Understanding the Honda GX240 Parts Diagram
Understanding the internal structure of engines is crucial for maintaining their efficiency and longevity. A well-organized visual representation of a machine’s assembly can provide invaluable insight into how each component functions and interacts with the others. This guide delves into the key elements of engine assembly, offering a detailed look at how various parts fit together to ensure smooth operation.
In many cases, having a clear visual reference of the engine’s internal and external layout can simplify troubleshooting and repairs. By closely examining how each element is connected, one can better grasp the function of individual components and anticipate potential issues. This guide will help you explore the different sections and their roles in the overall performance.
Whether you are performing regular maintenance or addressing specific mechanical concerns, gaining a deeper understanding of how the core elements of the engine work in harmony will allow for more effective care. This overview provides a thorough examination of the system’s layout, ensuring you are well-equipped to handle both minor adjustments and more extensive repairs.
Overview of Engine Components
Understanding the different elements that make up a powerful small engine is key for maintenance and performance. The internal and external elements work together to ensure smooth functionality, efficiency, and reliability, which are essential in various machines powered by this type of motor.
Main Engine Structure
- Cylinder Block – Houses the core moving components, providing structure and support.
- Crankshaft – Converts linear motion into rotational energy, driving the machinery.
- Camshaft – Works in synchronization with the crankshaft to control valve timing.
Essential Support Systems

The motor relies on several subsystems that ensure its continuous and efficient operation. Key systems include fuel delivery, cooling, and ignition.
- Carburetor – Mixes fuel with air in the proper ratio for combustion.
- Cooling System – Regulates temperature through airflow or liquid to prevent overheating.
- Ignition Coil – Provides the necessary spark for fuel ignition, ensuring consistent starts.
Each component plays a crucial role in the overall functionality of the engine, working in harmony to deliver reliable performance
Key Features of the Honda GX240
This model is well-known for its reliable performance, durability, and efficiency, making it a popular choice for a variety of applications. Designed to deliver consistent power, it stands out due to its solid construction and user-friendly features.
- High Durability: Built with strong materials, this engine offers exceptional longevity even in tough working conditions.
- Efficient Fuel Consumption: The engine is optimized to use fuel effectively, reducing the need for frequent refueling and lowering operational costs.
