2006 Dodge Charger Parts Diagram Overview
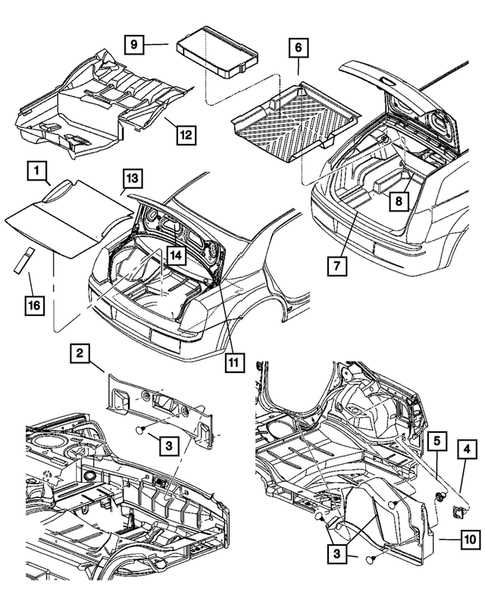
When working on an automobile, it’s crucial to have a clear understanding of its internal structure. This knowledge can greatly enhance the ability to perform repairs, replacements, and maintenance with precision. A detailed visual guide showcasing how various components are arranged within a specific model can serve as an invaluable reference for anyone working with or maintaining the vehicle.
In this section, we will explore the layout of key mechanical elements and electrical systems. Understanding the placement and connections of each part ensures that all components work together harmoniously. This guide will focus on highlighting the essential connections and configurations necessary for effective service and repair.
Key areas of focus will include powertrain assemblies, suspension systems, and electrical wiring networks. Each element has been carefully arranged to maximize functionality and safety, and understanding their relationship is vital for anyone looking to optimize their vehicle’s performance.
Having a comprehensive visual aid allows for more efficient troubleshooting and part identification. With this guide, you’ll gain insight into the intricate design and operational flow of essential systems, providing a deeper understanding of the vehicle’s inner workings.
2006 Dodge Charger Components Overview
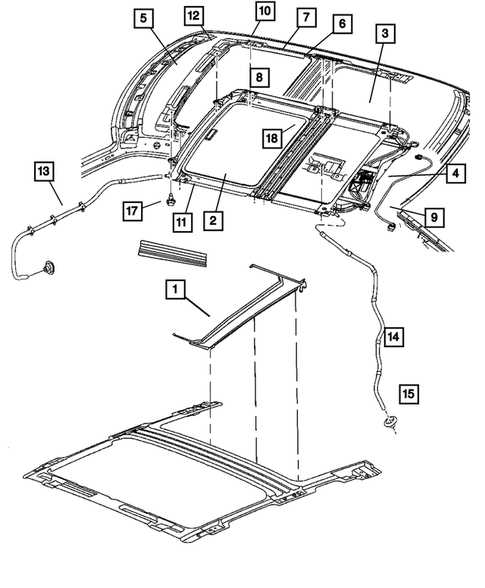
This section provides a comprehensive look at the essential elements that make up the vehicle. Understanding the arrangement and function of each part is key to ensuring optimal performance and ease of maintenance. The components are carefully designed to work in harmony, contributing to the overall functionality and driving experience. Below, we will break down some of the key components and their respective functions in the vehicle’s system.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Engine Assembly | The heart of the vehicle, responsible for powering the car and providing torque for movement. |
| Transmission | Controls the power distribution between the engine and the wheels, allowing the vehicle to shift gears. |
| Suspension System | Includes components like springs and shock absorbers that help smooth the ride and provide stability. |
| Braking System | A crucial safety feature, this system includes brakes and sensors to ensure proper stopping power and control. |
| Electrical System | Comprises the battery, alternator, and wiring that provide power to the vehicle’s accessories and ensure smooth operation. |
| Fuel System | Consists of the fuel pump, injectors, and filter that ensure proper fuel delivery to the engine for combustion. |
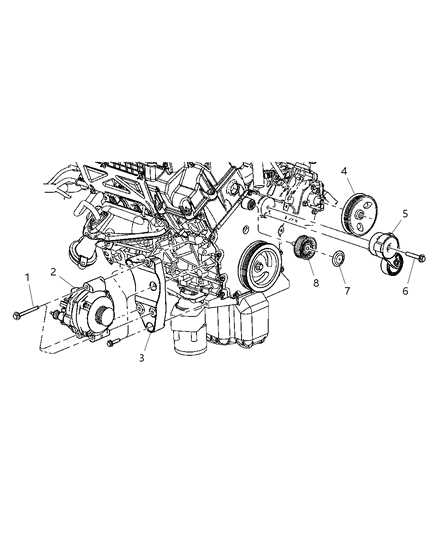
Engine Assembly and Key Parts
The heart of any vehicle consists of several intricate components that work in unison to ensure smooth operation. Understanding how each element of the engine contributes to overall performance is essential for maintenance and repair. This section delves into the main assembly, focusing on crucial elements that drive the vehicle’s powertrain functionality.
