Understanding the Components of a Brake Caliper Diagram
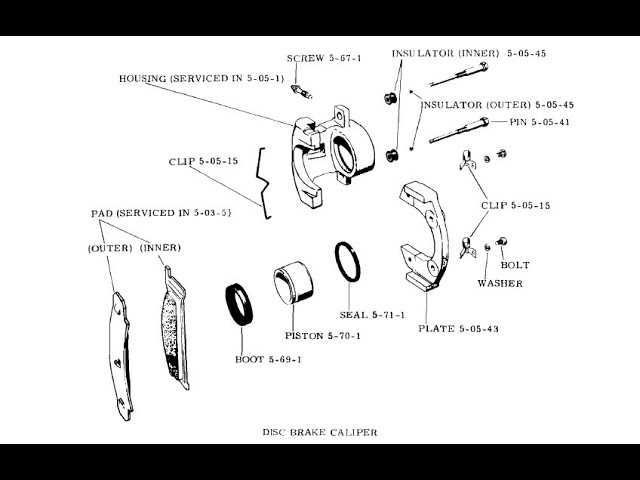
The intricate system responsible for slowing down a vehicle is composed of several essential elements, each playing a critical role in ensuring safety and performance. Grasping the layout and functionality of these components can enhance one’s appreciation for automotive engineering and maintenance.
Every element within this assembly has a specific purpose, contributing to the overall efficiency of the deceleration process. From the initial force applied to the system to the ultimate friction that brings the wheels to a halt, understanding how these pieces interact is vital for both enthusiasts and professionals alike.
In this exploration, we will delve into the various components that make up this crucial system, providing a detailed overview that aids in comprehending their function and importance. By visualizing how each section fits together, one can gain valuable insights into the mechanics at work behind the scenes of any vehicle.
Understanding Brake Caliper Components
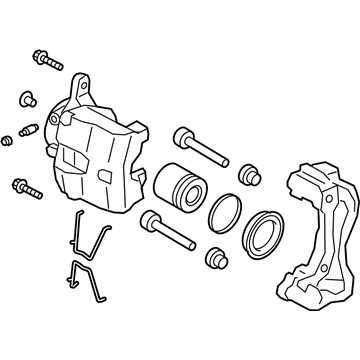
When it comes to the intricate mechanisms of vehicle deceleration systems, grasping the various elements involved is crucial. Each component plays a vital role in ensuring effective and reliable stopping power, contributing to overall safety and performance on the road.
Key Elements of the System
Several main components work together harmoniously to facilitate the desired functionality. Understanding their individual roles can help in troubleshooting and maintenance, enhancing the lifespan of the entire assembly.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Piston | Applies pressure to the friction material to create stopping force. |
| Friction Material | Grips the rotating disc to slow down the vehicle. |
| Housing | Encases and protects the internal components while providing structural integrity. |
| Seals | Prevent fluid leakage and contamination, ensuring efficient operation. |
Importance of Regular Inspection
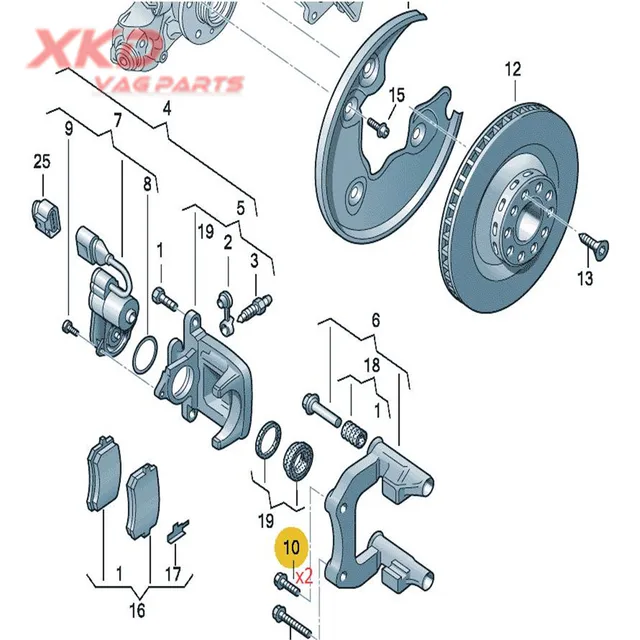
Routine checks of these elements can prevent wear and ensure the system operates optimally. Addressing issues early can save time and resources, contributing to safer driving experiences.
Types of Brake Calipers Explained
Understanding the various types of stopping mechanisms is essential for anyone interested in automotive systems. Each variation serves a specific purpose, adapting to different performance needs and vehicle designs. This overview will highlight the main classifications, shedding light on their unique characteristics and applications.
| Type | Description | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Floating | Utilizes a single piston and moves laterally to engage with the rotor, offering a lightweight and cost-effective solution. | Common in everyday vehicles, especially sedans and small SUVs. |
| Fixed | Features multiple pistons on either side, providing superior stopping power and response due to its rigid design. | Often found in performance cars and heavy-duty trucks. |
| Sliding | Similar to floating types but incorporates additional mechanisms for better alignment and performance during operation. | Used in various applications, from commuter vehicles to mid-range sports cars. |
| Multi-Piston | Equipped with several pistons that allow for more even pressure distribution, enhancing performance and reducing wear. | Ideal for high-performance and racing applications. |
Each variation is engineered to meet specific demands, ensuring vehicles can handle different conditions effectively. Understanding these classifications helps in making informed choices when it comes to maintenance or upgrades.
