Essential Bike Parts and Their Names Explained
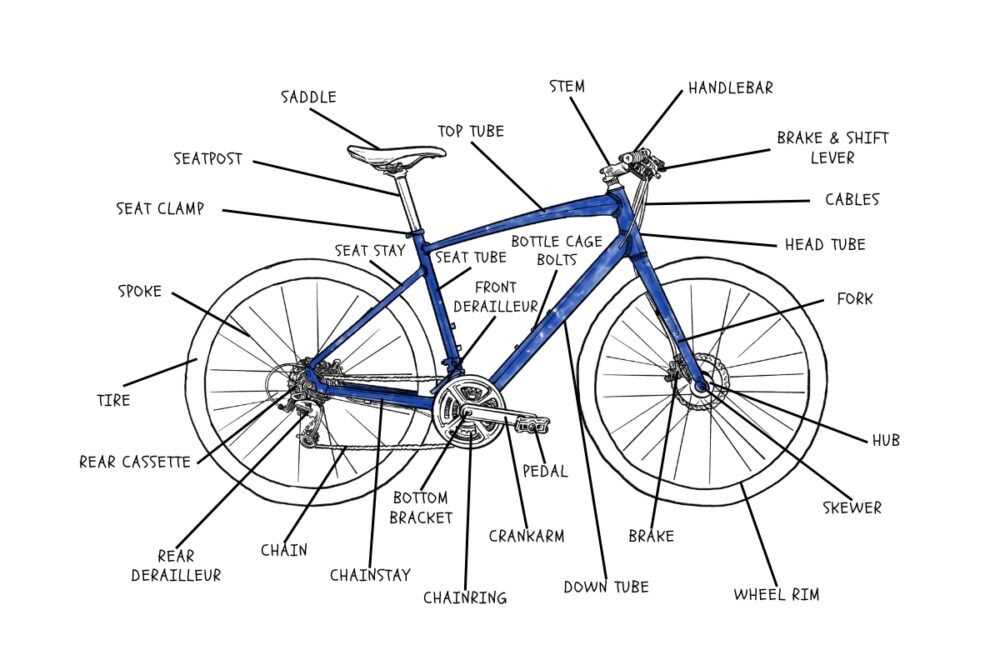
In the realm of cycling, every enthusiast knows that the functionality and performance of a ride are deeply intertwined with its various components. A thorough comprehension of these elements not only enhances the overall experience but also empowers riders to make informed choices regarding maintenance and upgrades.
Exploring the intricate relationships between each element reveals the engineering marvels that enable smooth travel and efficiency. From the frame that provides structure to the intricate systems that facilitate movement, each segment plays a vital role in the overall design.
By delving into the intricate details of these components, cyclists can better appreciate the art and science of their machines. Whether it’s understanding how each piece contributes to balance or recognizing the importance of precision in performance, gaining insight into this mechanical world is essential for every rider aiming for excellence.
Understanding the Bicycle Anatomy
Exploring the intricate structure of a two-wheeled vehicle reveals a blend of engineering and design that enhances both performance and comfort. Each element plays a crucial role in the overall functionality, contributing to a seamless riding experience. By familiarizing oneself with these components, enthusiasts can better appreciate the mechanics behind their journeys.
Core Components
- Frame: The backbone that supports the entire structure.
- Wheels: Crucial for movement, composed of rims, spokes, and tires.
- Drivetrain: The system responsible for transferring energy from the rider to the wheels.
- Brakes: Essential for safety, allowing control over speed and stopping.
- Handlebars: Provide steering and comfort for the rider’s grip.
Additional Elements
- Seat: Designed for comfort during extended rides.
- Suspension: Absorbs shocks, enhancing stability and ride quality.
- Pedals: The interface for foot movement, crucial for propulsion.
- Chain: Links the pedals to the rear wheel, crucial for motion.
- Gears: Allow for adjustments in resistance and speed, catering to various terrains.
Understanding these components not only enriches the riding experience but also aids in maintenance and repairs, ensuring that enthusiasts can enjoy their adventures without interruption.
Key Components of a Bike
Understanding the fundamental elements that contribute to the functionality of a two-wheeled vehicle is essential for any enthusiast or novice. These critical components work in harmony to ensure a smooth and efficient riding experience.
- Frame: The core structure that supports all other elements.
- Wheels: Essential for movement and stability, consisting of rims, spokes, and hubs.
- Tires: Provide grip and cushioning, influencing performance and comfort.
- Handlebars: Allow steering and control over direction.
- Seat: Offers comfort and support during rides.
- Brakes: Critical for safety, enabling the rider to slow down or stop.
- Drivetrain: Includes gears and chains, facilitating efficient power transfer from the rider to the wheels.
