Understanding the Three Main Parts of the Brain
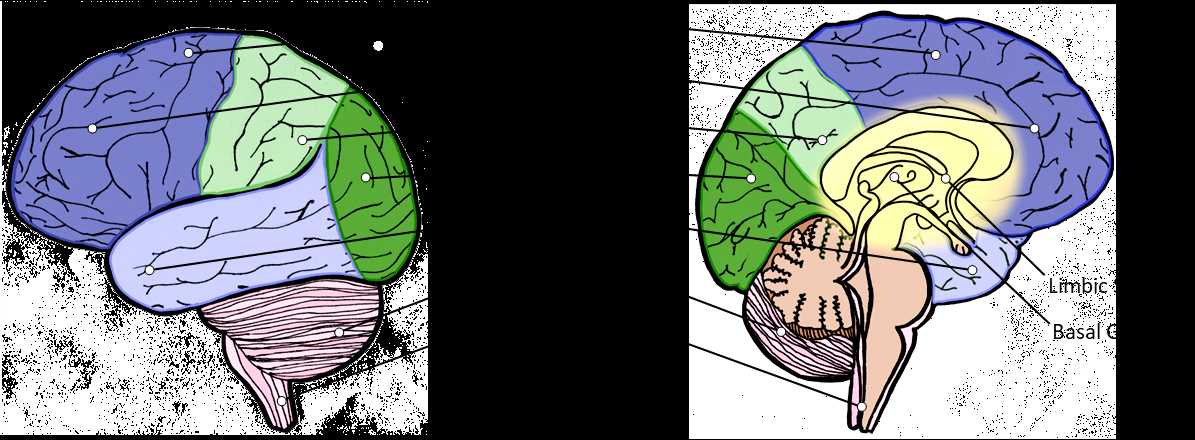

The human nervous system is an intricate structure, responsible for processing information and controlling various functions. Each region within this complex system plays a vital role in regulating everything from emotions to movement. By exploring its primary zones, we gain a deeper appreciation of how different processes come together to shape our thoughts and actions.
In this exploration, we will delve into the core areas responsible for cognition, coordination, and sensory interpretation. These regions interact continuously, ensuring smooth operation of both voluntary and involuntary activities. Grasping the significance of each zone provides essential insight into the functionality of our neural system.
This journey through human anatomy allows us to observe how specific areas contribute to fundamental tasks such as communication, memory, and decision-making. Each section is a crucial component, working in harmony to create the capabilities that define human experience.
Understanding the Brain’s Structure
Exploring how our mental organ is organized helps us better grasp how various functions are distributed and controlled. This overview delves into the primary sections of this complex organ, emphasizing its key roles in coordination, cognition, and emotional regulation. Each region is uniquely specialized, contributing to an array of vital processes that keep our body functioning smoothly.
| Region | Main Function |
|---|---|
| Cerebrum | Handles reasoning, creativity, and memory. |
| Cerebellum | Regulates balance, movement, and coordination. |
| Medulla | Controls automatic functions like breathing and heartbeat. |
Main Regions of the Human Brain
Understanding the key divisions within our central control system helps us appreciate how different areas contribute to essential activities like thought, movement, and sensation. These zones, while interconnected, each play specialized roles in supporting life and complex functions.
