2010 Ford Flex Parts Diagram Overview
Understanding the intricate network of essential elements within a modern vehicle can be challenging. However, having a detailed overview of each critical element offers a clearer perspective on how the entire system functions. In this guide, we will explore various crucial components of a well-known mid-size crossover, focusing on structural and mechanical aspects that keep it running smoothly.
The focus will be on the essential mechanisms responsible for performance, safety, and comfort. Each section will provide insights into the configuration of key systems, from the powertrain to the interior layout. This approach ensures that both novice enthusiasts and experienced mechanics can benefit from a thorough explanation of this vehicle’s layout and functionality.
Overview of 2010 Ford Flex Components
The vehicle in question is a complex machine made up of many interdependent elements, each contributing to its overall performance and functionality. From the engine to the smallest internal mechanisms, every aspect is designed to work seamlessly together, providing the driver with a smooth and reliable experience on the road. Understanding these elements helps ensure the proper maintenance and longevity of the vehicle.
Some of the most significant components include the powertrain, electrical systems, and structural elements. Each of these plays a critical role in driving dynamics, safety, and comfort. By gaining insight into the various systems and their individual functions, users can appreciate how this intricate design keeps everything running efficiently.
Engine Assembly and Specifications
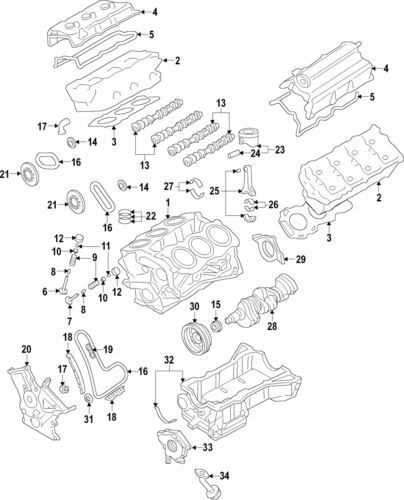
The design and configuration of the engine system play a crucial role in ensuring optimal performance and longevity. This section explores the key components that make up the entire system, highlighting how various elements work together to deliver efficient power and reliable operation. The focus is on the structural arrangement, materials used, and the engineering choices that influence functionality and durability.
The assembly features a combination of mechanical and electronic systems, each precisely aligned to meet performance goals. Detailed attention is given to the layout, ensuring the smooth integration of moving parts and the seamless flow of fluids. Each component, from the combustion chamber to the exhaust system, is examined for its contribution to overall efficiency and emissions control.
Understanding the specifications of this system involves looking into factors such as displacement, compression ratio, and fuel delivery methods. These details provide insight into how power is generated and maintained under different conditions. In addition, the section covers how modern advancements in materials and manufacturing processes have improved durability and reduced maintenance needs.
Transmission System Details
The transmission system plays a critical role in ensuring efficient power delivery from the engine to the wheels. It manages the distribution of torque, allowing the vehicle to adapt to different driving conditions, whether accelerating on highways or cruising through city streets. Understanding its components and their functions can help diagnose potential issues and maintain smooth performance.
- Gearbox: The heart of the system, responsible for adjusting speed and torque by shifting between various gears.
- Clutch Assembly: A key interface that connects and disconnects the engine from the gearbox, allowing smooth gear changes and stopping the vehicle without stalling.
- Driveshaft: This component transfers the power generated by the system to the wheels, ensuring they receive the necessary force to move the vehicle.
- Torque Converter: In automatic versions, it replaces the clutch and provides smooth power transfer by regulating engine load and wheel speed.
- Fluid System: Essential for lubrication and cooling, ensuring all moving parts operate smooth
Suspension and Steering Parts
In this section, we will explore the key components responsible for ensuring smooth movement and control of a vehicle. These elements play a critical role in maintaining stability, comfort, and precise handling during driving, especially on varied road surfaces.
