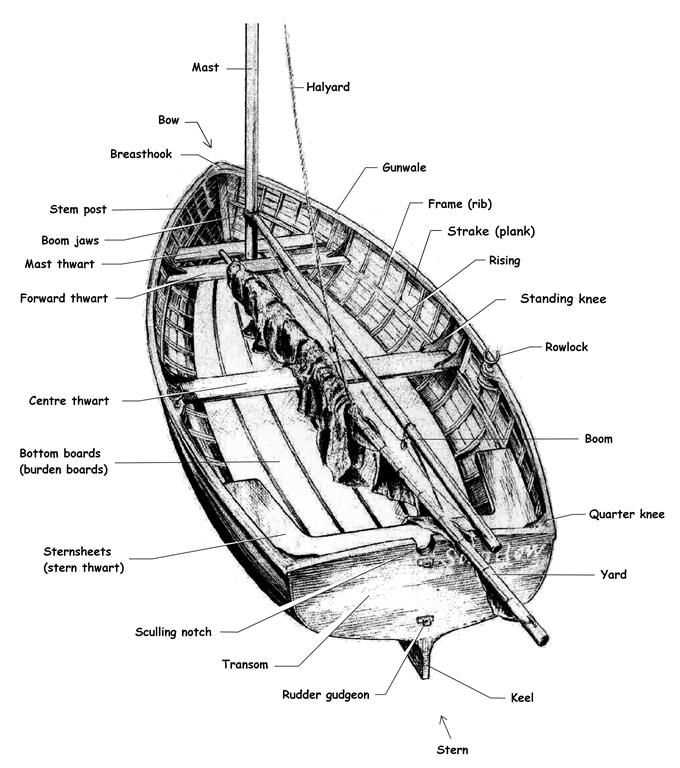
Exploring the intricacies of a vessel designed for movement across water unveils a fascinating interplay of elements that contribute to its overall functionality. Each section serves a specific purpose, working harmoniously to enhance performance and stability. This intricate design allows for efficient navigation, ensuring a seamless experience on the water.
In this exploration, we will delve into the various sections that comprise this aquatic craft, revealing their significance and interrelationships. From the structure that provides buoyancy to the mechanisms that facilitate movement, each component plays a crucial role in the vessel’s operation.
Understanding these elements not only deepens one’s appreciation of the craftsmanship involved but also highlights the ultimate goal of achieving optimal performance. Whether for leisure or competition, the synergy between these parts determines the success of any waterborne journey.
Understanding the Rowing Boat Structure
Grasping the fundamentals of a vessel’s design enhances the overall experience and performance on the water. Each component plays a crucial role in functionality, stability, and efficiency. This section delves into the essential elements that contribute to the seamless operation of these watercraft.
Key Elements of the Structure

- Hull: The body that provides buoyancy and shape, crucial for navigating through water.
- Deck: The upper surface offering protection and serving as a working area.
- Gunnels: The edges of the deck, reinforcing the structure and providing stability.
- Keel: A vital element that aids in directional control and reduces drift.
Importance of Design
The architecture of each vessel is meticulously crafted to optimize performance. Key considerations include:
- Weight Distribution: Proper balance ensures smoother navigation.
- Material Selection: The choice of materials affects durability and speed.
- Hydrodynamics: Streamlined designs enhance efficiency and reduce resistance.
Understanding these foundational aspects equips individuals with the knowledge to appreciate and utilize these vessels more effectively.
