Understanding the Components of Bike Brake Levers
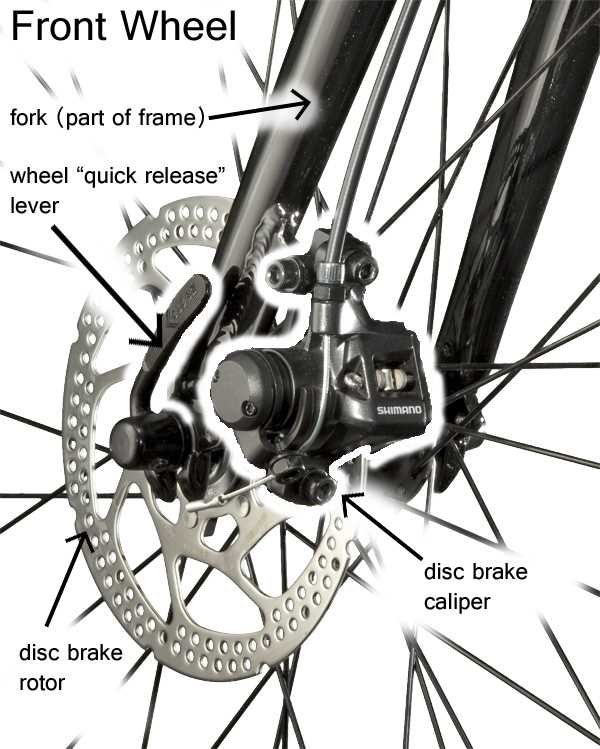
In the world of two-wheeled transport, the ability to effectively manage speed and ensure safety is paramount. The control systems that allow riders to execute such maneuvers are intricate assemblies, designed to provide both functionality and comfort. Each component plays a vital role in the overall performance and reliability of these systems.
Analyzing the structure reveals how different elements interact to create a seamless experience for the user. The integration of mechanical components ensures that the rider can respond swiftly to various conditions encountered on the road. Understanding the configuration and function of these elements can greatly enhance both performance and safety.
Moreover, comprehending the assembly of these systems allows for better maintenance and potential upgrades. With a clear grasp of how each piece contributes to the whole, enthusiasts and regular users alike can make informed decisions, leading to improved handling and durability of their equipment.
Understanding the functionality of these mechanisms is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and safety. Each component plays a significant role in the overall system, contributing to the efficiency and responsiveness of the equipment.
- Components Overview
- Examine each element that comprises the mechanism.
- Identify materials used in construction and their impact on durability.
- Discuss variations in design across different models.
- Functionality
- Analyze how each element interacts with others.
- Explore the mechanics behind activation and force transmission.
- Discuss common issues and troubleshooting methods.
- Maintenance and Care
- Provide tips for cleaning and lubricating components.
- Outline inspection routines for longevity.
- Recommend replacement timelines for various elements.
Components of a Brake Lever
Understanding the individual elements of a stopping mechanism is crucial for effective maintenance and performance. Each component plays a significant role in ensuring smooth operation and safety. Below are the primary components that contribute to the overall functionality of this essential device.
- Handle: The portion that the user grips, providing leverage and control.
- Pivot Point: A crucial fulcrum around which the handle moves, affecting the force applied.
- Spring: Responsible for returning the handle to its original position after being engaged.
- Cable Housing: The protective casing that guides the cable to prevent damage and ensure smooth movement.
- Cable: Transmits the force from the handle to the stopping mechanism, crucial for effective engagement.
- Adjustment Screw: Allows for fine-tuning of the handle’s position and responsiveness, enhancing user control.
- Mounting Bracket: Secures the assembly to the main frame, ensuring stability during operation.
Each of these components works together to provide reliable functionality, enhancing the overall experience of the user. Regular inspection and maintenance of these elements can greatly improve safety and performance.
Types of Brake Levers
When it comes to controlling the stopping mechanism of a two-wheeled vehicle, various styles of actuators are designed to cater to different riding experiences and preferences. Each variant offers unique features that enhance functionality and comfort, ensuring optimal performance under various conditions.
