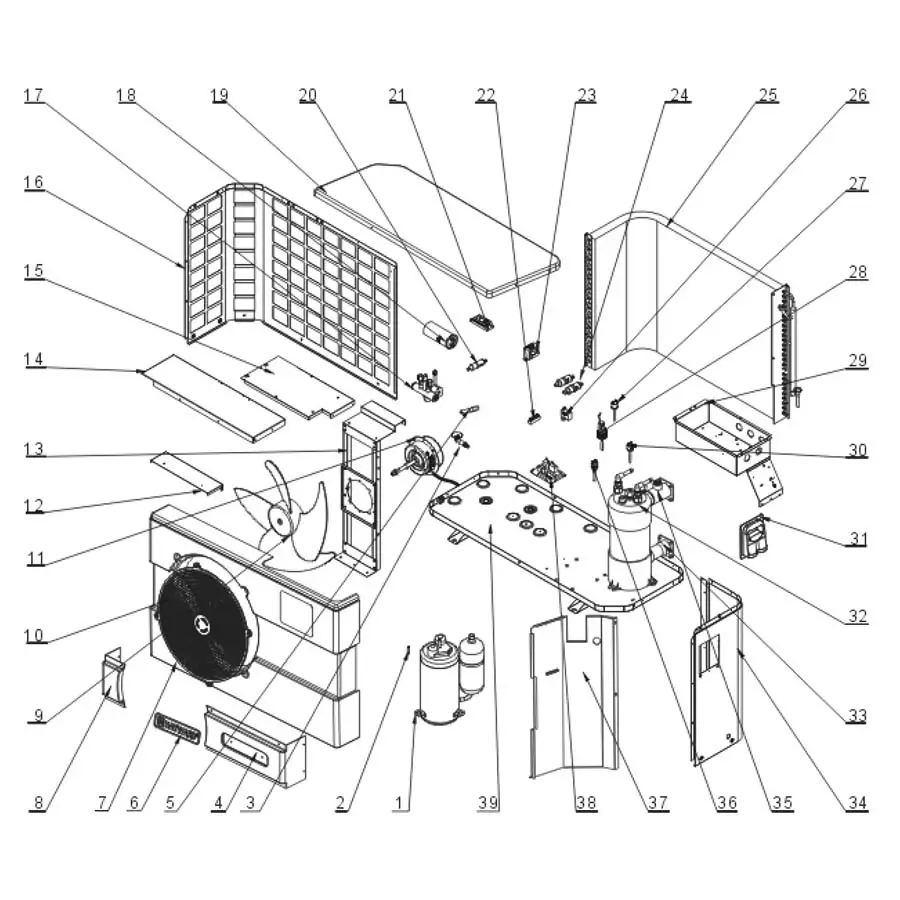
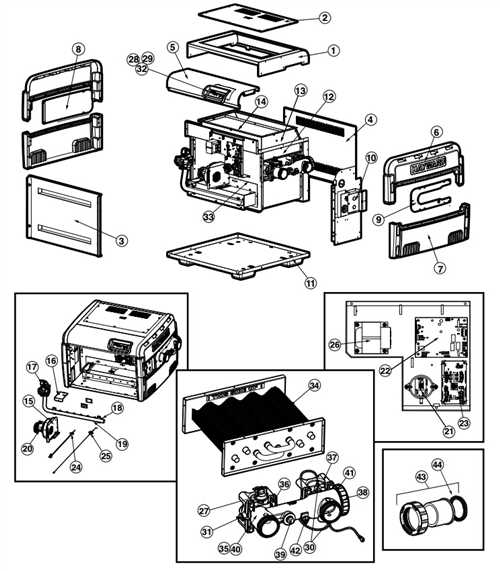
Aquacal Heat Pump Parts Diagram Explained
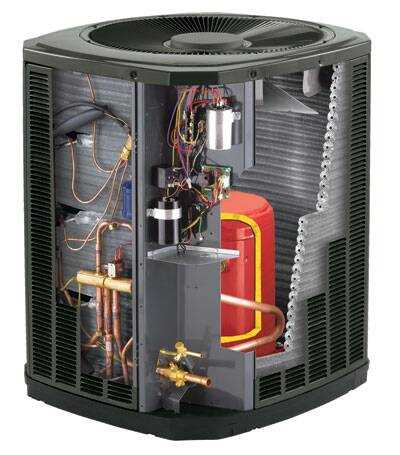

In the realm of thermal management solutions, comprehending the configuration of essential components is crucial for optimizing performance and efficiency. By exploring the intricate relationships between various elements, users can ensure smoother operation and longevity of their systems.