Importance of Brake Caliper Maintenance
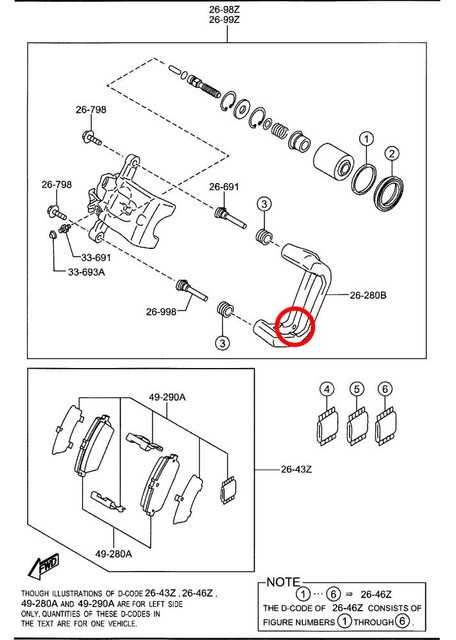
Regular upkeep of critical components in your vehicle’s stopping system is essential for ensuring optimal performance and safety. Neglecting these elements can lead to significant issues, including decreased responsiveness and increased wear on surrounding mechanisms. Understanding the necessity of proper maintenance can prevent costly repairs and enhance overall driving experience.
Enhancing Safety
Routine inspection and servicing of the stopping mechanism play a vital role in maintaining vehicle safety. Properly functioning elements help prevent accidents by ensuring quick and effective stopping power. Regular checks can identify early signs of wear or damage, allowing for timely intervention and minimizing risks on the road.
Extending Lifespan
Taking care of essential components can significantly prolong their lifespan. Regular maintenance helps avoid premature failures, saving you both time and money in the long run. By addressing minor issues before they escalate, you ensure that your vehicle remains reliable and efficient for years to come.
How Brake Calipers Function
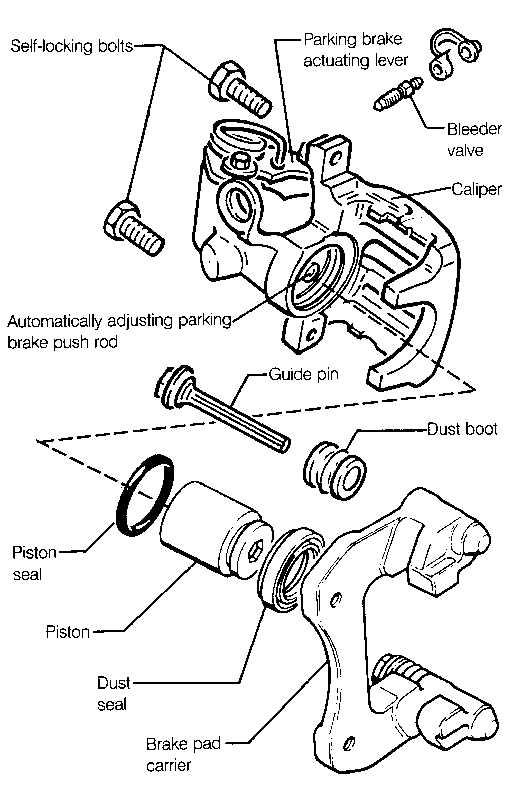
The components responsible for slowing down or stopping a vehicle play a crucial role in its overall safety and performance. Understanding how these mechanisms operate helps in maintaining optimal functionality and ensuring the vehicle responds effectively during deceleration.
Key Mechanisms Involved
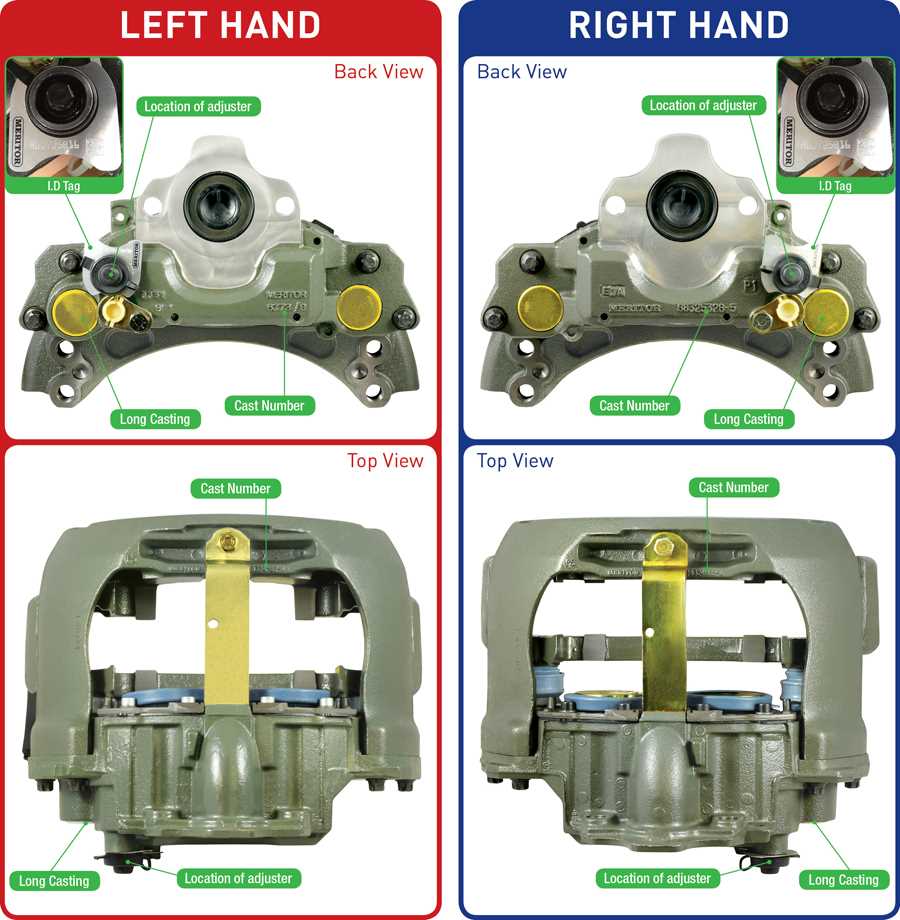
Several essential elements contribute to the effective functioning of the slowing system:
- Force Application: When the driver presses the pedal, hydraulic fluid is pushed through the system, creating pressure.
