Understanding the Master Cylinder Parts Diagram
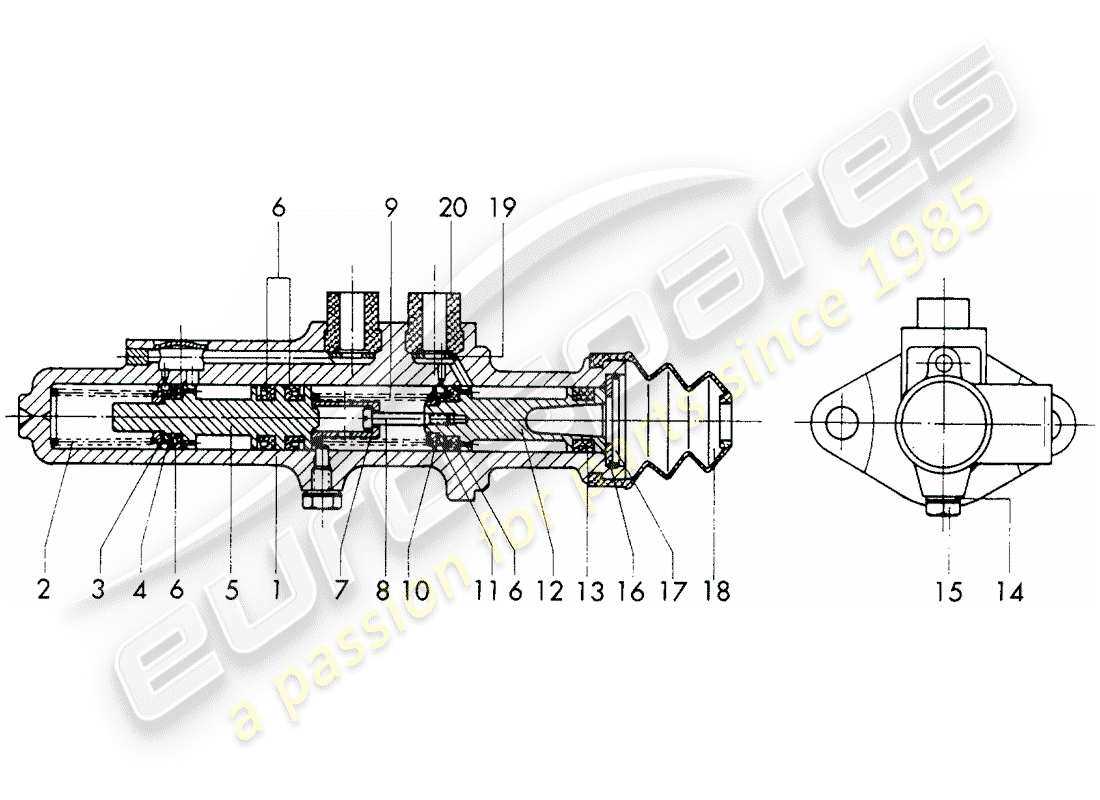
The intricate world of hydraulic systems is essential for numerous applications, ensuring smooth operation and control. By exploring the various elements that contribute to these systems, one can gain a clearer perspective on their functionality and importance in modern machinery.
Within this framework, a detailed examination of specific components reveals how each plays a critical role in the overall mechanism. Grasping the relationship between these individual elements can ultimately enhance one’s understanding of hydraulic efficiency and performance.
To facilitate this exploration, visual representations of these components can serve as valuable tools. They provide clarity and insight into how these crucial pieces interact and work together, making the learning process more intuitive and engaging.
Understanding Master Cylinder Components
In the realm of hydraulic systems, a crucial element plays a vital role in converting mechanical force into fluid pressure. This transformation is essential for the effective operation of braking systems and other hydraulic applications. A thorough comprehension of the individual elements involved is necessary for both maintenance and troubleshooting.
