2012 Dodge Grand Caravan Parts Diagram Overview
For those interested in maintaining or repairing their own vehicles, gaining insights into the arrangement of various elements under the hood can be extremely valuable. By understanding the specific configuration of components, owners can not only enhance their knowledge but also address mechanical issues with greater confidence.
Having a clear overview of the setup can make it easier to locate and identify different elements. This kind of detailed information is essential when tackling both routine maintenance and more complex repairs. Recognizing where each component is positioned will empower you to handle a variety of tasks more efficiently.
In this guide, we will explore the arrangement of essential elements for a popular vehicle model, providing a closer look at how they interconnect and function together. Whether you’re a seasoned mechanic or just beginning your journey in car maintenance, this information can help you navigate through the layout with ease.
Understanding Your Vehicle’s Structure and Components
Comprehending the layout and organization of your vehicle’s internal elements is essential for maintaining and repairing it effectively. This section provides an overview of the major components, highlighting the interconnected systems that contribute to the smooth operation of your automobile.
Key Systems and Their Functions

Each system within the vehicle plays a unique role in overall performance. Familiarizing yourself with these areas–such as the electrical system, transmission, and braking–will help you identify where potential issues may arise and understand how various parts contribute to a well-functioning vehicle.
Benefits of Knowing the Configuration

By understanding the arrangement and roles of different systems, you can gain confidence in addressing minor maintenance tasks. This knowledge empowers you to recognize signs of wear and to seek timely repairs, ensuring longevity and safety for your vehicle.
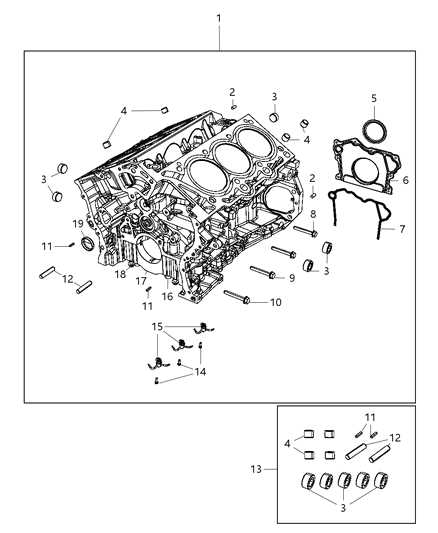
Engine Components Overview
The engine system is composed of multiple interconnected parts that work together to ensure smooth operation and optimal performance. This section provides a detailed look at the essential components that make up this system, offering insight into their roles and how they contribute to overall functionality.
- Cylinder Block: The foundation of the engine, housing various essential parts, and forming the basis of the internal combustion process.
- Pistons: These move up and down within the cylinder block, converting fuel into mechanical power for movement.
- Crankshaft: Connected to the pistons, it translates their linear movement into rotational force, ultimately powering the vehicle.
- Camshaft: This component regulates the opening and closing of the intake and exhaust valves, coordinating with the crankshaft for precise timing.
- Timing Belt: A crucial belt that synchronizes the movement between the crankshaft and camshaft, ensuring that the engine runs smoothly.
- Fuel Injectors: These deliver fuel into the combustion chamber, precisely controlling the amount and timing for efficient fuel use.
- Exhaust Manifold: Collects exhaust gases from the engine’s cylinders and directs them to the exhaust system for safe expulsion.
Transmission Parts and Functionality
The transmission system is a crucial component that manages the distribution of power from the engine to the wheels. This system ensures that the vehicle can operate smoothly at various speeds and provides the necessary torque to get the vehicle moving. Understanding the key elements within this system helps in identifying potential issues and ensuring efficient maintenance.
Main Components of the Transmission System
The transmission consists of several essential parts, each with a unique role. These include the gears, which adjust the torque and speed; the clutch, which controls the engagement between the engine and transmission; and the torque converter, which helps transfer power smoothly. Together, these parts allow for seamless acceleration and efficient energy use.