- Movement Transfer: This pressure transfers to specific components, prompting them to move and apply friction.
- Friction Creation: The friction materials engage with the rotating surfaces, generating the necessary resistance to slow down the wheels.
Efficiency and Performance Factors
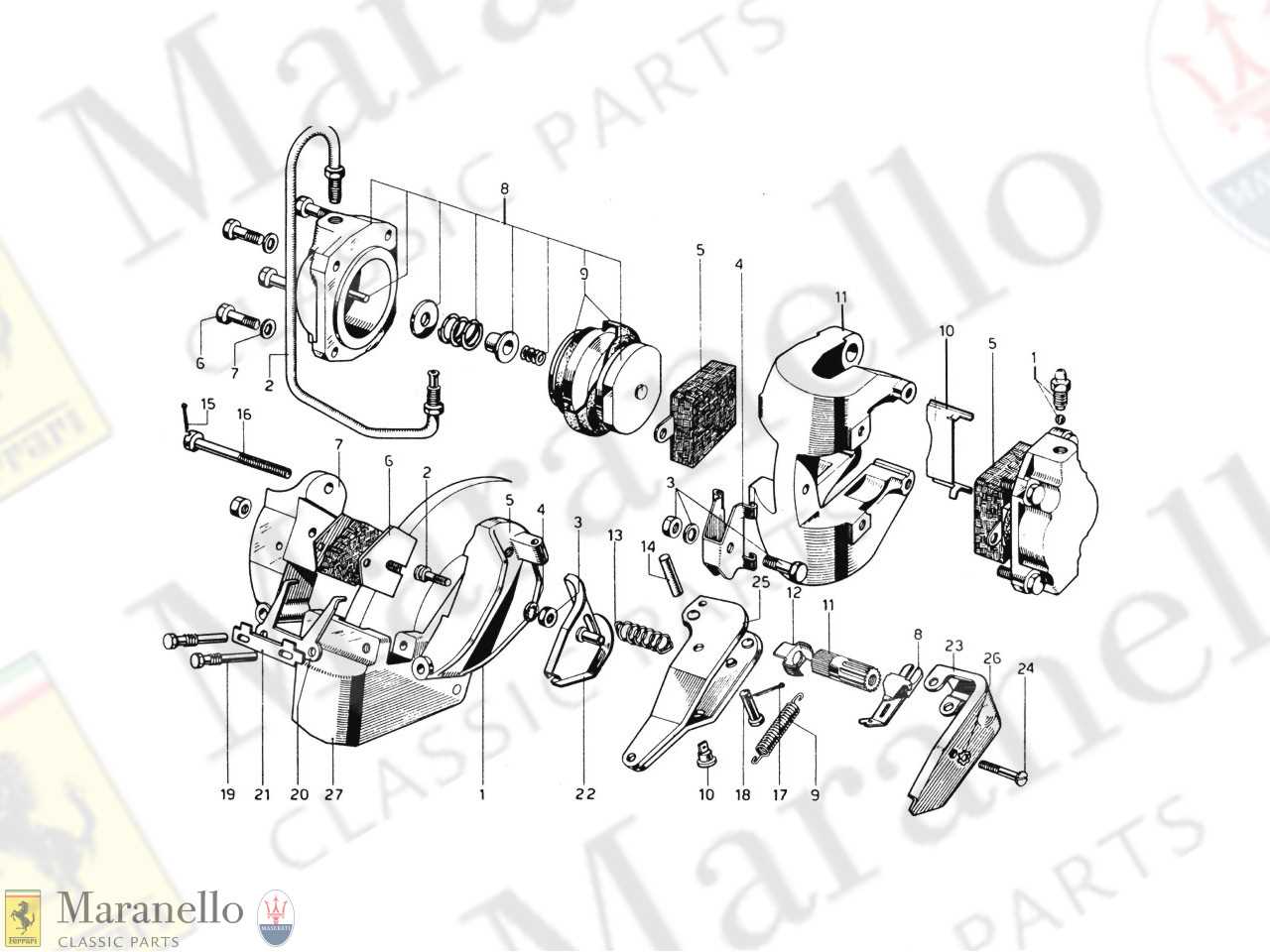
Several factors influence how effectively the system operates:
- Material Quality: High-quality materials improve heat dissipation and reduce wear.