- Easy Maintenance: Maintenance is simplified with accessible components, allowing for quick and hassle-free servicing.
- Low Noise and Vibration: Designed to run smoothly, the engine produces minimal noise and vibration, ensuring a more comfortable user experience.
- Reliable Starting Mechanism: Equipped with an efficient starting system, it ensures dependable operation even in challenging environments.
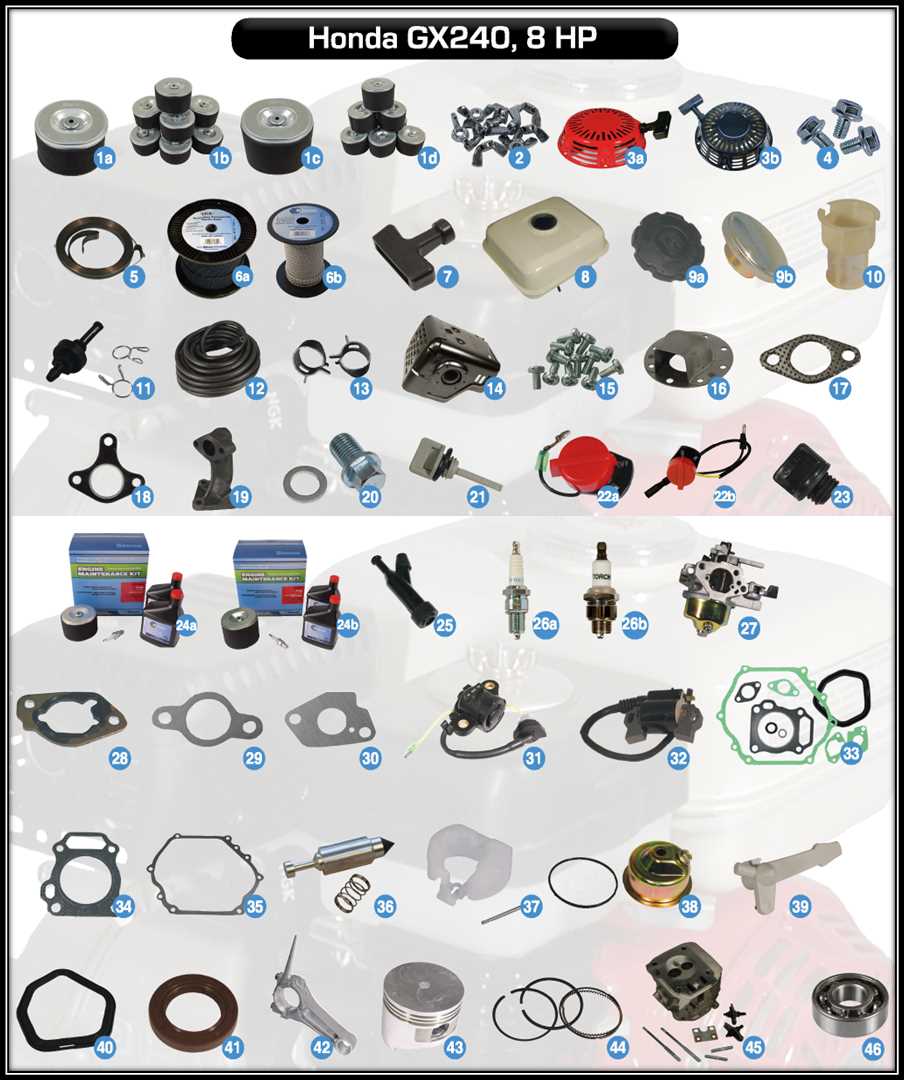
Internal Parts of the GX240 Engine
The internal components of this engine model play a crucial role in ensuring smooth and efficient operation. These elements work together to convert fuel into mechanical power, enabling the machine to perform a variety of tasks. The design and quality of these internal elements are key to the durability and reliability of the engine.
The combustion chamber houses key mechanisms that initiate power generation. The arrangement of moving elements like the piston, crankshaft, and valves allows for controlled energy transfer. Proper lubrication and cooling systems support these movements, preventing wear and overheating.
Another essential group of elements ensures fuel is mixed correctly and combusted efficiently. Precision in the construction of these systems is vital for maintaining consistent performance and fuel efficiency, contributing to the overall longevity of the engine.
Understanding the Carburetor and Fuel System
The carburetor and fuel system play a vital role in ensuring smooth engine performance by regulating the mixture of air and fuel required for combustion. These components work together to provide the engine with the right amount of fuel at the right time, ensuring efficient operation under various conditions. Maintaining this system is essential for proper engine functionality and longevity.
Carburetor Functionality: The carburetor controls how much air and fuel mix before entering the engine. By adjusting this mixture, it ensures that the engine runs smoothly, whether it’s idling or operating at higher speeds. A well-maintained carburetor ensures fuel efficiency and reduces emissions.
Fuel System: The fuel system is responsible for delivering fuel from the tank to the carburetor. This process involves various components, including filters and fuel lines, that ensure clean and uninterrupted fuel flow. Keeping the fuel system in good condition helps prevent blockages and ensures optimal engine performance.
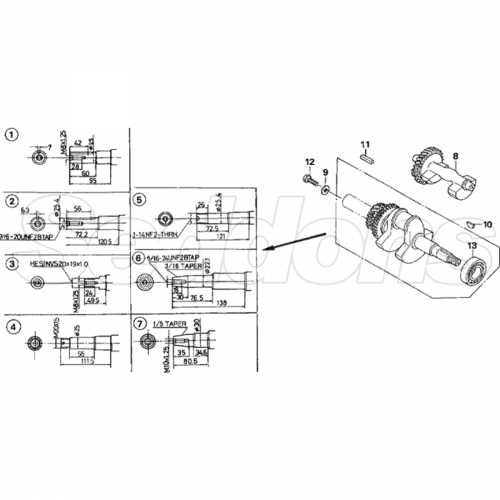
Crankshaft and Piston Configuration
The structure of the crankshaft and piston system is essential for the efficient operation of any internal combustion engine. This system transforms the linear motion of the piston into the rotational movement needed to drive mechanical components. Understanding the relationship between these elements is key to grasping how power is generated and transferred within an engine.
