Understanding Chainsaw Part Diagrams for Effective Maintenance
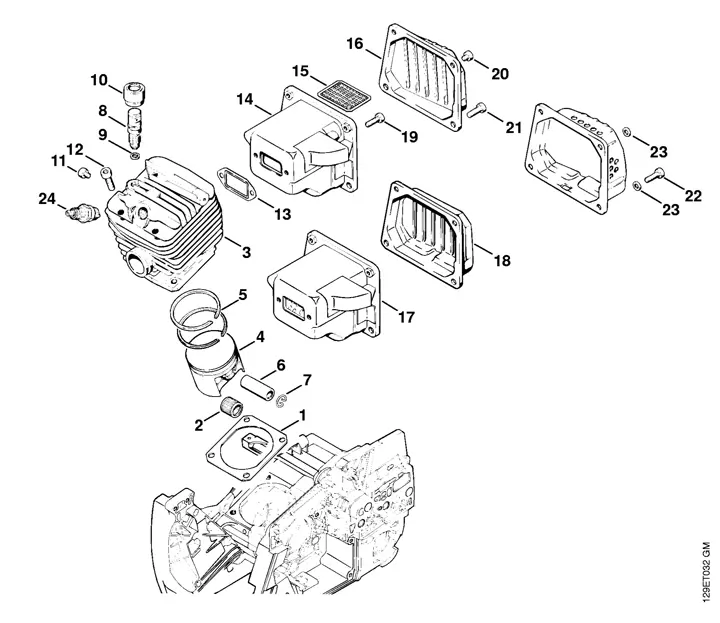
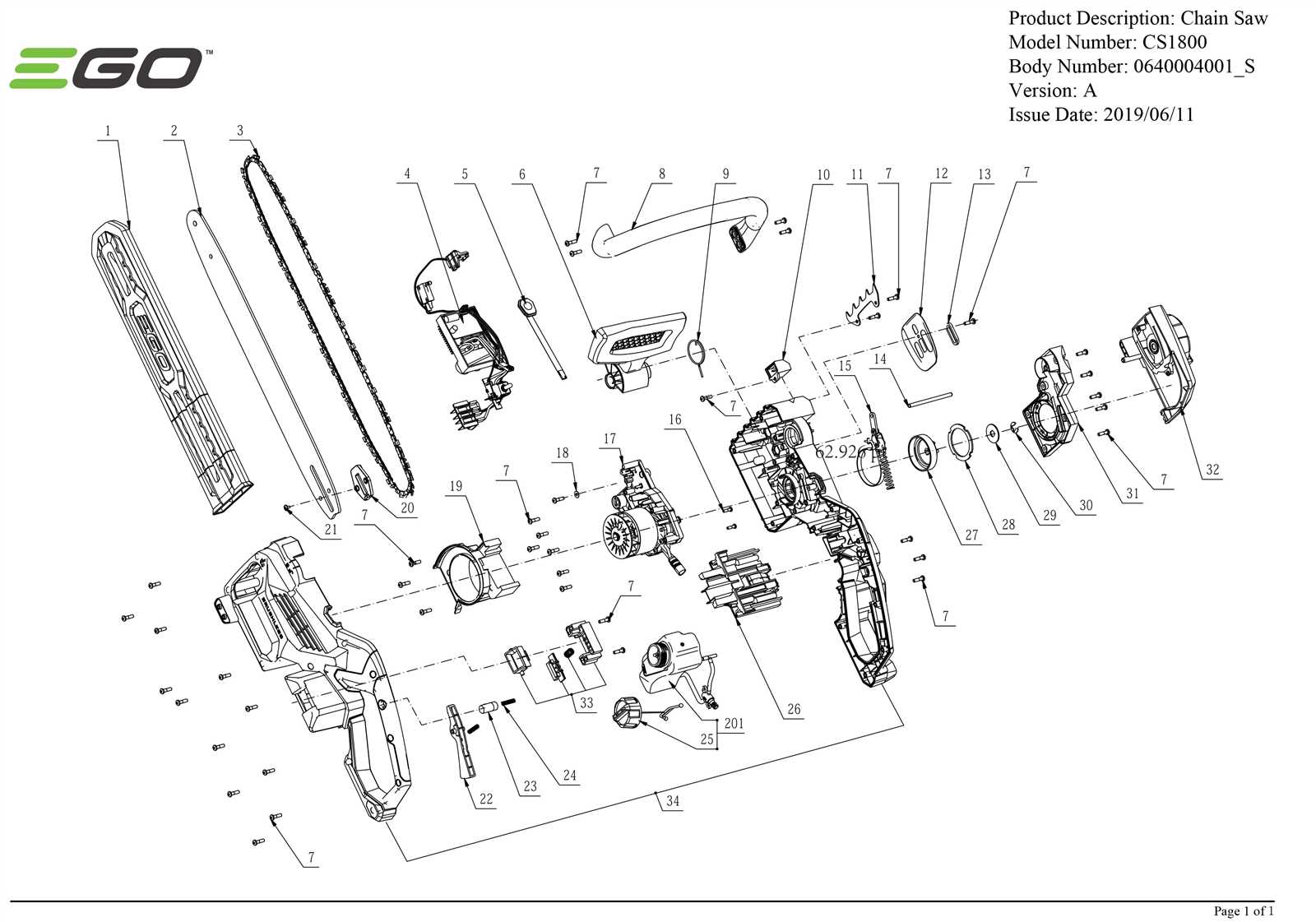
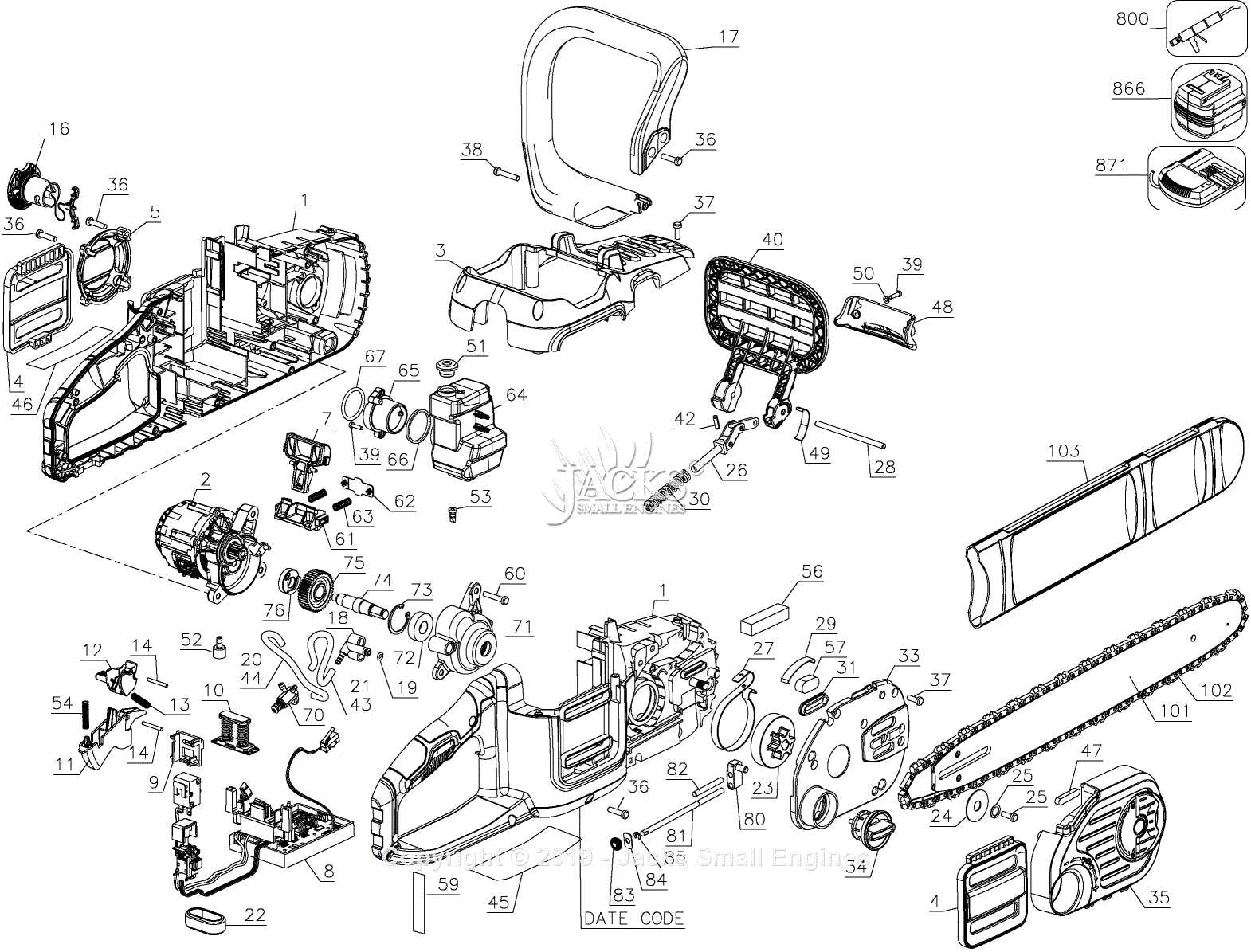
In the realm of mechanical devices designed for cutting tasks, a comprehensive grasp of their various elements is essential for effective operation and maintenance. Each individual segment plays a critical role in the overall functionality, contributing to the performance and reliability of the tool. By dissecting these components, one can gain insights into how they work together seamlessly.
