Understanding the Components of a Monitor

In today’s digital age, the devices we use for visual output play a crucial role in our daily lives. From personal computers to large-scale presentations, the effectiveness of these units relies on a harmonious integration of various elements. Each segment of these systems is designed to enhance functionality, providing users with an immersive and efficient experience.
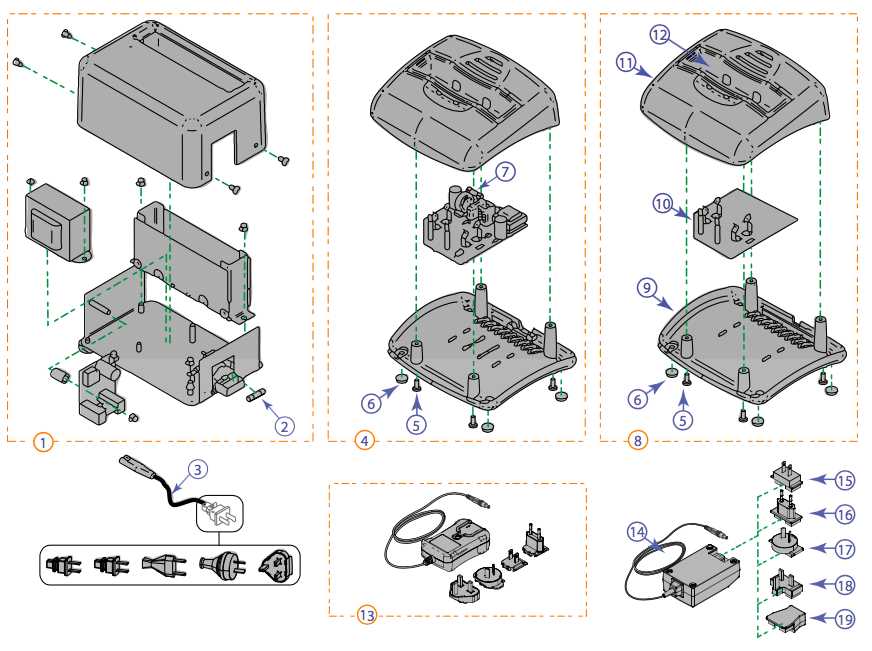
Grasping the intricate layout of these visual units can offer insights into their performance and maintenance. By exploring the arrangement and interaction of essential components, one can appreciate the technology that powers everything from basic display functions to advanced features. This knowledge not only aids in troubleshooting but also fosters a deeper understanding of the underlying mechanisms that drive visual media.
As we delve into the specifics, it becomes apparent that recognizing the distinct roles of each segment can empower users to make informed decisions regarding upgrades, repairs, or enhancements. The interplay of these elements is vital for achieving optimal performance, making this exploration both practical and enlightening.
Understanding the essential elements that constitute a display unit is crucial for comprehending its functionality and performance. Each component plays a specific role, contributing to the overall operation and user experience. By exploring these fundamental elements, one can appreciate how they interact to produce high-quality visuals.