Common Variants
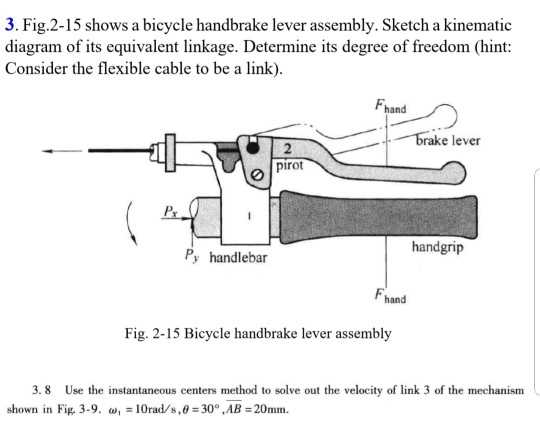
- Short Pull: Ideal for road applications, this type is designed to work with specific calipers that require minimal pulling distance.
- Long Pull: Typically used in conjunction with wider rim brakes, this style provides more leverage for improved stopping power.
- Dual Control: Combining shifting and stopping mechanisms, this variant allows for seamless gear changes and deceleration without changing hand position.
Specialized Designs
- Mountain Style: Engineered for off-road use, these are often more robust to handle rough terrains and provide enhanced grip.
- Ergonomic Models: Focused on rider comfort, these are shaped to fit the hand more naturally, reducing fatigue during extended rides.
- Electronic Variants: Utilizing technology, these models offer precise control through electronic signals, enhancing response time and consistency.
Functionality of Each Component
The efficiency and safety of a stopping mechanism depend significantly on the interaction and roles of its various elements. Understanding how each component contributes to the overall performance is crucial for maintenance and optimization. Each element plays a distinct role, working together to ensure reliable and responsive action when needed.
Primary Mechanism
The central mechanism serves as the heart of the system, converting the user’s input into the necessary force. This component translates motion into a powerful reaction, facilitating smooth operation. Its design is engineered to maximize leverage while minimizing resistance, ensuring optimal functionality under different conditions.
Connecting Elements
The connecting elements link the primary mechanism to other components, enabling the transfer of force and movement. These elements are designed for durability, withstanding repetitive stress while maintaining flexibility. Their precision in alignment and material quality is vital for a seamless response, enhancing overall control and stability.
Common Materials Used
In the construction of various control mechanisms for cycles, the selection of materials plays a crucial role in ensuring performance and durability. Understanding the characteristics of commonly utilized substances can aid in selecting the best components for specific requirements.
The following table outlines the typical materials employed in the fabrication of these controls, along with their key properties:
| Material | Properties |
|---|---|
| Aluminum | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, good strength-to-weight ratio |
| Plastic | Light, cost-effective, available in various colors, moderate strength |
| Steel | High strength, durable, prone to rusting if not treated |
| Carbon Fiber | Extremely lightweight, very strong, high cost |
| Rubber | Excellent grip, vibration-dampening properties, weather-resistant |
Each of these materials offers distinct advantages, influencing the functionality and longevity of the components they comprise. Selecting the appropriate substance is vital for achieving optimal performance in various riding conditions.
Assembly Process Overview
This section provides a comprehensive look at the steps involved in the assembly of a crucial component used for controlling speed and stopping in various two-wheeled vehicles. Understanding the process enhances the ability to maintain, troubleshoot, and optimize the performance of this essential mechanism.
Initial Preparation
Before beginning assembly, it is vital to gather all necessary components and tools. Each element should be inspected for quality and compatibility to ensure a smooth integration process. Proper organization of these items minimizes errors and accelerates the workflow.
Step-by-Step Assembly
The assembly procedure involves several key actions, starting with the alignment of primary components followed by securing them using appropriate fastening methods. Lubrication of moving parts is crucial to enhance functionality and prolong lifespan. Finally, a thorough testing phase ensures that the assembly meets safety standards and performs efficiently under various conditions.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
To ensure optimal performance and extend the lifespan of your stopping mechanism, regular upkeep is essential. By following a few straightforward practices, you can maintain efficiency and prevent unnecessary wear and tear.
Regular Cleaning
Keeping all components free from dirt and debris is vital. Utilize a soft cloth and gentle cleaning solution to remove grime from surfaces. Pay particular attention to any movable elements, ensuring they operate smoothly without obstruction.
Lubrication
Applying appropriate lubricants to pivot points and other friction areas enhances functionality. Use a lubricant designed for mechanical applications, and avoid over-application, as excess can attract dirt. Regularly check for signs of corrosion and address any issues promptly to maintain optimal operation.
By implementing these practices, you can significantly enhance the durability of your stopping system and ensure a safer riding experience.
