Understanding the Components of a Motorcycle Brake Caliper Diagram

In the realm of two-wheeled vehicles, the ability to halt efficiently is paramount. This section will explore the intricate elements that contribute to the overall functionality of stopping systems, shedding light on their design and operation.
Identifying individual components is essential for grasping how these mechanisms work together to ensure safety and performance. By examining each element closely, enthusiasts and technicians can gain insights into the maintenance and enhancement of these critical systems.
Additionally, a thorough understanding of these elements can lead to better troubleshooting practices. When challenges arise, knowing the layout and interaction of these components becomes the ultimate advantage in achieving optimal performance.
Understanding Motorcycle Brake Systems
Effective stopping power is crucial for safety and control in two-wheeled vehicles. This section delves into the fundamental elements that ensure reliable deceleration, examining how different components interact to provide optimal performance during various riding conditions.
Key Components
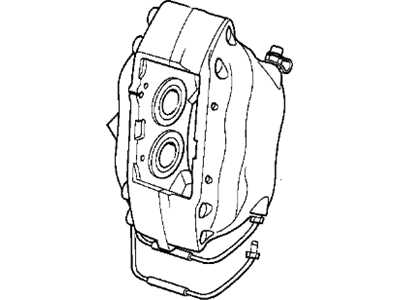
Central to the stopping mechanism are the elements that convert the rider’s input into controlled slowing. Each component plays a vital role in the overall functionality, from the initial pressure applied by the rider to the resulting friction that brings the machine to a halt. Understanding the specific roles and characteristics of these elements is essential for maintenance and performance enhancement.
Maintenance and Performance
Regular upkeep of the stopping system is essential to ensure longevity and reliability. This involves inspecting and replacing worn components, checking fluid levels, and ensuring proper alignment. By understanding how these systems work together, riders can make informed decisions to enhance safety and riding experience.
Key Components of Brake Calipers
Understanding the essential elements of the stopping mechanism is crucial for ensuring safety and optimal performance. Each component plays a vital role in the overall function, working together to provide effective deceleration when needed.
- Piston: This component is responsible for creating hydraulic pressure, pushing against the friction material to bring the vehicle to a halt.
- Housing: The structure that encloses the piston and other elements, providing protection and support.
- Friction Material: Also known as pads, these are the surfaces that contact the wheel assembly to generate the necessary friction for stopping.
- Seal: A critical element that prevents fluid leakage and maintains the integrity of the hydraulic system.
- Slider Pins: These allow for the movement of the assembly, ensuring that the friction material makes even contact with the wheel assembly.
Each of these components must be well-maintained to ensure reliability and safety during operation. Regular inspection and timely replacement can prevent malfunctions and enhance performance.
How Brake Calipers Function
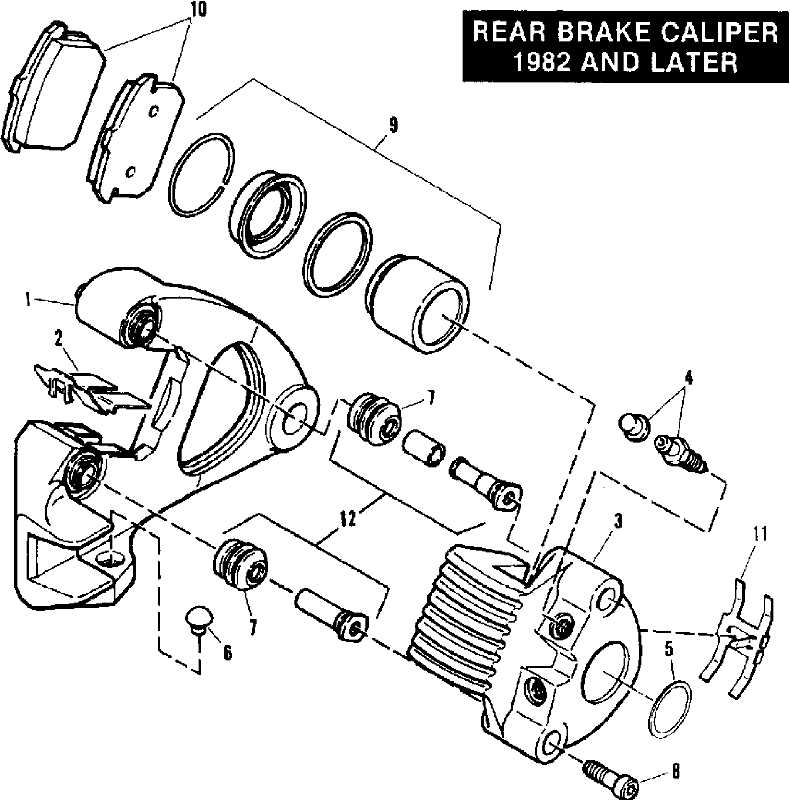
Understanding the operation of this critical component reveals how vehicles effectively slow down. The mechanism relies on hydraulic force and friction to ensure safety during travel.