These instruments consist of numerous interconnected parts, each with a specific function. From the powerful motor that drives the mechanism to the intricate assembly of blades and safety features, understanding the arrangement and role of each piece is vital for both users and technicians. This knowledge not only enhances operational efficiency but also facilitates troubleshooting and repairs when necessary.
Exploring the layout of these components reveals a systematic design that prioritizes safety and effectiveness. By familiarizing oneself with these elements, users can ensure optimal performance and extend the lifespan of their cutting equipment. This article aims to provide a detailed exploration of the arrangement and significance of each section, fostering a deeper appreciation for the engineering behind these powerful tools.
Understanding Chainsaw Components
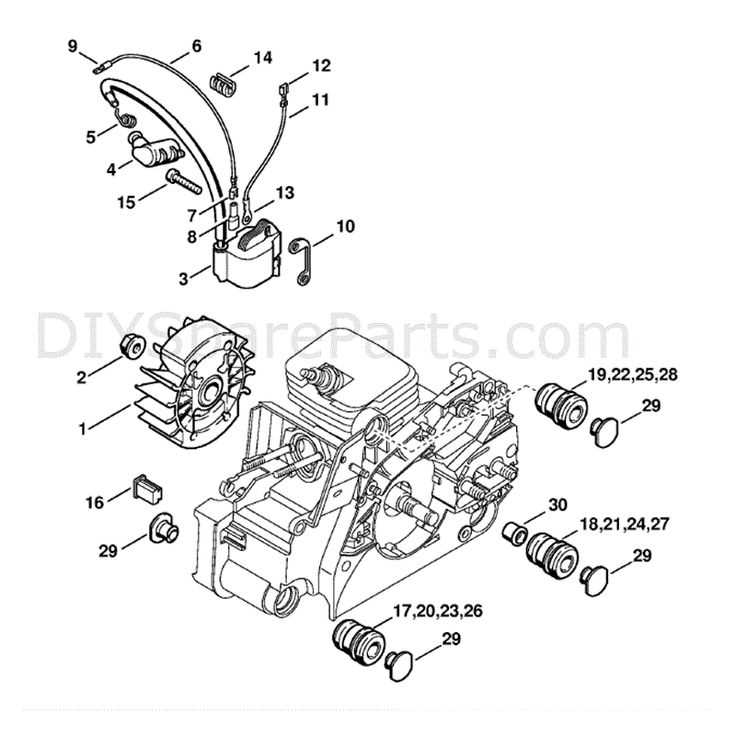
To effectively operate and maintain this powerful tool, it is essential to grasp the various elements that contribute to its functionality. Each component plays a crucial role, ensuring efficient performance and safety during use. By familiarizing oneself with these individual parts, users can enhance their understanding of how the device works as a whole.