Cerebrum
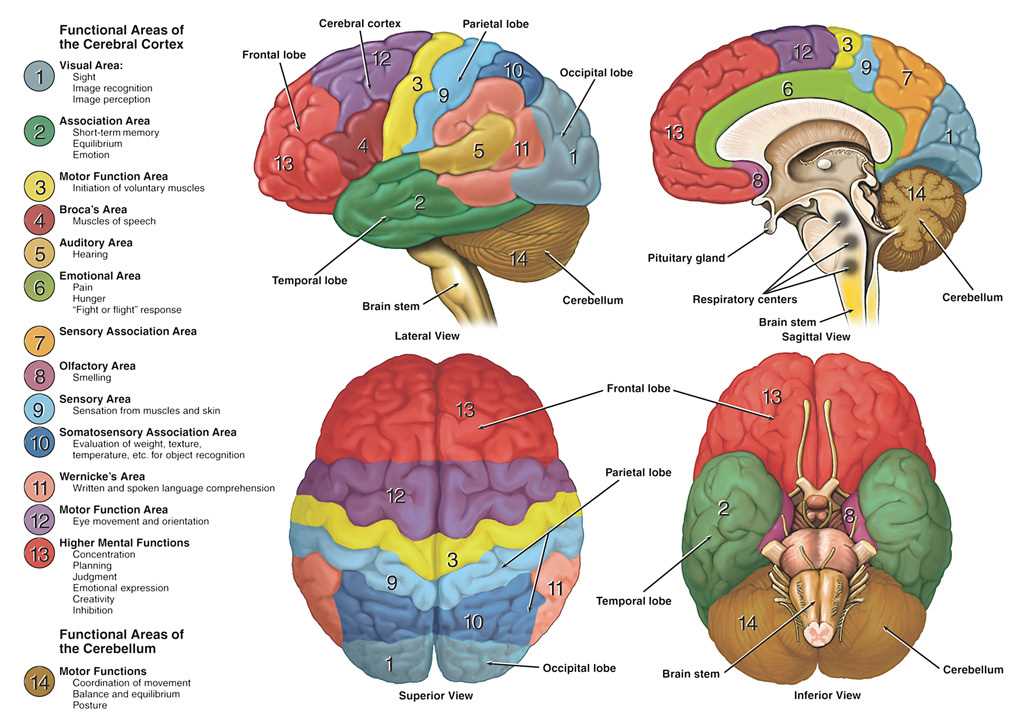
The largest section is responsible for cognitive abilities, voluntary actions, and sensory interpretation. It manages decision-making, reasoning, and memory processing, acting as the center for higher mental functions.
Cerebellum
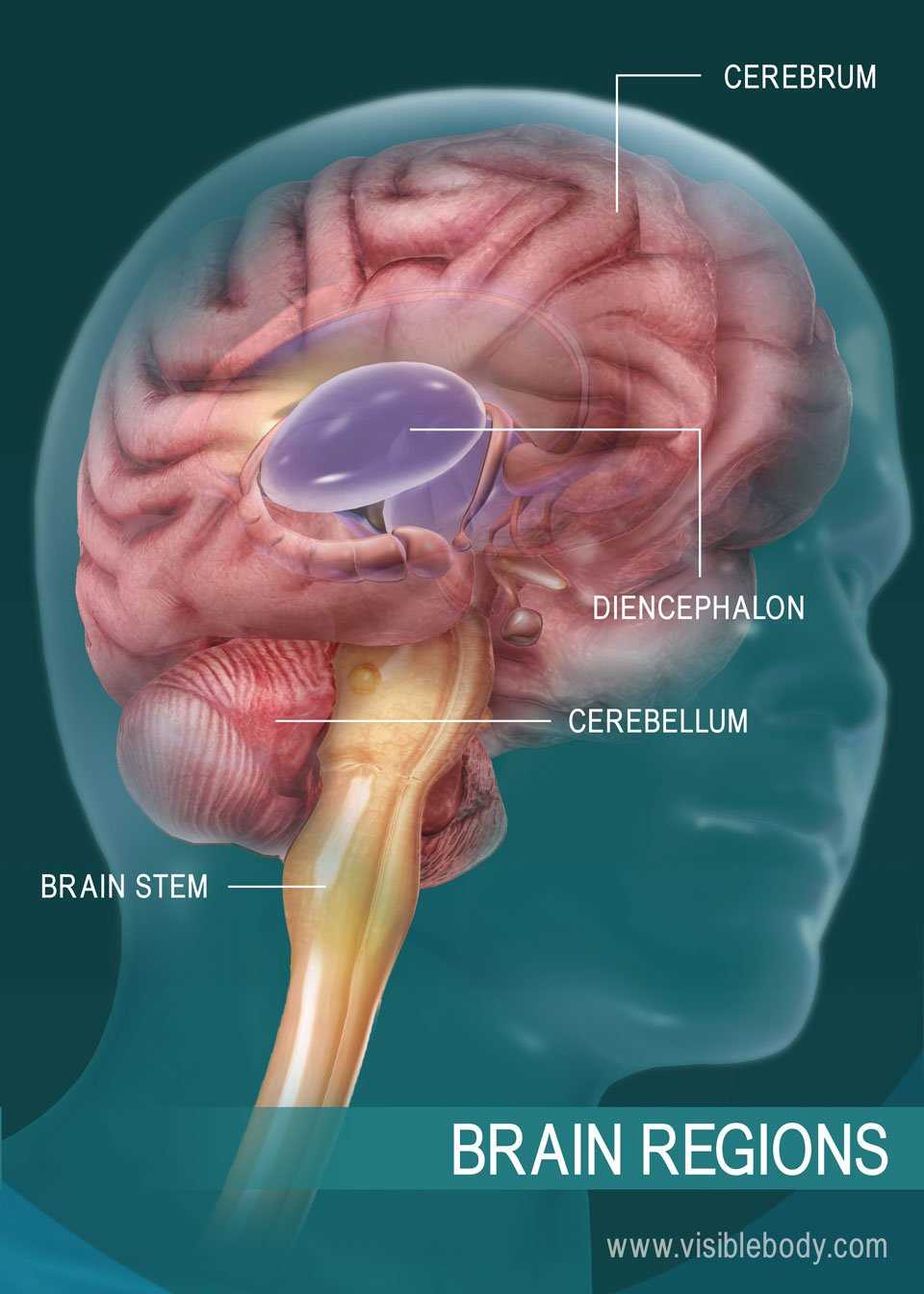
This smaller area located at the back is crucial for coordinating movement and maintaining balance. It ensures smooth physical actions and posture by fine-tuning motor responses.