Visual representations serve as invaluable tools in this context, allowing for a clearer understanding of how each component interacts within the overall assembly. These illustrations facilitate a deeper appreciation of functionality and maintenance requirements.
Moreover, an effective grasp of these layouts can empower users to troubleshoot issues more efficiently. By delving into the specifics of each section, one can achieve the ultimate mastery over system operations and enhance overall effectiveness.
Aquacal Heat Pump Overview
This section provides a comprehensive examination of a vital component in climate control systems, focusing on its functionality, efficiency, and design. Understanding the underlying mechanisms and structure can enhance user awareness and maintenance strategies.
Key Features
The system boasts several attributes that contribute to its performance. Key elements include energy efficiency, user-friendly operation, and durable construction. These features ensure optimal functionality and longevity.
Component Breakdown

| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Compressor | Circulates refrigerant to facilitate heat exchange. |
| Evaporator | Absorbs heat from the surrounding environment. |
| Condenser | Releases absorbed heat to the designated area. |
| Expansion Valve | Regulates refrigerant flow and pressure. |
Key Components of Heat Pumps
The efficient functioning of thermal transfer systems relies on several crucial elements. Each component plays a specific role in ensuring optimal performance, energy efficiency, and reliability. Understanding these elements is essential for anyone interested in the mechanics of climate control technology.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Compressor | Increases the pressure of the refrigerant, enabling it to circulate through the system. |
| Condenser | Facilitates the release of heat from the refrigerant to the surrounding environment. |
| Evaporator | Absorbs heat from the surroundings, causing the refrigerant to evaporate. |
| Expansion Valve | Regulates the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator, reducing its pressure. |
| Refrigerant | Circulates through the system, transferring heat between components. |
Understanding these fundamental elements helps in grasping how thermal management systems operate and their importance in maintaining comfortable indoor environments.
Functionality of Aquacal Systems
The innovative systems designed for temperature regulation offer a range of functionalities that enhance comfort and efficiency in various environments. These mechanisms are engineered to transfer thermal energy, ensuring optimal climate control throughout the year. By harnessing the principles of thermodynamics, they create a seamless experience for users, balancing performance and energy conservation.
One of the core features of these systems is their ability to absorb ambient heat from the environment, even in cooler conditions. This characteristic enables them to provide warmth during colder months while also maintaining a refreshing coolness in warmer seasons. The versatility of operation ensures year-round usability, making them a valuable investment for both residential and commercial applications.
Additionally, advanced control systems allow users to customize settings according to their preferences, optimizing both comfort and energy usage. The integration of smart technology further enhances user experience, enabling remote access and real-time monitoring. This level of control ensures that users can achieve their desired climate effortlessly while minimizing operational costs.
Overall, the effectiveness of these systems lies in their robust design and functionality, offering reliable performance that meets the diverse needs of users. Their commitment to sustainability and efficiency makes them a preferred choice for those looking to enhance their indoor environment while being mindful of energy consumption.
Common Issues with Heat Pumps
When it comes to maintaining a comfortable environment in your home, certain challenges may arise with your system. Understanding these common complications can help you troubleshoot effectively and ensure optimal performance.
Here are some frequent problems encountered:
- Inefficiency: Systems may struggle to maintain desired temperatures, often due to inadequate insulation or age.
- Strange Noises: Unusual sounds can indicate mechanical issues, such as loose components or foreign objects obstructing operation.
- Frost Build-up: Excessive ice formation can hinder functionality, typically caused by low refrigerant levels or airflow restrictions.
- Frequent Cycling: Systems turning on and off too often can lead to wear and increased energy consumption, often linked to thermostat malfunctions or improper sizing.
- Leaking Fluid: Any signs of leakage require immediate attention, as they may indicate serious internal issues.
Addressing these concerns promptly can prolong the lifespan of your equipment and maintain a consistent climate within your living space. Regular maintenance and professional check-ups are advisable to avoid more significant problems in the future.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity

Ensuring the long-lasting functionality of your system requires regular attention and care. Implementing a few simple practices can significantly enhance efficiency and prevent premature wear and tear. This section provides essential guidance for maintaining optimal performance over time.
Regular Cleaning
Debris accumulation can hinder efficiency. Regularly inspect and clean the exterior components to ensure proper airflow. This includes removing leaves, dirt, and any obstructions that may block vents. Consider scheduling seasonal cleanings to maintain peak performance.
