Understanding the Components of Mini Fridges
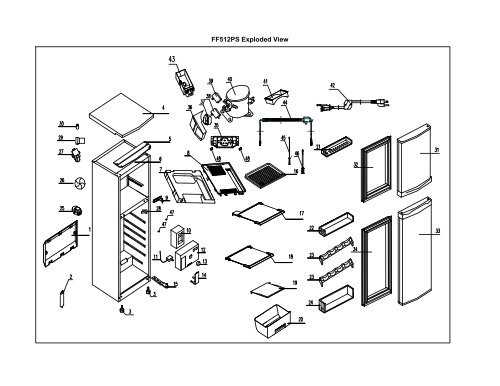
In the realm of household appliances, certain devices play a crucial role in enhancing our comfort and convenience. One such essential apparatus is designed to maintain a cool environment for perishable items, ensuring their freshness over time. This segment aims to explore the intricate design and functionality of such a cooling solution, providing insight into its essential elements.
Each segment of this system contributes significantly to its overall efficiency and operation. By examining these individual elements, one can gain a deeper appreciation for the engineering that underpins this appliance. Understanding how these components interact allows for better maintenance and troubleshooting, ultimately prolonging the lifespan of the unit.
From the chilling mechanism to the control systems, each feature plays a vital role in achieving optimal performance. Grasping the relationship between these aspects fosters a comprehensive understanding of the entire structure, empowering users to make informed decisions regarding usage and care.
Key Elements of Refrigeration Systems
The efficiency and functionality of cooling appliances rely on several crucial components working in harmony. Understanding these elements is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. This section will delve into the primary constituents that facilitate the cooling process, ensuring optimal performance.
Compressor
The compressor acts as the heart of the cooling system, circulating the refrigerant throughout the unit. It increases the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant gas, allowing it to flow into the condenser. By compressing the gas, this component plays a pivotal role in maintaining the refrigeration cycle.
Evaporator Coil
The evaporator coil is where the magic of cooling happens. Located inside the appliance, this coil absorbs heat from the surrounding air, causing the refrigerant to evaporate and turn into gas. This process lowers the temperature inside the unit, effectively cooling the contents stored within.
Insulation Types for Mini Refrigerators
Efficient thermal barriers play a crucial role in maintaining optimal temperatures within compact cooling appliances. These materials minimize heat transfer between the internal and external environments, contributing to energy efficiency and performance stability. Understanding the various types of insulation available helps consumers make informed choices about their cooling solutions.
Common Insulation Materials
Different substances are utilized for thermal insulation in compact cooling devices. Here are some prevalent options:
- Polyurethane Foam: Known for its excellent thermal resistance, this lightweight material is commonly used in appliance manufacturing.
- Polystyrene: This rigid foam provides decent insulation and is often utilized in budget-friendly models.
- Fiberglass: Offering good thermal properties, fiberglass is a traditional choice, though it can be heavier than modern alternatives.
- Vacuum Insulation Panels: These high-performance panels provide superior insulation in a thinner profile, ideal for space-constrained designs.