Each of these components plays a significant role in enhancing the overall performance and safety of the vehicle, making their understanding vital for maintenance and improvement.
Importance of Each Part
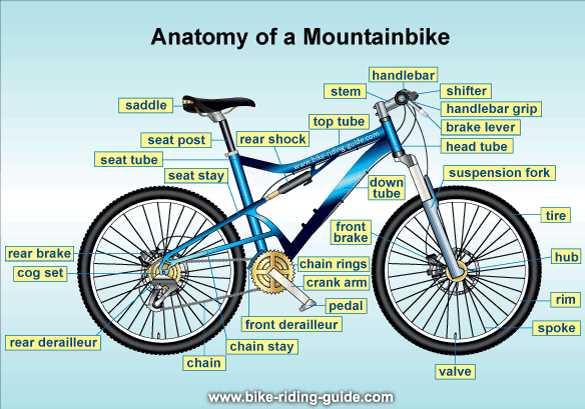
Every component of a two-wheeled vehicle plays a crucial role in ensuring its functionality and overall performance. Understanding the significance of each element allows for better maintenance, improved safety, and enhanced riding experience. Each segment is designed to work in harmony with others, contributing to the vehicle’s efficiency and reliability.
Wheels serve as the foundation, providing stability and enabling movement. The frame offers structural integrity, supporting the rider and the system’s weight. The braking system is vital for safety, allowing for controlled stops and effective handling.
Transmission mechanisms ensure smooth gear changes, adapting to various terrains and speeds. Meanwhile, handlebars offer steering control, enhancing maneuverability. Additionally, seats contribute to comfort during rides, influencing overall enjoyment and endurance.
Each component, from the smallest screw to the largest assembly, plays a distinct role, and neglecting any part can lead to reduced performance or potential hazards. Regular inspections and timely replacements are essential for maintaining the integrity of the entire system.
How Gears Function on Bicycles
Understanding the mechanics of gear systems is essential for optimizing performance and enhancing the riding experience. These systems enable smooth transitions between different speeds and provide better control over various terrains.
Basic Components
The primary elements of a gear mechanism include sprockets, derailleurs, and a chain. Each component plays a vital role in transferring power from the rider to the wheels, allowing for efficient movement.
Shifting Mechanism
Shifting gears involves a coordinated action that changes the position of the chain across the sprockets. This process allows the rider to adjust the level of resistance encountered while pedaling, facilitating ease of movement uphill or acceleration on flat surfaces.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Sprockets | Provide various gear ratios for speed control |
| Derailleurs | Guide the chain between different sprockets |
| Chain | Transfers energy from the pedals to the rear wheel |
Brakes: Types and Mechanisms
Effective stopping is a crucial aspect of any two-wheeled vehicle, ensuring safety and control during rides. Various systems are employed to achieve reliable deceleration, each designed to cater to specific conditions and preferences. Understanding these mechanisms helps enthusiasts choose the right setup for their needs.
Types of Braking Systems
There are primarily two categories of braking systems: rim brakes and disc brakes. Rim brakes operate by applying pressure to the outer edges of the wheel, utilizing pads that grip the rim to slow down or halt motion. Conversely, disc brakes function by squeezing a rotor attached to the wheel, providing enhanced stopping power and heat dissipation, making them popular in various riding conditions.
Mechanisms of Action
Braking systems can utilize different mechanisms for engagement. Mechanical brakes rely on cables to transmit force from the lever to the pads, offering simplicity and ease of maintenance. In contrast, hydraulic brakes use fluid pressure to operate, delivering smoother and more powerful stopping performance. Each mechanism has its advantages, affecting responsiveness and modulation, which are critical for a rider’s experience.
Wheels: Anatomy and Design
The wheels serve as the foundation of motion, translating energy into movement and stability. Their construction embodies a blend of engineering principles and aesthetic appeal, crucial for performance and efficiency. Understanding their structure reveals the intricacies that contribute to the overall functionality of a cycle.
Key Components
At the core of every wheel lies the rim, providing a sturdy outer edge that holds the tire. The spokes radiate from the hub, distributing weight and maintaining tension, while the hub itself serves as the central axle, allowing rotation. Each element works harmoniously to ensure smooth navigation across various terrains.
Design Variations
Wheels come in diverse designs tailored to specific uses. Lightweight options are favored for speed, while wider versions offer enhanced grip and stability. Materials such as aluminum and carbon fiber contribute to performance differences, impacting durability and responsiveness. The choice of design significantly influences the riding experience, reflecting the rider’s preferences and intended use.
Frame Materials: A Comparative Overview
When selecting a structure for a two-wheeled vehicle, the choice of material significantly impacts performance, comfort, and durability. Various materials offer unique characteristics that cater to different riding styles and preferences.