Key Elements
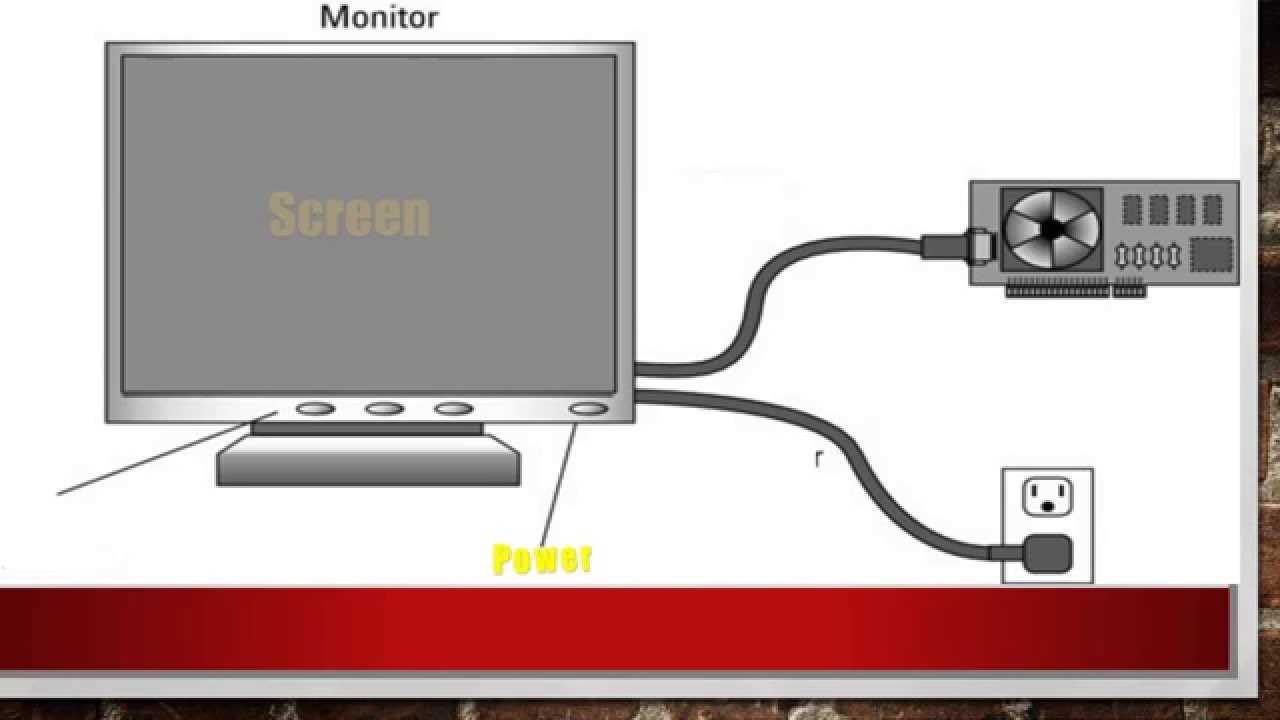
The following table highlights the primary components found in a display unit, along with their respective functions:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Display Panel | Responsible for producing the images and graphics displayed to the user. |
| Backlight | Illuminates the display panel, enhancing visibility and color reproduction. |
| Control Board | Processes input signals and manages the overall operation of the unit. |
| Power Supply | Converts electrical energy to power the various components of the unit. |
| Connector Ports | Facilitate the connection to external devices for input and output of data. |
Importance of Each Component
Each element of the display unit is essential for delivering optimal performance. The display panel determines the quality of images, while the backlight influences brightness and color accuracy. The control board ensures that signals are processed correctly, and the power supply maintains the necessary energy flow. Finally, connector ports allow seamless integration with other devices, enhancing versatility and usability.
Role of the Display Panel
The display panel serves as the essential interface between digital content and users, converting electronic signals into visual representations. Its quality and functionality significantly influence the overall experience, as it directly impacts clarity, color accuracy, and responsiveness.
Functionality is paramount in this context. The display panel is designed to render images and videos, allowing users to interact with software applications, watch media, or conduct various tasks. High-resolution panels provide sharper images, making fine details more visible, while refresh rates affect the smoothness of motion during video playback or gaming.
In addition to functionality, the construction of the display plays a crucial role in determining its performance. Different technologies, such as LCD, LED, and OLED, each have unique characteristics that affect brightness, contrast, and viewing angles. For example, OLED displays are known for their deep blacks and vibrant colors, while LCDs may offer better longevity and cost-effectiveness.
Furthermore, an ergonomic design of the display can enhance user comfort. Features such as adjustable stands, anti-glare coatings, and blue light filters contribute to prolonged usage without discomfort, supporting healthier viewing habits.
Ultimately, the display panel is not just a component but a vital element that shapes how users perceive and interact with digital information. Its impact on usability, visual fidelity, and overall satisfaction cannot be overstated.
Importance of the Backlight System
The backlighting mechanism plays a crucial role in the overall functionality of display devices. It ensures that the images and content rendered are visible under various lighting conditions. Without an effective illumination source, even the most advanced screens would struggle to deliver clear and vibrant visuals.
One of the primary functions of the backlighting system is to enhance contrast and brightness, allowing users to enjoy a more immersive viewing experience. This is particularly important in environments with varying ambient light levels, where inadequate lighting can lead to poor visibility and eye strain.
