2013 Hyundai Elantra Parts Diagram Overview
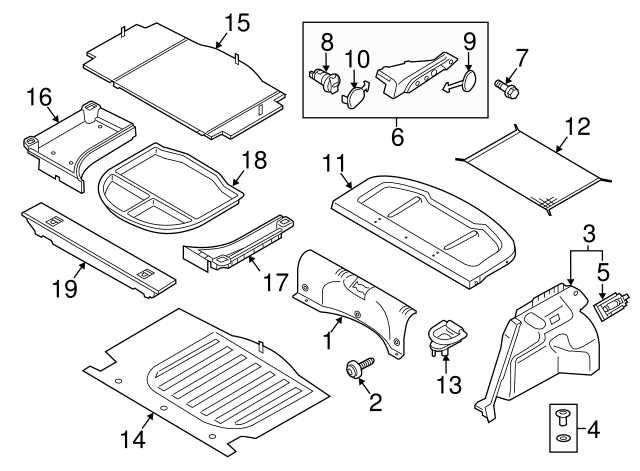
Understanding the arrangement of various components within a well-known sedan model can be crucial for maintaining and repairing the vehicle efficiently. Each section of the car, from the engine to the interior features, is meticulously organized to ensure optimal performance and ease of access during repairs. This guide aims to offer a clear visualization of these structures, helping users identify the necessary elements with ease.
Whether it’s for a simple replacement or a more complex repair task, having a detailed breakdown of the internal and external setups is invaluable. It allows for quicker identification of areas that may need attention, reducing downtime and ensuring the vehicle remains in top condition. The comprehensive layout offered here covers all the essential aspects of the car’s build, providing clarity for both professionals and enthusiasts.
By exploring the structure of the vehicle, users can gain a better understanding of how different elements interact. This helps in diagnosing issues more accurately and ensuring the correct part is addressed, promoting smoother maintenance processes and prolonging the car’s lifespan.
2013 Hyundai Elantra Parts Diagram Overview
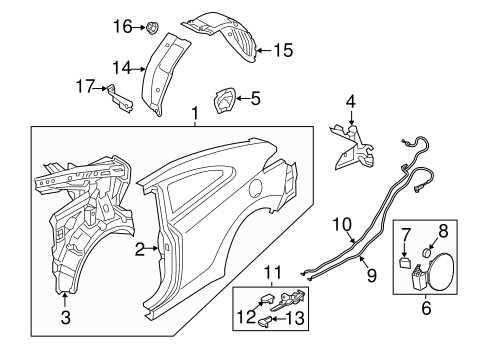
The layout of mechanical components in this model showcases a well-organized structure that ensures efficient performance and durability. Every section is carefully designed to facilitate easy access for maintenance and repairs, offering a clear understanding of how different elements work together. This visual representation serves as a guide for identifying key elements and understanding their interactions within the system.
Key Sections and Layout
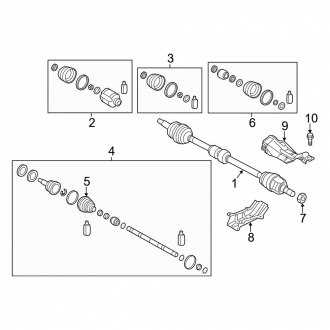
The vehicle’s mechanical map includes various assemblies, such as the powertrain, suspension, and electrical systems. Each of these sections is arranged logically, enabling smooth operation while providing room for future adjustments or part replacements. The detailed positioning of components ensures compatibility and smooth integration.