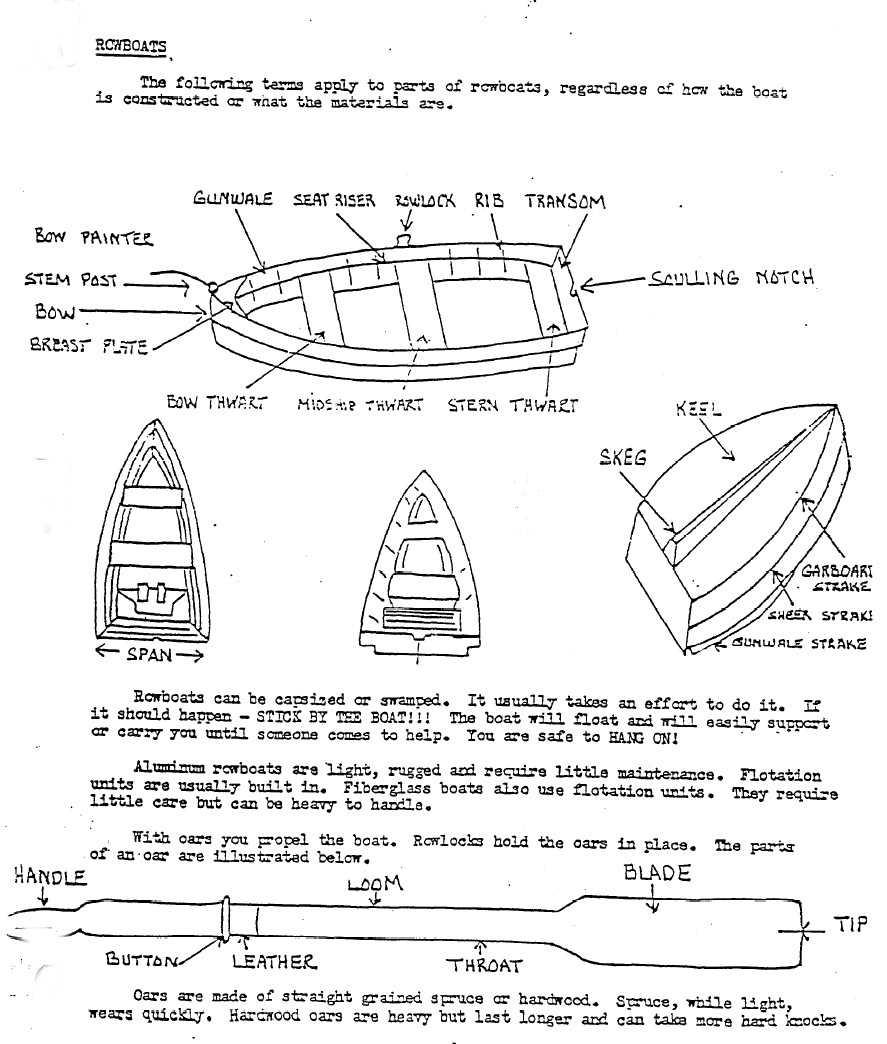
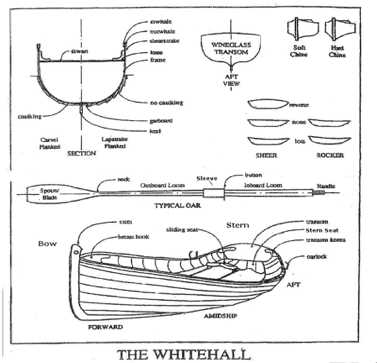
Main Components of Rowing Boats
Understanding the essential elements that make up a vessel designed for propelling through water is crucial for enthusiasts and novices alike. Each component plays a vital role in ensuring functionality, stability, and overall performance. This section explores the fundamental aspects that contribute to the effective operation of these watercraft.
Structure and Framework
The hull serves as the primary structure, providing buoyancy and stability. Its design influences how well the craft glides through water, impacting speed and maneuverability. Additionally, the deck forms the upper surface, facilitating access and offering protection from the elements. The transom at the rear supports various attachments, including propulsion systems.
Propulsion Mechanisms
The oars are fundamental tools for movement, allowing the operator to harness their strength to drive the vessel forward. Their design, including blade shape and length, affects efficiency and power. In some cases, alternative systems such as paddles may be employed, depending on the desired performance and conditions of the waterway.
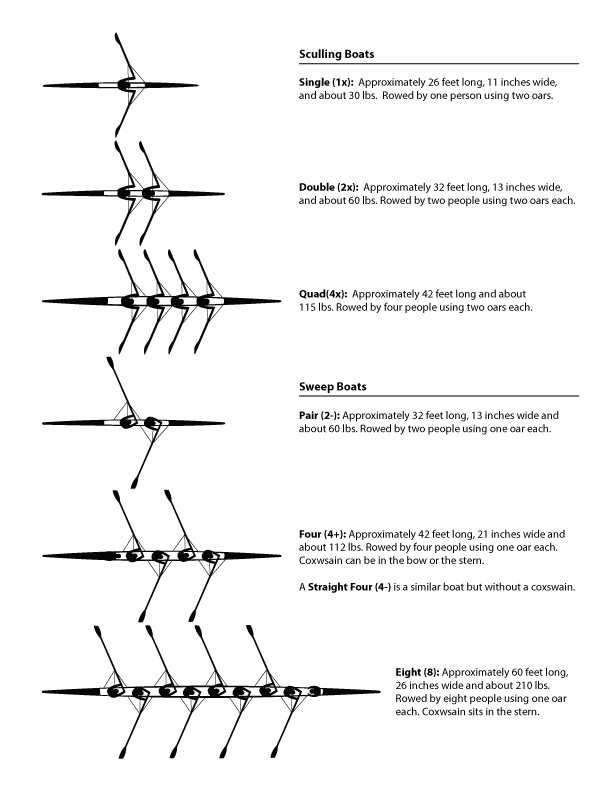
Types of Rowing Boats Explained
This section explores the diverse categories of vessels designed for oar propulsion, each tailored for specific activities and environments. Understanding these classifications enhances appreciation for their unique features and applications.