The main components involved in maintaining optimal driving dynamics include a range of items designed to absorb shock, provide flexibility, and direct the vehicle accurately. Below is a breakdown of the essential elements and their functions:
- Shocks and Struts: These elements absorb road impact, ensuring a smoother ride by minimizing the force transferred to the vehicle’s body.
- Control Arms: They connect the frame to the wheels, allowing the wheels to move vertically while keeping them aligned with the road.
- Tie Rods: These parts help steer the vehicle by transmitting the input from the steering wheel to the wheels.
- Ball Joints: Acting as pivotal points, these enable a range of motion while securing the suspension to the wheels.
- Stabilizer Bar: This bar helps reduce body roll during sharp turns, providing a more stable and controlled drive.
Understanding how these elements work together is crucial for ensuring safe and efficient operation. Regular maintenance of these components ensures better handling and a comfortable driving experience.
Electrical Wiring and Schematics
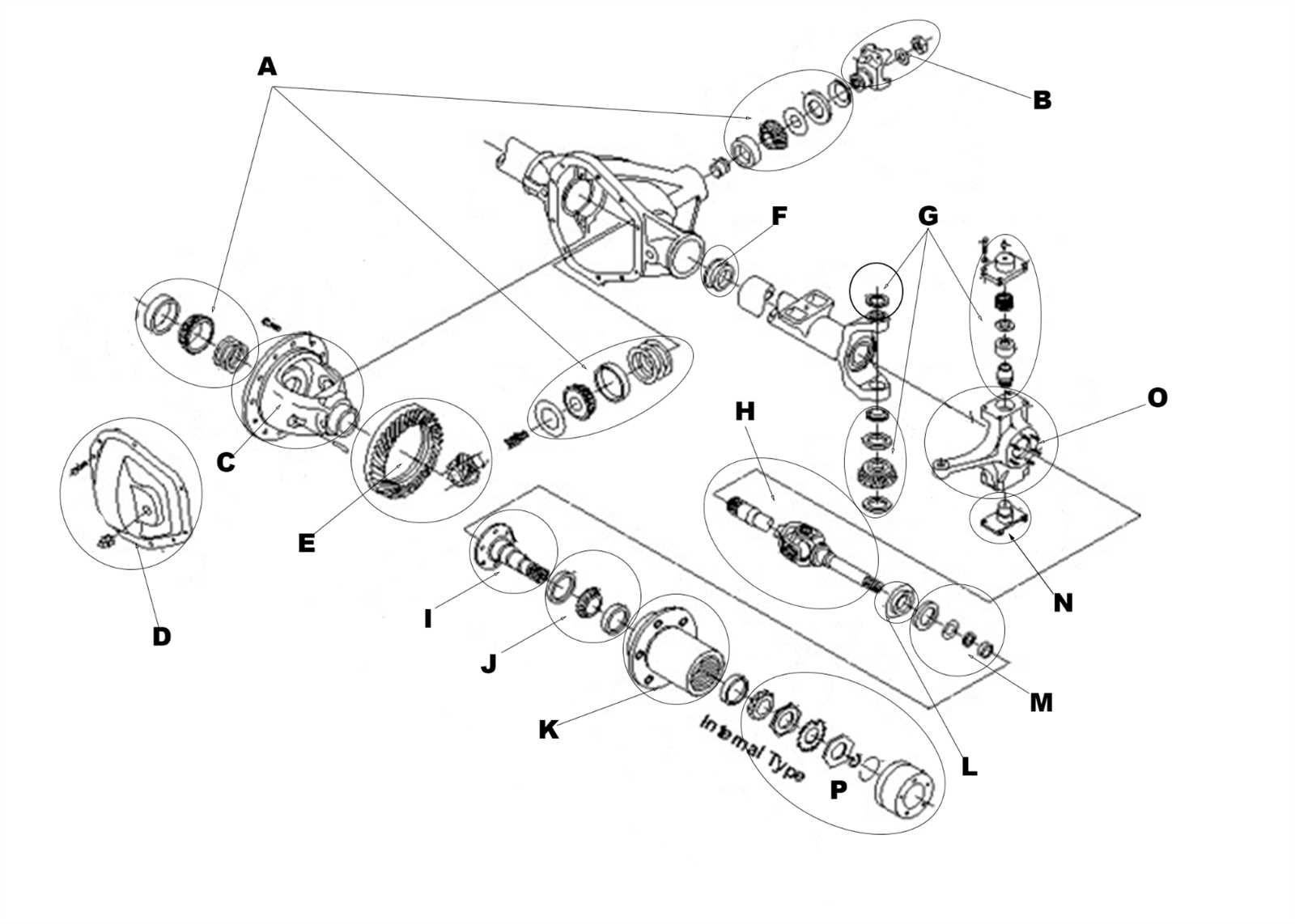
Understanding the network of electrical connections within a vehicle is essential for maintaining, troubleshooting, and upgrading its various systems. Electrical routing plays a key role in managing energy flow, signaling, and ensuring that all components function harmoniously. This section provides an overview of how these networks are structured and represented in technical illustrations.
