Joy Con Components Breakdown
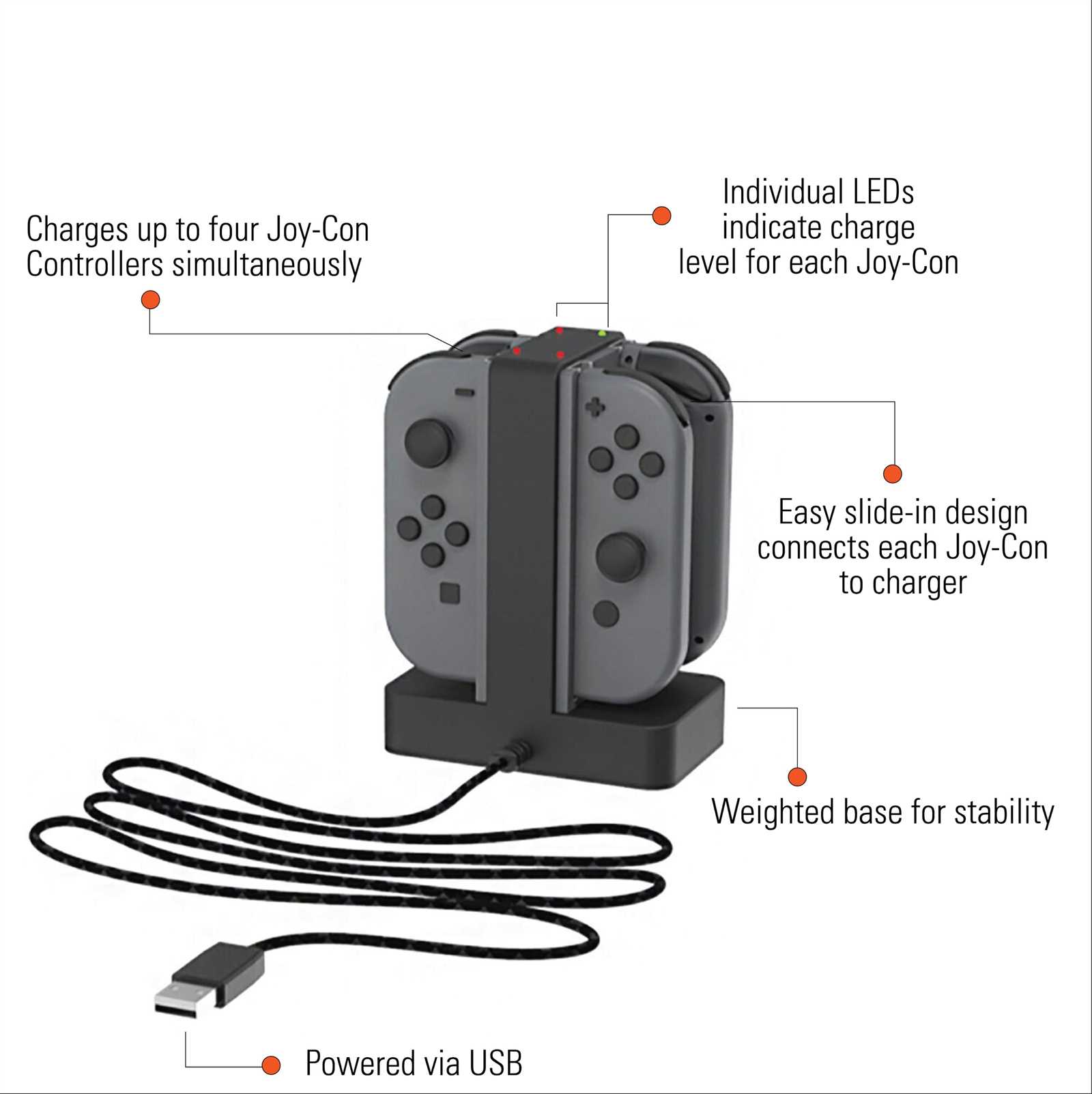

Understanding how various elements of modern controllers are constructed is crucial for ensuring smooth operation and repair. This guide provides a detailed look into the internal structure of a widely used gamepad model, highlighting each essential element without diving into unnecessary technical jargon.