Identifying Wear and Tear
Understanding the signs of deterioration is crucial for maintaining optimal functionality and safety in any mechanical system. Regular inspection can help ensure that components remain in good condition, preventing potential failures and enhancing overall performance.
Signs of Degradation
Look for visible indicators that suggest components may be losing their integrity. Cracks, fraying, or unusual wear patterns can signify that elements are approaching the end of their operational lifespan. Additionally, any noticeable increase in friction or unusual sounds during use may indicate a need for further examination.
Regular Maintenance Checks
Implementing routine assessments is essential for early detection of issues. Cleaning and lubricating can help extend the life of components and improve efficiency. Keeping an eye on specific metrics, such as response time and force application, can also provide insight into the condition of the system.
Brake Lever Adjustment Techniques
Proper alignment and tuning of the control mechanism are crucial for optimal performance and safety. By adjusting the setup, users can enhance the response and comfort while ensuring efficient operation. This section covers essential methods to achieve the desired configuration for better handling and effectiveness.
Common Adjustment Methods
There are several techniques to modify the setup for improved functionality. Here are some widely used approaches:
- Fine-tuning the reach for easier access.
- Modifying the angle to suit the rider’s preference.
- Adjusting the tension to achieve a suitable feel during operation.
- Aligning the mechanism to ensure smooth engagement and disengagement.
Steps for Effective Adjustment
Follow these steps to properly adjust the control system:
- Start by loosening the securing screws.
- Adjust the reach to fit your hand comfortably.
- Alter the angle to optimize your grip position.
- Tighten the screws securely once adjustments are made.
- Test the setup in a safe environment to ensure functionality.
Implementing these techniques will lead to a more enjoyable and safer experience during use.
Tools Required for Repairs
Proper maintenance and repair of control mechanisms necessitate a specific set of instruments. Having the right tools not only simplifies the process but also ensures precision and safety during adjustments or replacements. This section outlines the essential equipment needed for effective repairs.
Essential Instruments

- Wrench Set
- Screwdriver Set (flathead and Phillips)
- Torque Wrench
- Pliers
- Hex Key Set
- Utility Knife
Additional Supplies
- Lubricant (for smooth operation)
- Cleaning Cloths
- Replacement Hardware (screws, nuts, bolts)
- Protective Gear (gloves, goggles)
Equipping yourself with these tools will significantly enhance the efficiency of the repair tasks. Regular maintenance is key to prolonging the lifespan of components and ensuring optimal performance.
Impact on Bike Performance
The efficiency of stopping mechanisms significantly influences overall cycling experience and safety. Proper functionality and responsiveness of these systems ensure that riders can control their speed and come to a halt when necessary, impacting their confidence and performance on various terrains.
Key factors that contribute to the effectiveness of these systems include the design, material quality, and ergonomic considerations. When these elements work harmoniously, they allow for smoother operation and enhanced grip, which directly translates to better handling and maneuverability.
Moreover, maintenance plays a crucial role in sustaining optimal performance. Regular inspections and timely adjustments can prevent issues that might lead to reduced efficiency or even failure. This proactive approach not only prolongs the lifespan of the components but also ensures safety during rides.
Ultimately, the quality of stopping systems can elevate a rider’s experience, making it essential for enthusiasts to understand their significance and invest in high-quality equipment.
Upgrading Your Brake System
Enhancing your stopping mechanism can significantly improve performance and safety. Whether for racing or everyday use, investing in superior components can lead to better responsiveness and control. This section explores options and considerations for upgrading your stopping system.
When contemplating an enhancement, evaluate the existing assembly to identify areas for improvement. Factors to consider include the type of hydraulic or mechanical setup, the materials used, and the overall efficiency of the current configuration.
Here are some key upgrades to consider:
| Upgrade Type | Description |
|---|---|
| High-Performance Calipers | These offer improved clamping force and weight savings, enhancing overall stopping power. |
| Upgraded Cables | Opt for cables that reduce friction and improve response times, leading to a more direct feel. |
| Advanced Rotors | Consider lightweight or slotted versions that provide better heat dissipation and improved grip. |
| Lever Ratio Adjustments | Changing the ratio can lead to increased modulation and control, providing a custom feel. |
Investing in these enhancements not only boosts performance but can also enhance safety and confidence during use. Evaluate each option based on personal riding style and requirements.