Routine Inspections
Performing routine checks is crucial for identifying potential issues early. Look for signs of wear, unusual noises, or leaks. Addressing minor concerns promptly can prevent more significant problems and costly repairs. Additionally, consulting a professional for annual servicing can enhance reliability and longevity.
Understanding Refrigerant Flow Process
The refrigerant flow process is crucial for the efficient operation of various cooling systems. This process involves the circulation of a fluid that absorbs and releases thermal energy, allowing for temperature regulation in different environments. A deeper understanding of this cycle can enhance the performance and longevity of the systems involved.
In general, the flow of refrigerant occurs in several key stages:
- Evaporation: The refrigerant absorbs heat from the surrounding environment, causing it to change from a liquid to a gas.
- Compression: The gaseous refrigerant is compressed, raising its temperature and pressure.
- Condensation: The high-pressure gas releases heat as it cools and transitions back into a liquid state.
- Expansion: The liquid refrigerant passes through an expansion valve, reducing its pressure and temperature before re-entering the evaporator.
This cycle repeats continuously, ensuring consistent temperature control. Understanding each stage allows for better troubleshooting and maintenance, ultimately leading to improved system efficiency.
Energy Efficiency Ratings Explained
Understanding energy efficiency ratings is crucial for making informed decisions about appliances and systems that utilize energy. These ratings provide insight into how effectively a device converts energy into useful output, allowing consumers to compare options based on their performance and impact on utility costs.
One of the primary metrics used to gauge efficiency is the Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER), which measures cooling output during a typical cooling season divided by the total electric energy input. A higher SEER value indicates better efficiency, leading to lower energy bills and a reduced environmental footprint.
Another important rating is the Energy Efficiency Ratio (EER), which is similar but evaluates efficiency under specific operating conditions. This measurement can be particularly useful for assessing performance in varying climates, as it reflects real-time energy usage rather than seasonal averages.
Additionally, the Coefficient of Performance (COP) is used to express the efficiency of systems that provide heating, showcasing the ratio of useful heating provided to the energy consumed. Like the SEER and EER, a higher COP signifies better efficiency and cost savings over time.
When selecting an energy-consuming device, considering these ratings can help consumers make choices that not only align with their financial goals but also contribute to sustainability efforts by reducing overall energy consumption.
Installation Requirements and Considerations
When setting up a system for temperature regulation, various factors must be addressed to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Proper planning and execution of installation can significantly influence efficiency and user satisfaction.
Site Preparation
- Select a level surface to avoid operational issues.
- Ensure adequate space for maintenance and air circulation.
- Verify local climate conditions that may affect functionality.
Electrical and Plumbing Considerations
- Consult a licensed electrician for power requirements.
- Check compatibility with existing plumbing systems.
- Install dedicated circuits to prevent overloads.
Comparing Aquacal Models
This section aims to explore the various versions of a specific brand known for its efficient climate control systems. By examining their distinctive features, performance metrics, and user feedback, we can uncover which model aligns best with specific needs and preferences.
Performance and Efficiency

Different models exhibit varying levels of energy efficiency and output capacity. Understanding these metrics is crucial for selecting the optimal unit that not only meets the desired temperature but also minimizes energy consumption. Efficiency ratings can often guide consumers toward a more sustainable choice.
User Experience and Features
Feedback from users often highlights the practicality and ease of use of each model. Additional features such as smart controls, noise levels, and maintenance requirements can significantly influence satisfaction. By comparing these aspects, potential buyers can make an informed decision that enhances their overall experience.