Maintenance and Repair Considerations
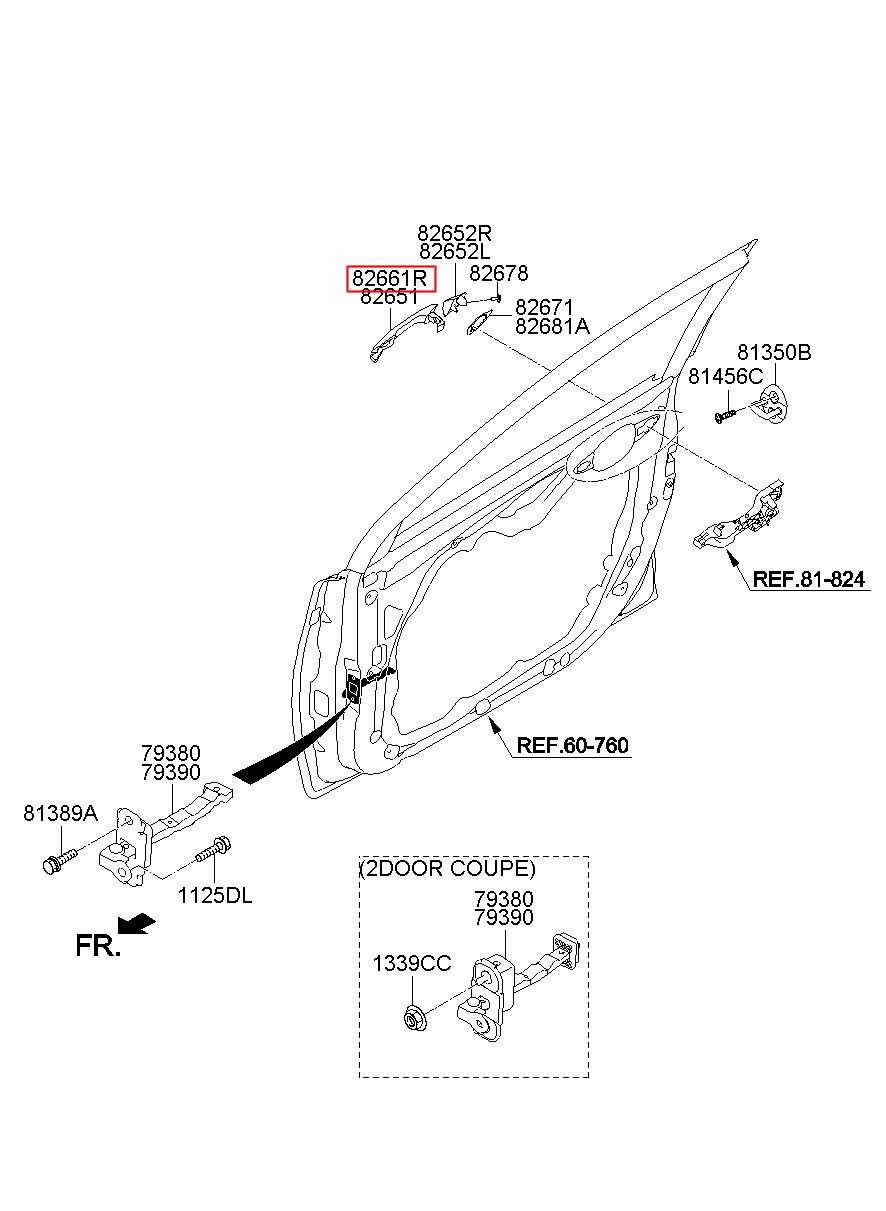
Understanding the layout is essential for any repairs or maintenance tasks. The clear distribution of assemblies allows for pinpointing potential issues and ensures a seamless workflow during service. With all elements clearly marked, maintaining optimal performance is straightforward and efficient.
Key Components in the Engine Bay
The engine bay houses crucial elements that contribute to the overall functioning and performance of the vehicle. These components work in harmony to ensure smooth operation, regulating power delivery, airflow, and maintaining the temperature within optimal limits. Understanding the layout and roles of these parts helps in diagnosing issues and performing maintenance tasks efficiently.
Power Generation and Distribution
At the heart of the engine bay lies the engine block, responsible for generating mechanical power. This power is distributed to various systems through the alternator, ensuring electrical components receive sufficient energy. Additionally, the battery serves as a storage unit, providing power during start-up and supporting electrical functions when the engine is off.