Benefits of Effective Insulation
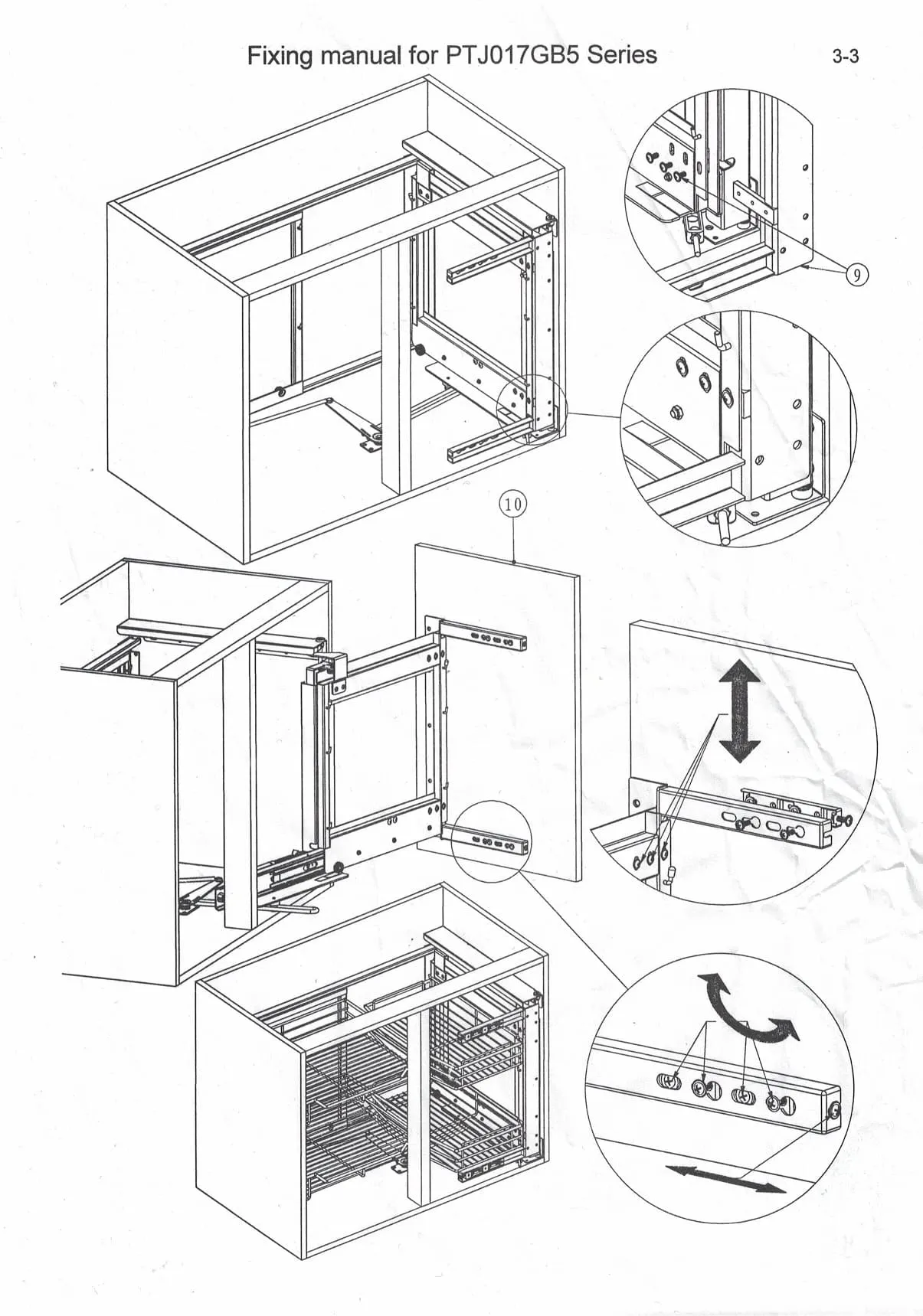
Choosing the right thermal barrier material brings several advantages, such as:
- Improved energy efficiency, leading to lower electricity bills.
- Enhanced temperature stability, ensuring food and beverages remain fresh.
- Reduced environmental impact through lower energy consumption.