Overview of Circuitry Layouts
The architecture of electrical systems can be complex, with numerous connections intertwining across various subsystems. Diagrams are used to simplify these connections, showing how different elements interact with each other. They allow users to visualize the path of current and help identify potential issues when malfunctions occur.
- Power distribution networks
- Signal transmission routes
- Grounding points and their importance
Common Electrical Symbols
When examining these technical illustrations, it’s crucial to recognize the standardized symbols used to represent electrical components. This helps in reading the schematic efficiently and understanding the role of each part.
- Switches: Controlling power flow
- Relays: Automatic circuit control
- Connectors: Joining various wiring paths
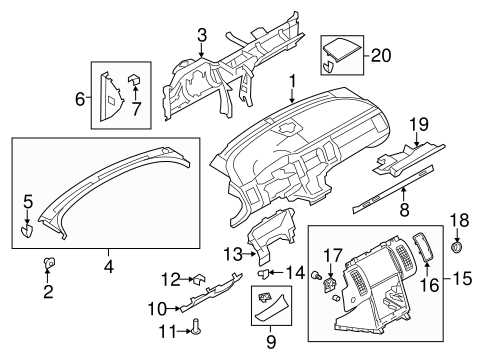
Interior Features and Controls
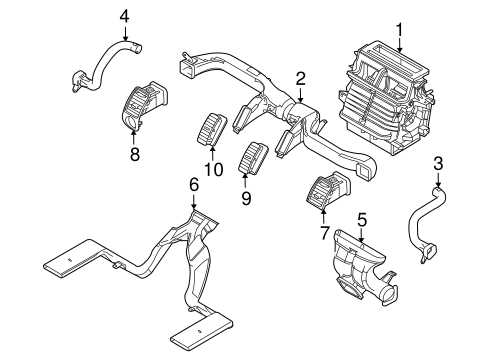
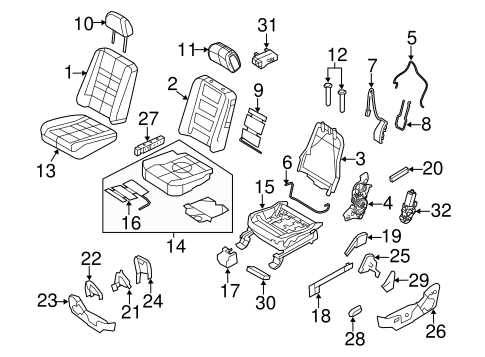
The cabin of this vehicle model offers a thoughtfully designed space that prioritizes comfort, accessibility, and driver convenience. With an intuitive layout, every control is positioned for ease of use, ensuring that the driver can focus on the road while easily managing all essential functions. Passengers also benefit from the well-organized setup, allowing them to enjoy a pleasant and hassle-free experience.
