Understanding the Components of a Bike Disc Brake Parts Diagram
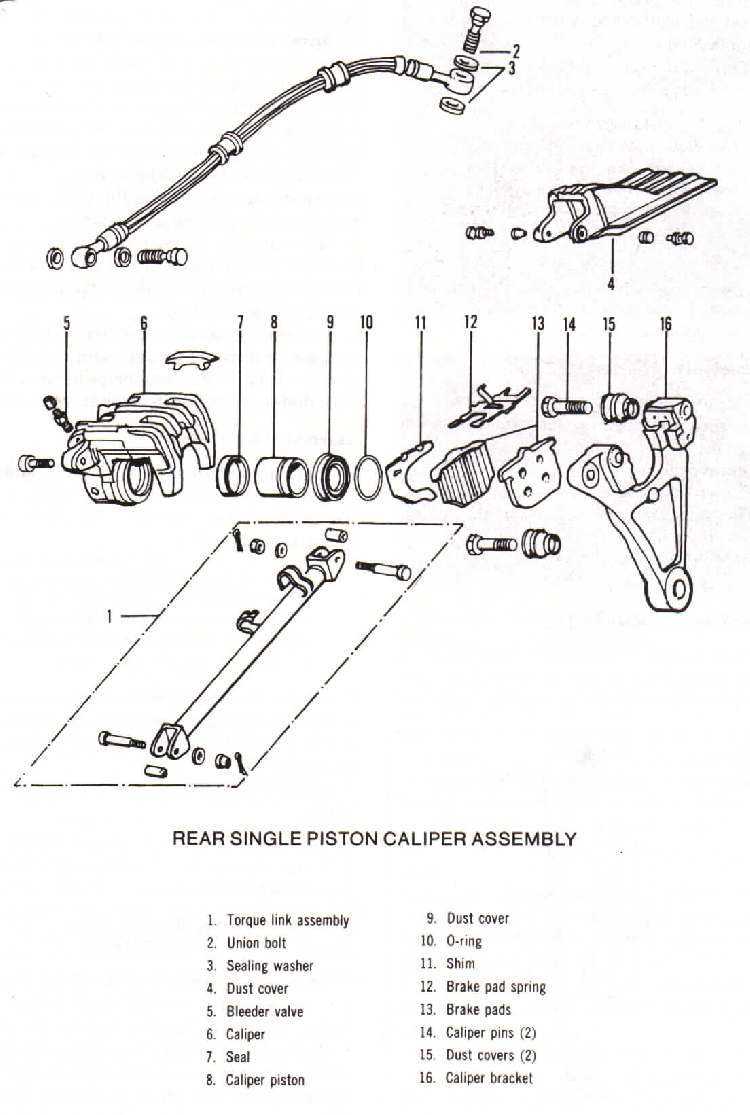
In the world of two-wheeled vehicles, the mechanism responsible for halting movement plays a critical role in ensuring safety and performance. A comprehensive overview of this intricate assembly allows enthusiasts and mechanics alike to appreciate the engineering behind effective deceleration. By exploring its various elements, one can gain insight into how each contributes to the overall functionality.
Every aspect of this stopping system serves a purpose, from the main actuator to the auxiliary elements that enhance efficiency. The interplay between these components highlights the necessity for precision and durability, ensuring riders can trust their equipment in various conditions. By understanding how they work together, one can delve into the ultimate mechanics of stopping power.
Whether for maintenance or upgrade purposes, knowledge of these key elements empowers users to make informed decisions. This exploration not only aids in better performance but also promotes a deeper connection to the vehicle itself, transforming how one engages with the riding experience.