Conclusion: Each area within our neural system has a specific role, working in harmony to manage both mental and physical activities.
Functions of the Forebrain
The forebrain is crucial for a variety of advanced functions, playing a key role in processing sensory information, regulating emotions, and facilitating conscious thought. Its influence extends to decision-making, learning, and memory, as well as governing basic survival mechanisms like sleep and hunger.
Sensory Processing and Interpretation
One of the primary roles of this region is handling input from our environment. It interprets signals from various senses, enabling us to understand what we see, hear, touch, and feel. This allows for meaningful responses to surroundings, contributing to perception and awareness.
- Visual recognition and interpretation
- Auditory processing and sound localization
- Tactile sensation and spatial awareness
Cognitive Functions and Emotional Control
The forebrain is essential for higher-level thinking, organizing thoughts, planning
The Importance of the Midbrain
Midbrain plays a crucial role in coordinating numerous vital functions within our nervous system. It influences essential processes, helping regulate activities that maintain equilibrium in bodily functions and sensory responses.
One of the significant tasks of this central region is its involvement in transmitting signals that affect motor control. Its function ensures the smooth execution of voluntary movements, which are key to our everyday interactions and actions.
| Key Role | Function |
|---|---|
| Movement Regulation | Coordinates voluntary actions, ensuring fluid motion. |
| Visual and Auditory Response | Processes visual and sound signals, contributing to reflexes and spatial awareness. |
| Alertness and Attention | Maintains alertness, allowing focused responses to external stimuli. |
This small yet complex structure is
Role of the Hindbrain in Motor Control
The hindbrain is essential in coordinating movement and maintaining balance. It ensures smooth execution of actions, whether voluntary or reflexive, by regulating muscle coordination. This part of the nervous system supports various motor functions crucial for everyday tasks, from basic movement to complex physical activities.
Cerebellum, a critical structure located in this region, plays a key role in adjusting movements, allowing for precision and accuracy. It fine-tunes actions by analyzing signals related to motion and position, ensuring steady posture and fluid motion.
The medulla, another vital structure, controls reflexes necessary for vital movements like breathing and heart rate, contributing to overall coordination. Together, these components enable a harmonious interaction between muscles and nerves, providing stability and agility in motion.
How the Brain Processes Information

This intricate organ manages a wide array of functions by receiving, interpreting, and responding to stimuli. Through complex networks, signals are transmitted, enabling an organism to adapt and react to various situations. Understanding these mechanisms offers insights into cognitive processes and behavioral responses.