Each section focuses on a specific component, providing insights into its functionality and interaction with other parts. By examining this, users can gain a deeper understanding of the mechanisms involved, which enhances troubleshooting and potential modifications.
The content is designed for users who wish to explore the inner workings of their device, with practical explanations that can guide them through repairs, adjustments, or upgrades. This breakdown will serve as a reliable reference for enthusiasts and professionals alike.
Key Elements of the Joy-Con Controller
The small handheld device designed for gaming provides intuitive control and flexibility in gameplay. This section will outline the main components that contribute to its ease of use and versatility in various gaming environments.
- Directional Controls: A set of buttons or sticks that allow for precise navigation and movement within games.
- Action Buttons: These buttons enable various in-game actions, such as jumping, shooting, or interacting with objects.
- Shoulder Triggers: Positioned on the top edges, these buttons are often used for additional commands or secondary actions in games.
- Motion Sensors: Advanced sensors detect movement, enabling motion-based interactions for a more immersive experience.
- Haptic Feedback: The vibration system provides tactile responses to in-game events, enhancing the overall gaming feel.
Exploring Internal Mechanisms of Joy-Con
The inner workings of these compact controllers reveal a complex arrangement of electronic and mechanical components that contribute to their precise functionality. By examining the internal structure, one can gain insight into how the different elements interact to deliver responsive input and motion control.
Key Components: The interior hosts several critical elements such as circuits, buttons, and motion sensors, all interconnected to provide seamless user interaction. Understanding how these pieces collaborate enhances the overall comprehension of the device’s performance.
Challenges in Maintenance: Despite the intricate assembly, maintaining or repairing these controllers can be challenging due to the delicacy of the internal elements. Proper handling is essential to avoid damaging the interconnected systems during disassembly or maintenance.
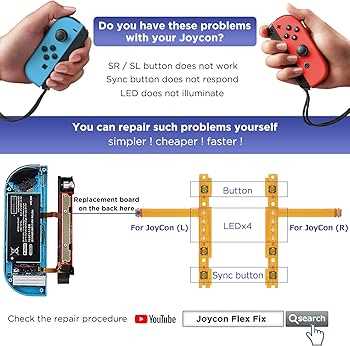
Common Issues in Joy-Con Parts
Many users experience technical difficulties with handheld controllers, especially after extended use. These problems can affect the overall gaming experience, making it crucial to understand the potential causes and solutions.
Drift and Movement Problems
One of the most frequent complaints involves unintended movements. This occurs when the joystick doesn’t properly register commands or moves on its own, disrupting gameplay.
- Wear and tear on internal components
- Accumulation of dust or debris
- Improper calibration
Button Functionality Issues
Another common issue is with buttons not responding correctly. This can result from physical damage, loss of sensitivity, or electrical malfunctions.