Understanding Bike Disc Brake Functionality
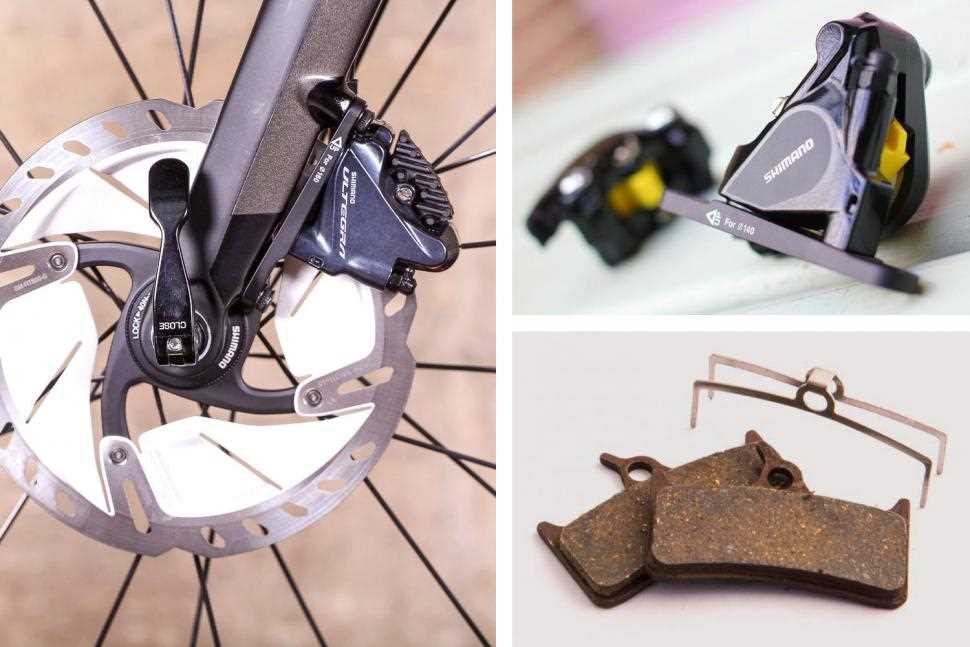

Efficient stopping power is crucial for maintaining control and safety while cycling. The system responsible for this ensures a reliable way to slow down or halt, especially during high-speed descents or wet conditions. By converting the motion into controlled friction, the mechanism provides a smooth and responsive experience when handling various terrains.
Key Components Overview
The entire system includes several interconnected elements that work together harmoniously. These elements must be properly aligned and maintained to ensure optimal performance during usage. The positioning of the key elements ensures that force is evenly distributed, providing a balanced and secure grip.
Mechanism and Force Distribution
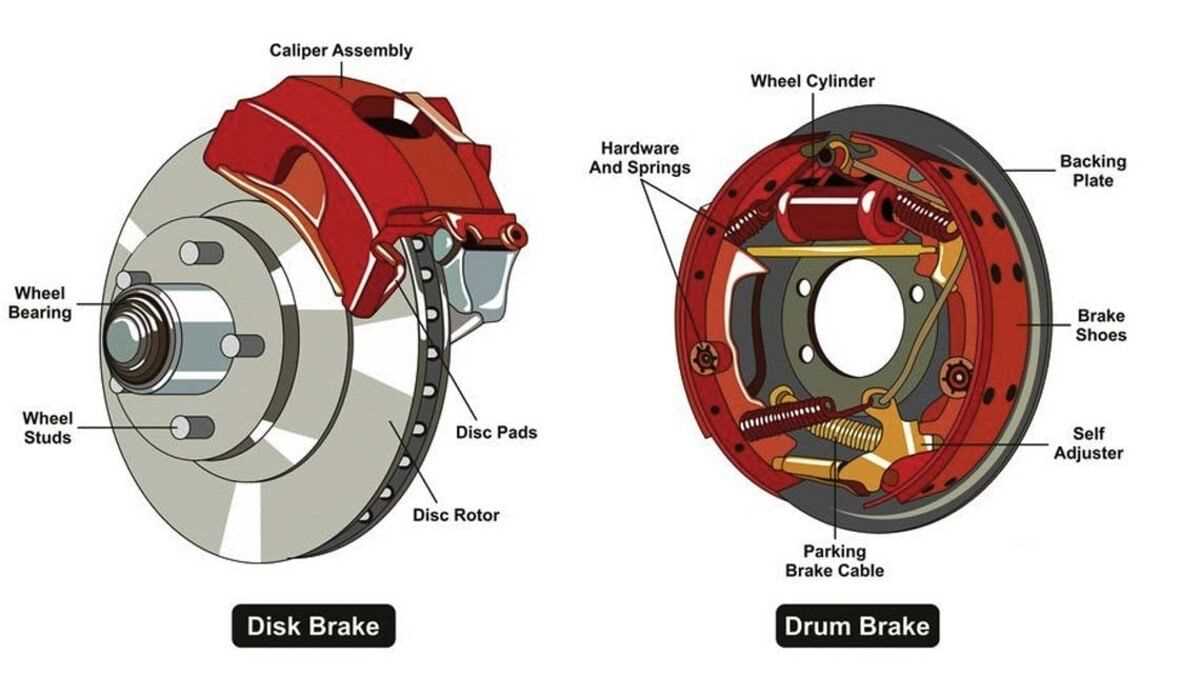
The system’s core function is based on transferring pressure from the user’s action into a controlled response. This pressure activates the key elements, which in turn generate the necessary friction for deceleration. The efficient distribution of force guarantees smooth operation and minimizes wear.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Levers | Transmit the rider’s input to the system. |
| Friction Surfaces | Create the necessary resistance for slowing down. |
| Fastening Elements | Hold the entire setup securely in place. |
Key Components of Disc Brake Systems
The system responsible for halting motion consists of several interconnected elements, each playing a vital role in ensuring smooth and reliable performance. These elements work in harmony to convert kinetic energy into heat, providing consistent control during deceleration. Understanding the individual roles of these elements helps to maintain and optimize overall functionality.
Rotating Mechanism: The central piece that directly interacts with the stopping force, providing the surface area needed to manage heat and friction.
Friction Pads: These pieces press against the rotating mechanism to create the necessary resistance. Their material and positioning ensure that slowing down is effective and efficient.
Caliper Assembly: This component holds the pads in place and applies the necessary pressure, often controlled hydraulically or mechanically, to ensure the right amount of force is applied.
Fluid Pathway: In systems where hydraulic action is used, this pathway transfers force from the control lever to the caliper, providing smooth and responsive action.
Levers and Cables: These parts transmit the rider’s input into mechanical or hydraulic force, ensuring the system responds to the command to slow down.
How Disc Brakes Work in Bicycles
