Exploring Plant Parts with a Comprehensive Diagram Worksheet
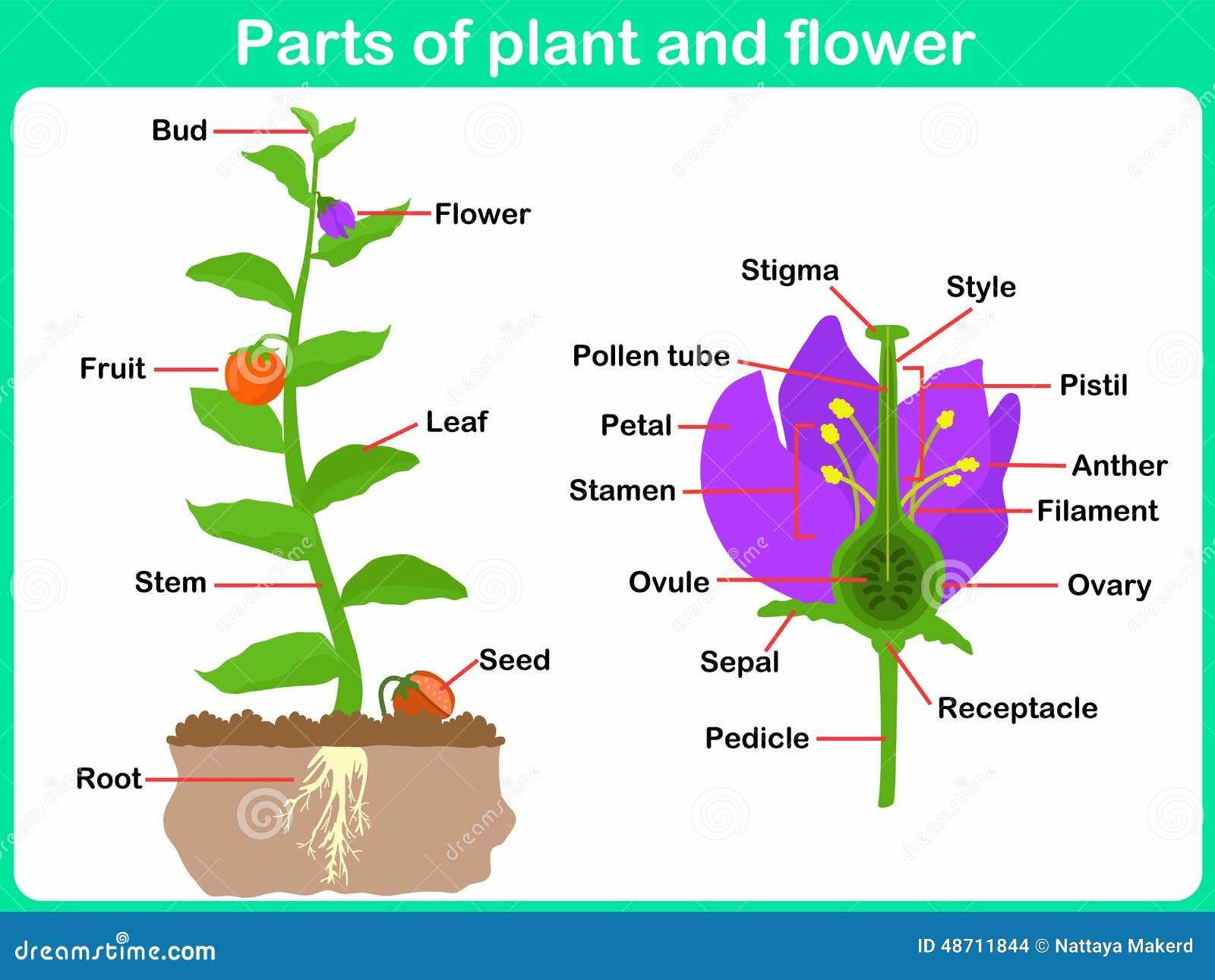
Exploring the intricate world of flora reveals a fascinating array of components, each playing a crucial role in the life cycle of a living organism. These elements work in harmony to ensure growth, reproduction, and survival in diverse environments. A comprehensive grasp of these biological entities not only enhances our appreciation of nature but also deepens our understanding of ecosystems.
