Understanding Dewalt DXAEJ14 Parts Diagram
Understanding the structure and internal components of any technical device is essential for both troubleshooting and proper maintenance. By familiarizing yourself with the layout of each part, you can ensure smoother operation and address any potential issues efficiently.
Proper organization of the various elements allows for quick access when repairs or replacements are necessary. Having a clear breakdown of the internal workings will help users identify key elements more easily, minimizing downtime.
When delving into mechanical or electrical assemblies, a comprehensive overview of the system’s composition enables accurate identification of issues. This knowledge contributes to maintaining optimal performance and longevity of the equipment.
Essential Component Breakdown
The device is designed with several critical elements that work together to ensure optimal performance. Understanding the key features of the unit helps to identify potential issues and maintain efficiency over time.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Power Source | Supplies energy for the unit to operate effectively in various situations. |
| Display Panel | Shows important data, such as charge levels and operational status, for user convenience. |
| Cables and Connectors | Allow for connection to external devices, enabling power transfer and communication. |
| Housing | Protects internal elements from environmental damage and physical wear. |
Key Features of the Dewalt DXAEJ14

This versatile tool combines advanced functionality and reliability, making it a valuable addition to any garage or workshop. It is designed to provide multiple functions in one compact, portable unit, ensuring ease of use and convenience for a wide range of tasks.
Powerful Performance
With a robust energy output, this device can handle demanding tasks effortlessly. Whether used in challenging conditions or for simple maintenance, its ability to perform consistently makes it a dependable tool in various situations.
Multi-functionality
Engineered for versatility, this tool offers several features that contribute to its all-around usefulness. From assisting with emergency situations to providing routine support, its capabilities extend beyond a single function, making it a practical solution for numerous needs.
Battery System and Charging Mechanism Overview
The battery system and its charging mechanism are essential components of any portable power solution. They ensure a reliable energy source and allow efficient recharging for extended use. Understanding how these elements work together helps optimize the performance and longevity of the device.
Energy Storage and Delivery
The energy storage system typically uses rechargeable cells, designed to store a high amount of electrical power in a compact form. These cells provide consistent power output during usage, ensuring that the device operates smoothly without interruptions. The delivery of energy is regulated by internal circuits to maintain a stable flow of electricity.
Charging Process and Safety
The charging process involves transferring power from an external source to the internal cells. Advanced mechanisms control the charging rate, preventing overheating and ensuring the safety of both the device and the user. Overcharge protection and temperature monitoring are some of the key features integrated into the system to enhance durability and safety during recharging cycles.
Internal Wiring and Circuitry Analysis
The internal wiring and electrical setup form the foundation of a device’s functionality. Understanding how the connections and pathways are arranged is essential to grasp the overall performance of the unit. The intricate network of wires and circuits manages the flow of electricity, ensuring that each component operates smoothly within the system.
Electrical Pathways Overview
The wiring system is carefully designed to maintain balance between power distribution and safety. It consists of multiple pathways that transport current from the power source to various internal components. These paths must be insulated properly to prevent short circuits and potential failures.
Circuit Board and Connections
The circuit board serves as the main hub where various electrical components communicate. It regulates the flow of current, distributing energy as needed. Connections between wires and the board are critical to avoid voltage drops and maintain consistent performance across all elements.
| Component | Function | Wiring Type | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Power Input | Supplies electricity to the system | High-gauge wire
Display Panel and Indicator Lights StructureThe structure of the display panel and indicator lights is designed to provide clear and intuitive feedback on the device’s operational status. Through a combination of visual signals, users can quickly interpret the current conditions and any required actions, ensuring effective usage.