- Regular Maintenance: Routine checks help in identifying wear and tear, ensuring optimal performance.
- System Design: The overall layout and design impact how effectively force is transmitted and friction is created.
By comprehending these mechanisms and factors, vehicle owners can better appreciate the importance of maintaining these essential components for safe driving experiences.
Common Brake Caliper Issues
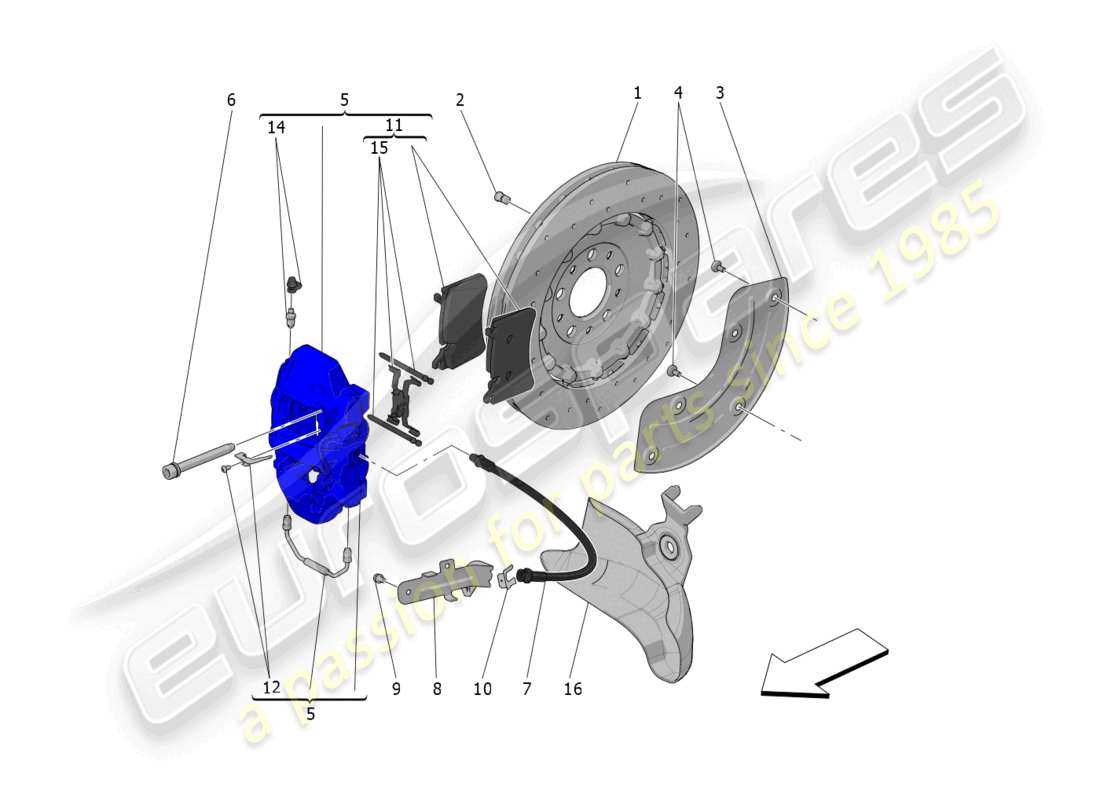
Understanding the common challenges faced by a specific component of the vehicle’s stopping mechanism is essential for ensuring safety and performance. Several issues can arise, leading to decreased efficiency and potential hazards on the road.
1. Uneven Wear: One frequent problem is uneven wear of the friction material. This can occur due to misalignment or malfunction, resulting in reduced contact and effectiveness during operation.
2. Fluid Leaks: Another concern is the presence of leaks in the hydraulic system. These leaks can stem from damaged seals or connections, compromising the system’s pressure and leading to diminished performance.
3. Sticking Mechanism: A sticking mechanism can cause the unit to remain partially engaged even when not in use. This may result in excessive heat generation, leading to premature wear and potential overheating of surrounding components.
4. Corrosion: Corrosion can also pose significant issues. Exposure to moisture and road salt can lead to deterioration of metal parts, which may impede functionality and increase the risk of failure.
5. Noise and Vibration: Unusual noises or vibrations during operation can indicate underlying issues. These symptoms often suggest problems with alignment, wear, or other mechanical failures that need immediate attention.
Addressing these issues promptly is crucial to maintaining optimal performance and safety on the road. Regular inspections and maintenance can help identify and resolve these common challenges before they escalate into more significant problems.