At the core of the system is the block, housing the pistons, crankshaft, and camshaft, all of which play vital roles in converting fuel into mechanical energy. Additionally, the cylinder head, with its valves and rocker arms, controls the intake and exhaust flow, maintaining engine efficiency. Proper understanding of these key components allows for more precise diagnosis and timely intervention when issues arise.
Further, the timing belt and the oil pump ensure synchronization of the internal parts while maintaining lubrication for smooth operation. By understanding the interconnection between these elements, one can effectively troubleshoot and extend the life of the engine.
Transmission and Drivetrain Breakdown
The transmission and drivetrain components work in unison to transfer power from the engine to the wheels. These systems are integral to a vehicle’s performance, efficiency, and handling. Understanding the layout and function of each part can help identify potential issues and enhance overall maintenance strategies.
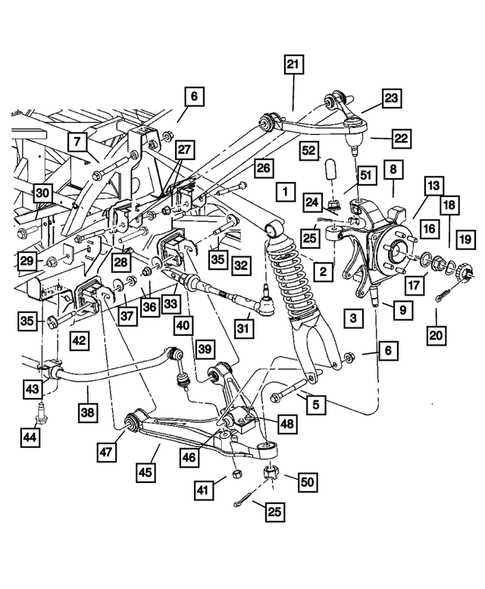
Key Components of the Transmission System
- Transmission Gearbox: This mechanism controls the power flow to the driveshaft, allowing the vehicle to shift between gears smoothly.
- Clutch: It connects and disconnects the engine from the transmission, enabling smooth gear transitions.
- Torque Converter: A fluid coupling that transfers rotational power between the engine and transmission.
- Shift Linkage: The system that allows the driver to select the desired gear using a lever or shifter.
Drivetrain and Power Distribution
- Driveshaft: This rotating shaft transfers power from the transmission to the differential.
- Differential: A gear assembly that divides the engine’s power between the drive wheels, allowing them to rotate at different speeds.
- Axles: These components transfer the power from the differential to the wheels, enabling them to rotate and move the vehicle.
- CV Joints: Constant velocity joints ensure that power is delivered to the wheels even when they are turned at sharp angles.