- Aluminum: Lightweight and corrosion-resistant, aluminum is popular for its balance of strength and weight. It’s often used in mid-range models.
- Carbon Fiber: Known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, carbon fiber provides superior shock absorption and responsiveness, ideal for competitive use.
- Steel: Traditionally used, steel offers durability and comfort due to its natural flex. It’s favored for touring and commuting.
- Titanium: A premium option, titanium combines the best of both worlds–lightweight and strength, with excellent resistance to fatigue.
Ultimately, the best choice depends on individual riding needs, budget, and intended use.
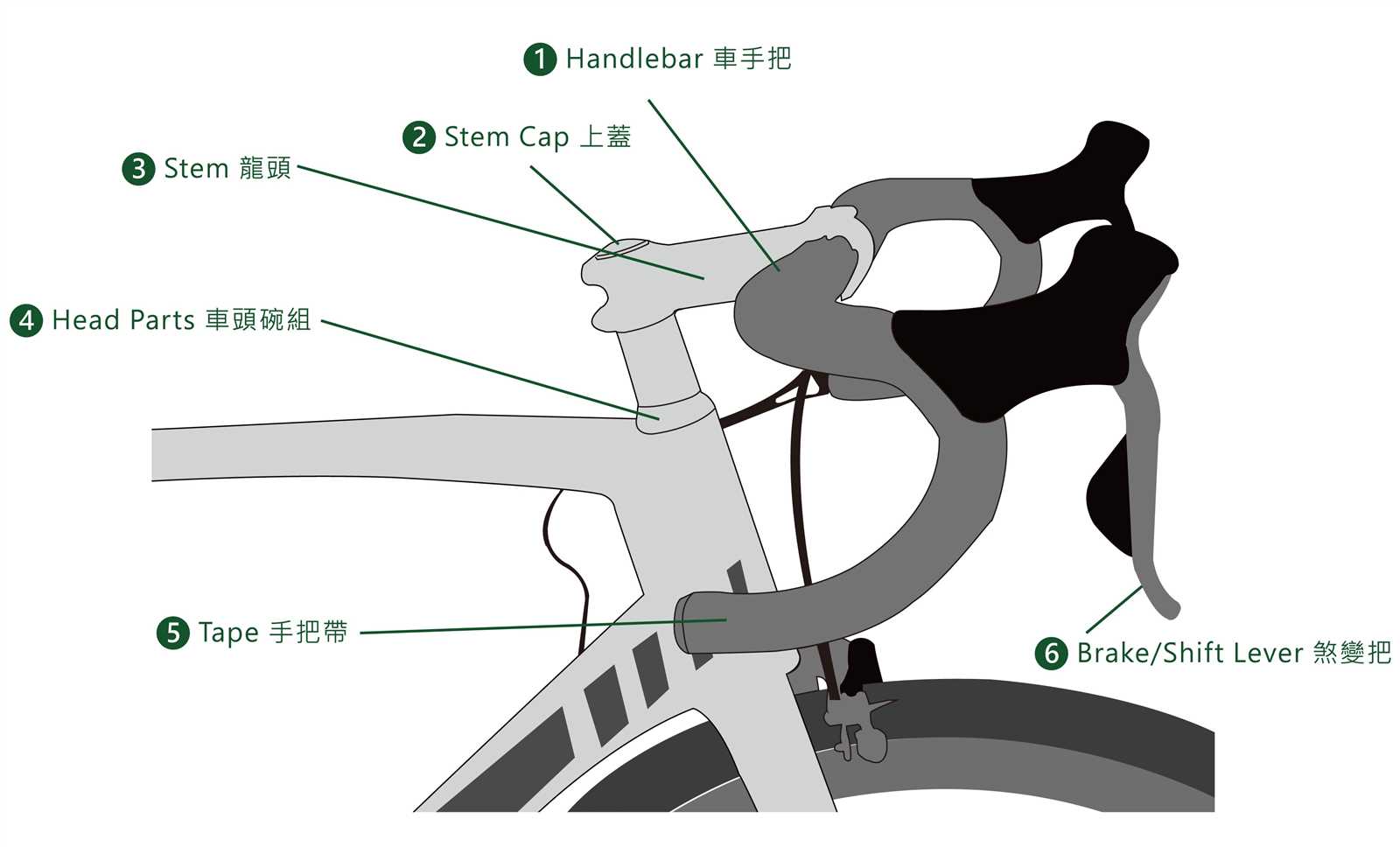
Handlebars: Styles and Functions
When exploring the realm of steering components, it’s essential to understand their diverse styles and functionalities, each tailored to enhance rider experience and control. These elements play a pivotal role in the overall performance and comfort, influencing both handling and aesthetic appeal.