Furthermore, advancements in backlight technology have significantly improved energy efficiency and color accuracy. Modern systems utilize LEDs that not only consume less power but also provide a wider color gamut, enriching the overall visual quality. As such, a well-designed illumination setup is essential for achieving optimal performance and user satisfaction.
Functionality of the Circuit Board
The circuit board plays a pivotal role in ensuring the smooth operation of electronic displays. It serves as the backbone, facilitating communication between various components and orchestrating their interactions. By providing the necessary pathways for electrical signals, this essential element enables the execution of complex functions and enhances the overall performance of the device.
Central to its operation is the integration of various components, including capacitors, resistors, and integrated circuits. Each element contributes to the regulation and distribution of power, ensuring that all parts function harmoniously. For instance, capacitors store and release energy, while resistors manage the flow of current, preventing overload and damage.
Moreover, the circuit board also houses control interfaces that allow users to interact with the display. This interaction is facilitated through a series of connections and inputs, which relay user commands to the internal systems. In this manner, the circuit board not only supports functionality but also enhances user experience by enabling responsive control over the device’s features.
Analyzing the Power Supply Unit
The power supply unit is a crucial component responsible for delivering the necessary electrical energy to the various elements of a display system. Understanding its function and structure is essential for effective troubleshooting and maintenance. This section delves into the fundamental aspects of the power supply, highlighting its significance in ensuring optimal performance.
Key Functions of the Power Supply
At its core, the power supply unit converts alternating current (AC) from a wall outlet into direct current (DC) that is suitable for internal components. This conversion process not only provides the required voltage levels but also regulates and stabilizes the output to protect sensitive components from damage. Additionally, the power supply unit plays a vital role in managing power distribution, ensuring that each section receives adequate energy for operation.
Common Issues and Solutions
One of the most frequent challenges encountered with the power supply unit is failure due to overheating or electrical surges. Signs of malfunction may include flickering screens or complete failure to power on. Troubleshooting these issues typically involves inspecting the unit for damaged capacitors or burnt circuits. Regular maintenance can help prevent these problems, ensuring longevity and reliable performance.
Cooling Mechanisms in Monitors
Effective thermal management is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and longevity of electronic displays. As these devices generate heat during operation, implementing reliable cooling solutions becomes essential to prevent overheating, which can lead to reduced efficiency and potential damage. Various techniques are employed to dissipate heat and ensure stable operation.
Types of Cooling Techniques
Different cooling strategies are utilized based on the design and requirements of the device. The following table outlines the primary methods used in electronic displays:
| Cooling Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Passive Cooling | Utilizes heat sinks and natural airflow to dissipate heat without the use of additional power. |
| Active Cooling | Involves fans or liquid cooling systems that actively remove heat, improving efficiency under high workloads. |
| Heat Pipes | Employs phase change to transfer heat away from critical components, effectively managing temperatures. |
| Thermal Interface Materials | Enhances thermal conductivity between components and heat sinks, facilitating better heat transfer. |
Importance of Cooling Systems
Implementing efficient cooling systems not only prolongs the lifespan of electronic displays but also enhances their overall performance. Proper thermal management minimizes the risk of thermal throttling, ensuring that devices operate at their full potential. As technology continues to advance, the development of more sophisticated cooling methods remains a vital aspect of electronic design.
Connecting Cables and Ports Explained
Understanding how to connect various cables and ports is essential for establishing a seamless link between devices. Proper connections ensure optimal performance and enhance the user experience by enabling effective communication between components.
When dealing with different devices, it is crucial to recognize the types of cables and ports available. Here are some common types:
- HDMI: Widely used for high-definition video and audio transfer.
- DisplayPort: Known for its ability to support high resolutions and refresh rates.
- VGA: An older standard primarily used for video output.
- DVI: Often found in older models, providing digital and analog connections.
- USB-C: A versatile connector for data transfer, video output, and power delivery.
Choosing the correct cable and port is vital for compatibility and functionality. Here’s a brief guide on how to connect them:
- Identify the output port on the source device.
- Choose the appropriate cable that fits both the output and input ports.