Cooling and Air Management
To prevent overheating, the radiator and coolant system are essential in regulating engine temperature. These systems, along with the air intake mechanism, ensure that fresh air flows into the engine, enhancing combustion and efficiency. The proper balance of air and cooling helps maintain performance and avoid potential damage from excessive heat.
Suspension System Breakdown
The suspension system plays a crucial role in maintaining vehicle stability, comfort, and handling by absorbing road irregularities and ensuring that tires maintain proper contact with the surface. This section will provide an overview of the key components that work together to create a smooth driving experience and contribute to overall vehicle safety.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Shock Absorbers | Control the impact and rebound movement of the vehicle’s springs to ensure a smooth ride. |
| Springs | Support the vehicle’s weight and absorb bumps by compressing and releasing energy. |
| Control Arms | Link the wheels to the frame, allowing up and down movement while keeping the wheel’s angle steady. |
| Stabilizer Bar | Reduces body roll during cornering, helping to keep the vehicle level and balanced. |
| Ball Joints | Allow pivoting between the steering knuckles and control arms for smooth movement and steering. |
Understanding the Exhaust Layout
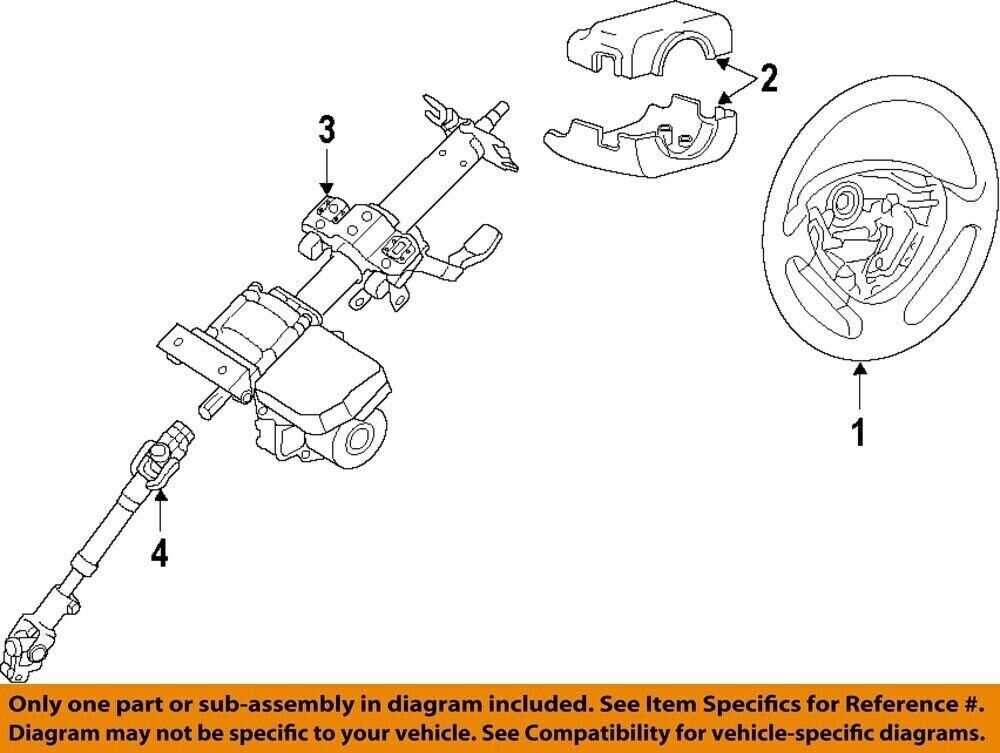
The exhaust system is a critical component that directs and manages the gases produced during engine combustion. Its design ensures the efficient removal of emissions while maintaining optimal engine performance. The layout typically follows a standard flow, guiding gases from the engine to the tailpipe while controlling noise and filtering harmful substances.
- Exhaust Manifold: The starting point, it collects gases from the engine’s cylinders and funnels them into the exhaust pipe.