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Skiff | A lightweight, narrow craft ideal for racing and speed, often featuring a streamlined design. |
| Gigs | Longer vessels typically used for crew competitions, designed for both speed and stability. |
| Yole | A versatile option used in recreational settings, combining elements of both speed and stability. |
| Drifter | Designed for leisure activities, this craft focuses on comfort and ease of use rather than speed. |
Importance of the Hull Design
The structure beneath the waterline plays a crucial role in the overall performance and efficiency of any vessel. Its shape and construction significantly influence speed, stability, and maneuverability, determining how well the craft interacts with water. A well-thought-out design ensures that the craft can glide smoothly, reducing drag and maximizing propulsion.
Performance and Efficiency
A streamlined configuration enhances speed by minimizing resistance against the water. This optimization allows for better energy use, leading to faster travel and lower energy costs. The balance achieved through intelligent design is essential for achieving the desired velocity while maintaining control.
Stability and Safety
The underwater structure also impacts the vessel’s stability and safety in various conditions. A well-designed hull can prevent capsizing and ensure a safe experience, even in choppy waters. Proper distribution of weight and a robust framework contribute to resilience against forces encountered during navigation.
Functionality of the Oars
The implements used for propulsion play a crucial role in enhancing the movement and efficiency of the vessel on water. Their design and application contribute significantly to the overall performance and maneuverability, allowing for smooth navigation through various aquatic environments.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Propulsion | Creating thrust to move forward by pushing against the water. |
| Steering | Enabling directional control by varying the angle and position. |
| Stability | Providing balance and support during movement, especially in choppy conditions. |
| Coordination | Facilitating teamwork among users to achieve synchronized motion. |
Role of the Bow and Stern
The front and rear sections of a vessel serve crucial functions that significantly impact its overall performance and navigation. Each of these areas is designed to address specific challenges encountered on the water, contributing to both stability and efficiency during movement.
Bow: The Leading Edge
The foremost section is vital for cutting through waves, reducing resistance and ensuring a smoother experience. Its shape is engineered to enhance hydrodynamics, allowing for better speed and maneuverability. Additionally, the bow often houses equipment or features that facilitate visibility and safety, playing a key role in the vessel’s overall functionality.
Stern: The Steering Authority
In contrast, the rear section plays a pivotal role in steering and stability. This area is typically where propulsion systems are located, providing the necessary power for forward motion. Furthermore, the stern is integral to maintaining balance, allowing for smooth navigation even in challenging conditions. Its design influences how effectively the craft responds to the captain’s commands.
Features of the Cockpit Area
The cockpit area serves as the central hub where control and communication converge, playing a crucial role in the overall experience. This space is designed for efficiency and comfort, accommodating the needs of the user while ensuring optimal functionality during various activities.
One of the most significant aspects of this area is its ergonomic layout. Careful consideration is given to the placement of controls and instruments, allowing for intuitive access and operation. This design enhances responsiveness and minimizes distractions, enabling the individual to focus on performance.
Moreover, storage solutions are strategically integrated within the cockpit. These compartments keep essential gear organized and readily accessible, promoting a streamlined experience. By ensuring that everything has its place, users can maintain a clutter-free environment that fosters efficiency.
The incorporation of weather protection elements also enhances the functionality of the cockpit area. These features shield occupants from the elements, ensuring comfort and safety during varied conditions. Effective insulation and covering contribute to a more enjoyable experience, regardless of external factors.
Lastly, visibility is a key feature, with designs that prioritize an unobstructed view of the surroundings. This aspect not only aids navigation but also enriches the overall interaction with the environment, fostering a deeper connection to the experience.
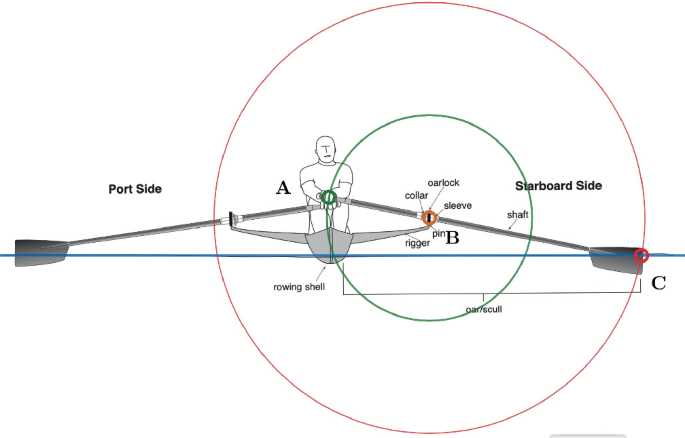
Understanding the Rigger System
The rigger system plays a crucial role in the mechanics of performance on the water. It is a carefully designed framework that influences how athletes interact with their equipment, ultimately affecting speed and efficiency. This section delves into the components and functions of this essential structure.