Common Transmission Features
In addition to the main components, transmissions often include elements such as the valve body, which directs fluid through the system, and the transmission fluid pump, which maintains proper lubrication. These features work in harmony to ensure that the transmission functions effectively, providing a reliable driving experience.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Gears | Adjust torque and speed to match driving conditions. |
| Clutch | Controls the connection between the engine and the transmission. |
| Torque Converter | Facilitates power transfer from the engine to the transmission smoothly. |
| Valve Body | Directs transmission fluid through various passages. |
| Fluid Pump | Maintains lubrication and fluid pressure within the system. |
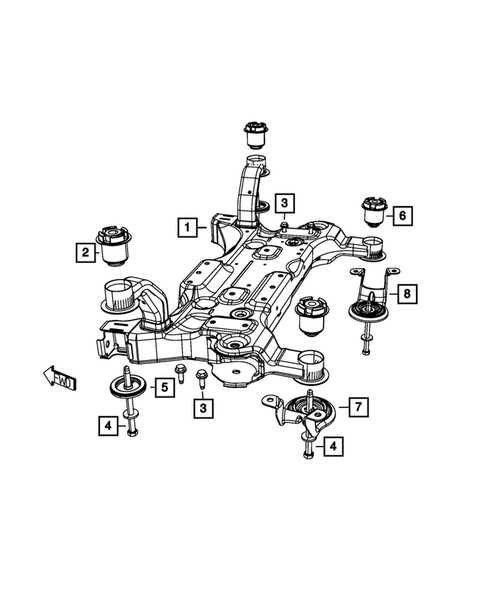
Suspension System Layout
The suspension system plays a vital role in providing stability, comfort, and control while driving. By absorbing shocks and maintaining tire contact with the road, it ensures a smoother ride and better handling. This section delves into the main components that make up the suspension layout, giving an overview of their individual roles and how they work together to enhance vehicle performance.
The setup typically includes shock absorbers, springs, and control arms, each designed to respond to different aspects of road conditions. Additionally, anti-roll bars contribute to reducing body roll during cornering, improving overall stability. Each element works cohesively to deliver a balance of comfort and control, adjusting dynamically as you navigate various driving environments.
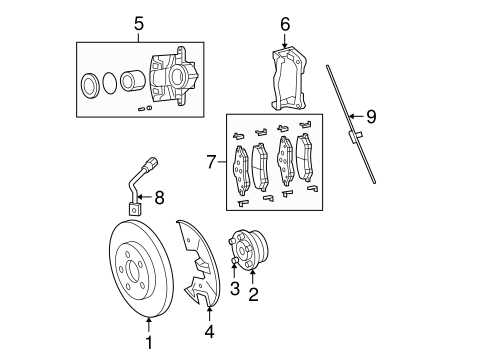
Brake System Components Explained
The brake system is essential for safe driving, providing the ability to slow down and stop the vehicle effectively. This section explores the main components involved in the braking process, describing their functions and how they work together to ensure smooth and reliable braking performance.
- Brake Pedal: The brake pedal is the component pressed by the driver’s foot to initiate braking. It transmits force to other parts of the system to engage the brakes.
- Master Cylinder: This component converts the force from the brake pedal into hydraulic pressure, which is then distributed through brake lines to other parts.
- Brake Lines and Hoses: These carry the hydraulic fluid under pressure from the master cylinder to the brake calipers or wheel cylinders at each wheel.
- Brake Calipers: Found in disc brakes, calipers house the brake pads and squeeze them against the brake rotor to create friction and slow down the vehicle.
- Brake Pads: These pads are friction materials that press against the rotors (in disc brakes) or drums (in drum brakes) to create the necessary friction for stopping.
- Rotors and Drums: Rotors are part of disc brakes, while drums are used in drum brake systems. They are directly attached to the wheels and experience friction from the brake pads or shoes to decelerate the vehicle.