Stopping power in modern two-wheelers relies on a mechanism that uses friction to control speed. This system operates by transferring force from the handle to a rotating component attached to the wheel, generating resistance and slowing down the rider. The efficiency of this process depends on the interaction between the gripping parts and the rotating surface.
When you pull the lever, the force activates a system that tightens components around the moving surface. This action creates friction, which in turn reduces the rotation speed, allowing the cyclist to stop smoothly. The effectiveness of this method relies on the precision of how the parts fit and respond to each other.
Heat management is essential in this system, as the friction generates high temperatures during use. Good ventilation and material quality ensure the setup works efficiently without losing performance due to overheating or wear. Proper maintenance and alignment are critical for achieving consistent, safe performance.
Types of Bike Disc Brake Designs

There are various designs used in modern two-wheeler stopping systems, each offering distinct advantages depending on the conditions and intended use. These designs are created to provide smooth and reliable performance while ensuring maximum control over speed adjustments during rides.
Mechanical Systems

Mechanical designs rely on a cable system to engage the components, pulling them into contact to create friction. These systems are known for their simplicity and ease of maintenance, making them a popular choice for many cyclists.
Hydraulic Systems
Hydraulic designs, on the other hand, use fluid pressure to transmit force, offering more consistent and powerful performance. This type provides greater modulation, meaning it allows finer control over speed reduction, especially on steep terrains or in wet conditions.
Materials Used in Brake Components
The efficiency and longevity of modern stopping systems depend heavily on the materials chosen for each part. Manufacturers utilize a range of substances that offer specific advantages in terms of durability, heat resistance, and overall performance. These components are designed to withstand high levels of friction and wear, ensuring reliable function under various conditions.
Metals such as steel and aluminum are commonly selected for their strength and resilience. Steel provides excellent durability and can handle extreme stress, while aluminum offers a lighter alternative without compromising structural integrity.
Composites also play a crucial role, particularly in areas where weight reduction and heat dissipation are essential. These materials, often combining fibers with resins, enhance the balance between performance and endurance.