Signal Transmission and Processing
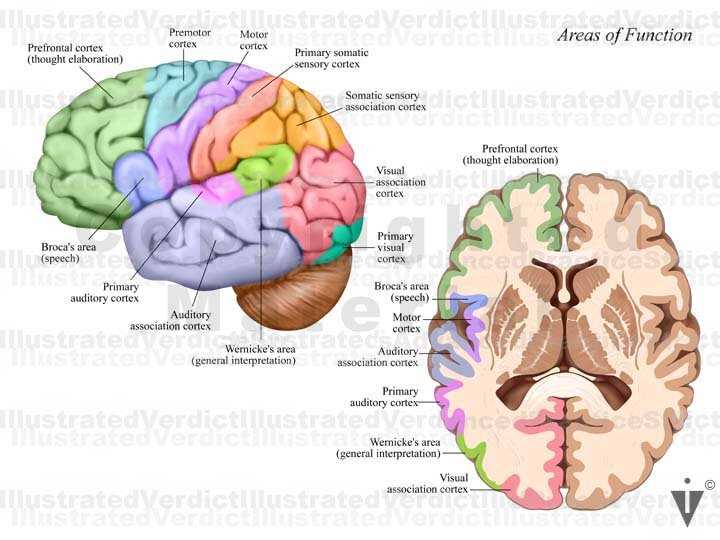
Communication within this organ occurs through specialized cells, which transmit impulses across synapses. These signals are processed in various regions, each contributing uniquely to overall functionality. The interplay between different areas is crucial for efficient information handling.
Role of Different Regions
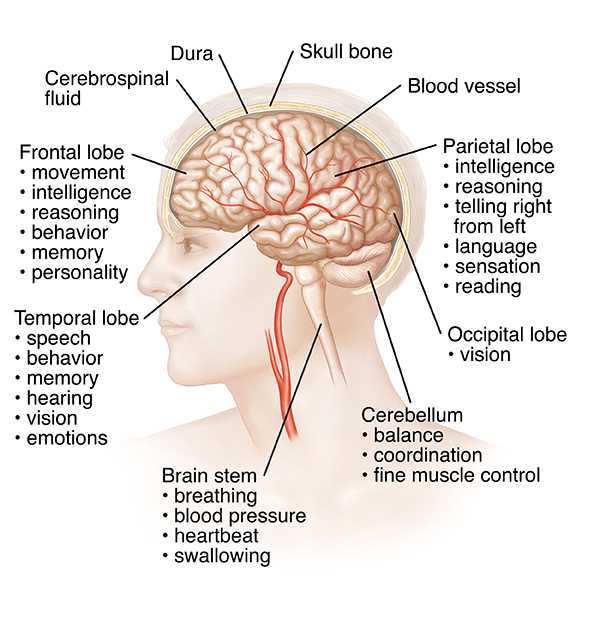
Distinct areas perform specialized tasks, enabling diverse capabilities such as memory formation, sensory perception, and motor control. This division of labor ensures that complex tasks are managed effectively, allowing for a seamless experience in interacting with the environment.
| Function | Region Involved |
|---|---|
| Memory Formation | Hippocampus |
| Emotional Responses | Amgydala |
| Motor Control | Cerebellum |
| Visual Processing | Occipital Lobe |
Connections Between Brain Parts

The intricate network within our central nervous system showcases a remarkable web of interactions that facilitate various functions. These connections allow for seamless communication and coordination among different regions, contributing to our ability to process information, respond to stimuli, and execute complex behaviors. Understanding these interrelations is crucial for comprehending how cognitive and physical activities are performed.
Neural Pathways
Neural pathways serve as highways for transmitting signals across different regions, enabling rapid response and interaction. These routes are formed by a combination of nerve fibers, which connect clusters of neurons, thus allowing various areas to share information efficiently. This connectivity is essential for activities ranging from reflex actions to advanced cognitive tasks.
Functional Integration
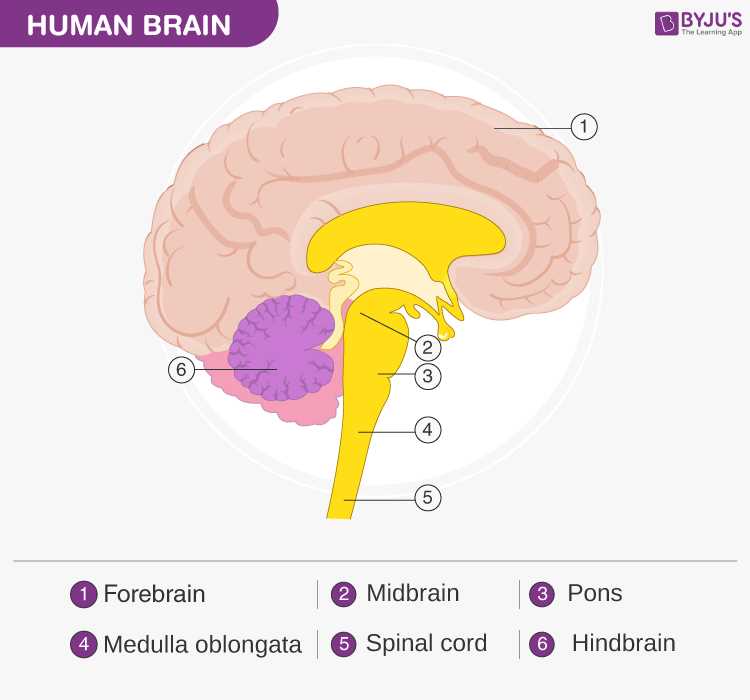
Functional integration refers to how various regions collaborate to perform specific tasks. Different clusters work in harmony to ensure that responses are appropriate and timely. This collaboration not only enhances individual functionalities but also supports overall efficiency, enabling an organism to adapt to its environment and make informed decisions.