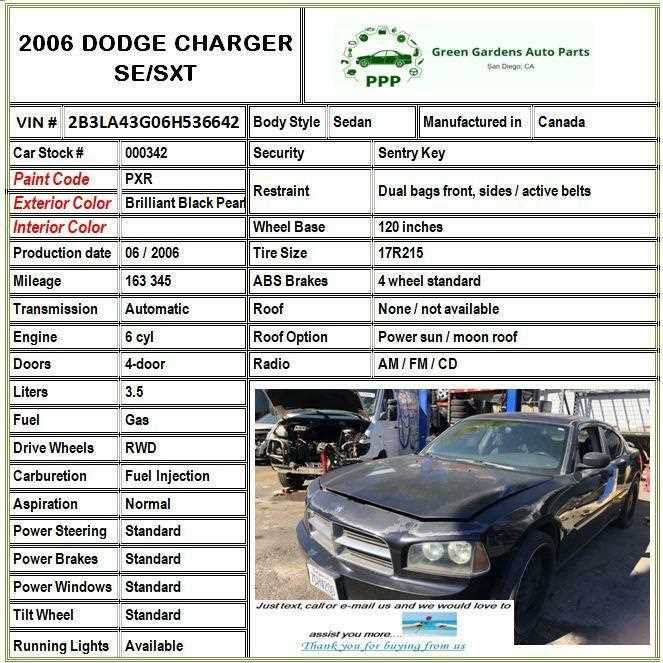
Suspension System Essentials

The suspension system plays a critical role in maintaining comfort and safety while driving. It connects the vehicle’s body to its wheels and helps absorb impacts from road irregularities, ensuring a smooth and stable ride. Understanding its components and functions is essential for anyone involved in vehicle maintenance or repairs.
This system consists of various parts that work together to manage the forces of movement and provide support. The primary components include:
- Shocks and Struts – These dampers control the oscillations of the springs, minimizing the effect of bumps and vibrations on the ride.
- Springs – Often coil, leaf, or air-based, springs support the weight of the vehicle and absorb shock from the road.
- Control Arms – These parts connect the frame of the vehicle to the wheel assembly, allowing controlled movement.
- Ball Joints – Located between the control arms and the steering knuckles, ball joints allow for smooth movement of the steering system.
Regular inspection of these components is crucial for ensuring vehicle safety and performance. Any failure or wear can result in poor handling, decreased comfort, or even complete loss of vehicle control. Proper maintenance and timely repairs are key to prolonging the life of the suspension system.
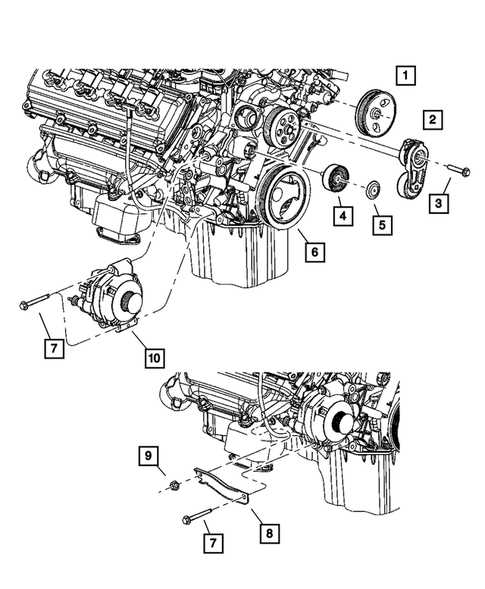
Electrical Wiring and Circuitry
The system that powers and connects various components within a vehicle relies heavily on a well-organized network of electrical pathways. Proper functioning of these pathways ensures that everything from the ignition system to the lighting works smoothly. Understanding the design and layout of these connections is crucial for troubleshooting and repairs.
Key Elements of Vehicle Wiring
Electrical circuits in modern vehicles are composed of wires, connectors, and control units that form intricate pathways. These components are vital for transferring signals and power throughout the vehicle, enabling devices such as sensors, the battery, and multimedia systems to work in unison. A robust wiring setup allows for effective communication between these devices, ensuring a reliable and safe operation.
Maintaining Circuit Integrity
Regular inspection of wiring connections helps prevent failures caused by wear and tear. Corrosion, fraying, or loose connections can disrupt the flow of electricity, leading to malfunctioning systems. Proper maintenance and the use of quality materials are essential for preserving the integrity of these critical connections. Adhering to factory standards ensures that circuits function as intended, avoiding costly damage or vehicle breakdowns.