- Stuck or unresponsive buttons due to dirt
- Worn-out connection points inside the device
- Software miscommunication affecting inputs
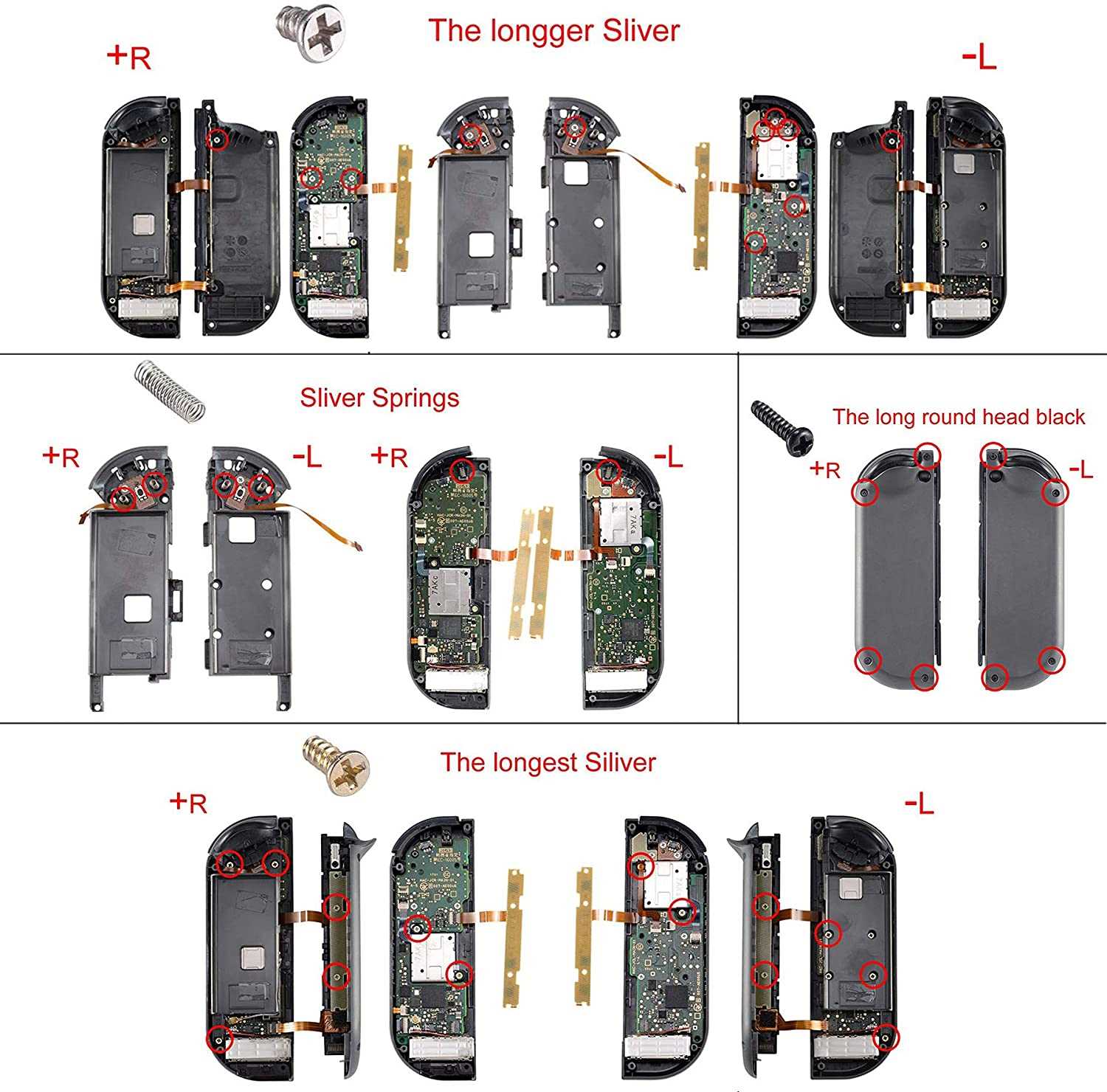
Controller Assembly and Disassembly Guide
In this guide, we will explore the process of putting together and taking apart your handheld controller. The following steps will help ensure proper handling of each component, making sure that reassembly goes smoothly after you have taken it apart for cleaning or repairs.
Preparing for Disassembly
Before starting, make sure you have the necessary tools on hand, such as a small screwdriver and a prying tool. It’s important to work carefully and patiently, as some of the internal elements can be delicate. Start with the external casing, gently removing screws and prying open the shell without applying too much pressure.
Steps for Reassembly
Once the necessary adjustments or replacements have been made, you can begin putting the controller back together. Align each section properly before securing it with screws. Take extra care to reconnect any internal wiring in the correct order, ensuring that the functionality is fully restored.
Materials Used in Joy-Con Construction

The design of modern gaming controllers involves the use of a variety of materials to ensure both durability and comfort. These devices are built to withstand extensive usage while providing an ergonomic experience for the user. The choice of materials plays a crucial role in achieving a balance between lightweight handling and structural integrity.