- The assembly consists of several key elements that work in harmony.
- When the lever is engaged, hydraulic fluid is pushed through the system.
- This fluid transfer activates pistons that exert pressure on the friction material.
The interaction between these elements is essential for effective deceleration:
- The pistons move outward, pressing the pads against the disc.
- This contact generates friction, which slows the rotation of the wheels.
- Upon release, the pressure is alleviated, allowing for movement once again.
Regular maintenance ensures optimal functionality and longevity, contributing to overall vehicle performance.
Types of Motorcycle Brake Calipers
Understanding the various designs of stopping mechanisms is crucial for enthusiasts and riders alike. Different configurations not only impact performance but also influence maintenance and replacement options. Here, we delve into the primary variations found in these essential components.
Floating vs. Fixed Designs
One of the fundamental distinctions lies between floating and fixed types. Floating units are designed to move slightly in relation to the mounting bracket, allowing for better alignment with the rotor. This design helps distribute pressure evenly and can enhance stopping power under certain conditions. In contrast, fixed options feature a rigid structure, which can offer improved stability and responsiveness during deceleration, making them suitable for high-performance applications.
Single vs. Multi-Piston Configurations
Another significant classification involves the number of pistons used in these mechanisms. Single-piston designs are generally simpler and lighter, providing adequate performance for standard applications. However, multi-piston configurations, often utilized in racing or high-performance models, deliver superior force and quicker response times. The increased number of pistons allows for more even pressure distribution across the rotor, enhancing overall efficiency.
Common Issues with Brake Calipers
Understanding the typical problems associated with stopping mechanisms is crucial for ensuring safe operation. Various components can experience wear and tear, leading to decreased performance and potential safety hazards. Recognizing these issues early can prevent more severe complications down the road.