- Catalytic Converter: A key element responsible for reducing harmful emissions by converting toxic gases into less harmful byproducts before they exit the vehicle.
- Muffler: Designed to reduce noise, the muffler quiets the engine’s sound waves as the gases pass through its chambers.
- Resonator: Often working in tandem with the muffler, this component further tunes and quiets the sound output from the engine.
- Tailpipe: The final section, where the cleaned and quieted gases are released into the atmosphere.
Each part of the exhaust system contributes to the vehicle’s overall efficiency, ensuring that it runs smoothly, reduces noise pollution, and complies with emission standards.
Electrical Wiring and Connections

Understanding the intricacies of the electrical system is crucial for maintaining vehicle functionality and safety. The wiring and connections play an essential role in distributing power and ensuring that all components operate efficiently. Faulty or damaged connections can lead to various operational issues, which makes it important to regularly inspect and service the electrical system.
The electrical wiring is composed of multiple circuits that connect the battery, lights, ignition, and other vital systems. Each circuit has its own designated function, and any break or short circuit can cause malfunctions. Regular maintenance and awareness of common issues help in preventing long-term damage and costly repairs.
Connections between different components, such as connectors and terminals, are designed to ensure secure transmission of electrical signals. Corrosion, loose connections, or exposure to moisture can disrupt these pathways, leading to performance problems. Ensuring that all connections are clean and properly secured is vital for the overall reliability of the vehicle’s systems.
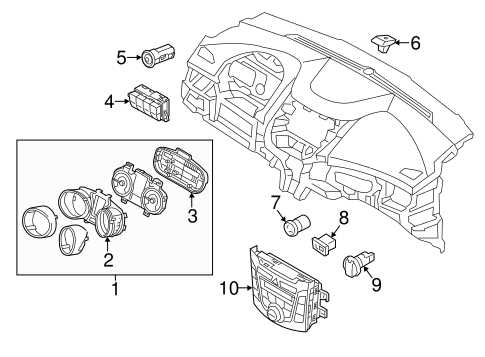
Interior Control Panel Components
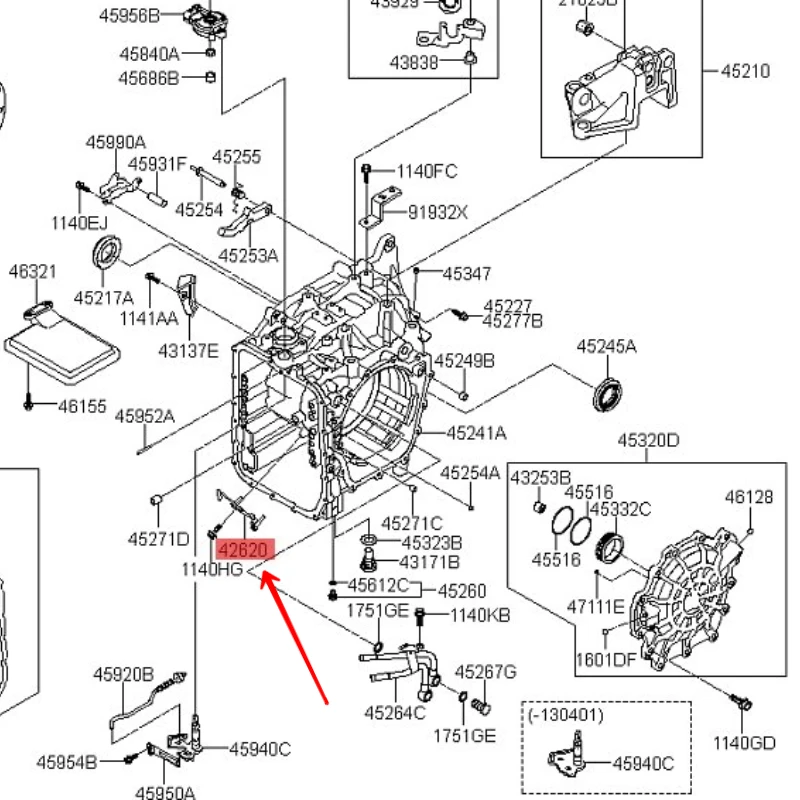
The control panel located within the cabin plays a vital role in managing various features of the vehicle. It acts as the central hub for user interaction, enabling access to essential functions that enhance driving comfort and convenience. Understanding the components of this interface is crucial for effective maintenance and repair.