Types of Handlebars
- Drop Bars: Ideal for racing, offering a streamlined position.
- Flat Bars: Popular for urban riding, providing a more upright stance.
- Riser Bars: Common in mountain cycling, enhancing control on rugged terrain.
- Bullhorn Bars: A blend of style and aerodynamics, great for triathlons.
Functions of Handlebars
- Steering Control: Allows for precise navigation.
- Comfort: Affects the rider’s posture and overall comfort level.
- Stability: Provides balance and stability, especially on uneven surfaces.
- Aesthetics: Complements the overall look of the vehicle.
Pedals: Choosing the Right Type
Selecting the appropriate foot interface is crucial for enhancing your cycling experience. With various options available, understanding their functionalities can significantly impact your performance and comfort during rides. This guide will help you navigate through the essential types and considerations when making your choice.
| Type | Description | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Platform | Flat surface, allows for easy foot placement. | Casual riders and beginners. |
| Clipless | Securely connects shoes to the interface for improved power transfer. | Serious cyclists and those looking for efficiency. |
| Cage | Enhances grip on regular footwear while offering some support. | Commuters and recreational cyclists. |
| Spd | Dual-sided design, great for quick engagements. | Mountain bikers and off-road enthusiasts. |
When deciding on the most suitable option, consider your riding style, frequency, and terrain. Each type presents unique advantages, enabling you to optimize your performance while ensuring a comfortable and enjoyable journey.
Chain and Sprockets Explained
The connection between movement and energy in a two-wheeled machine is crucial for its efficiency and performance. Understanding how the elements work together enhances the overall experience of riding.
At the core of this system are two main components:
- Chain: This flexible link mechanism transfers power from one point to another.
- Sprockets: These toothed wheels engage with the chain to facilitate motion.
Here’s how they interact:
- The chain wraps around the sprockets, creating a seamless connection.
- As one sprocket turns, it drives the chain, leading to movement of the other sprocket.
- This process converts the rider’s effort into forward motion.
Proper maintenance of both elements is essential for optimal performance and longevity, ensuring a smooth ride and efficient energy use.
Suspension Systems: Why They Matter
Suspension mechanisms play a crucial role in enhancing the overall experience of riding by providing stability and comfort. These systems absorb shocks and vibrations from uneven terrain, allowing for a smoother journey. Their design directly impacts handling and control, making them essential for performance and safety.
Understanding the importance of suspension lies in its ability to maintain tire contact with the ground, which improves traction and maneuverability. This connection is vital, especially in challenging conditions, as it ensures better responsiveness and a more secure ride.
Ultimately, investing in a quality suspension system can elevate your overall riding experience, transforming a regular journey into an enjoyable adventure. Properly tuned mechanisms not only enhance comfort but also extend the longevity of the vehicle, making them indispensable for any enthusiast.
Lighting and Safety Accessories
Ensuring visibility and protection is crucial for any journey, especially when navigating through low-light conditions or busy environments. Utilizing appropriate illumination and protective gear enhances overall security and contributes to a safer experience for everyone involved.
Illumination Solutions
Effective lighting options are essential for enhancing visibility. Headlights and taillights provide illumination for the rider while making them noticeable to others. Options range from basic battery-operated devices to advanced rechargeable models with multiple brightness settings, catering to various needs and preferences.
Protective Gear
Safety accessories such as reflective vests, helmets, and signal devices play a vital role in reducing risks on the road. Wearing a well-fitted helmet can significantly decrease the likelihood of serious injury, while reflective materials ensure that riders are seen by motorists, especially at dusk or dawn.
Maintenance Tips for Bike Parts
Ensuring the longevity and performance of your two-wheeled companion requires regular care and attention. Proper upkeep not only enhances functionality but also guarantees a smoother and safer riding experience.
Here are essential maintenance tips to keep everything in top shape:
- Regular Cleaning: Dirt and grime can lead to wear and tear. Clean the frame, wheels, and components regularly using mild soap and water.
- Lubrication: Apply appropriate lubricants to moving parts, such as chains and gears, to prevent rust and ensure smooth operation.
- Check Tire Pressure: Maintain optimal air pressure in the tires to enhance traction and avoid flats. Check pressure before every ride.
- Brake Inspection: Regularly inspect brakes for wear and adjust or replace pads as necessary to ensure effective stopping power.
- Gear Adjustment: Keep shifting smooth by checking the alignment and tension of the cables regularly.
- Inspect Bearings: Check bearings in wheels and hubs for smooth rotation. Clean and re-grease them periodically.
By following these straightforward tips, you can significantly extend the life of your machine and enjoy many miles of worry-free riding.