The primary components involved in this hydraulic mechanism include:
- Housing: This outer structure provides protection and support for internal components.
- Piston: A cylindrical piece that moves within the housing, creating pressure when force is applied.
- Reservoir: A chamber that holds fluid, ensuring a consistent supply to the system.
- Seals: Essential for preventing leaks and maintaining pressure within the unit.
- Spring: A component that aids in returning the piston to its original position after force is removed.
Understanding the function of each component is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity of the hydraulic system. Regular inspection and maintenance can prevent failures and enhance safety in operations.
Importance of Master Cylinder in Vehicles
The component responsible for initiating the braking action in automobiles plays a crucial role in vehicle safety and performance. This essential element ensures that the force applied by the driver is effectively transmitted to the braking system, enabling smooth and controlled deceleration.
Functionality and Reliability
Without this vital mechanism, the entire braking system would fail to operate efficiently. Its design allows for a seamless conversion of mechanical force into hydraulic pressure, ensuring responsiveness in various driving conditions. Regular maintenance of this system is imperative to avoid failures that could lead to serious accidents.
Key Features and Maintenance
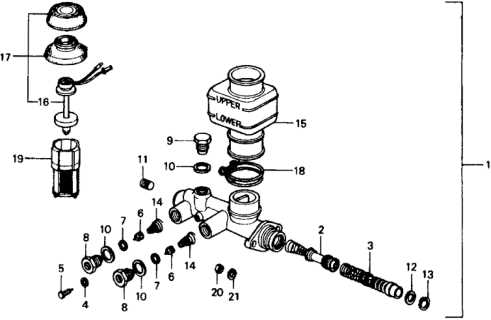
Understanding the key features of this component can help vehicle owners appreciate its significance. Proper upkeep, including regular inspections and timely replacements, ensures longevity and optimal performance. Below is a summary of the essential characteristics and maintenance tips.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Hydraulic Pressure Generation | Transforms driver input into hydraulic force for braking. |
| Sealing Mechanism | Prevents fluid leaks and maintains pressure. |
| Corrosion Resistance | Materials used are designed to resist wear and tear. |
| Maintenance Frequency | Regular checks recommended every 6 months. |
Key Parts of Master Cylinder Assembly
This section explores the essential components involved in the hydraulic assembly that plays a critical role in vehicle braking systems. Understanding these elements is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and ensuring safety during operation.
- Bore: The inner cylindrical space where hydraulic fluid is contained and pressurized.
- Piston: A movable element that generates pressure when force is applied, pushing fluid through the system.
- Reservoir: A chamber that holds the hydraulic fluid, ensuring a consistent supply for operation.
- Seals: Vital components that prevent fluid leakage and maintain pressure within the assembly.
- Push Rod: Connects the pedal to the piston, transmitting the driver’s input to the hydraulic system.
Each component plays a significant role in ensuring that the hydraulic system functions effectively, allowing for smooth and reliable braking performance.
How to Read a Parts Diagram
Understanding a schematic representation of components is crucial for effective maintenance and repairs. This guide provides insights into interpreting these visual aids, allowing users to identify and locate essential elements efficiently.
- Familiarize with Symbols: Each component is represented by unique symbols. Knowing what each symbol stands for is the first step.
- Follow the Flow: Pay attention to the direction of arrows and lines, which indicate the movement and connection between elements.
- Identify Key Components: Look for highlighted sections that denote important pieces or systems.
By applying these strategies, users can delve deeper into the functionality of the assembly and enhance their troubleshooting skills.
Common Issues with Master Cylinder Parts
Understanding the frequent problems associated with the components responsible for hydraulic braking systems can greatly enhance vehicle safety and performance. Identifying and addressing these issues early on can prevent more significant complications down the line.
Frequent Problems
- Fluid Leaks: One of the most common issues is the leakage of hydraulic fluid, which can lead to a decrease in braking efficiency.