Key elements of the control panel include climate control switches, which regulate temperature and airflow, and infotainment controls, allowing the driver to operate audio and navigation systems effortlessly. Additionally, instrument cluster displays provide real-time information regarding speed, fuel levels, and engine status, ensuring that the driver remains informed about the vehicle’s performance.
Moreover, lighting controls contribute to visibility and safety by managing exterior and interior lights, while power window switches facilitate the operation of side windows. Each component plays a significant role in creating a user-friendly environment, ultimately enhancing the overall driving experience.
Brake System Parts and Diagram
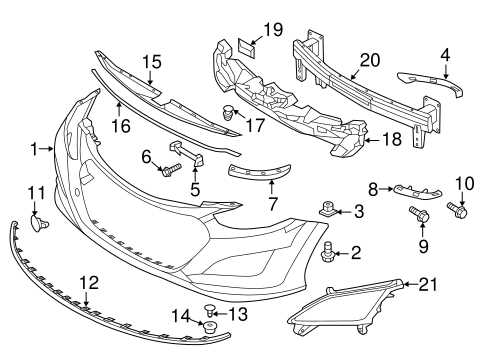
The braking system is a crucial component of any vehicle, ensuring safety and control during operation. Understanding its various elements can enhance maintenance and performance, contributing to a smoother driving experience. This section outlines the essential components involved in this vital system.
- Brake Pedal: The driver applies pressure to this component to initiate the braking process.
- Master Cylinder: Converts the force from the brake pedal into hydraulic pressure, activating the brakes.
- Brake Lines: Transport hydraulic fluid from the master cylinder to the braking mechanisms.
- Calipers: Clamp down on the brake pads to create friction against the rotors.
- Brake Pads: Provide the friction necessary to slow down or stop the vehicle when pressed against the rotors.
- Rotors: Disc-shaped components that work with the pads to create friction and stop the wheels from turning.
- Brake Fluid: The hydraulic fluid that transmits pressure from the master cylinder to the calipers.
Familiarity with these components can aid in diagnosing issues, ensuring optimal functionality. Regular inspections and maintenance are recommended to prolong the lifespan of these crucial elements.
Fuel System Design and Layout
The fuel system is a critical component of any vehicle, responsible for storing and delivering fuel to the engine for combustion. This system is designed to ensure efficient fuel flow, optimal pressure, and proper filtration to maintain engine performance and longevity. A well-structured fuel system layout facilitates smooth operation and minimizes the risk of issues such as fuel leaks or contamination.
In general, the fuel system consists of several key components, including the fuel tank, fuel pump, fuel filter, and fuel injectors. The tank is where the fuel is stored, while the pump is responsible for transporting it to the engine. The filter ensures that any impurities are removed before the fuel reaches the injectors, which precisely deliver the fuel into the combustion chamber.
The arrangement of these components is essential for maintaining proper pressure and flow. Various factors, such as the location of the fuel tank and the routing of fuel lines, are taken into account during the design process. By optimizing these elements, manufacturers can enhance the efficiency of the fuel system, leading to improved engine performance and reduced emissions.
Furthermore, modern vehicles often incorporate advanced technologies such as returnless fuel systems, which help streamline the fuel delivery process. This innovation reduces the complexity of the fuel layout while improving responsiveness and overall efficiency. Understanding the design and layout of the fuel system is vital for effective maintenance and troubleshooting, ensuring that the vehicle operates at its best.