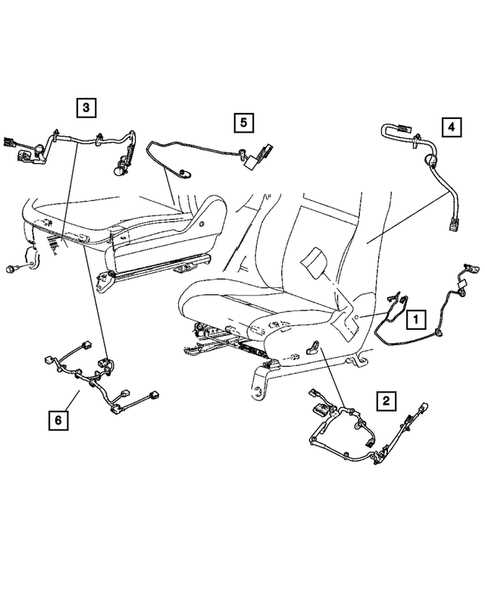
Interior Features and Assembly
The interior of a vehicle plays a crucial role in the overall driving experience, providing comfort, convenience, and functionality. Proper assembly of various components ensures that each feature works seamlessly together to enhance the user’s experience. From seating arrangements to dashboard configurations, the attention to detail in the design and assembly process is paramount.
Seating and Upholstery
The seating structure is designed to offer both support and comfort, with adjustable positions and high-quality materials used in upholstery. The seats are equipped with mechanisms for customization, such as lumbar support and heated options, contributing to a more comfortable ride.
Dashboard and Control Units
The dashboard serves as the central control hub, integrating various functions like climate control, infotainment systems, and vehicle diagnostics. These units are designed for ease of use, ensuring that the driver can access key functions without distraction. The assembly of these components must be precise, with all wiring and connections secured for optimal performance.
Brake System and Components
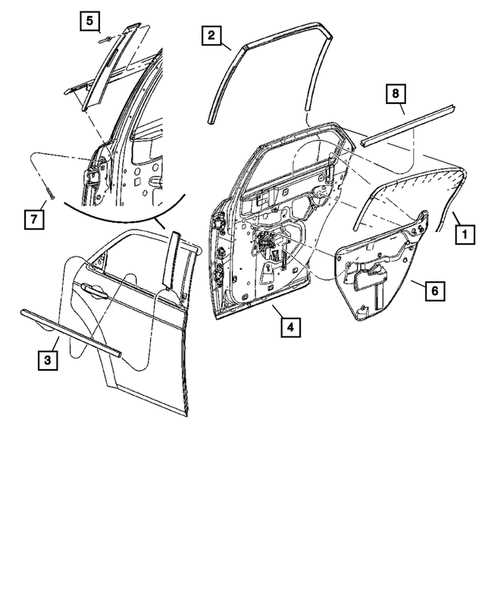
The braking mechanism of a vehicle plays a crucial role in ensuring safety by enabling controlled deceleration and complete stopping. Various parts work in unison to bring the vehicle to a halt. Understanding each component’s function helps in maintaining optimal performance and preventing potential failures.
Key Elements of the Braking Mechanism
- Brake Pads – These create the necessary friction against the rotor to slow down the vehicle.
- Rotors – Metal discs that work with the brake pads to slow or stop the wheel’s rotation.
- Brake Calipers – The component that houses the brake pads and applies pressure to the rotors.
- Brake Lines – Tubes that transport brake fluid, transferring force to the calipers.
- Master Cylinder – Transmits hydraulic pressure to the braking system when the brake pedal is pressed.
Maintenance and Care

- Regularly check brake fluid levels to ensure smooth operation.
- Inspect brake pads and rotors for wear and replace them as necessary.
- Test the brake calipers to ensure they apply pressure evenly across both pads.
- Examine brake lines for any leaks or signs of corrosion that could reduce braking efficiency.
Steering and Control Mechanisms
The steering and control systems of a vehicle are essential for ensuring smooth navigation and maintaining stability during operation. These components are designed to transmit the driver’s input to the wheels, allowing for precise direction adjustments. A reliable system contributes to the overall handling and safety of the vehicle, making it crucial for both comfort and control under various driving conditions.