- Air Contamination: The presence of air in the hydraulic system can result in a spongy brake feel and reduced responsiveness.
- Corrosion: Moisture exposure can cause corrosion on internal surfaces, leading to malfunctioning components.
- Worn Seals: Deteriorated seals can compromise the system’s integrity, allowing fluid to escape.
Signs of Trouble
- Unresponsive braking when pressure is applied.
- Soft or spongy brake pedal feel.
- Fluid puddles beneath the vehicle.
- Warning lights on the dashboard.
By recognizing these common issues and their signs, vehicle owners can take proactive steps to maintain optimal functionality and ensure safe driving conditions.
Maintenance Tips for Master Cylinders
Proper care and regular upkeep of hydraulic components are crucial for optimal performance and longevity. Here are some effective strategies to ensure these critical elements function smoothly.
- Regularly check fluid levels and top up with the appropriate type.
- Inspect for leaks or signs of wear, especially around seals and connections.
- Clean the exterior to prevent dirt and grime buildup, which can lead to corrosion.
- Test the system periodically for responsiveness and performance under pressure.
- Replace any damaged or worn components promptly to avoid further issues.
By following these guidelines, you can maintain optimal functionality and extend the lifespan of your hydraulic systems.
Identifying Master Cylinder Failure Symptoms
Recognizing issues within the hydraulic control unit is crucial for maintaining vehicle safety and performance. Several signs can indicate that this essential component is not functioning properly, potentially leading to serious problems with the braking system.
Decreased Brake Response: One of the primary indicators of failure is a noticeable lag when applying the brakes. If the vehicle does not respond as swiftly as expected, this may signal a malfunction.
Fluid Leaks: Inspecting the area around the hydraulic system for fluid pooling can reveal leaks. The presence of brake fluid outside the designated reservoir suggests a breach that needs immediate attention.
Spongy Pedal Feel: A pedal that feels soft or spongy during braking is a clear warning. This sensation often results from air entering the hydraulic lines or a failing mechanism that requires investigation.
Unusual Noises: Any strange sounds, such as grinding or squeaking, when engaging the brakes may indicate wear or failure in the hydraulic assembly. These noises should not be ignored.
Warning Lights: Dashboard indicators designed to alert drivers about brake system issues can illuminate when there is a problem with the hydraulic unit. Paying attention to these alerts is essential for timely maintenance.
By being aware of these symptoms, drivers can take proactive steps to address potential failures, ensuring their vehicle operates safely and effectively.
Replacement Parts for Master Cylinders
Ensuring the optimal functioning of hydraulic systems often requires the replacement of essential components. Understanding which elements can be substituted is crucial for maintaining performance and safety. This section highlights various items that can be found in these systems, enabling better repair and upkeep practices.
Common Replacement Items
When addressing wear and tear, several components frequently need to be changed. Below is a list of typical elements that may require attention:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Seals | Prevent fluid leaks and maintain pressure within the system. |
| Pistons | Control the flow of hydraulic fluid, essential for system operation. |
| Reservoirs | Store hydraulic fluid, ensuring a steady supply during operation. |
| Push Rods | Transmit force from the pedal to the hydraulic system. |
| Spring Kits | Provide necessary tension and return force for the components. |
Choosing the Right Components
Selecting suitable replacements is vital for effective repairs. Quality and compatibility are key factors that affect the overall efficiency and reliability of the system. Always consult with professionals or refer to specifications to ensure optimal performance after replacement.
Differences in Hydraulic and Mechanical Systems
Understanding the distinctions between fluid-based and traditional physical systems is essential for grasping their applications and functionalities. While both systems aim to transfer energy and control motion, they operate on fundamentally different principles that influence their design, performance, and maintenance.
Fluid-based systems utilize incompressible liquids to transmit force. This allows for smooth and precise control over movement, making them ideal for applications requiring high efficiency and responsiveness. The system’s ability to multiply force through the incompressibility of fluids often results in more powerful performance in compact designs.