- Brake Shoes: Typically found in drum brakes, brake shoes press outward against the brake drum to produce friction and halt the wheel’s rotation.
- Parking Brake: The parking brake, or emergency brake, is a separate system that applies braking force independently, useful for keeping the vehicle stationary when parked.
Electrical System Parts Guide
This section provides a comprehensive overview of the components that comprise the electrical system of a vehicle. Understanding these elements is crucial for troubleshooting issues and performing maintenance. The electrical network includes various devices that work together to ensure the functionality of the automobile’s electronic features.
Key Components of the Electrical Network
The electrical network consists of several vital components, including the battery, alternator, starter motor, and wiring harnesses. Each element plays a significant role in delivering power to the vehicle’s systems. The battery supplies energy, while the alternator recharges it during operation. The starter motor initiates the engine’s operation, and the wiring harnesses connect these parts, allowing for seamless electrical flow.
Importance of Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance of the electrical system is essential to prevent potential issues that may arise from wear and tear. Periodic inspections can help identify damaged wires or faulty connections before they lead to significant problems. Ensuring that all components are functioning properly contributes to the overall efficiency and reliability of the vehicle.
Cooling System Parts and Operation
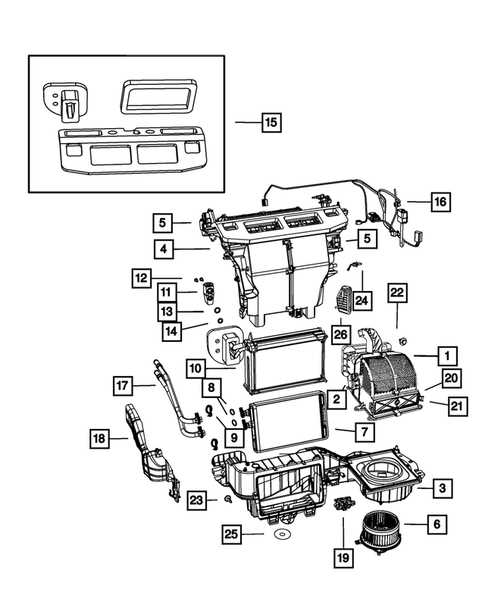
The cooling system plays a vital role in maintaining optimal engine temperature and ensuring efficient performance. It consists of various components that work in harmony to dissipate heat generated during engine operation. Understanding the function of these elements is essential for diagnosing issues and performing maintenance.
At the heart of the system is the radiator, which facilitates the transfer of heat from the coolant to the surrounding air. The thermostat regulates the flow of coolant, ensuring that the engine warms up quickly and operates within the ideal temperature range. Water pumps circulate the coolant throughout the system, while hoses connect various components, allowing for seamless fluid movement.
Additionally, cooling fans help draw air through the radiator to enhance cooling efficiency, especially during slow-moving traffic or idling. Regular inspection of these elements is crucial to prevent overheating and potential engine damage, ensuring a smooth and reliable driving experience.
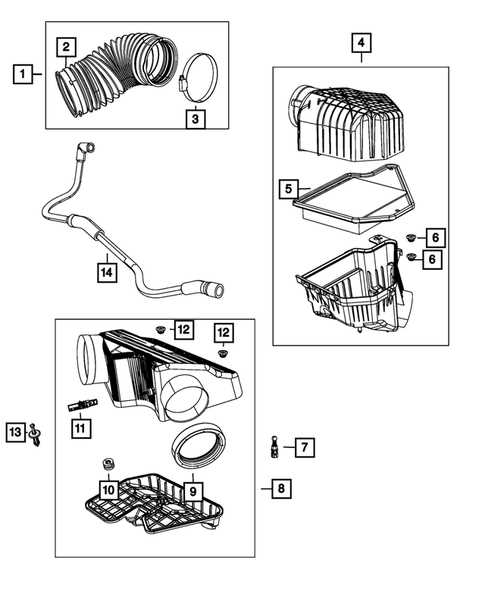
Fuel System Diagram Breakdown
The fuel delivery mechanism plays a critical role in ensuring optimal engine performance. Understanding the layout and components of this system is essential for diagnosing issues and performing maintenance effectively. This section provides an overview of the various elements involved in the fuel supply process, offering insight into their functions and interconnections.