Key elements involved in these systems include mechanisms that enable the driver to modify wheel orientation, as well as those that regulate the vehicle’s behavior under different forces. This section provides an overview of the fundamental components and their roles in maintaining effective steering control.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Steering Wheel | The primary interface for the driver to direct the vehicle, connected to the steering shaft. |
| Steering Column | A shaft connecting the steering wheel to the steering mechanism, allowing for smooth input transmission. |
| Rack and Pinion | The mechanism responsible for converting rotational movement from the steering wheel into lateral motion, turning the wheels. |
| Power Steering Pump | A hydraulic system that assists in turning the wheels with reduced effort from the driver. |
| Suspension Links | Structural elements that connect the vehicle’s wheels to the chassis, impacting handling and stability. |
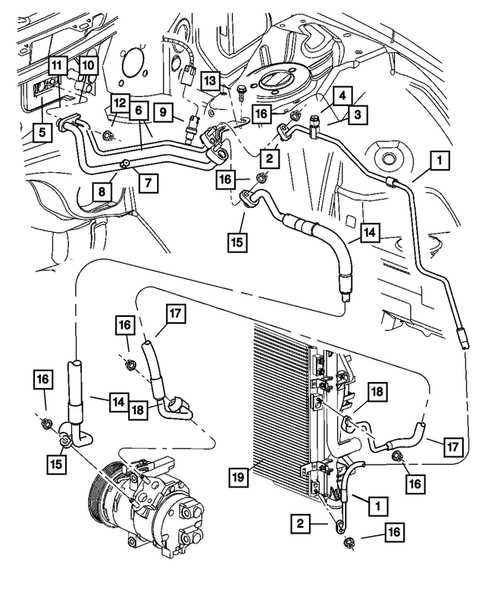
Cooling System Configuration

The cooling system plays a vital role in maintaining optimal operating temperatures within an engine. It ensures that the engine does not overheat while also contributing to efficient performance. The configuration of this system involves several key components working in harmony to regulate temperature effectively.
At the heart of this setup is the radiator, which dissipates heat from the engine coolant. Connected to the radiator are hoses that transport the coolant between the engine and the radiator. A water pump circulates the coolant, ensuring a continuous flow throughout the system. Additionally, the thermostat regulates the coolant’s flow based on temperature, allowing for precise control over the engine’s thermal condition.
Further enhancing efficiency, a fan may be integrated to assist in cooling the radiator, particularly at lower speeds when airflow is minimal. This configuration ensures that the engine operates within the ideal temperature range, promoting longevity and performance while minimizing the risk of overheating.
Fuel System and Components
The fuel delivery system plays a critical role in ensuring that the engine receives the proper amount of fuel for optimal performance. It consists of various interconnected elements that work together to store, transport, and inject fuel into the engine. Each component is designed to perform a specific function, contributing to fuel efficiency and engine reliability.
The fuel pump is responsible for drawing fuel from the tank and delivering it under pressure to the engine. Fuel lines transport the fuel to the injectors, which then deliver precise amounts into the combustion chamber. The fuel filter ensures that any debris or impurities are removed from the fuel before reaching the engine, preventing damage and maintaining engine performance.
Additionally, sensors such as the fuel pressure regulator monitor and control fuel flow, helping to adjust fuel delivery according to the engine’s needs. Proper maintenance of these components ensures smooth operation and efficient fuel usage, contributing to better overall performance and reduced emissions.
Exhaust System and Parts
The system responsible for guiding emissions from the engine to the atmosphere is crucial for vehicle efficiency and environmental compliance. This section explores the components that make up the exhaust structure, focusing on their roles in reducing harmful substances and optimizing performance.
Main Components
- Exhaust Manifold: Directs gases from the engine’s cylinders to the rest of the system.
- Oxygen Sensors: Monitors the air-fuel mixture for proper combustion and ensures efficiency.
- Catalytic Converter: Transforms harmful gases into less harmful emissions before they exit the system.
- Resonator: Aids in reducing noise produced by the engine and exhaust gases.
- Muffler: Further reduces sound and noise by dissipating exhaust flow.