Main Elements
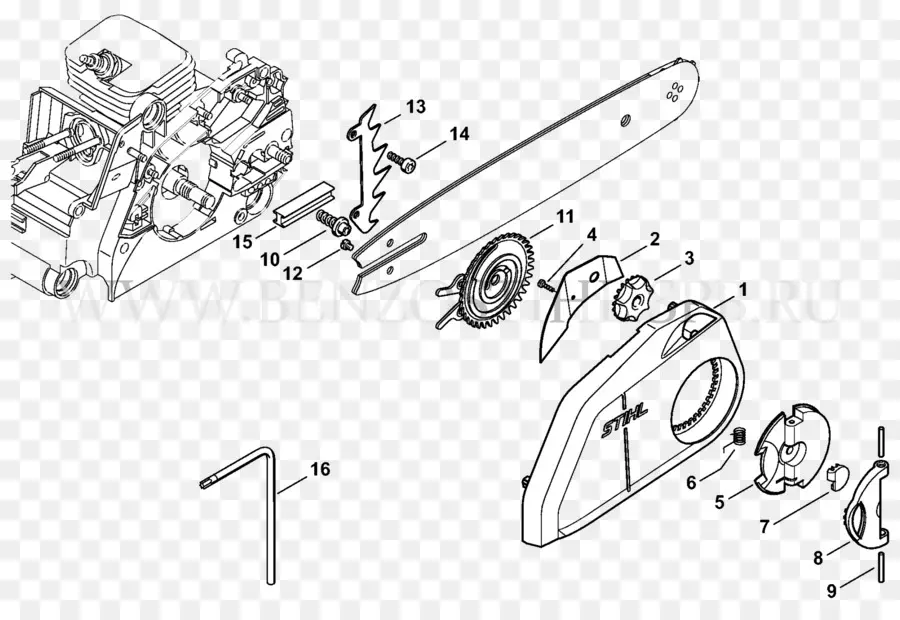
- Engine: The heart of the machine, responsible for providing the necessary power.
- Guide Bar: A metal strip that supports the cutting chain and guides it during operation.
- Cutting Chain: The loop of interconnected links that performs the actual cutting.
- Clutch: Engages and disengages the cutting chain, allowing for safe operation.
- Fuel System: Supplies the engine with the necessary fuel mixture for combustion.
Supportive Features
- Handle: Provides a secure grip, ensuring control during operation.
- Chain Brake: A safety feature that stops the chain in case of kickback.
- Air Filter: Prevents debris from entering the engine, maintaining efficiency.
- Lubrication System: Ensures the cutting chain remains properly oiled for smooth operation.
Understanding these essential components not only improves the user’s ability to operate the tool effectively but also aids in troubleshooting and maintenance tasks, contributing to a safer and more efficient experience.
How Chainsaw Parts Work Together
Understanding the interaction of various components in a cutting tool is essential for optimal performance. Each element plays a specific role, contributing to the overall efficiency and functionality of the machine. The collaboration between these components enables smooth operation and precise cutting.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Engine | Provides power to drive the entire mechanism. |
| Guide Bar | Supports and directs the cutting chain during operation. |
| Cutting Chain | Engages with the material, performing the actual cutting action. |
| Clutch | Connects and disconnects the engine from the chain for safety and control. |
| Fuel System | Supplies energy to the engine, ensuring it runs efficiently. |
| Starter Mechanism | Facilitates the initial ignition of the engine. |
| Chain Tensioner | Allows for the adjustment of chain tightness for optimal cutting performance. |
Each component is designed to work harmoniously, allowing users to handle various cutting tasks effectively. Proper maintenance and understanding of these interactions can significantly enhance the tool’s longevity and performance.