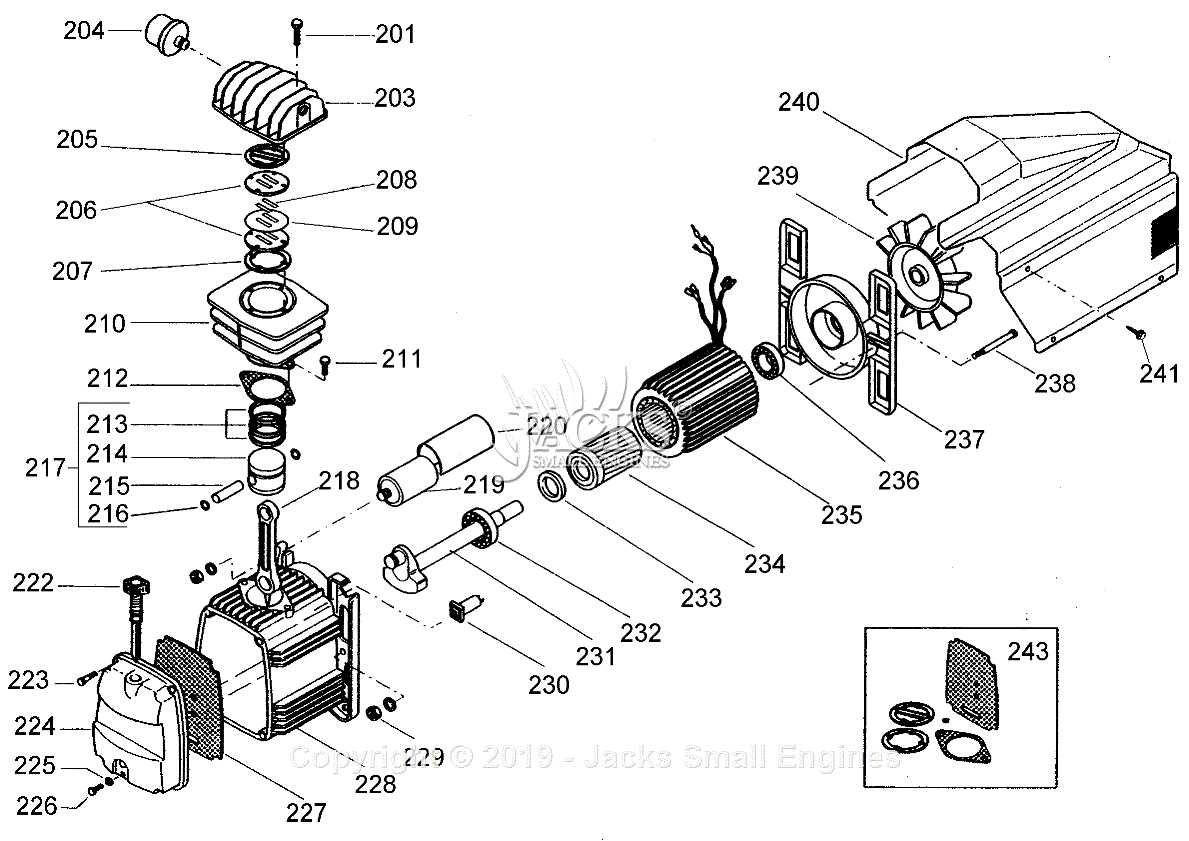
The display panel and lights are strategically placed for easy visibility, enhancing the overall user experience and making operation straightforward even in low-light conditions. Detailed Examination of Air Compressor UnitThe air compressor unit plays a crucial role in various applications, delivering the necessary pressure and airflow for tools and equipment. This section provides an in-depth analysis of its components, functionality, and maintenance requirements, ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Understanding the intricate parts of the compressor is essential for troubleshooting and effective use. Below is a breakdown of the key components and their functions:
Regular maintenance of these components is essential to prolong the lifespan of the unit and maintain efficiency. Periodic inspections and timely replacements of worn parts can prevent unexpected failures and ensure reliable operation. Jump Starter Clamps and Cables ExplainedJump starter clamps and cables are essential components used to initiate the engine of a vehicle with a depleted battery. Understanding their structure and functionality can enhance your ability to jump-start a vehicle efficiently and safely. These components typically consist of:
The cables serve as conductors between the jump starter and the vehicle battery. Key features include:
When selecting jump starter clamps and cables, consider the compatibility with your vehicle and the specifications suited for your engine type. Proper maintenance and regular checks can prevent potential issues and ensure reliable performance. Power Inverter Design and Key FunctionsPower inverters play a crucial role in converting direct current (DC) electricity into alternating current (AC) electricity, enabling a range of devices to operate efficiently. Understanding the structure and primary functions of these devices is essential for both users and manufacturers. This section explores the fundamental aspects of power inverter design and highlights their significance in various applications. Structure and ComponentsThe design of a power inverter typically includes several key components, such as the inverter circuit, control mechanisms, and protective features. The inverter circuit is responsible for the actual conversion process, utilizing semiconductor devices to switch the input current in a specific manner. Control mechanisms ensure that the output voltage and frequency remain stable, while protective features safeguard against overloads and short circuits. Functional AdvantagesPower inverters offer numerous functional advantages, including efficient energy conversion, compact size, and versatility in application. By transforming DC power into AC, these devices enable the use of household appliances and industrial machinery that require AC for operation. Their portability allows users to harness power in various settings, from mobile applications to backup power systems, ensuring reliability and convenience in energy use. Fuses and Safety Mechanisms in the DXAEJ14Electrical devices are equipped with various protective elements designed to prevent damage from overloads and short circuits. These components play a crucial role in ensuring safe operation and prolonging the lifespan of the equipment. Understanding the function and significance of fuses and safety mechanisms is essential for users to maintain optimal performance. Fuses serve as vital safety devices that interrupt the electrical circuit in case of excessive current flow. This action prevents potential hazards such as overheating and fire. It is important to choose the correct fuse rating to ensure proper protection while allowing normal operation. In addition to fuses, safety mechanisms may include circuit breakers and thermal protectors. These elements work in tandem to provide an added layer of security, ensuring that the device operates within safe parameters. Regular inspection and replacement of these components are necessary to maintain the reliability and safety of the unit.