Dashboard and Console Layout
The central panel presents a clean, user-friendly design that integrates various key functions, including climate control, media management, and navigation access. The layout is optimized for quick access to frequently used features, while secondary controls are within easy reach, ensuring an intuitive user experience for both the driver and passengers.
Comfort and Entertainment Options
The seating and entertainment features cater to the comfort of all passengers. Adjustable seats, climate regulation, and audio options contribute to a personalized travel experience, while the well-placed controls ensure seamless operation of these features without causing distractions during the drive.
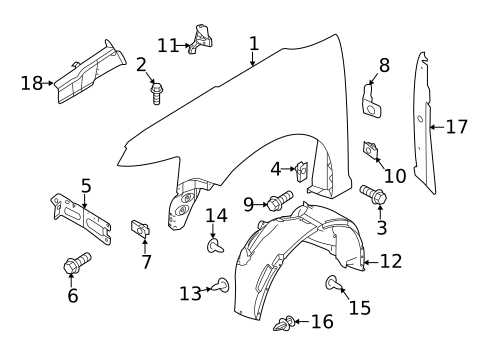
Exterior Body Components Breakdown
The outer structure of a vehicle is composed of various elements that contribute to both its appearance and functionality. Each component plays a crucial role in protecting internal mechanisms and ensuring a sleek, cohesive design. Understanding the different sections of this external framework allows for easier identification and maintenance, which ultimately improves the durability and aesthetics of the vehicle.
Main Structural Elements
The core elements of the vehicle’s exterior include sections such as the front and rear panels, which provide foundational support. Additionally, the side panels, roof, and underbody ensure a balanced and resilient form. These parts are often designed to seamlessly integrate with one another, creating a streamlined exterior that enhances both aerodynamics and visual appeal.
Functional and Protective Components
Beyond the core structure, various additional elements serve specific functions. These include protective coverings around vulnerable areas, such as the wheel arches, which shield against debris, and weatherproof trims that prevent water ingress. Meanwhile, features like door handles, mirrors, and lighting systems are strategically placed to offer both convenience and safety while maintaining the design’s overall flow.
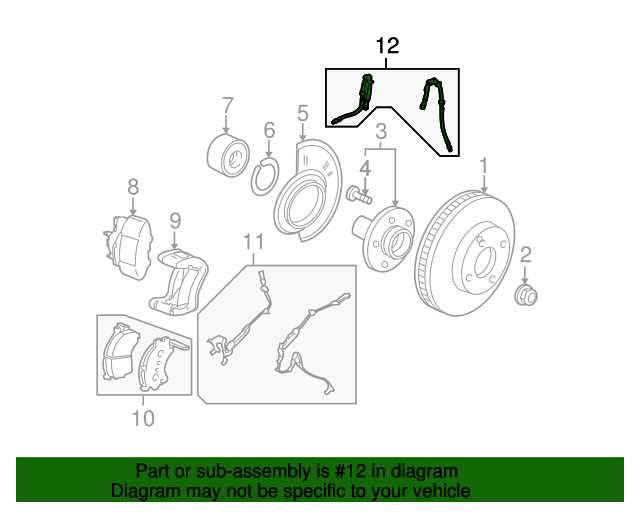
Brake System Overview
The braking mechanism is a crucial component in any vehicle, designed to ensure safety and control during operation. This system operates through a network of interconnected elements that work in harmony to slow down or halt the motion of the vehicle efficiently. Understanding the key components and their functions is essential for maintaining peak performance and addressing potential issues promptly.
Main Components
- Pedal assembly
- Master cylinder
- Hydraulic lines
- Brake calipers
- Rotors and drums
- Pads and shoes
Functionality
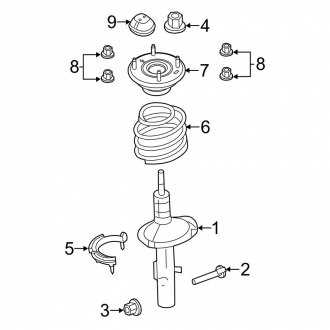
When the driver applies force to the pedal, it activates the master cylinder, which generates hydraulic pressure. This pressure travels through the lines, causing the calipers to press the pads against the rotors or the shoes against the drums, depending on the type of system. This friction reduces the vehicle’s speed and ultimately brings it to a stop.