Essential Tools for Chainsaw Maintenance

Proper upkeep of your cutting tool is crucial for ensuring its longevity and optimal performance. A well-maintained device not only operates efficiently but also guarantees safety during use. To achieve this, a selection of specific instruments is necessary to address various maintenance tasks effectively.
Basic Maintenance Tools

To start, having a set of fundamental tools at your disposal is essential. These tools facilitate routine checks and minor adjustments, ensuring your equipment remains in top shape.
| Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Wrench Set | For tightening and loosening bolts and nuts. |
| Screwdriver | Used for adjusting screws on various components. |
| File | Essential for sharpening cutting edges. |
| Chain Breaker | For repairing or replacing the cutting chain. |
Advanced Maintenance Tools
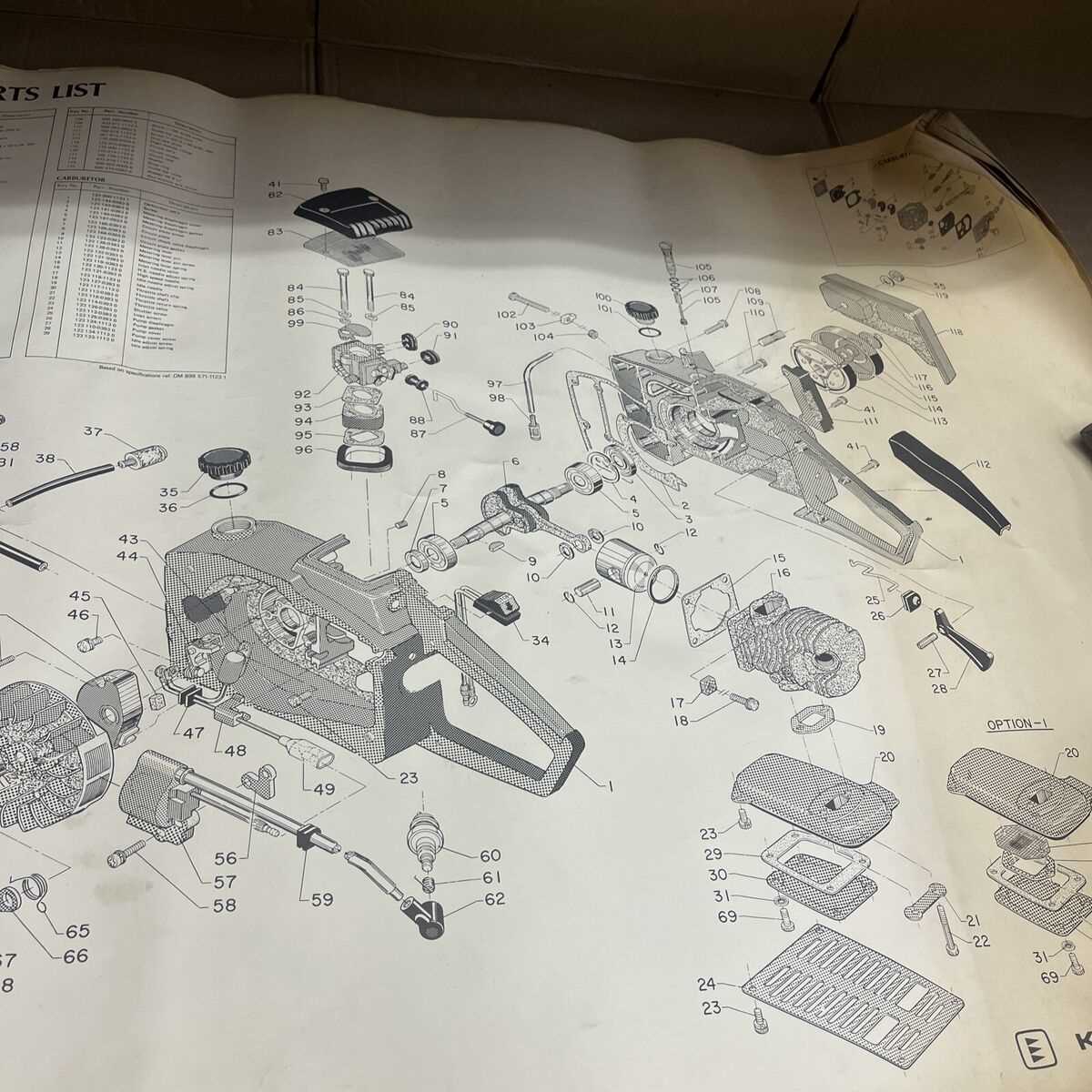
In addition to basic tools, advanced maintenance equipment can enhance the performance and safety of your cutting instrument. Investing in these specialized tools can save time and ensure precision during upkeep.
| Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Depth Gauge Tool | To measure and set the depth of the cutting teeth. |
| Lubrication Pump | For applying oil to the moving parts efficiently. |
| Protective Gear | To ensure safety while performing maintenance tasks. |
Common Chainsaw Problems Explained

When operating outdoor power tools, users often encounter various issues that can impede performance. Understanding these challenges is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. This section highlights frequent problems and their potential causes, ensuring smooth operation and longevity of the equipment.
Typical Issues and Their Causes
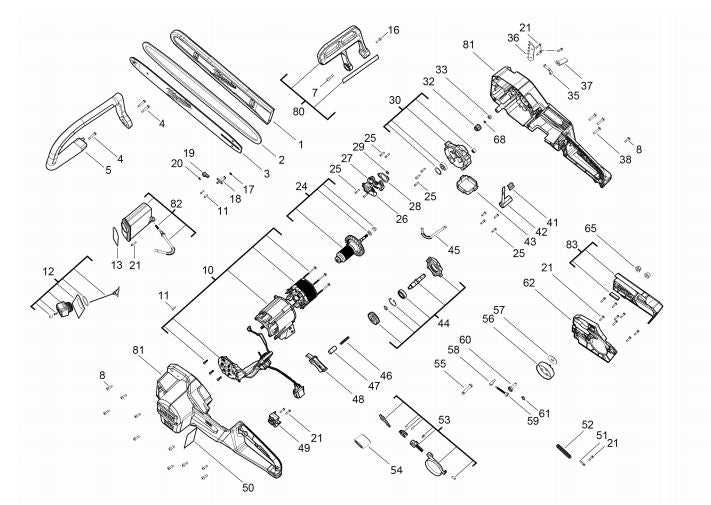
- Starting Difficulties:
- Insufficient fuel or stale gasoline.
- Clogged air filter.
- Faulty spark plug.
- Loss of Power:
- Dull cutting chain.
- Fuel mixture problems.
- Overheating due to debris buildup.
- Excessive Vibration:
- Worn or misaligned chain.
- Improperly mounted components.
- Damaged anti-vibration system.
Maintenance Tips
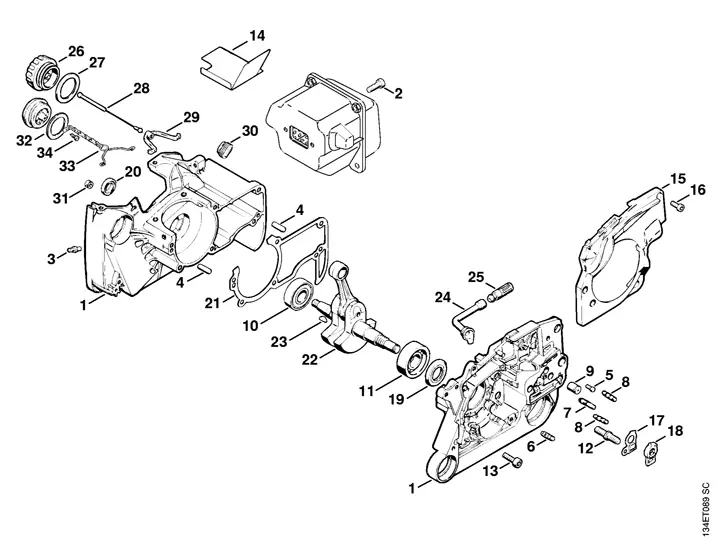
- Regularly check and replace the air filter.