In contrast, mechanical systems rely on solid components to transmit force through direct contact. These systems typically involve levers, gears, and linkages, which can be simpler in design but may require more physical space and involve greater wear and tear over time. The dependence on physical contact often leads to increased friction and decreased efficiency compared to their fluid-based counterparts.
Ultimately, the choice between fluid-based and mechanical systems depends on specific application requirements, including desired responsiveness, efficiency, and space constraints. Understanding these differences helps in selecting the most suitable system for a given task.
Tools Needed for Master Cylinder Repair
Repairing hydraulic components requires a specific set of instruments to ensure efficiency and precision. Proper tools facilitate the disassembly, inspection, and reassembly of the mechanisms involved, ultimately leading to optimal functionality and longevity.
Essential Tools
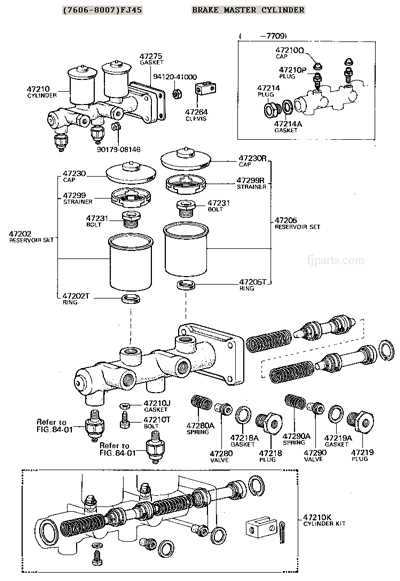
First and foremost, a wrench set is vital for loosening and tightening fittings. Additionally, a torque wrench ensures that components are secured to manufacturer specifications. A brake line wrench is also recommended for gripping and turning without stripping.
Specialized Equipment
In some cases, bleeding tools are necessary to remove air from the system, enhancing performance. A fluid transfer pump may also be required for fluid changes, while a cleaning kit helps maintain the integrity of the components throughout the process.
Step-by-Step Disassembly Guide
This section provides a comprehensive approach to safely and efficiently taking apart a hydraulic component. Proper disassembly is crucial for effective maintenance and repair, ensuring all pieces are handled with care and precision.
-
Prepare your workspace:
- Choose a clean, well-lit area.
- Gather necessary tools, such as wrenches, screwdrivers, and pliers.
- Wear safety goggles and gloves to protect yourself.
-
Depressurize the system:
- Disconnect any power source.
- Release pressure by opening the bleed valve, if applicable.
-
Remove external components:
- Detach any hoses or connections.
- Take off any brackets or covers that may obstruct access.
-
Disassemble the internal mechanisms:
- Carefully unscrew any fasteners holding the assembly together.
- Remove individual components in a systematic order to avoid confusion.
-
Inspect each part:
- Look for signs of wear, damage, or debris.
- Clean components as needed before reassembly.
By following these steps, you can ensure a thorough and organized approach to disassembling the hydraulic system, facilitating effective maintenance and repairs.
Upgrading Master Cylinder Components
Enhancing the core elements of your braking system can significantly improve performance and safety. By selecting superior components, you can achieve better responsiveness and durability, ensuring a smoother driving experience.
One of the key areas for improvement is the piston assembly. Upgrading to high-performance materials can reduce wear and enhance efficiency, resulting in a more reliable operation. Additionally, considering upgraded seals can prevent leaks and extend the lifespan of the system.
Another critical component is the reservoir. Opting for a larger or redesigned reservoir can enhance fluid capacity and reduce the risk of air intrusion. Furthermore, improving the fluid path by upgrading lines and fittings ensures optimal fluid flow, contributing to overall system performance.
Finally, don’t overlook the importance of maintenance. Regular checks and timely replacements of worn components will keep your system functioning at its best, allowing you to fully experience the ultimate benefits of these upgrades.