In educational settings, visual representations serve as essential tools for learners to identify and comprehend the functionality of each component within a living organism. By engaging with these illustrations, students can connect theoretical knowledge with practical application, fostering a more profound interest in the study of life sciences.
Through the examination of these essential structures, one can uncover the intricate relationships and processes that sustain life. This knowledge is vital for anyone aspiring to delve into botany, horticulture, or environmental science, as it lays the groundwork for more advanced exploration and inquiry.
Understanding Plant Anatomy
The study of the structure and organization of flora reveals the intricate systems that support life. By exploring these configurations, we can appreciate the vital functions they perform in the ecosystem and their remarkable adaptations to diverse environments.
Key Components of Flora
Every organism comprises various segments, each with distinct roles. For instance, the network that anchors the organism and absorbs nutrients plays a crucial role in its overall health and stability. Similarly, the structures that capture sunlight are essential for energy conversion, facilitating growth and development.
Functionality and Interrelationships
The interconnection among different segments ensures the organism’s survival and efficiency. For example, the relationship between the nutrient-absorbing structures and the energy-capturing components exemplifies the ultimate collaboration necessary for sustaining life. Understanding these relationships is fundamental for anyone interested in the science of flora.
Importance of Plant Diagrams
Visual representations serve as crucial tools for understanding the complexities of botanical structures. By illustrating the various components of flora, these images enhance comprehension and foster a deeper appreciation of nature’s intricacies.
Facilitating Learning
Utilizing visual aids significantly improves educational outcomes. Students can grasp concepts more effectively when they can see the relationships between different elements, leading to a stronger foundation in botanical sciences.
Promoting Research and Discovery
These visuals play an essential role in scientific inquiry. They allow researchers to analyze morphology, facilitating advancements in taxonomy and ecological studies. Such insights ultimately drive the quest for sustainable practices.
Key Parts of a Plant

Understanding the essential components of a green organism is fundamental to grasping how these entities grow, reproduce, and interact with their environment. Each element plays a unique role, contributing to the overall health and functionality of the whole system.
The first element, typically found above ground, is crucial for capturing sunlight and facilitating photosynthesis. It often displays a variety of shapes and sizes, adapted to the organism’s environment. Below the surface, another vital structure anchors the organism and absorbs necessary nutrients and moisture from the soil.
A third component is responsible for reproduction, producing seeds that ensure the continuation of the species. This aspect often showcases stunning colors and intricate designs to attract pollinators. Lastly, some structures provide protection and support, maintaining the integrity and stability of the entire system.
Roots: Functions and Structure
This section explores the essential underground components that support growth and stability in various organisms. Their role is critical, encompassing multiple functions that contribute to overall health and survival.
- Anchorage: These components secure the organism in the substrate, preventing displacement by external forces.
- Nutrient Absorption: They absorb vital minerals and water from the environment, facilitating nourishment.
- Storage: Some serve as reservoirs for energy, storing carbohydrates and other nutrients for later use.
- Growth Regulation: They produce hormones that influence the development of other structures.
Structurally, these components can vary significantly. They typically consist of:
- Primary Structure: The main elongated segment that grows downward.
- Lateral Extensions: Smaller branches that increase surface area for absorption.
- Root Hairs: Microscopic extensions that enhance nutrient uptake.
Understanding these aspects provides insight into their pivotal role in the life cycle of various organisms.
Stems: Types and Purposes
In the world of greenery, the structures that rise above the ground serve crucial functions, contributing to the overall vitality of organisms. These essential components can vary significantly in form and role, each adapted to fulfill specific needs within their environment.