Key Brain Regions in Emotion Control
Understanding how feelings are regulated involves exploring several vital regions that play a significant role in emotional processing. These areas interact closely, influencing various aspects of emotional responses and behavioral outcomes. Recognizing their functions offers insight into the complexity of human emotions and the mechanisms that govern them.
Among the most critical areas associated with emotional regulation are the amygdala, prefrontal cortex, and hippocampus. Each of these regions contributes uniquely to how emotions are experienced and expressed, forming a network that facilitates emotional intelligence and response.
| Region | Function |
|---|---|
| Amygdala | Involved in processing fear and pleasure responses. |
| Prefrontal Cortex | Regulates complex behaviors, decision-making, and moderates social interactions. |
| Hippocampus | Essential for forming new memories and connecting emotions to those memories. |
These regions not only shape emotional experiences but also work in harmony to adapt responses based on past encounters and situational contexts. This intricate interplay is fundamental for effective emotional control and overall mental health.
The Brain’s Influence on Memory
Memory is a complex function that significantly shapes our experiences and identity. It allows individuals to store, retain, and retrieve information, impacting various aspects of daily life. This cognitive process involves multiple interconnected regions, each contributing uniquely to how memories are formed, organized, and recalled.
Key Mechanisms of Memory Formation
Several essential processes are involved in creating lasting impressions. Initially, sensory information is collected, then transformed into a format that can be stored. Consolidation, the next step, solidifies these impressions for long-term retention. Retrieval is the final stage, where stored information is accessed and brought to consciousness.
Factors Affecting Memory
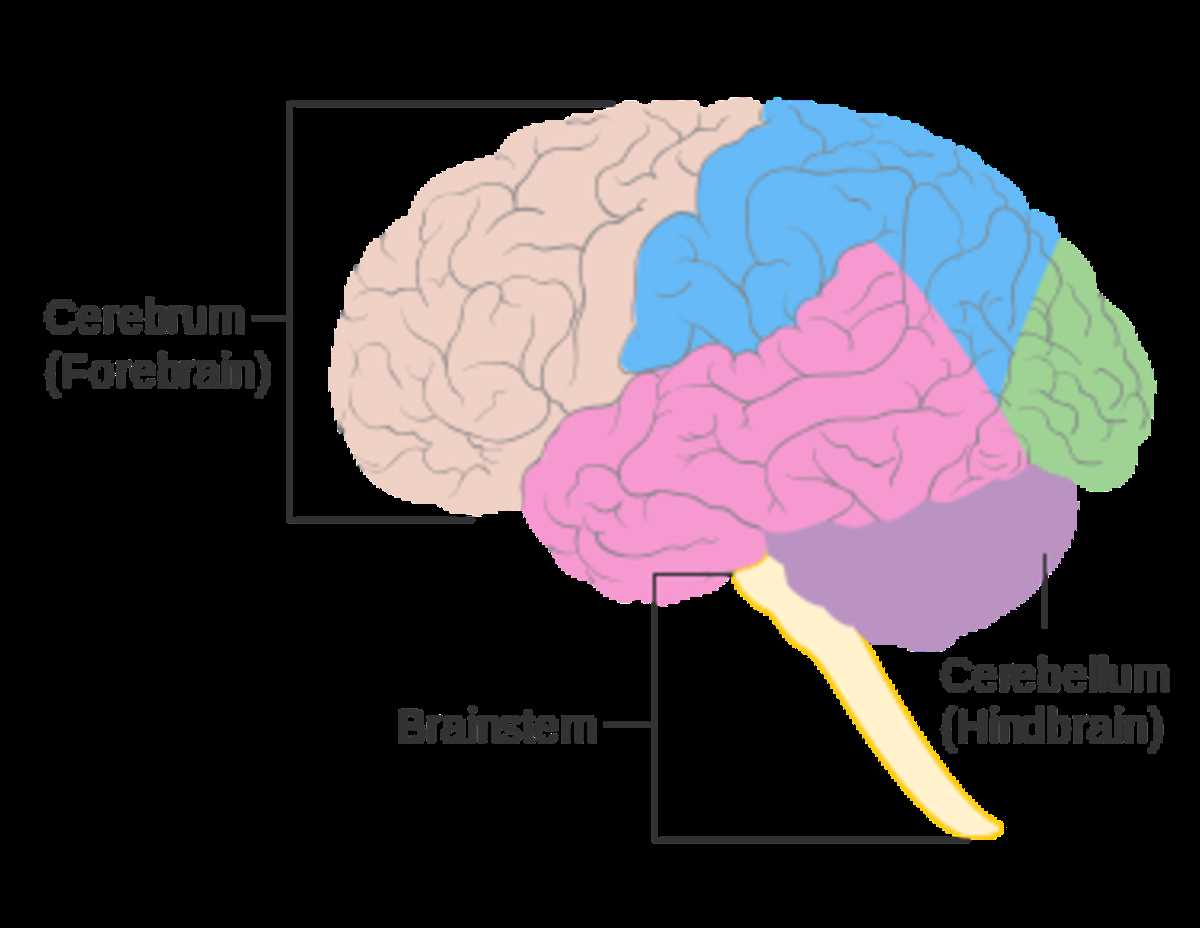
Various elements can influence the efficiency of these mechanisms. Factors such as age, emotional state, and environmental context play crucial roles in how well information is processed and recalled. Understanding these influences can enhance strategies for improving retention and recall.
| Influencing Factor | Effect on Memory |
|---|---|
| Age | Memory capacity often declines with age. |
| Emotional State | Strong emotions can enhance or impair recall. |
| Environment | Familiar surroundings can aid memory retrieval. |
Coordination and Movement Regulation by the Brain