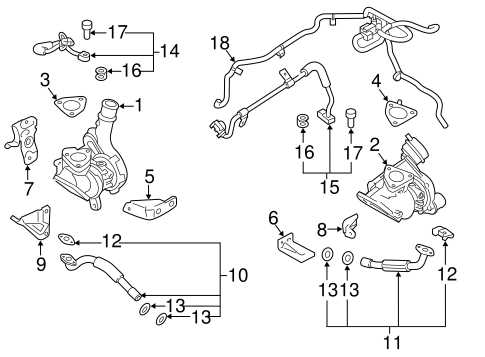
Cooling and Heating System Layout
The structure responsible for temperature regulation in a vehicle ensures optimal engine performance and passenger comfort. It involves a series of components designed to control airflow, fluid circulation, and temperature moderation. The coordination between these elements helps maintain the engine at an ideal operating temperature while also providing a comfortable environment inside the cabin.
Key Components: A network of channels, pumps, and valves work together to transport the necessary fluids through the system. Heat exchange units, strategically placed, assist in dissipating excess heat or in warming up the system when required. This intricate setup operates efficiently to manage the vehicle’s thermal environment.
Airflow distribution plays a crucial role in balancing the heating and cooling effects. It involves several pathways that allow controlled circulation of cooled or heated air throughout the cabin and under the hood. This balance ensures smooth and consistent performance, regardless of external conditions.
Fuel System Configuration
The fuel delivery system in vehicles is a critical component responsible for supplying the engine with the necessary fuel for optimal performance. This system includes various elements that work together to ensure efficient combustion and overall functionality of the powertrain. Understanding the configuration of this system is essential for proper maintenance and troubleshooting.
Key components of the fuel delivery system typically include the fuel tank, pump, injectors, and lines, each playing a distinct role in the process of delivering fuel to the engine. The arrangement and specifications of these components can vary, influencing the efficiency and performance of the vehicle.
Component Description Fuel Tank Stores fuel before it is pumped to the engine. Fuel Pump Transfers fuel from the tank to the engine under pressure. Fuel Injectors Spray a precise amount of fuel into the combustion chamber. Fuel Lines Transport fuel between the tank, pump, and engine. Maintaining each component in good working order is vital for the vehicle’s efficiency and longevity. Regular inspections can help identify issues early, ensuring the system operates smoothly and effectively.
Maintenance and Replacement Tips
Regular upkeep and timely component substitutions are crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity of your vehicle. A proactive approach can prevent minor issues from escalating into significant problems, leading to costly repairs. This section will cover essential strategies for effective maintenance and when to consider replacements.
Regular Maintenance Practices

- Routine Inspections: Conduct frequent checks on vital systems such as brakes, tires, and fluid levels to identify potential issues early.
- Oil Changes: Change engine oil and filters at recommended intervals to ensure smooth operation and reduce wear.
- Tire Care: Regularly inspect tire pressure and tread depth. Rotate tires as per the manufacturer’s recommendations to promote even wear.
- Brake System Checks: Inspect brake pads and rotors periodically to maintain stopping power and safety.
When to Replace Components
- Timing Belt: Replace if it shows signs of wear or according to the service schedule, typically between 60,000 to 100,000 miles.
- Battery: Check the battery’s condition; consider replacement every 3-5 years or if you notice slow engine cranking.
- Filters: Change air and cabin filters at regular intervals to maintain air quality and engine efficiency.
- Fluids: Replace coolant, brake fluid, and transmission fluid as specified in the owner’s manual to prevent system failures.
By adhering to these maintenance tips and knowing when to replace crucial components, you can enhance the reliability and safety of your vehicle, ensuring a smooth driving experience for years to come.