Types can be broadly categorized into various forms, including herbaceous, woody, and modified versions. Herbaceous structures are typically soft and green, providing flexibility, while woody varieties offer sturdiness and support. Additionally, there are specialized adaptations such as tuberous or rhizomatous types, which help in storage and reproduction.
Each type serves distinct purposes. Support is one of the primary functions, enabling organisms to reach sunlight effectively. Moreover, these structures play a vital role in nutrient transport, connecting the roots to the foliage and facilitating the flow of essential substances. Some also engage in photosynthesis, showcasing their versatility beyond mere structural support.
Leaves: Photosynthesis Role
The green structures that capture sunlight play a crucial role in transforming energy into a usable form for life. Through a remarkable process, they convert light into chemical energy, enabling various organisms to thrive and sustain themselves.
Process of Photosynthesis
This transformation involves several key steps where light energy, carbon dioxide, and water interact to produce glucose and oxygen. The overall process can be summarized as follows:
| Inputs | Outputs |
|---|---|
| Sunlight | Glucose |
| Carbon Dioxide | Oxygen |
| Water |
Importance of Photosynthesis
This process not only provides energy for growth and development but also contributes significantly to the atmosphere by releasing oxygen, making it essential for life on Earth. Understanding this function deepens our appreciation for these vital structures and their contributions to ecosystems.
Flowers: Reproductive Functions
Within the intricate world of nature, certain structures play a vital role in the continuation of species. These vibrant formations are essential for the process of reproduction, serving as the site for various crucial interactions that lead to the formation of new life. Understanding their functions unveils the complexity of these natural systems and highlights their significance in biodiversity.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Pollination | The transfer of pollen from the male to the female elements, facilitating fertilization. |
| Attraction | Bright colors and enticing fragrances draw in pollinators, enhancing reproductive success. |
| Fertilization | The union of male and female gametes, resulting in the formation of seeds. |
| Seed Development | Post-fertilization, the development of seeds occurs within protective structures. |
| Dispersal | The spreading of seeds to new locations, aiding in the establishment of new organisms. |
These essential functions ensure the survival and proliferation of diverse life forms, underscoring the remarkable adaptations that have evolved over time.
Seeds: Lifecycles and Growth
Understanding the journey from a tiny capsule to a thriving organism reveals the incredible processes of development and regeneration in nature. Each stage in this transformation plays a crucial role in the continuation of life, highlighting the intricate balance within ecosystems. This exploration delves into the stages of growth and the factors influencing their success.
Stages of Development
The lifecycle begins with a dormant entity, awaiting the right conditions for activation. Upon exposure to moisture and warmth, the seed undergoes germination, initiating the growth of roots and shoots. These early stages are critical as they establish a foundation for future development.
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Dormancy | Period of inactivity until conditions are favorable. |
| Germination | Activation of growth processes leading to sprouting. |
| Seedling | Initial growth phase with emerging roots and leaves. |
| Maturity | Fully developed organism capable of reproduction. |
Environmental Influences
Numerous external factors impact the success of these stages, including soil quality, water availability, and light exposure. Understanding these influences helps in fostering optimal conditions for healthy growth and sustainable populations, ensuring the continuation of diverse life forms.
Using Worksheets for Education
Engaging students through interactive activities is essential for effective learning. Educational resources that encourage hands-on participation can significantly enhance comprehension and retention. These tools facilitate a dynamic learning environment where students can explore concepts in a structured manner.
Benefits of utilizing educational resources include:
- Promoting active engagement and critical thinking.
- Allowing for individualized learning paths.
- Encouraging collaboration among peers.
- Providing a clear framework for assessment and feedback.
To maximize the effectiveness of these resources, educators can consider the following strategies:
- Incorporate various formats to cater to diverse learning styles.
- Use them as supplementary tools alongside traditional instruction.
- Regularly update materials to keep content relevant and stimulating.
- Encourage student input in creating or modifying resources for a sense of ownership.
In summary, the thoughtful integration of these educational tools can lead to a more vibrant and productive learning experience. By fostering interaction and exploration, educators can better equip students for future challenges.