Cooling Mechanism Explained
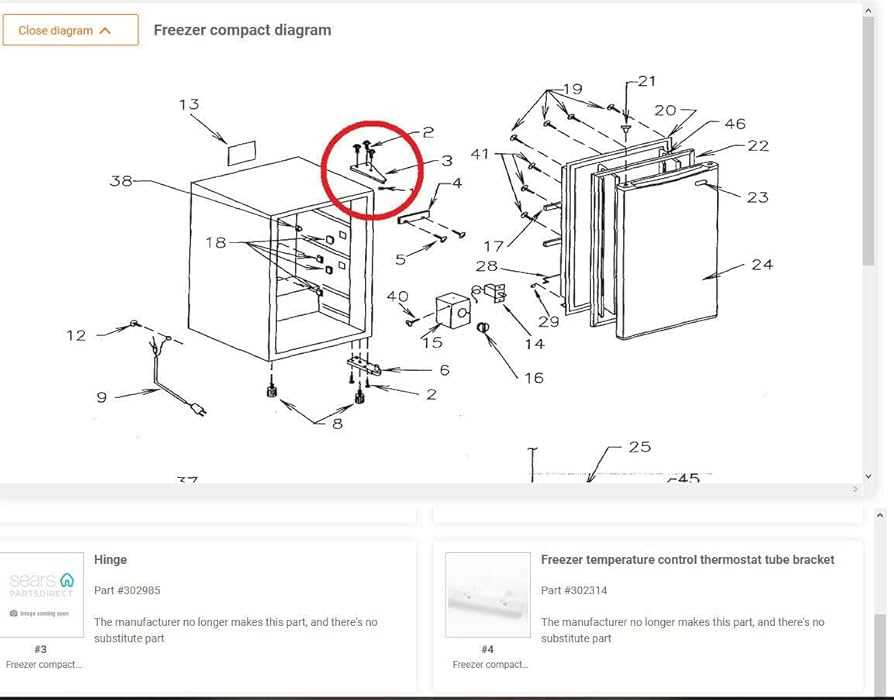
The process of temperature reduction within a compact refrigeration unit involves a sophisticated interplay of various components working in harmony. This system is designed to transfer heat from the interior to the exterior, ensuring that stored items remain at a consistently low temperature. By utilizing principles of thermodynamics, these units efficiently manage thermal energy, creating an optimal environment for preservation.
At the heart of this mechanism lies a refrigerant, a specialized fluid that circulates through the system, absorbing heat from the internal space and releasing it outside. This cycle begins with the evaporator, where the refrigerant transitions from a liquid to a gas, absorbing heat in the process. The gaseous refrigerant then moves to the compressor, which increases its pressure and temperature. Following this, the hot gas passes through the condenser, where it releases heat and condenses back into a liquid state, ready to continue the cycle. This continuous loop is crucial for maintaining the desired coolness within the storage compartment.
Role of the Compressor in Cooling
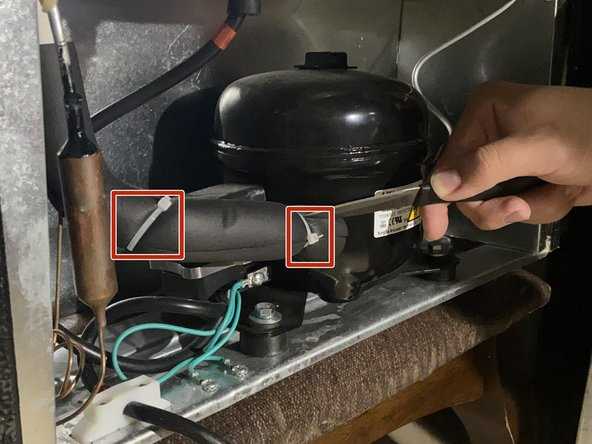

The compressor serves as a critical component in the refrigeration cycle, playing a vital role in regulating temperatures within enclosed spaces. It is responsible for converting low-pressure refrigerant gas into high-pressure gas, thereby facilitating the continuous flow of the cooling medium through the system. This process ensures that heat is effectively removed from the interior environment, allowing for optimal temperature control.
Functionality of the Compressor
As the heart of the cooling system, the compressor draws in the refrigerant vapor from the evaporator. By compressing this vapor, it raises both the pressure and temperature before directing it towards the condenser. This transformation is essential for expelling heat outside, thus maintaining the desired cool conditions within the insulated area.
Impact on Energy Efficiency
The efficiency of the compressor directly affects the overall performance of the cooling system. A well-functioning compressor minimizes energy consumption while maximizing cooling output. Regular maintenance and timely servicing can enhance its lifespan, ensuring sustained efficiency and effectiveness in temperature regulation.