Tools for Brake Caliper Inspection
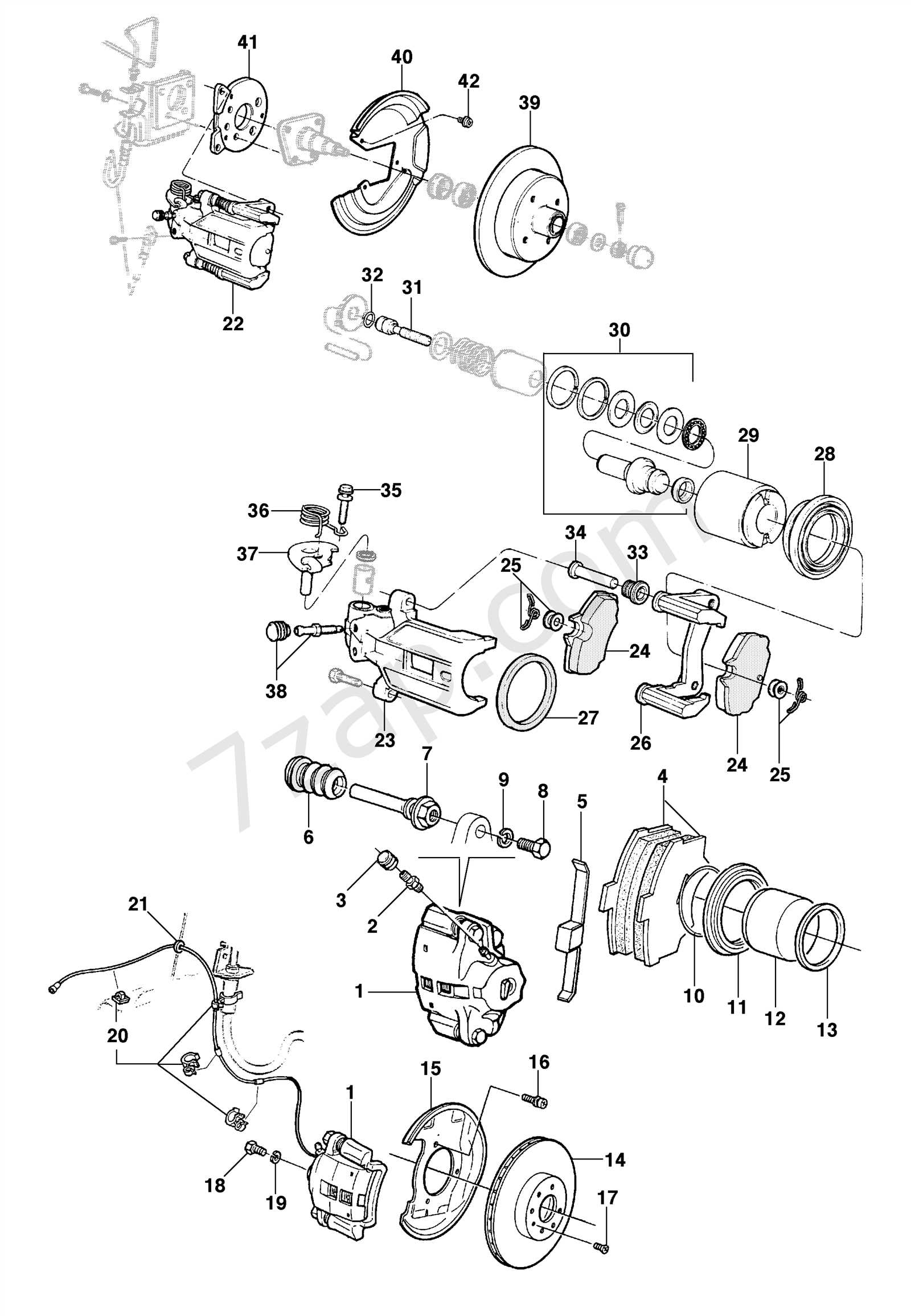
Proper evaluation of your vehicle’s stopping mechanism is crucial for safety and performance. To achieve accurate results, having the right instruments on hand can make all the difference. This section will cover essential tools that facilitate thorough examination and maintenance of this vital component.
1. Torque Wrench: A torque wrench ensures that fasteners are tightened to the manufacturer’s specifications. This precision prevents over-tightening, which can lead to damage or malfunction.
2. Brake Pad Thickness Gauge: This tool allows you to measure the thickness of the friction material. Regular checks can indicate when replacements are necessary, ensuring optimal stopping power.
3. C-Clamp or Piston Tool: Useful for retracting the piston when replacing pads, these tools help manage pressure and make the process smoother.
4. Cleaning Brushes: Keeping the surfaces clean is vital for performance. Specialized brushes can remove debris and contaminants, promoting longevity and effectiveness.
5. Inspection Mirror: A small, angled mirror can help you view hard-to-reach areas, making it easier to identify wear or damage that may not be visible otherwise.
6. Digital Caliper: This device measures the internal and external dimensions with great accuracy. It’s beneficial for checking component sizes against specifications.
Having these instruments readily available can greatly enhance the efficiency and accuracy of any inspection or maintenance task related to your vehicle’s braking system.