Maintenance Tips for Core ComponentsProper upkeep of essential elements is vital for ensuring optimal performance and longevity of your equipment. By implementing a few straightforward practices, you can significantly enhance the reliability and efficiency of your tools.
Following these guidelines will help maintain the integrity of your equipment, prolonging its lifespan and ensuring consistent performance. Disassembly Guide: Step-by-Step InstructionsThis section provides a comprehensive guide for safely taking apart the device. Following these steps will ensure that you can access the internal components without damaging any parts. Whether you are performing maintenance or troubleshooting issues, a methodical approach to disassembly is essential. Before beginning, gather the necessary tools, including screwdrivers and pliers. Ensure that you work in a well-lit area and keep small components organized to avoid misplacing them. Step 1: PreparationStart by unplugging the device from any power source. This ensures safety while working on the equipment. Lay down a soft cloth to protect the surface and the device. Step 2: Remove the Outer ShellUsing a screwdriver, carefully remove the screws securing the outer casing. Set these screws aside in a designated container. Gently pull apart the casing, taking care not to force it, as this may cause damage to the clips. Step 3: Access Internal ComponentsWith the outer shell removed, you can now see the internal mechanisms. Identify and document the placement of each component, as this will aid in reassembly. Step 4: Detach Individual PartsTo remove specific elements, follow these steps:
After detaching each part, inspect them for wear and tear. Store all components securely to prevent loss during the process. Step 5: ReassemblyTo reassemble the device, reverse the disassembly steps. Ensure that all components are correctly aligned and secured before closing the outer shell. Test the device to verify that it functions properly after reassembly. Common Parts Replacement and AvailabilityMaintaining power tools often requires the timely replacement of various components to ensure optimal performance. Understanding the availability of these components can significantly enhance the longevity and functionality of the equipment. Users should be aware of common replacements and how to access them to keep their tools in excellent working condition. Replacement items typically include wear-and-tear components, such as batteries, chargers, and brushes. These elements play a crucial role in the overall efficiency of the equipment. Users are encouraged to consult authorized retailers or service centers for genuine replacements, as this ensures compatibility and quality. Additionally, many retailers offer online catalogs where users can easily locate the necessary components. This convenient access allows for quick order fulfillment and helps in planning maintenance schedules effectively. Always check the compatibility of the replacement parts with your specific tool model to avoid any issues during installation. Troubleshooting Diagram for Frequent IssuesThis section provides a comprehensive overview of common problems encountered with electrical equipment and their corresponding solutions. Understanding these issues can significantly enhance performance and extend the lifespan of your tools. Here are some typical challenges and their troubleshooting steps:
By following these guidelines, users can effectively address frequent issues and ensure reliable operation of their tools. |