Evaporator and Its Functionality
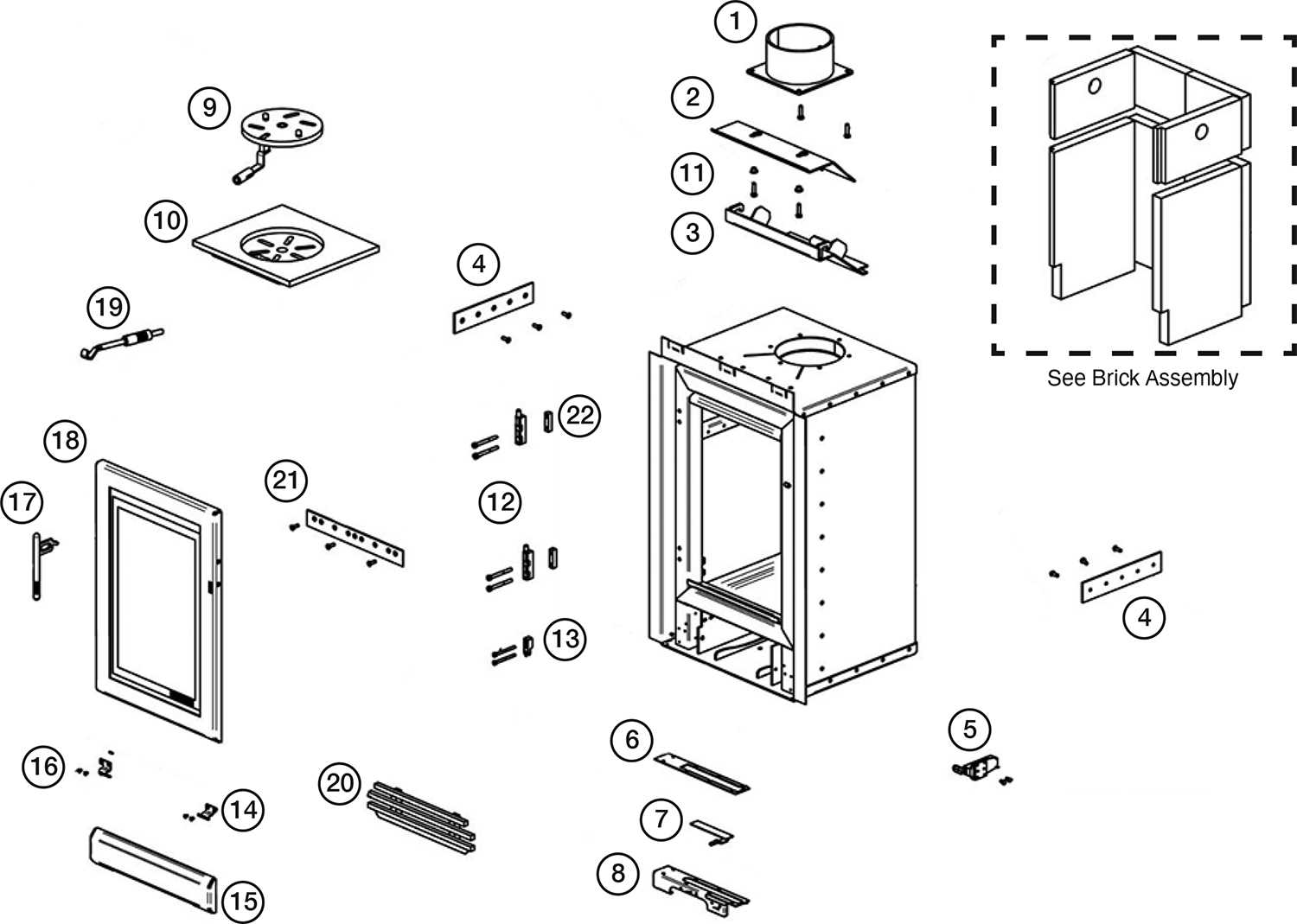
The evaporator plays a vital role in the refrigeration cycle, facilitating the cooling process essential for maintaining low temperatures. It serves as a key component where heat absorption occurs, allowing the surrounding environment to be effectively cooled. Understanding its structure and operations is crucial for grasping how refrigeration systems function.