Brake Caliper Replacement Guide
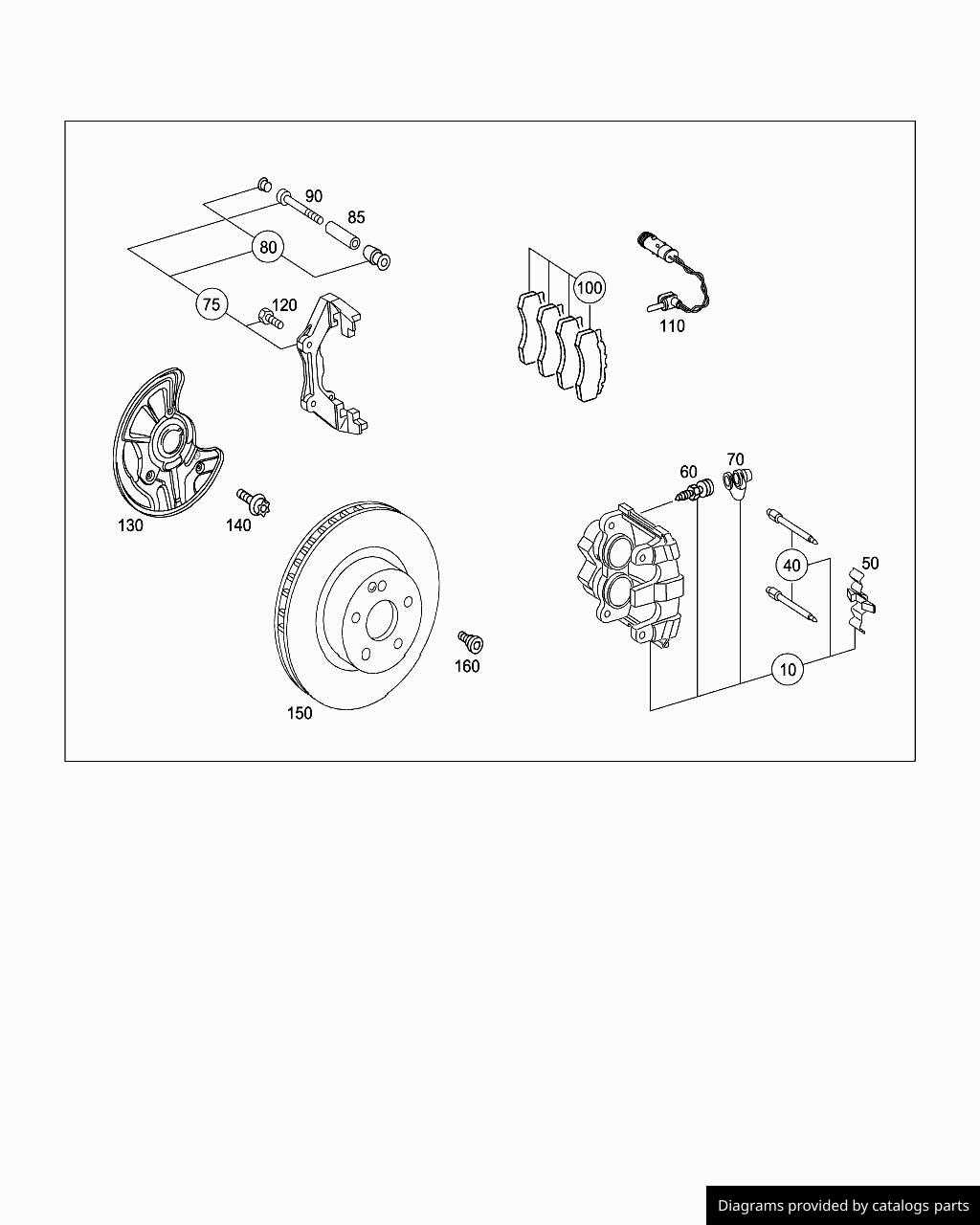
Replacing essential components of the stopping system is crucial for maintaining vehicle safety and performance. This guide outlines the steps involved in the removal and installation of these crucial elements, ensuring that you can confidently undertake this task with the right knowledge and tools.
Preparation and Tools
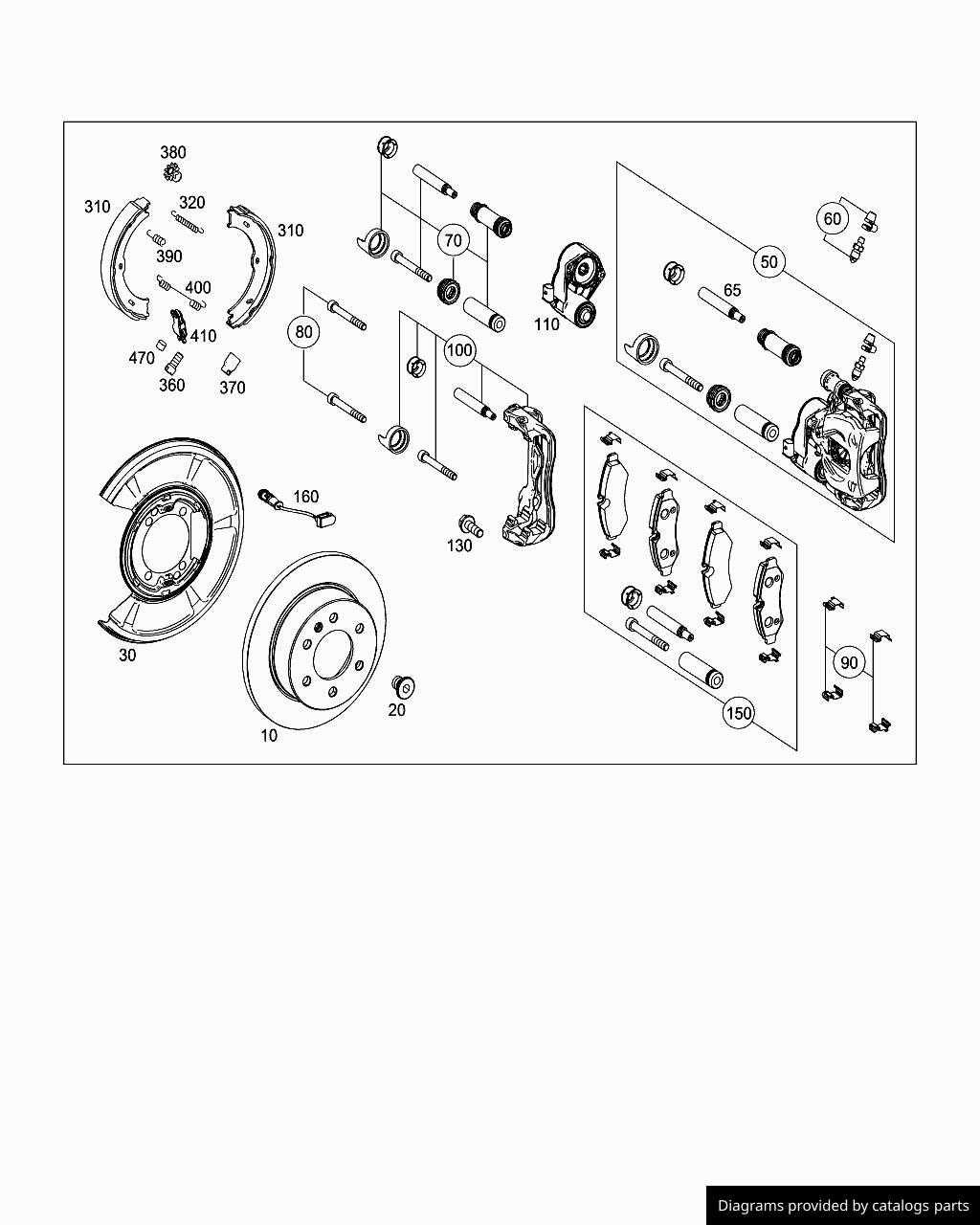
Before starting the replacement process, gather the necessary tools, including a socket set, torque wrench, and brake fluid. Ensure you have a safe working environment, preferably on a flat surface with ample space. Familiarize yourself with your vehicle’s manual for any specific instructions related to your model.
Step-by-Step Process
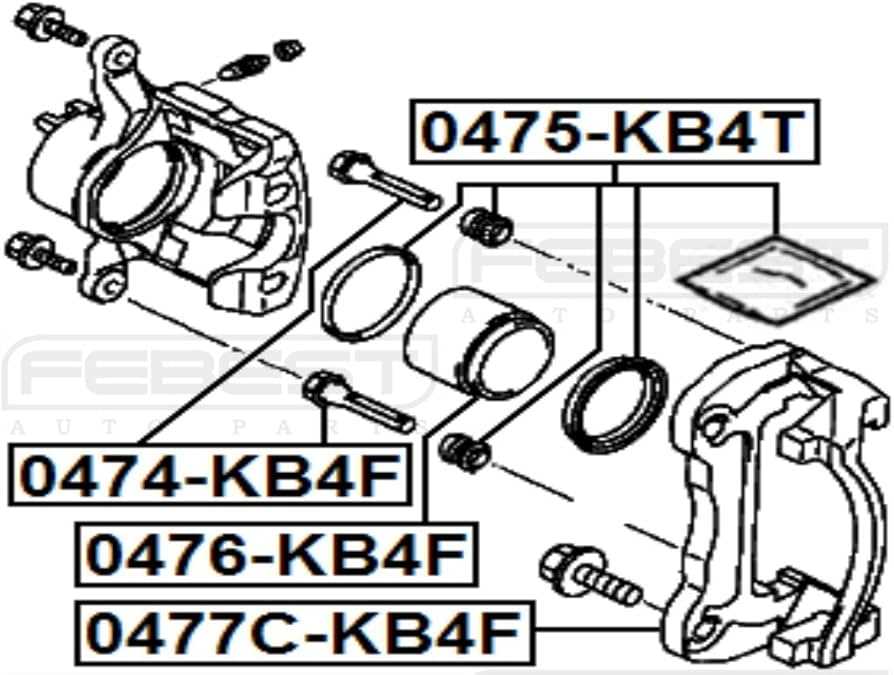
1. Lift the Vehicle: Use a jack to elevate the vehicle and secure it with jack stands. This will provide adequate access to the wheel assembly.
2. Remove the Wheel: Unscrew the lug nuts and take off the wheel to expose the working area.
3. Detach the Component: Carefully disconnect the required elements, taking note of the arrangement for reinstallation. Be cautious of any remaining fluid.
4. Install the New Component: Position the new piece, ensuring it aligns properly with the mounting points. Tighten all bolts to the manufacturer’s specifications using a torque wrench.
5. Reassemble and Test: Reattach the wheel and lower the vehicle. Once on the ground, test the functionality by applying the stopping system several times before taking it for a short drive.
Following these steps will ensure a smooth transition and restore the effectiveness of the vehicle’s stopping system. Regular checks and timely replacements are key to optimal performance and safety.
Caliper Design Variations
In the realm of automotive engineering, the configurations of friction components can vary significantly to meet specific performance and aesthetic requirements. These variations often reflect advancements in technology, materials, and the unique demands of different vehicle types.