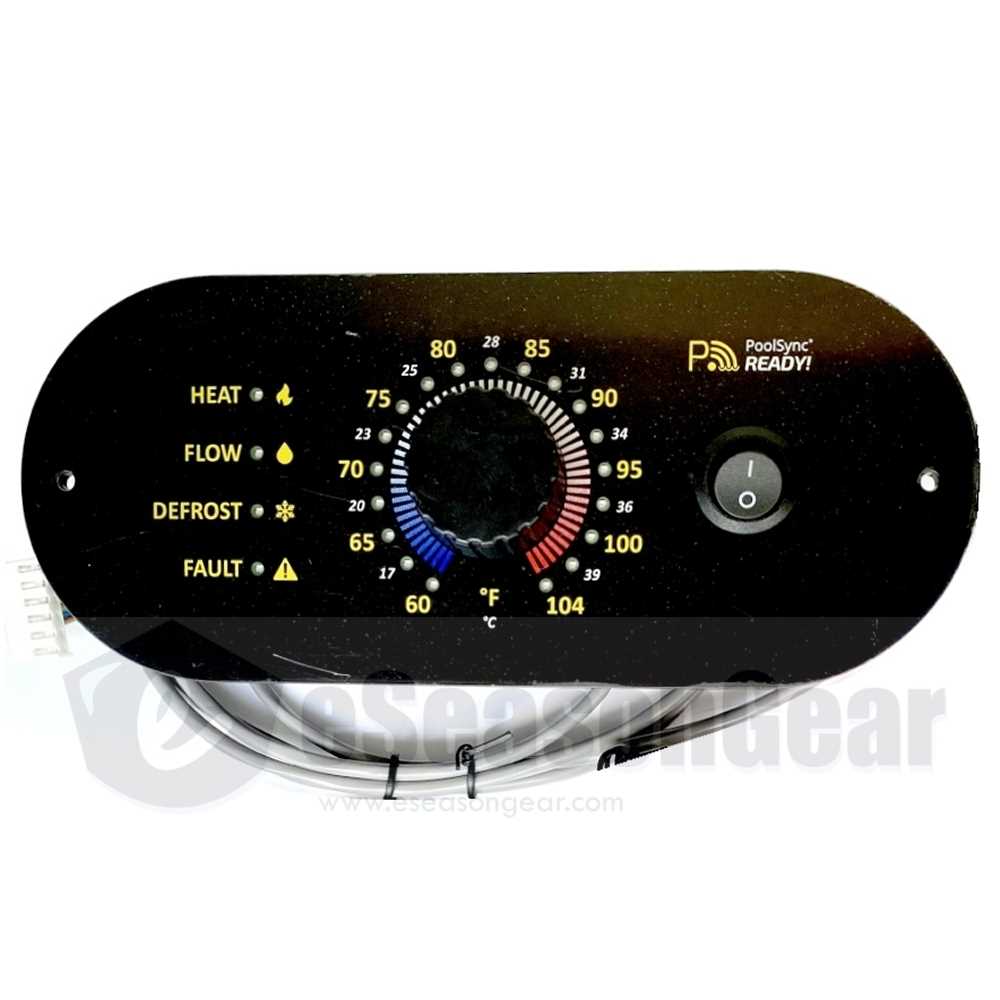
Understanding the Control Panel
The control interface serves as the central hub for managing your system’s performance. It provides essential functions and displays critical information to optimize operation efficiently.
- Display Screen: Shows temperature settings and system status.
- Buttons: Allows users to adjust settings easily.
- Indicators: Visual signals that convey operational modes or alerts.
Familiarizing yourself with these components can significantly enhance user experience and ensure smooth functioning.
- Access settings for temperature adjustments.
- Monitor system alerts for maintenance needs.
- Utilize the interface for efficient operation.
Choosing the Right Heat Pump Size

Selecting the appropriate size for your climate control unit is crucial for ensuring optimal efficiency and comfort in your space. An incorrectly sized system can lead to excessive energy consumption and inadequate temperature regulation, ultimately affecting both your utility bills and indoor environment.
Understanding Load Calculations
To determine the right dimensions for your system, it’s essential to perform load calculations. These calculations take into account various factors such as the size of your area, insulation levels, and local climate conditions, helping you to find the balance between performance and energy efficiency.
Consulting Professionals
Engaging with experienced technicians can provide valuable insights into selecting the ideal unit size for your needs. Their expertise can guide you through the decision-making process, ensuring that your investment aligns with your specific requirements and expectations.
Cost Analysis of Aquacal Units
Understanding the financial implications of these systems is crucial for potential buyers. A thorough evaluation includes not only the initial investment but also the ongoing operational expenses, maintenance costs, and potential savings over time. This section will explore various factors influencing the total cost of ownership.
Initial Investment and Installation
The upfront cost encompasses the unit’s price, installation fees, and any necessary modifications to existing infrastructure. It is essential to consider the quality and efficiency of the model chosen, as these elements can significantly affect long-term savings.
Operational Costs and Efficiency
Ongoing expenses such as energy consumption, maintenance, and repair should be factored into the overall budget. Efficiency ratings play a vital role in determining these costs, with more efficient models typically resulting in lower energy bills. Assessing these elements carefully can lead to more informed financial decisions.