Key Components

- Fuel Tank: The primary reservoir that holds the fuel before it is transported to the engine.
- Fuel Pump: Responsible for moving the fuel from the tank to the engine at the necessary pressure.
- Fuel Filter: Removes impurities and contaminants from the fuel, protecting the engine components.
- Fuel Injectors: Sprays the fuel into the combustion chamber, ensuring proper mixing with air for efficient combustion.
- Fuel Lines: Hoses that connect the various components, allowing for the flow of fuel throughout the system.
Functionality Overview
- The fuel is drawn from the tank by the fuel pump.
- It then travels through the fuel filter to eliminate any debris.
- After filtration, the clean fuel is directed to the fuel injectors.
- The injectors atomize the fuel, mixing it with air before it enters the engine cylinders.
- This process supports the combustion cycle, promoting efficient engine operation.
Steering System Layout and Parts
The steering mechanism is a crucial component of a vehicle, enabling the driver to control its direction effectively. Understanding the configuration and components of this system is essential for maintenance and troubleshooting. This section outlines the primary elements involved in the steering assembly and their functions.
Key Components of the Steering System
- Steering Wheel: The primary interface for the driver, allowing for manual direction input.
- Steering Column: Connects the steering wheel to the steering gear, providing a pathway for driver commands.
- Steering Gear: Converts the rotational motion of the steering wheel into lateral movement of the wheels.
- Linkages: Components that transmit movement from the steering gear to the wheels, ensuring precise control.
- Power Steering Pump: Assists in reducing the effort needed to steer, enhancing the driving experience.
Functionality and Operation
Each component plays a vital role in ensuring smooth and responsive steering. The steering wheel transmits the driver’s inputs through the column to the gear mechanism. The gear then engages the linkages, which move the wheels according to the desired trajectory. Power assistance from the pump makes steering lighter and more manageable, particularly at low speeds.
Exhaust System Components Overview
The exhaust system plays a crucial role in a vehicle’s overall performance and efficiency. Its primary function is to direct harmful gases produced during combustion away from the engine and passenger compartment. Understanding the various elements of this system is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
Typically, the exhaust system comprises several key components, including the manifold, which collects gases from the engine; the catalytic converter, which reduces harmful emissions; and the muffler, designed to minimize noise. Each component works in harmony to ensure optimal functionality and compliance with environmental regulations.
Additionally, exhaust pipes connect these components, guiding the exhaust gases safely out of the vehicle. Regular inspections and timely replacements of these parts are vital for maintaining performance and prolonging the lifespan of the vehicle.
Air Conditioning System Diagram

The air conditioning mechanism in a vehicle plays a crucial role in ensuring comfort by regulating temperature and humidity. Understanding the components and their interconnections helps in diagnosing issues and performing maintenance effectively.
Key Components of the Cooling System
- Compressor: This device compresses refrigerant and circulates it through the system.
- Condenser: It cools and condenses the refrigerant, converting it from gas to liquid.
- Evaporator: Located inside the cabin, it absorbs heat from the air, cooling it before it enters the vehicle.
- Expansion Valve: It controls the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator.
- Receiver-Drier: It filters moisture and impurities from the refrigerant.
Operation Process
- The compressor draws in low-pressure refrigerant gas and compresses it into a high-pressure gas.
- This high-pressure gas then travels to the condenser, where it dissipates heat and turns into a liquid.
- The liquid refrigerant passes through the expansion valve, reducing its pressure before entering the evaporator.
- In the evaporator, the refrigerant absorbs heat from the interior air, cooling it before it circulates back into the cabin.
Maintaining these components in optimal condition is essential for efficient cooling performance and overall vehicle comfort.