Maintenance and Upkeep
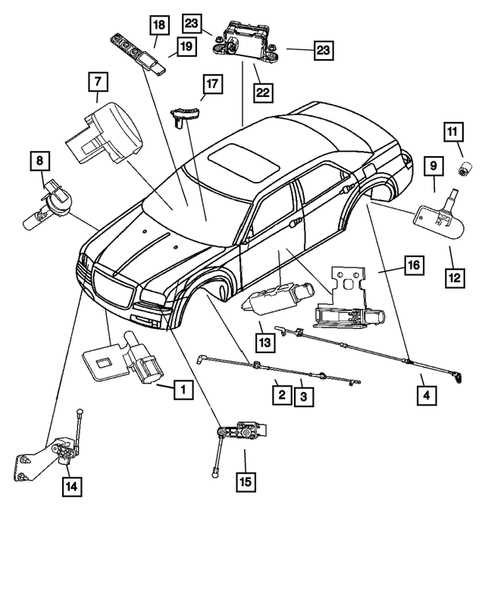
- Inspect regularly for leaks, rust, and damage to ensure optimal function.
- Replace worn components such as gaskets and seals to maintain airtight connections.
- Monitor the catalytic converter for any signs of blockage or reduced efficiency.
- Clean the system periodically to prevent carbon buildup and maintain emission standards.
Lighting and Signal Components
The lighting and signaling systems of a vehicle are essential for visibility and communication with other road users. These elements, including headlights, taillights, turn signals, and various indicators, play a vital role in ensuring safety and compliance with traffic regulations. Understanding the setup and connections of these components can assist in their maintenance and replacement when necessary.
| Component | Function | Location |
|---|---|---|
| Headlights | Provide forward illumination for night driving and poor visibility conditions. | Front of the vehicle |
| Taillights | Alert other drivers of the vehicle’s presence and intentions from behind. | Rear of the vehicle |
| Turn Signals | Indicate the driver’s intent to change direction or lane. | Front and rear corners of the vehicle |
| Brake Lights | Signal to other drivers when the vehicle is slowing down or stopping. | Rear of the vehicle |
| Fog Lights | Provide additional illumination in foggy or low-visibility conditions. | Front, near the lower bumper |
| Reverse Lights | Indicate when the vehicle is in reverse gear. | Rear of the vehicle |
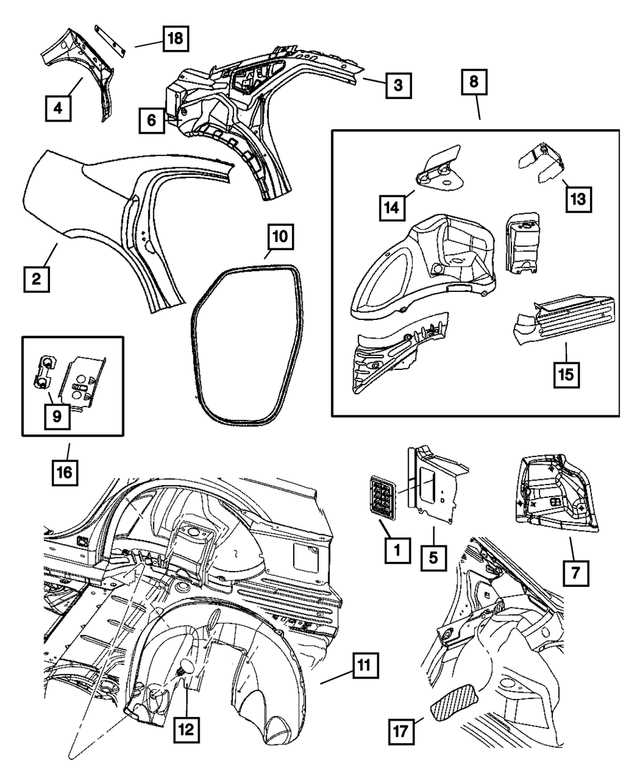
Body Structure and Panels

The framework and outer coverings of a vehicle play a crucial role in both its performance and aesthetic appeal. These components form the skeleton that supports all other parts while also contributing to the overall durability and safety of the car. The various panels, carefully designed for both function and style, offer protection from external forces and enhance the structural integrity of the entire system.
The core structure typically includes reinforced sections designed to absorb impact and protect passengers. These elements, combined with body panels such as doors, fenders, and bumpers, provide a solid barrier against the elements and potential damage. Additionally, precise design of these parts is essential for smooth aerodynamics and energy efficiency.
Each panel is strategically positioned to serve both practical and aesthetic purposes, allowing for easy access to internal mechanisms and contributing to the overall visual appeal. When damaged, these parts may need to be replaced to maintain both the safety and appearance of the vehicle.