Effective management of motion and spatial awareness involves a complex interplay of various regions within the central nervous system. These areas collaborate to fine-tune physical activities, ensuring seamless execution of tasks ranging from simple gestures to intricate athletic maneuvers. Understanding how this orchestration occurs provides insight into both ordinary functioning and potential disruptions that can affect mobility.
Key Mechanisms of Coordination
Motor control is influenced by multiple mechanisms that integrate sensory feedback and learned experiences. Essential components, such as proprioception, allow individuals to sense their body’s position in space, aiding in balance and coordination. Additionally, the establishment of muscle memory plays a vital role in automating repetitive actions, enhancing efficiency during physical exertion.
Role of Various Regions
Different regions contribute uniquely to regulating motion. For instance, structures responsible for planning and executing movements ensure that intentions translate into actions effectively. Meanwhile, areas linked to sensory processing enhance responsiveness to environmental stimuli, allowing for quick adjustments during dynamic activities. This intricate network highlights the significance of connectivity in achieving precise coordination.
The Brain and Its Role in Survival
The complex organ at the center of our nervous system plays a crucial role in ensuring our continued existence. Its functions encompass processing sensory information, regulating bodily functions, and enabling responses to external stimuli. This remarkable structure orchestrates various activities that are vital for adaptation and survival in ever-changing environments.
Through intricate networks, this organ integrates information from multiple sources, allowing individuals to respond effectively to threats and opportunities. It governs essential functions such as heartbeat, breathing, and hormonal regulation, ensuring homeostasis while also facilitating movement and communication. The ability to learn from experiences and make decisions is also deeply rooted in this structure, providing individuals with the means to navigate challenges and enhance their chances of survival.
Additionally, emotional responses play a significant role in survival, as they influence behavior and decision-making processes. By processing emotions, this organ helps individuals assess risks and react appropriately, fostering social connections that can further enhance survival prospects. Overall, the intricate interplay of functions within this vital organ underscores its importance in maintaining life and facilitating adaptation to the surrounding world.