Transmission and Drivetrain Overview

The transmission and drivetrain system is essential for the effective transfer of power from the engine to the wheels. This assembly plays a crucial role in ensuring smooth acceleration, optimal fuel efficiency, and overall vehicle performance. A well-functioning drivetrain is vital for maintaining control and stability during various driving conditions.
Transmission Types include automatic, manual, and continuously variable options, each offering distinct advantages. Automatic transmissions provide convenience and ease of use, while manual options allow for greater driver engagement and control. Continuously variable transmissions (CVTs) are designed to optimize power delivery by seamlessly adjusting the gear ratios.
The drivetrain components encompass several key elements, including the driveshaft, differential, and axles. The driveshaft transmits torque from the transmission to the differential, which splits the power between the wheels, allowing for smooth turns and enhanced traction. Axles connect the wheels to the differential, facilitating wheel rotation and supporting vehicle weight.
Regular maintenance of the transmission and drivetrain is vital for ensuring longevity and performance. This includes checking fluid levels, inspecting for leaks, and replacing worn components. Proper care helps to prevent costly repairs and ensures a safe and enjoyable driving experience.
Cooling System Components
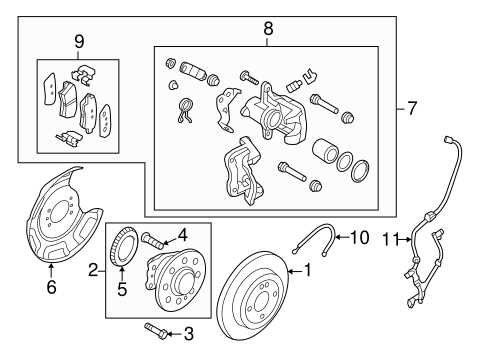
The cooling system is crucial for maintaining optimal engine temperature, ensuring efficient performance and preventing overheating. It consists of various components that work together to dissipate heat generated during engine operation, thereby safeguarding the engine and enhancing its longevity.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Radiator | Acts as the main heat exchanger, transferring heat from the coolant to the air. |
| Water Pump | Circulates coolant throughout the engine and radiator, maintaining constant flow. |
| Thermostat | Regulates coolant temperature by controlling flow to the radiator based on engine heat. |
| Cooling Fans | Enhance airflow through the radiator, especially during low-speed conditions. |
| Coolant Reservoir | Holds excess coolant and provides a source for the system to draw from as needed. |
Air Conditioning Unit Diagram
The air conditioning system is essential for maintaining a comfortable environment within the vehicle. This section provides a comprehensive overview of its components and their interconnections, allowing for a better understanding of how the system operates.
At the heart of the system is the compressor, which pressurizes the refrigerant and circulates it throughout the system. The refrigerant then passes through the condenser, where it releases heat and transforms into a liquid state. Following this, the liquid refrigerant travels to the expansion valve, which regulates its flow and pressure before entering the evaporator.
Inside the evaporator, the refrigerant absorbs heat from the cabin air, cooling it before it is circulated back into the vehicle. The blower motor plays a vital role here, as it pushes the cooled air through the vents. Each of these components works in harmony to provide efficient climate control, ensuring passenger comfort regardless of external conditions.
Understanding the layout and function of the air conditioning system is crucial for effective troubleshooting and maintenance. Proper knowledge of these components aids in identifying issues and performing repairs as necessary, keeping the system running smoothly.