In addition, ceramics have gained popularity for their superior ability to manage heat, making them ideal for high-performance systems. Their non-metallic nature allows for exceptional thermal management, reducing the risk of overheating and ensuring consistent operation over time.
Common Issues with Disc Brakes

Mechanical components responsible for stopping a vehicle can sometimes encounter problems that affect their overall performance. These issues often lead to a decrease in efficiency or even complete malfunction, which could result in unsafe riding conditions. Understanding common concerns and troubleshooting steps can help maintain proper functionality and extend the lifespan of these systems.
Noise During Operation
One of the most frequent issues involves unusual sounds when engaging the stopping mechanism. This can be caused by several factors, such as contamination, improper alignment, or worn-out components. Addressing the root cause of the noise is crucial to ensure smooth operation.
- Check for dirt or oil on the stopping surfaces.
- Realign the system if necessary to avoid uneven contact.
- Replace any worn elements that could be causing friction.
Reduced Efficiency
Over time, the stopping power may diminish due to wear or improper adjustment. This can result in a longer stopping distance or less reliable performance, particularly in challenging conditions.
- Inspect for uneven wear or thinning of components.
- Ensure that all mechanisms are properly adjusted for optimal performance.
- Replace elements that are no longer functioning as intended.
Maintenance Tips for Disc Brakes
Keeping your stopping system in top condition is essential for both performance and safety. Regular care ensures smooth operation and extends the lifespan of key components. It’s important to follow a few simple steps to prevent issues that can affect the overall efficiency of your system.
Clean Regularly
One of the most important maintenance tasks is keeping the components free from dirt and debris. After rides, use a gentle cleaner to remove grime that may accumulate. Avoid harsh chemicals that could damage sensitive areas. A clean system helps maintain responsiveness and reduces wear.
Inspect and Adjust
Periodically checking the alignment and wear levels can prevent bigger problems. Look for any uneven wear or misalignment in the system. If necessary, make small adjustments to keep everything properly aligned. Regular inspection helps catch potential issues early and ensures the system works efficiently.
Upgrading Your Disc Brake System
Enhancing your stopping mechanism can significantly improve both performance and control, especially in challenging conditions. Upgrades are often sought to increase reliability, power, and consistency when managing speed. With the right components, you can enjoy smoother operation, quicker response, and a longer-lasting system. These improvements are not only about adding power, but also about gaining confidence in your equipment, ensuring better handling on diverse terrains.
Choosing the Right Components is crucial when considering an upgrade. High-quality rotors, calipers, and levers can elevate the overall performance. It’s important to select parts that match your needs, whether you’re focusing on everyday reliability or tackling more demanding rides. Precision and durability are key factors in these decisions.
Installation Tips and Maintenance should also be considered when upgrading. A proper fit and regular care will ensure that your system operates at its best. Clean installation, paired with regular checks for wear and tear, will maximize the longevity of your new components, keeping you in control.
Choosing the Right Brake Pads
When selecting new pads for your vehicle, it’s essential to consider the riding conditions and personal preferences. The quality of the material affects both performance and durability, offering different experiences depending on the weather, terrain, and speed. Different compositions can provide either smoother or more aggressive stopping power, catering to various styles.
| Pad Material | Performance | Durability |
|---|---|---|
| Organic | Smoother, quieter stopping | Wears faster in wet conditions |
| Semi-Metallic | Balance between smooth and aggressive | Moderate wear, good in mixed conditions |
| Sintered | More aggressive stopping | Highly durable in wet and dry conditions |
Understanding these differences will help ensure you choose the right pads that meet your specific riding needs, ensuring safety and control across various environments.