Commonly, high-quality plastics are used for the outer shell, providing a smooth and sturdy surface. Internally, metals like stainless steel or aluminum may be incorporated to enhance the strength of internal components, ensuring long-lasting performance. Additionally, conductive materials are applied for the electrical systems, allowing seamless interaction between the different elements within the device.
How the Joy-Con Sensors Work
The sensors integrated into the controllers provide a remarkable interaction experience, allowing for precise movements and responses during gameplay. These devices utilize advanced technology to track motion and orientation, enhancing user engagement with various applications.
Key functionalities of the sensors include:
- Accelerometer: This component detects changes in speed and direction, enabling smooth navigation and responsiveness.
- Gyroscope: By measuring rotational motion, this sensor ensures accurate tracking of orientation, contributing to immersive gameplay.
- Infrared Sensor: This feature allows for distance measurement and gesture recognition, facilitating unique gameplay mechanics.
These components work together to create a seamless interaction between the user and the system, providing feedback that enhances the overall gaming experience. Understanding how these sensors function can help users appreciate the technology behind their controllers.
Button Layout and Functions in Joy-Con
The controller features a well-thought-out arrangement of buttons designed to enhance gameplay and user experience. Understanding the layout and functions of these controls is essential for maximizing the enjoyment of interactive experiences.
Below is a breakdown of the main components and their respective purposes:
- Analog Sticks: These are used for precise movement and navigation within games, allowing for smooth control.
- Face Buttons: Each button has a specific function, often tied to actions like jumping, shooting, or interacting with game elements.
- Trigger Buttons: Located on the back, these buttons provide additional control options, typically for acceleration or aiming.
- Shoulder Buttons: Positioned at the top, these are often used for quick actions or to toggle features during gameplay.
- Home Button: This button offers access to the main menu and system settings, providing a quick way to pause or switch applications.
Familiarity with this layout not only improves gameplay efficiency but also enhances overall enjoyment and engagement with various titles.
Joystick Components and Maintenance Tips
Understanding the various elements of a control stick is essential for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. This section explores the key components that contribute to the functionality of these devices and provides practical advice for keeping them in top condition.
Key Elements of a Control Stick
- Base: The foundational structure that supports all other components.
- Cap: The top part where the user interacts, often removable for cleaning or replacement.
- Sensor Mechanism: The internal system that detects movement and translates it into input.
- Spring: Provides resistance and return functionality, ensuring the cap returns to its neutral position.
Maintenance Recommendations
- Regularly clean the cap and base with a soft cloth to remove dust and grime.
- Inspect the sensor mechanism for any signs of wear or obstruction.
- Replace springs if they show signs of weakening or damage to maintain responsiveness.
- Store the device in a cool, dry place to prevent moisture damage.
Battery and Power System Breakdown
This section provides an overview of the energy storage and distribution mechanisms that are essential for optimal functionality. Understanding these components is crucial for maintaining performance and ensuring longevity in handheld devices.
| Component | Description | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Battery | A rechargeable energy source that powers the device. | Stores and supplies electrical energy for operation. |
| Power Management Circuit | Circuitry responsible for regulating voltage and current. | Ensures stable power supply and protects components. |
| Charging Port | Interface for connecting a power source for recharging. | Facilitates the replenishment of battery energy. |
| Voltage Regulator | Device that maintains a constant output voltage. | Prevents damage from voltage fluctuations. |
Fixing Joy-Con Connection Problems
Connection issues with wireless controllers can lead to frustration during gaming sessions. Understanding the common causes and solutions is essential for restoring seamless functionality. This section outlines the steps to troubleshoot and resolve connectivity challenges, ensuring an optimal gaming experience.
| Problem | Possible Solution |
|---|---|
| Controller not responding | Ensure the controller is charged and paired with the console. Try reconnecting it through the settings menu. |
| Delayed input | Check for interference from other wireless devices. Move closer to the console to improve signal strength. |
| Frequent disconnections | Inspect for any physical damage and reset the controller by pressing the sync button. If issues persist, consider updating the console’s firmware. |
| Unresponsive buttons | Clean the controller’s surface to remove dust and debris. If necessary, perform a factory reset to restore default settings. |