Monoblock versus Split Designs: One of the primary distinctions lies between monoblock and split configurations. The former consists of a single, solid unit, enhancing rigidity and reducing weight, while the latter allows for easier maintenance and replacement of individual elements.
Material Choices: The selection of materials also plays a crucial role in the overall efficiency and longevity of these components. Aluminum alloys are favored for their lightweight properties, whereas cast iron offers durability and heat resistance, making it a preferred choice in high-performance applications.
Pin Type vs. Sliding Type: Another variation can be seen in the mechanism of movement. Pin-type systems provide a more direct action, improving response times, while sliding designs can offer smoother operation and reduce wear over time.
Cooling Features: Innovative designs may incorporate additional cooling features to enhance performance under extreme conditions. Vents, ducts, and thermal barriers are increasingly common, aimed at dissipating heat more effectively and maintaining optimal operating temperatures.
These variations not only influence the functionality but also the overall driving experience, highlighting the importance of tailored solutions in modern automotive design.
Identifying Brake Caliper Parts
Understanding the components of a disc-braking system is essential for effective maintenance and repair. Each element plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal functionality and safety. Recognizing these key elements allows for better troubleshooting and informed decision-making when addressing issues.
Main Components Overview
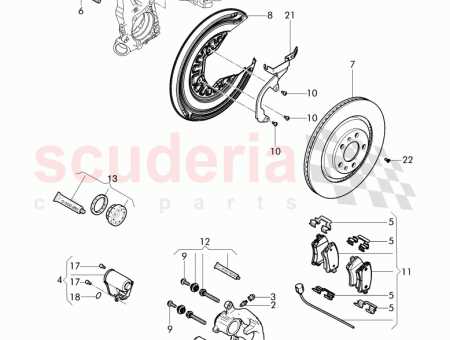
The primary components involved in this crucial assembly include various elements that interact to create friction, enabling the vehicle to slow down or stop. Familiarity with these elements is vital for both novice and experienced mechanics.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Housing | The main body that houses other elements, providing structural integrity. |
| Piston | A cylinder that generates pressure to engage the friction material against the rotor. |
| Friction Material | The pads that create the necessary friction against the rotor to slow down the vehicle. |
| Slide Pins | Elements that allow for the movement of the friction material, ensuring even wear. |
| Seals | Prevent contamination and fluid leakage, maintaining the pressure needed for operation. |
Importance of Component Identification
Recognizing each component’s function not only aids in maintenance but also helps in diagnosing potential problems. This knowledge ensures that all elements work harmoniously, contributing to the overall safety and performance of the vehicle.
Impact on Vehicle Performance
The efficiency of a vehicle’s stopping mechanism plays a crucial role in overall driving dynamics. The components involved in this system not only influence the ability to halt safely but also affect various performance metrics such as handling, stability, and wear on other systems. Understanding how these elements interact is essential for optimal vehicle operation.
Key Performance Factors
- Stopping Distance: The effectiveness of the mechanism directly impacts how quickly a vehicle can come to a complete stop.
- Heat Management: The generation of heat during operation can lead to fade, reducing efficiency and control.
- Response Time: The quicker the system reacts, the better the overall handling and driver confidence.
- Weight Distribution: The mass and positioning of components can affect vehicle balance and agility.
Maintenance and Upgrades
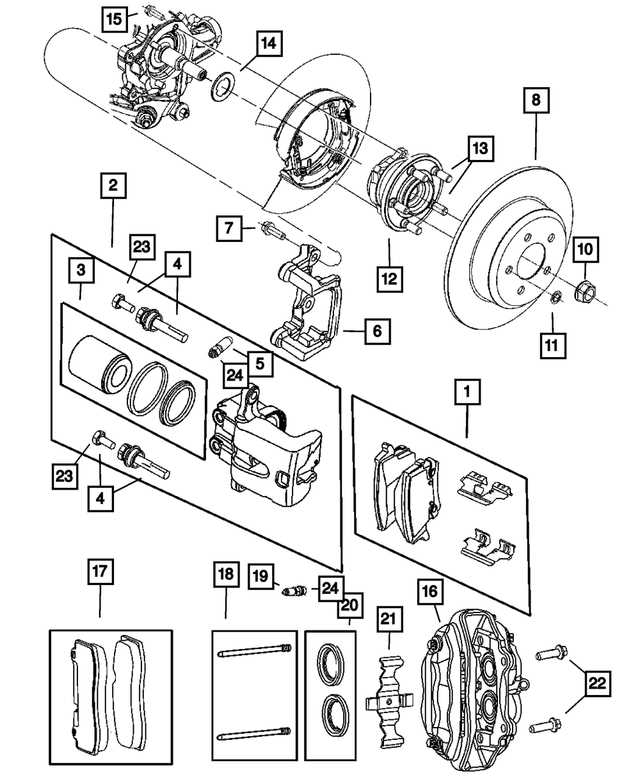
Regular inspection and timely replacement of components are vital to maintaining performance. Upgrading to high-quality alternatives can enhance efficiency and prolong the lifespan of related systems.
- Inspect components regularly for wear and damage.
- Consider upgrading to performance-oriented options if driving conditions require it.
- Ensure proper installation to avoid issues that could compromise performance.