Brake Rotor Variations Explained
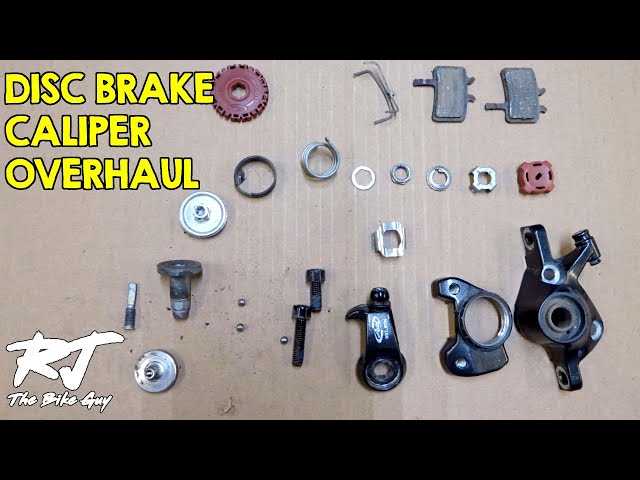

Rotors come in a range of styles and designs, each crafted to meet different performance needs. The differences lie in the shape, material, and size, which affect how the component handles heat, wear, and overall performance. Understanding these variations helps in selecting the right option for specific riding conditions and terrain.
- Size Variations: Larger options provide more stopping power and heat dissipation, while smaller ones offer a lighter weight and faster acceleration.
- Material Choices: Steel is common for durability, but lighter alloys or composite options can be used for performance-focused designs.
- Shape and Cutouts: Some models feature cutouts to reduce weight and improve cooling, while others have solid designs for more strength in demanding conditions.
Each of these factors influences how a rider experiences handling, control, and safety. By considering these variations, it’s easier to find the most suitable option for different uses and environments.
Impact of Weather on Brake Performance
Weather conditions play a crucial role in the effectiveness of stopping mechanisms. Variations in temperature, humidity, and precipitation can significantly influence how these systems function. Understanding these factors is essential for maintaining safety and performance.
In wet or rainy conditions, the presence of moisture can lead to reduced friction between components, making it more difficult to achieve the desired stopping force. This reduction in grip can result in longer stopping distances and compromised control. Similarly, when temperatures drop, materials may become less flexible, further affecting responsiveness.
On the other hand, extreme heat can lead to overheating, causing components to wear down more quickly or even fade, diminishing overall effectiveness. Moreover, dirt and debris can accumulate, especially in harsh environments, obstructing proper function and potentially leading to malfunctions. Regular maintenance and adjustments are necessary to ensure optimal performance regardless of external conditions.
Brake Adjustment Techniques for Riders