Key Components
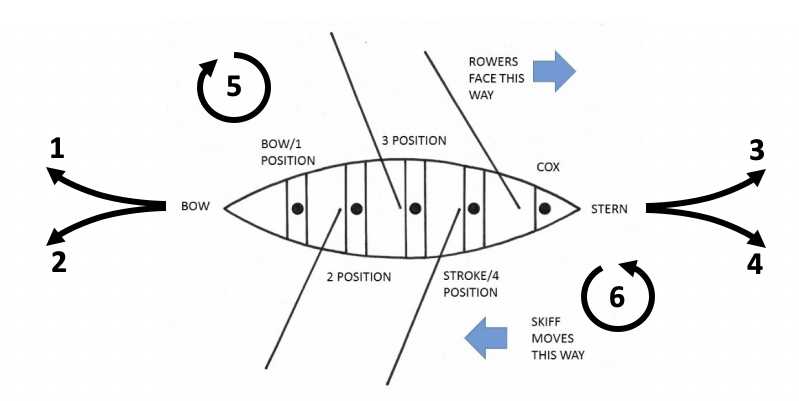
- Gunnels: The top edges that provide stability and support for the entire setup.
- Rigger Arms: These extend from the gunnels and support the oars, allowing for effective leverage during strokes.
- Mounting Points: Critical locations where the rigger arms attach, ensuring secure positioning.
- Oar Locks: These hold the oars in place while permitting rotation for smooth movement.
- Spread: The distance between the rigger arms, which can be adjusted for different techniques and preferences.
Functionality and Impact
The design and arrangement of the rigger system significantly impact the overall performance. Here are some considerations:
- Balance: Proper setup aids in maintaining equilibrium on the water.
- Power Transfer: An efficient rigger system ensures that the energy exerted by the athlete is effectively transferred to the water.
- Adjustability: Many systems allow for customization based on individual style and comfort.
- Weight Distribution: Strategic placement contributes to overall speed and handling.
Understanding the intricacies of the rigger system enables athletes to optimize their performance and enhances their overall experience on the water.
Materials Used in Construction
The choice of materials plays a crucial role in the overall performance and durability of watercraft. Various substances are utilized to balance strength, weight, and resistance to the elements, ultimately enhancing efficiency and lifespan.
Traditionally, wood has been favored for its natural beauty and workability, providing a classic aesthetic while requiring careful maintenance. However, advancements in technology have led to the adoption of fiberglass and aluminum, which offer superior durability and lower maintenance requirements.
In recent years, composite materials have gained popularity, combining the benefits of different substances to achieve optimal performance characteristics. These innovative options are lightweight yet robust, making them ideal for modern designs.
Environmental considerations also influence material selection, with a growing emphasis on sustainable practices. The use of eco-friendly resources not only meets regulatory standards but also appeals to the environmentally conscious consumer.
Impact of Weight Distribution

The way weight is arranged within a vessel plays a crucial role in its overall performance and stability. Proper distribution not only affects the balance but also influences speed, maneuverability, and the efficiency of the craft. Understanding these dynamics is essential for optimizing the experience on the water.
Effects on Stability
An even distribution of weight helps maintain a level position, reducing the risk of capsizing. When weight is concentrated in one area, it can lead to tilting, making the craft more vulnerable to external forces such as waves or wind. Achieving a harmonious balance allows for smoother navigation and greater control.
Influence on Speed
The placement of weight can also significantly impact velocity. A well-distributed load minimizes drag and enhances hydrodynamics, enabling the vessel to glide more efficiently through water. Conversely, improper arrangement can create additional resistance, slowing progress and exhausting the crew.
| Weight Position | Stability Effect | Speed Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Evenly Distributed | High Stability | Optimal Speed |
| Forward Heavy | Increased Tilting | Reduced Speed |
| Aft Heavy | Instability | Decreased Efficiency |
| Uneven Sides | Potential Capsizing | Increased Drag |
Maintenance Tips for Rowing Boats
Ensuring longevity and optimal performance of your watercraft requires regular upkeep and attention. By adopting a consistent maintenance routine, you can prevent issues and enhance your experience on the water. This section outlines key practices to keep your vessel in excellent condition.
Regular Inspections
Conducting frequent assessments is crucial. Look for signs of wear, such as cracks or deterioration, especially in the hull and structure. Check fittings and connections to ensure everything is secure. Early detection of potential problems can save time and money in repairs.
Cleansing and Storage
After each outing, rinse your craft to remove salt, sand, and debris. Use a gentle cleaner for tougher stains. Proper storage is equally important; keep it in a dry, shaded area to prevent mold and mildew. Covering it with a breathable tarp can protect against dust and UV damage.
By following these guidelines, you can maintain your watercraft in top shape, ensuring enjoyable outings for years to come.