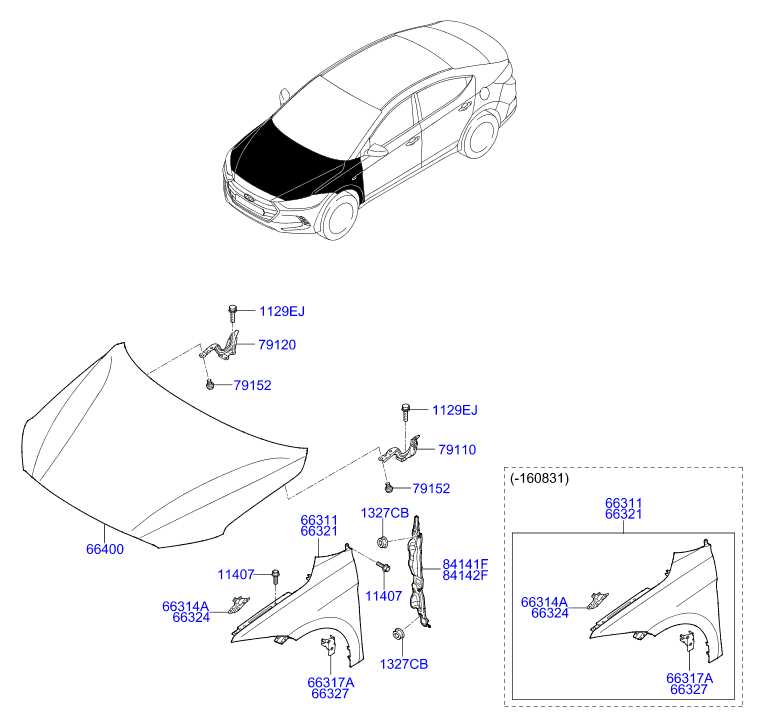
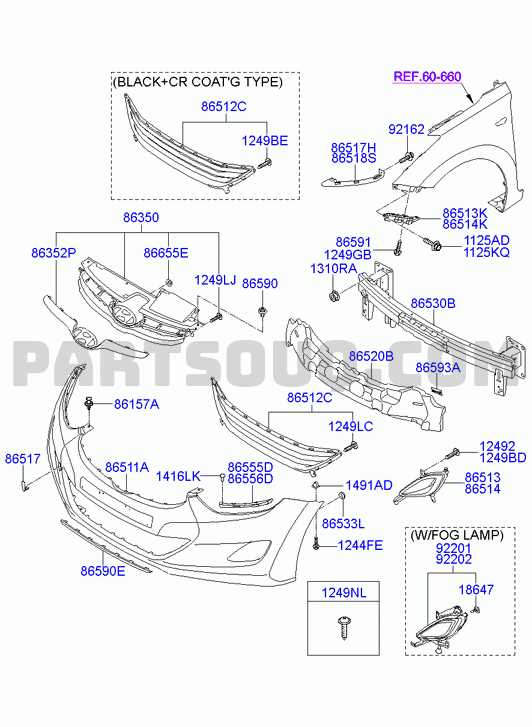
Exterior Body and Frame Components
The outer structure and framework of a vehicle are essential for both aesthetics and functionality. These elements play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of the vehicle while contributing to its visual appeal. Understanding the various components that constitute the exterior framework can aid in effective maintenance and repair.
Below is a table outlining some key elements found in the outer body and frame structure:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Fender | A panel that surrounds the wheel well, protecting the tires and enhancing aerodynamics. |
| Hood | The cover over the engine compartment, allowing access for maintenance and inspections. |
| Trunk Lid | The rear cover of the vehicle’s cargo area, providing access to storage space. |
| Door | Entry and exit points for passengers, often equipped with locking mechanisms. |
| Quarter Panel | A section of the vehicle’s body located behind the rear door, contributing to overall shape and stability. |
| Roof | The upper covering of the vehicle, providing structural integrity and protection from the elements. |
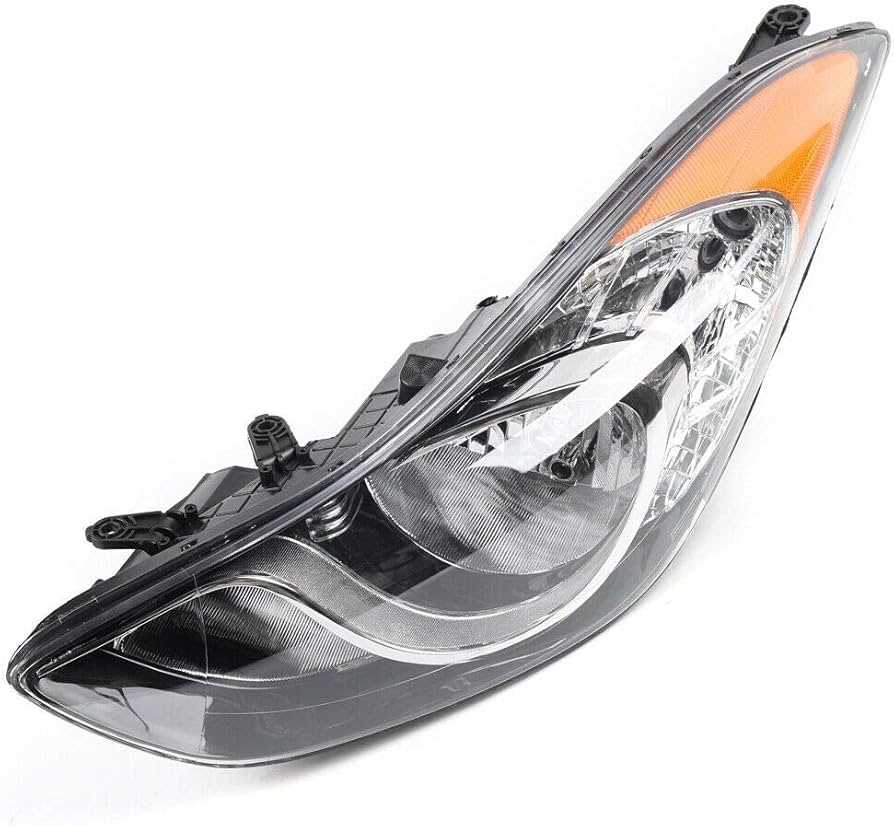
Lighting System Wiring and Parts
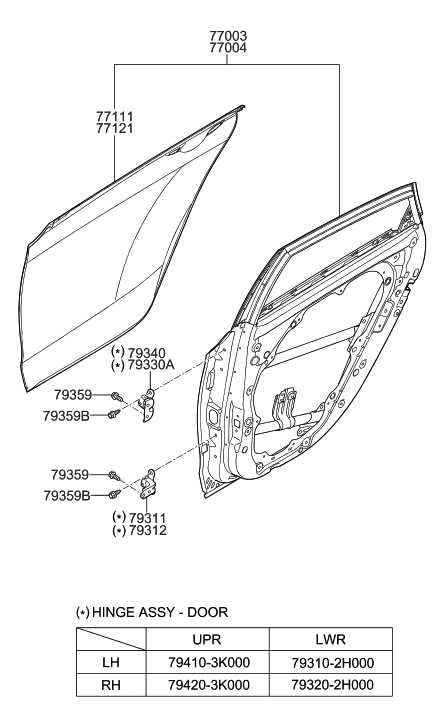
The illumination system of a vehicle plays a crucial role in ensuring safety and visibility during travel, particularly in low-light conditions. Understanding the wiring layout and the components involved is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. This section will provide an overview of the essential elements that make up the lighting system, including the connections and the various types of fixtures utilized.
The wiring configuration typically involves a network of cables that connect different lighting fixtures to the vehicle’s power source. This network facilitates the functioning of headlights, taillights, turn signals, and interior lights. Each component is designed to operate in harmony, providing optimal illumination and enhancing the overall driving experience.
Key components of the illumination system include the light bulbs, connectors, and relays. Light bulbs vary in type and brightness, impacting both visibility and energy consumption. Connectors serve as the interface between the wiring and the fixtures, ensuring a secure electrical connection. Relays are employed to control the flow of electricity, allowing for efficient operation of high-power lighting elements.
Regular inspection of the wiring and components is vital for preventing electrical failures and ensuring reliable performance. Signs of wear or damage, such as frayed wires or burnt-out bulbs, should be addressed promptly to maintain the integrity of the lighting system.