Interactive Learning with Diagrams
Engaging learners through visual representations can significantly enhance understanding and retention of complex concepts. Interactive visuals not only facilitate better comprehension but also stimulate curiosity and creativity. By incorporating elements that allow for exploration and manipulation, educational materials can transform passive learning into an active experience.
Such approaches enable students to connect theoretical knowledge with practical applications, making the learning process more meaningful. Below is a table that highlights the benefits of using engaging visuals in educational settings.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Engagement | Visual tools capture attention and motivate learners to explore topics more deeply. |
| Improved Retention | Interactive elements reinforce memory by allowing learners to actively participate. |
| Facilitated Understanding | Complex ideas become clearer through visual aids, helping students grasp difficult concepts. |
| Encouraged Collaboration | Group activities involving visuals promote teamwork and communication among peers. |
Ultimately, integrating interactive visuals into learning experiences empowers individuals to take charge of their education, paving the way for a more profound understanding of various subjects.
Benefits of Visual Learning
Visual learning engages the mind by incorporating imagery, enhancing understanding and retention. This approach allows individuals to grasp complex concepts quickly and fosters creativity by providing a unique perspective on information. Through the use of graphics and illustrations, learners can connect ideas more effectively, leading to deeper comprehension.
Enhanced Memory Retention
Utilizing visual elements significantly boosts memory retention. When information is presented visually, it becomes easier to recall, as the brain processes images more efficiently than text alone. This can be particularly beneficial in educational settings, where students can better remember facts and figures through diagrams and charts.
Improved Engagement
Visual learning captivates attention and keeps learners engaged. By incorporating various visual stimuli, such as videos and infographics, educators can create a dynamic learning environment that motivates students to participate actively. This engagement not only enhances interest but also promotes a collaborative atmosphere among learners.
Creating Your Own Plant Diagrams
Designing your own visual representations of botanical structures can be an enriching experience. This creative process not only enhances your understanding but also allows you to engage more deeply with nature. By illustrating various elements, you can develop a unique perspective on how they function together in a living organism.
Steps to Create Your Illustrations
- Choose a specific organism to study.
- Research the various components and their functions.
- Gather materials for your artistic representation, such as paper, colored pencils, or digital tools.
- Sketch a basic outline, ensuring to label each element clearly.
- Add details and color to enhance understanding and visual appeal.
Tips for Effective Visual Representation
- Use clear labels to avoid confusion.
- Incorporate different colors to differentiate between components.
- Consider including a legend or key for better clarity.
- Experiment with different artistic styles to find what resonates with you.
- Share your creations with others to gain feedback and insights.
Common Mistakes in Plant Identification
Identifying flora can be a rewarding yet challenging task. Many enthusiasts, from novices to experienced botanists, often encounter pitfalls that lead to incorrect conclusions. Understanding these common errors can enhance one’s observational skills and ensure more accurate classifications.
Overlooking Key Characteristics
One of the primary errors involves failing to consider essential traits. Relying solely on superficial features may result in misidentification. For instance, leaf shape, flower color, and growth habit are often emphasized, while critical aspects like habitat, seasonality, and reproductive structures are neglected.
Misinterpreting Similar Species
Another frequent mistake is confusing closely related varieties. Certain species exhibit minor differences that can be challenging to discern without a thorough examination. This can lead to assumptions that overlook vital distinguishing features. Here’s a comparison table to illustrate some commonly confused varieties:
| Species | Key Characteristics | Common Confusions |
|---|---|---|
| Species A | Broad leaves, yellow flowers | Often mistaken for Species B |
| Species B | Narrow leaves, yellow flowers | Similar to Species A in appearance |
| Species C | Small leaves, blue flowers | Frequently confused with Species D |
| Species D | Small leaves, purple flowers | Visual similarities to Species C |
Awareness of these mistakes fosters a more informed approach to recognizing various forms of life, ultimately leading to greater appreciation and understanding of biodiversity.