Fluid Leaks
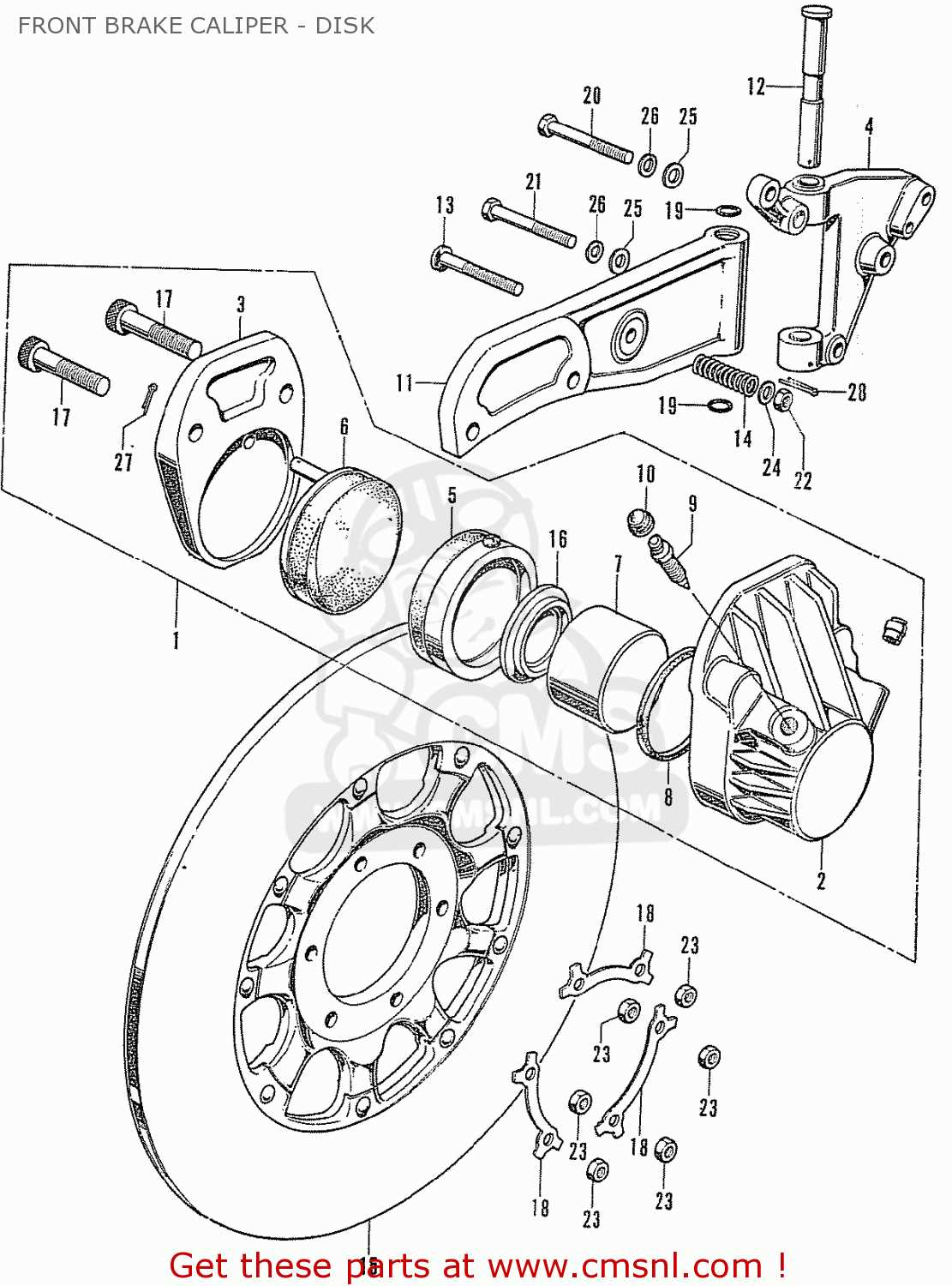
One prevalent concern involves the presence of fluid leaks. Over time, seals can degrade, allowing hydraulic fluid to escape. This not only compromises the system’s efficiency but can also lead to significant safety risks. Regular inspections are essential to detect any signs of leakage before they escalate.
Uneven Wear
Another common issue is uneven wear on the stopping surfaces. This can result from misalignment or malfunctioning components. Such irregularities can cause reduced effectiveness and lead to a noticeable decrease in overall performance. Addressing alignment and ensuring even distribution of pressure can help mitigate this problem.
Maintenance Tips for Brake Components
Ensuring optimal performance of your stopping system is crucial for safety and efficiency. Regular upkeep not only extends the lifespan of these elements but also enhances overall performance. Here are some essential practices to keep in mind.
1. Regular Inspection: Frequently examine the condition of your stopping system components for wear and damage. Look for signs of leaks or uneven wear, which may indicate the need for replacement or repair.
2. Cleanliness: Keep all components clean to prevent dirt and debris from affecting functionality. Use appropriate cleaning agents to remove grime without damaging sensitive surfaces.