Proper modification of stopping mechanisms is essential for enhancing safety and performance while cycling. Riders should be familiar with various methods to ensure their stopping systems are functioning optimally. Regular adjustments can lead to improved control and responsiveness during rides.
Understanding the Basics
Before diving into specific techniques, it’s crucial to comprehend the fundamentals of how these mechanisms operate. Riders should consider the following:
- Familiarize yourself with the components involved.
- Recognize the importance of alignment for effective operation.
- Understand the impact of wear and tear on performance.
Adjustment Techniques
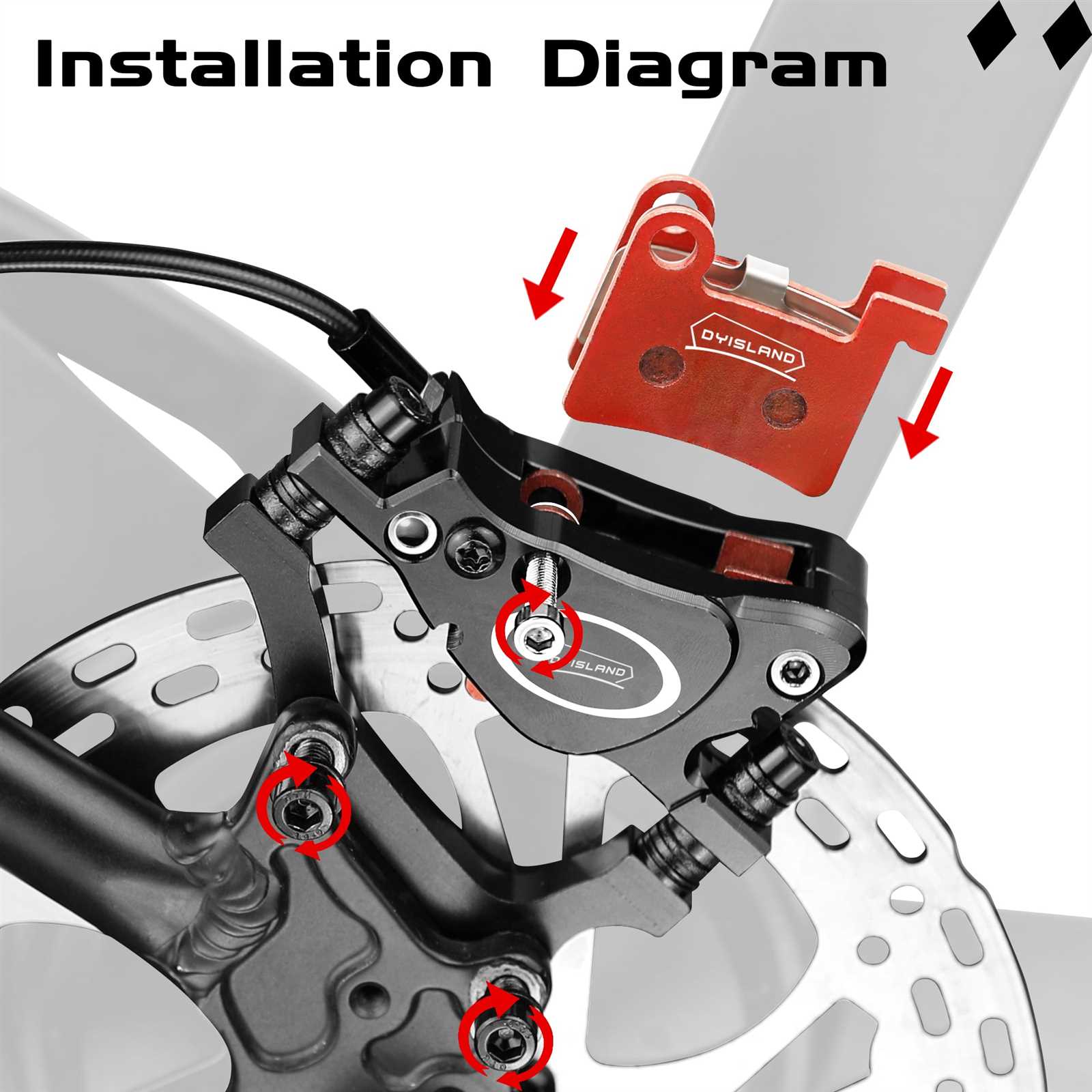
There are several methods to enhance the functionality of the stopping mechanisms. Here are some effective approaches:
- Checking Alignment: Ensure that the components are properly aligned to prevent uneven wear.
- Lever Reach Adjustment: Adjust the distance of the lever to suit personal comfort and accessibility.
- Fluid Level Maintenance: Regularly check and maintain the hydraulic fluid to ensure consistent pressure.
- Cleaning Components: Periodically clean the surfaces to remove debris that may affect performance.
- Inspecting for Damage: Regularly check for any signs of damage or wear that may require replacement.
By mastering these adjustment techniques, riders can significantly enhance their cycling experience, ensuring safety and improved performance on various terrains.
Disc Brake vs. Rim Brake Comparison
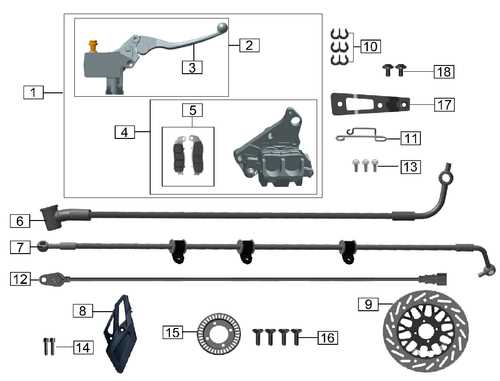
This section explores the differences between two popular stopping systems used in cycling. Each system has its unique features, advantages, and disadvantages that cater to various riding styles and conditions.
| Feature | Rotary Stopping Mechanism | Edge Stopping Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| Performance in Wet Conditions | Better performance, less affected by moisture | Can lose effectiveness when wet |
| Maintenance | Requires periodic adjustment | Generally lower maintenance needs |
| Weight | Usually heavier | Lighter overall |
| Heat Dissipation | Superior cooling, reducing fade | May overheat during prolonged use |
| Installation Complexity | More complex installation process | Easier to install and replace |