- Keep the cutting edge sharp and well-maintained.
- Ensure proper fuel mixture according to manufacturer recommendations.
By recognizing these common issues and adhering to maintenance guidelines, users can enhance the performance and reliability of their equipment.
Safety Features of Chainsaws
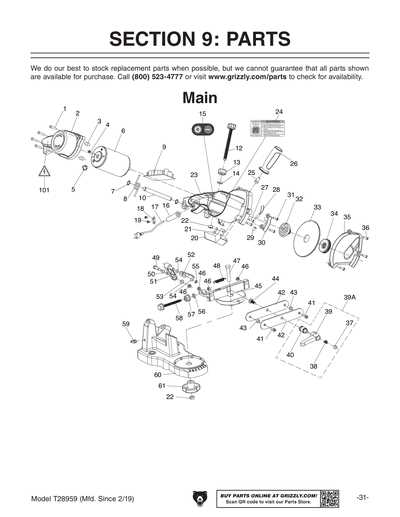
When operating powerful cutting tools, ensuring user protection is paramount. Various built-in mechanisms are designed to minimize risks and enhance safety during use. These features serve to protect the operator from potential accidents and improve overall handling.
One of the most critical safety mechanisms is the chain brake, which halts the blade’s movement in the event of kickback, a sudden upward motion that can occur if the tool contacts an object unexpectedly. This feature significantly reduces the likelihood of injury, allowing users to maintain better control.
Another essential component is the throttle lock, which prevents accidental acceleration of the cutting mechanism. By requiring deliberate action to engage the throttle, this feature helps to avoid unintentional activation, enhancing user security.
Additionally, many models are equipped with anti-vibration systems that diminish the impact of vibrations on the operator’s hands. This not only improves comfort during extended use but also helps to prevent long-term injuries associated with continuous exposure to vibration.
Protective guards are also standard, shielding the user from flying debris and providing an extra layer of safety during operation. These elements work together to create a more secure working environment, allowing for safer handling and increased confidence while using such powerful tools.
Understanding and utilizing these safety features is crucial for anyone who engages with cutting equipment. Proper knowledge of these mechanisms can significantly reduce the risk of accidents, ensuring a safer and more efficient experience.
Upgrading Chainsaw Parts for Performance
Enhancing the functionality of your cutting tool can significantly improve efficiency and durability. By selecting and installing superior components, users can experience better power output, reduced vibration, and improved handling. This section will explore various upgrades that can elevate performance and ensure longevity.
Key Upgrades to Consider
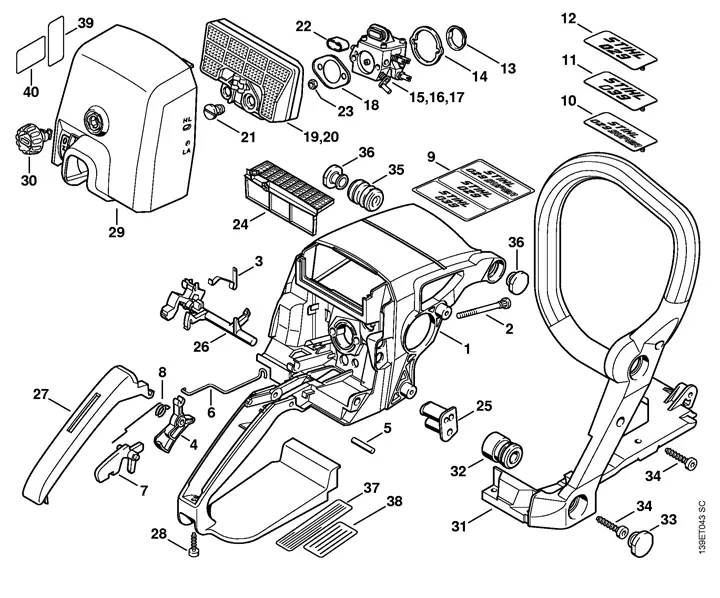
- Engine Modifications: Upgrading the motor can increase power and torque, allowing for more demanding tasks.