3. Fluid Quality: Monitor and replace the hydraulic fluid as needed. Contaminated fluid can lead to inefficient performance and potential failure.
4. Proper Adjustment: Ensure all components are correctly aligned and adjusted. Misalignment can cause uneven wear and reduce efficiency.
5. Professional Servicing: Consider having a professional evaluate your system periodically. Their expertise can help identify issues that may not be immediately apparent.
By following these guidelines, you can delve deeper into the maintenance of your stopping system, ensuring its ultimate reliability and effectiveness on the road.
Upgrading Your Brake Caliper
Enhancing the stopping system of your two-wheeled vehicle can significantly improve performance and safety. This section explores various options and considerations for those looking to elevate their stopping capabilities, ensuring a more responsive and reliable experience on the road.
Benefits of Upgrading
- Improved stopping power
- Enhanced modulation and feel
- Reduced weight
- Increased durability
- Custom aesthetics
Factors to Consider
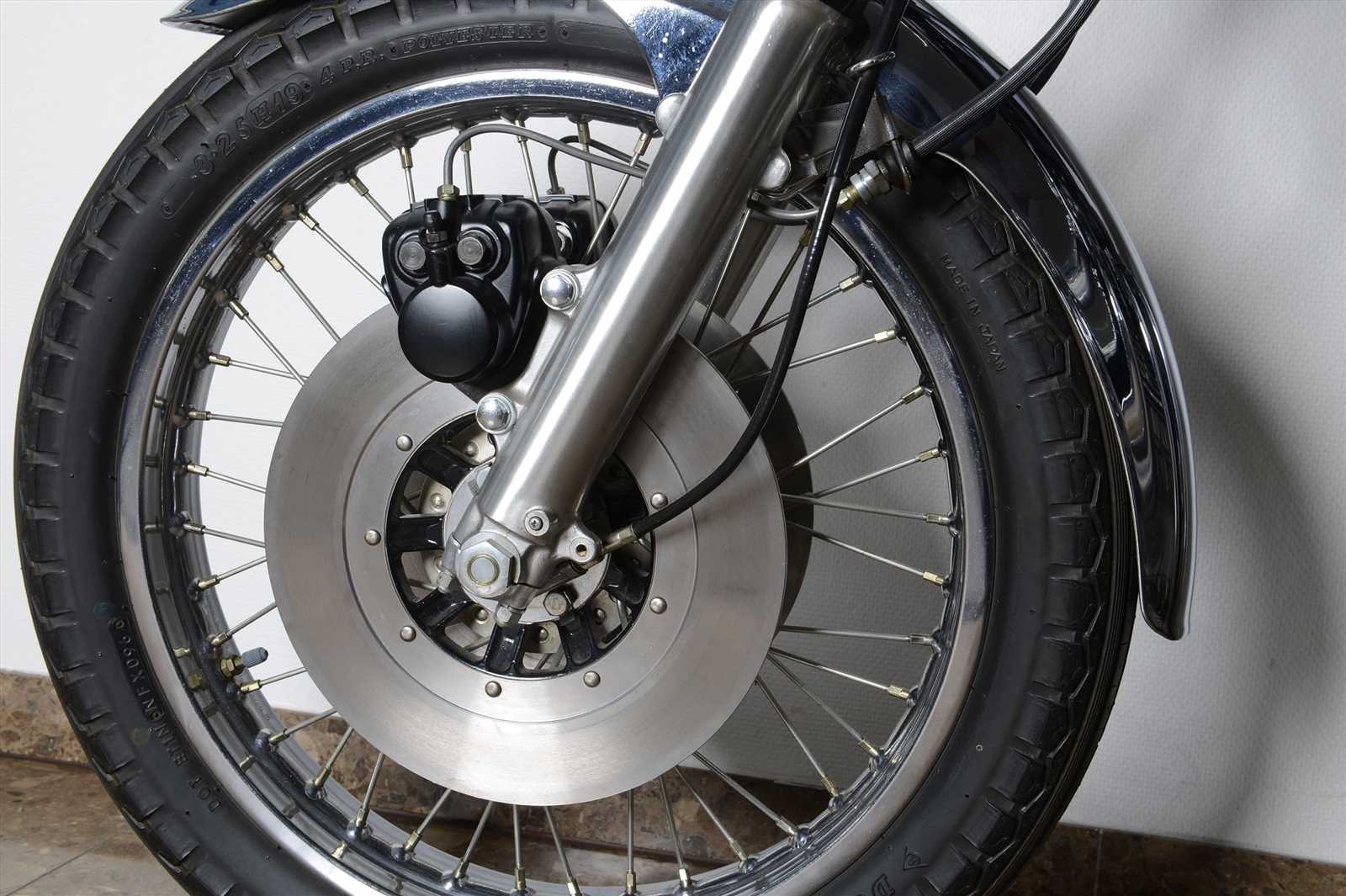

- Compatibility with existing systems
- Material selection (e.g., aluminum vs. stainless steel)
- Heat dissipation properties
- Cost versus performance benefits
- Installation complexity
Careful evaluation of these aspects will lead to an informed decision, ensuring that your enhancements align with your riding style and requirements.
Brake Caliper Installation Guide
This section provides a comprehensive overview of the installation process for essential stopping components in your vehicle. Proper fitting is crucial for optimal performance and safety.
- Preparation:
- Gather all necessary tools, including wrenches, sockets, and torque specifications.
- Ensure you have the correct replacement component suitable for your model.
- Read the manufacturer’s guidelines for specific requirements.
- Removal:
- Lift the vehicle securely and remove the wheel to access the assembly.
- Disconnect any hydraulic lines carefully to prevent fluid spillage.
- Unfasten the mounting bolts and gently take out the unit.
- Installation:
- Position the new unit in place, ensuring proper alignment with the mounting holes.
- Securely fasten the bolts to the specified torque, following the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Reconnect the hydraulic lines, ensuring there are no leaks.
- Final Checks:
- Inspect for any signs of misalignment or issues with fluid connections.
- Reattach the wheel and lower the vehicle.
- Perform a thorough test to ensure everything operates smoothly before taking it on the road.
Following these steps will help you achieve a safe and effective installation, enhancing the overall reliability of your vehicle’s stopping system.
Importance of Brake Fluid in Calipers

The fluid utilized within the stopping mechanism plays a crucial role in ensuring safe and effective performance. Its primary function is to transmit force from the lever to the stopping components, enabling them to engage and release smoothly. The efficiency of this medium directly impacts the overall functionality of the system.
Quality and Maintenance are essential when it comes to this vital liquid. Over time, exposure to moisture can lead to contamination, diminishing its effectiveness and potentially causing malfunctions. Regular checks and timely replacements are necessary to maintain optimal performance and ensure the safety of the rider.
Additionally, temperature resistance is a critical characteristic of this fluid. It must withstand high temperatures generated during usage without boiling or breaking down. This quality ensures reliable operation, especially in demanding conditions.
In summary, the significance of this hydraulic liquid cannot be overstated. Proper maintenance and understanding of its properties are key to achieving a responsive and safe stopping mechanism.
Visual Diagram of Brake Caliper Parts
This section provides a comprehensive visual representation of the components involved in the stopping mechanism of a two-wheeled vehicle. Understanding these elements is crucial for effective maintenance and performance enhancement.
Key Components Overview
Each element plays a vital role in ensuring optimal functionality. Below is a table outlining the primary features and their respective functions.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Piston | Engages the friction material to create stopping force. |
| Friction Material | Provides the necessary grip to halt motion. |
| Housing | Encases the internal elements for protection and stability. |
| Fluid Channel | Facilitates hydraulic fluid movement for enhanced pressure. |
Importance of Each Element
Recognizing the role of each component is essential for troubleshooting and improving the system’s overall performance. Proper care and understanding can significantly enhance safety and efficiency.