- Crankshaft: The crankshaft is responsible for converting the up-and-down movement of the piston into a rotational force. It connects directly to the piston through the connecting rod, which helps transfer the energy.
- Piston: The piston moves within the cylinder, compressing fuel and air. The force generated by combustion pushes the piston down, which in turn pushes the crankshaft, creating motion.
- Connecting Rod: This component links the piston to the crankshaft. It allows for the conversion of the piston’s vertical motion into the circular movement of the crankshaft.
By working together, these elements ensure that the engine operates smoothly, providing the necessary force to power various systems. The synchronization of the crankshaft and piston movements is a critical factor in overall performance and durability.
Ignition System Components Breakdown
The ignition system is crucial for the effective operation of small engines, ensuring that the fuel-air mixture ignites at the right moment. Understanding the various components of this system helps in diagnosing issues and performing maintenance effectively.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Ignition Coil | This device transforms the battery’s low voltage into the high voltage needed to create a spark for combustion. |
| Spark Plug | The spark plug ignites the fuel-air mixture within the combustion chamber by creating a spark. |
| Flywheel Magnet | This part generates a magnetic field that triggers the ignition coil, leading to spark generation. |
| Ignition Switch | The ignition switch allows the operator to start and stop the engine by controlling the electrical supply. |
| Timing Adjuster | This component ensures that the spark occurs at the optimal moment for efficient combustion. |
Air Filter and Intake System
The air filtration and intake mechanism plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal performance and longevity of an engine. It serves as the first line of defense against contaminants that can harm internal components. By maintaining a clean airflow, this system enhances combustion efficiency and overall functionality.
Air Filter: The air filter is designed to trap dust, dirt, and debris, preventing them from entering the combustion chamber. A high-quality filter not only enhances engine performance but also improves fuel efficiency. Regular maintenance, such as cleaning or replacing the filter, is essential to sustain the engine’s health.
Intake System: The intake system is responsible for directing the filtered air into the engine. It consists of various components, including the intake manifold and throttle body, which work together to ensure a steady airflow. Proper functioning of the intake system is vital for maintaining the right air-fuel mixture, which directly affects power output and emissions.
In summary, the air filtration and intake assembly are integral to an engine’s performance, necessitating regular inspections and maintenance to ensure optimal operation and efficiency.
Cooling System Overview
The cooling mechanism is essential for maintaining optimal performance in small engines, ensuring they operate efficiently without overheating. This system is designed to regulate temperature, preventing damage to internal components by dissipating heat generated during operation. Proper understanding of this system can enhance the longevity and reliability of the engine.
Components of the Cooling Mechanism
The cooling system comprises several key elements that work together to maintain temperature balance. It typically includes a radiator, a fan, and various hoses that facilitate fluid circulation. The coolant absorbs heat from the engine and transfers it to the radiator, where it is cooled by airflow generated by the fan.
Importance of Regular Maintenance
To ensure the cooling system functions effectively, regular inspection and maintenance are crucial. Checking coolant levels and examining hoses for wear or leaks can prevent overheating and potential engine failure. Additionally, cleaning the radiator and ensuring the fan operates smoothly are vital steps in maintaining the overall health of the engine.
Exhaust System and Muffler Layout
The exhaust assembly plays a crucial role in managing the gases produced during combustion, ensuring they are efficiently expelled from the engine. This system typically consists of various components designed to facilitate smooth gas flow while minimizing noise and emissions. Understanding the configuration of these elements is essential for maintenance and troubleshooting.