- Connect one end of the cable to the source device and the other end to the receiving device.
- Ensure both devices are powered on and configured to recognize the connection.
By understanding these connections, users can troubleshoot common issues, ensuring a smooth and efficient setup.
Common Monitor Displays Explained
In today’s digital age, various visual output technologies enhance user experience across a range of applications. Understanding these technologies can help individuals make informed choices when selecting display devices, whether for professional work, gaming, or entertainment.
Types of Display Technologies
- Liquid Crystal Display (LCD)
This technology utilizes liquid crystals to create images, known for its energy efficiency and slim profile. LCDs are commonly found in laptops and flat-screen televisions.
- Light Emitting Diode (LED)
LEDs are essentially advanced LCDs that use light-emitting diodes for backlighting. They offer brighter displays and improved color accuracy.
- Organic Light Emitting Diode (OLED)
Utilizing organic compounds, OLEDs provide exceptional color contrast and viewing angles. They are increasingly popular in high-end televisions and smartphones.
- Plasma Displays
These utilize small cells filled with gas that emit light when electrified. Known for their vibrant colors and deep blacks, they were popular before the rise of LED technology.
Key Features to Consider
- Resolution
The clarity of images on a screen is determined by its resolution, with higher numbers providing more detail.
- Refresh Rate
This refers to how often the image is updated per second. A higher refresh rate results in smoother visuals, especially important for gaming.
- Response Time
Measured in milliseconds, this indicates how quickly pixels can change colors, affecting motion blur during fast-paced scenes.
- Viewing Angles
This feature describes how well the display maintains image quality from different angles, crucial for collaborative work or shared viewing.
Troubleshooting Monitor Component Issues
When dealing with display technology, various components can sometimes encounter difficulties that affect performance. Identifying and resolving these issues requires a systematic approach to ensure proper functionality. Understanding common problems can help in diagnosing and effectively fixing the underlying causes.
Identifying Common Problems
One of the first steps in resolving issues is recognizing the symptoms. Common signs include flickering screens, color discrepancies, and failure to power on. These symptoms may stem from several factors, including faulty connections, malfunctioning circuitry, or even software conflicts. Checking cables for wear and tear or improper connections can often resolve simple problems quickly.
Effective Troubleshooting Steps
Once the initial signs are noted, a detailed examination is essential. Start by ensuring that all connections are secure. Next, inspect the internal circuitry for any visible damage or loose components. If the problem persists, consider resetting any software settings to their defaults, as this can eliminate potential conflicts. For more severe issues, consulting a professional may be necessary to address intricate hardware malfunctions. Patience and methodical analysis are key to successful resolution.
Future Trends in Monitor Technology
The evolution of display technologies is poised to bring about transformative changes in how users interact with visual media. As advancements continue, several key areas will shape the next generation of screens, enhancing functionality and user experience.
1. Enhanced Resolution and Clarity: The push towards higher resolutions, such as 8K and beyond, will enable unprecedented levels of detail and clarity. This shift will cater to professionals in fields like graphic design and video production, where precision is crucial.
2. Flexible and Foldable Displays: Innovations in materials are leading to the development of flexible and foldable screens, allowing for unique form factors and portable designs. These adaptable displays will redefine how users consume content on the go.
3. Improved Color Accuracy: With the growing demand for realistic visuals, advancements in color reproduction will ensure that screens deliver a wider color gamut and more accurate shades. This will be particularly significant for creative professionals and enthusiasts alike.
4. Sustainable Technologies: The focus on sustainability will drive the development of energy-efficient displays and eco-friendly manufacturing processes. This shift will not only reduce the environmental impact but also lower operating costs for users.
5. Integration of AI and Smart Features: Future displays will increasingly incorporate artificial intelligence, enabling smart functionalities such as automatic brightness adjustments and adaptive refresh rates based on content type. This technology will enhance usability and energy efficiency.
6. Immersive Experiences: The rise of augmented and virtual reality will push the boundaries of traditional display technology, offering immersive experiences that blend the digital and physical worlds. This will transform gaming, education, and training applications.
These trends indicate a significant shift towards more interactive, versatile, and environmentally conscious visual solutions, promising a dynamic future for visual technology.