- Bar and Chain: Choosing a longer bar or a specialized chain can enhance cutting speed and precision.
- Air Filters: Improved air filtration systems can lead to better airflow and performance.
- Fuel System: A high-performance carburetor can optimize fuel delivery for greater efficiency.
Benefits of Upgrading
- Enhanced cutting efficiency, resulting in faster job completion.
- Increased safety through better handling and stability.
- Longer lifespan of the equipment due to higher-quality materials.
- Improved user experience with reduced fatigue and better control.
Investing in quality enhancements not only improves performance but also transforms the overall experience, making every task easier and more enjoyable.
Choosing the Right Chainsaw Model
Selecting the appropriate model for cutting tasks can significantly enhance efficiency and safety. Various factors come into play when determining which option best suits individual needs, from power requirements to user experience.
Consider Your Needs
Before making a decision, it’s essential to assess the specific tasks you will undertake:
- Type of Work: Will you be doing light pruning or heavy-duty logging?
- Frequency of Use: Is this a tool for occasional projects or regular use?
- Portability: Do you require a lightweight option for easy maneuverability?
Evaluate Features
Once you’ve established your requirements, consider the following features that can influence performance:
- Power Source: Decide between gas, electric, or battery-powered models based on convenience and availability.
- Bar Length: Choose a length that matches the type of tasks, as longer bars are better for larger cuts.
- Safety Features: Look for options with chain brakes and safety switches to protect against accidents.
By carefully evaluating your needs and the features available, you can select the most suitable model for your cutting tasks, ensuring a successful and safe experience.
DIY Repairs for Chainsaw Owners
Owning a cutting tool can be rewarding, especially when you have the skills to maintain it yourself. Many enthusiasts prefer to tackle repairs on their own, saving time and money while gaining a deeper understanding of their equipment. This section explores essential repairs and tips for ensuring your device remains in optimal condition.
Here are some common issues you might encounter and how to address them:
- Fuel System Troubles:
- Check for blockages in the fuel line.
- Replace the fuel filter if it appears dirty.
- Ensure the carburetor is clean and properly adjusted.
- Cutting Performance:
- Sharpen the chain regularly to maintain efficiency.
- Inspect the bar for wear and replace if necessary.
- Adjust the tension of the chain for optimal performance.
- Electrical Components:
- Examine the spark plug for wear and replace it if needed.
- Check the ignition system for proper operation.
- Inspect wiring for damage or corrosion.
Maintaining your equipment not only prolongs its life but also enhances your safety during use. Always refer to your owner’s manual for specific guidance and recommendations tailored to your model.
History of Chainsaw Design Evolution
The development of mechanical cutting tools has undergone significant transformations since their inception. Innovations in design and technology have continually reshaped these devices, enhancing their efficiency, safety, and usability. The journey of these implements reflects a fascinating interplay between engineering ingenuity and practical necessity.
Initially, cutting tools were simple handheld devices, primarily reliant on manual labor. However, as the demand for more efficient solutions grew, inventors began to experiment with powered mechanisms. This led to a series of breakthroughs, culminating in designs that integrated advanced features for improved performance.
| Year | Key Innovation | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1920 | First Electric Model | Introduction of the first electrically powered tool, enabling more efficient cutting. |
| 1950s | Portable Versions | Development of lightweight, portable tools, making them more accessible for various users. |
| 1970s | Safety Features | Implementation of safety mechanisms, reducing the risk of accidents during operation. |
| 2000s | Environmental Considerations | Focus on eco-friendly designs, utilizing low-emission technologies and sustainable materials. |
The continuous refinement of these machines showcases the ongoing commitment to innovation within the industry. As technology progresses, future advancements promise to enhance both functionality and user experience, further transforming how these tools are perceived and utilized in various fields.