The primary element of the exhaust setup is the muffler, which serves to reduce sound levels. Its design often includes internal baffles that disrupt the sound waves generated by the engine. Additionally, the layout features pipes that direct exhaust gases away from the engine and into the atmosphere, preventing backpressure that could hinder performance.
Furthermore, the exhaust manifold collects gases from the engine’s cylinders and channels them towards the muffler. The configuration of this manifold can impact overall efficiency, as it is crucial for maintaining optimal airflow. Regular inspection and maintenance of the exhaust system ensure that it operates effectively, providing both performance and environmental benefits.
Fuel Tank and Related Parts
The fuel reservoir and its associated components play a crucial role in the overall functionality of the engine. These elements are responsible for storing and supplying the necessary fuel, ensuring efficient operation and optimal performance. Understanding the structure and features of these components is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
Fuel Reservoir Overview
The fuel reservoir is designed to hold a specific volume of fuel, allowing for a steady supply to the engine. Typically constructed from durable materials, this tank is engineered to withstand various environmental conditions. Additionally, it features openings for venting and connections for fuel lines, which facilitate the movement of fuel to the engine.
Additional Components
In conjunction with the fuel reservoir, several related elements contribute to the system’s overall efficiency. These include fuel lines, filters, and fittings. Fuel lines transport the liquid from the tank to the engine, while filters ensure that impurities do not interfere with performance. Proper inspection and maintenance of these components are essential for preventing fuel-related issues and enhancing engine reliability.
Valve System and Cylinder Head Structure
The valve system and cylinder head are crucial components that ensure efficient airflow in internal combustion engines. Their design influences performance, fuel efficiency, and overall functionality. This section delves into the intricate features of these elements, highlighting their roles and interconnections within the engine framework.
Components of the Valve System
The valve system comprises various elements, including intake and exhaust valves, springs, and rockers. These components work in harmony to regulate the entry of air and the expulsion of exhaust gases, maintaining optimal combustion conditions. Proper timing and alignment are essential for maximizing engine efficiency and preventing mechanical failures.
Cylinder Head Design
The cylinder head serves as a vital interface between the combustion chamber and the engine’s upper sections. Its architecture includes passages for coolant and oil flow, as well as ports for valves. An effective cylinder head design facilitates improved airflow, enhances thermal management, and contributes to overall engine longevity. Material choice and structural integrity are paramount in withstanding the high pressures and temperatures typical of engine operation.
Recoil Starter and Charging System
The recoil starter and charging assembly play a crucial role in the functionality of small engines. These components work together to ensure that the engine starts reliably and maintains power supply for various applications. Understanding how these systems operate is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
The recoil starter is designed to facilitate the initial crank of the engine, providing the necessary force to ignite the fuel-air mixture. When the starter rope is pulled, a series of mechanisms engage, transferring energy to the crankshaft. This process enables the engine to start and run smoothly. Additionally, the charging system is responsible for replenishing the electrical energy required for ignition and other electrical components.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Recoil Starter Assembly | Engages the engine to initiate starting through a pull mechanism. |
| Starter Rope | Durable cord used to pull the recoil starter, triggering the starting process. |
| Spring Mechanism | Stores energy during the pull and releases it to engage the engine. |
| Charging Coil | Generates electrical current to power the ignition and recharge the battery. |
| Rectifier | Converts alternating current from the charging coil to direct current for battery charging. |
Oil Pump and Lubrication Parts
The oil pump and lubrication components play a crucial role in maintaining the smooth operation of small engines. These elements ensure that moving parts receive adequate lubrication, reducing friction and wear, thereby enhancing performance and extending the engine’s lifespan.
In a typical setup, the oil pump is responsible for circulating oil throughout the engine. It draws oil from the sump and delivers it under pressure to critical areas, ensuring that all parts function efficiently. Components like gaskets and seals are essential for preventing leaks and maintaining pressure, while oil filters help keep contaminants at bay.
Regular maintenance of these systems is vital. Checking oil levels, replacing filters, and inspecting the pump for wear can prevent significant damage and costly repairs. By prioritizing the upkeep of lubrication elements, users can ensure reliable operation and longevity of their engines.