During the cooling cycle, the evaporator absorbs heat from the interior, causing the refrigerant within to evaporate and transform from liquid to gas. This process not only lowers the temperature inside the cooling unit but also ensures the efficient removal of heat. Proper functionality of the evaporator is paramount for achieving optimal cooling performance.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Heat Absorption | Extracts heat from the internal environment, leading to a temperature drop. |
| Phase Change | Converts refrigerant from liquid to gas, facilitating the refrigeration cycle. |
| Efficiency | Ensures optimal cooling performance by maintaining consistent temperatures. |
Condenser Importance in Refrigeration
The condenser plays a crucial role in the cooling mechanism of refrigeration systems. This component is responsible for dissipating heat extracted from the interior space, allowing the refrigerant to release its thermal energy efficiently. By converting the refrigerant from a gas to a liquid state, it ensures the cycle continues seamlessly, maintaining the desired low temperatures.
In essence, the effectiveness of the cooling system heavily relies on the performance of the condenser. If this element fails to operate optimally, it can lead to inadequate cooling and increased energy consumption. Therefore, regular maintenance and monitoring of this component are vital for ensuring long-term efficiency and functionality.
Thermostat Operation in Mini Fridges
The component responsible for regulating temperature plays a crucial role in maintaining the ideal environment for preserving various items. It ensures that the internal atmosphere remains consistent, allowing for optimal storage conditions.
This device functions by continuously monitoring the temperature within the compartment. When the temperature deviates from the desired level, the mechanism activates to adjust the cooling system accordingly. This operation can be broken down into several key steps:
- Temperature Sensing: The mechanism detects the current temperature and compares it to the preset value.
- Signal Activation: If a difference is noted, the device sends a signal to the cooling unit to initiate operation.
- Cooling Regulation: The cooling system works to lower the temperature until it reaches the desired setting.
- Continuous Monitoring: The component keeps tracking the temperature, ensuring it stays within the set range.
In summary, the device plays an essential role in maintaining a controlled environment, ensuring the longevity and freshness of stored items. Understanding its operation helps in troubleshooting and optimizing its performance.
Understanding the Power Supply Unit
The power supply unit plays a crucial role in providing the necessary energy for the functioning of compact cooling appliances. It transforms electrical energy from the outlet into a form that can be utilized by the internal components. This process ensures that the device operates efficiently and reliably.
Key Functions: The primary responsibility of the power supply unit is to convert the incoming voltage into suitable levels for various internal systems. It maintains a steady output, regardless of fluctuations in the input voltage. This stability is vital for preventing damage to sensitive electronic components.
Components Involved: Typically, this unit includes transformers, capacitors, and regulators that work together to achieve the desired voltage levels. Each component is essential for ensuring the overall efficiency and longevity of the appliance.
Cabinet Design and Layout Features
The design and arrangement of storage units play a crucial role in enhancing functionality and aesthetics. These elements not only determine the overall appearance but also impact the efficiency and organization of the space. A well-thought-out configuration can optimize storage capabilities while providing easy access to items within.
Structural Integrity and Materials
Utilizing high-quality materials ensures durability and longevity of the unit. The selection of robust components contributes to the overall strength, allowing the structure to withstand the weight of contents. Wood, metal, and composite materials are popular choices, each offering distinct advantages in terms of insulation and resistance to wear.
Accessibility and User Convenience
Thoughtful layout design focuses on user convenience, ensuring that all compartments and shelves are easily accessible. Adjustable shelving and sliding drawers enhance versatility, accommodating various storage needs. Effective use of space, including the incorporation of door configurations, can further streamline access while maintaining an organized appearance.
Common Accessories for Mini Refrigerators
Various components enhance the functionality and convenience of compact cooling appliances. These items contribute to improved organization, temperature control, and overall user experience, making them essential for maximizing efficiency and usability.
Some popular accessories include adjustable shelving, which allows users to customize the interior space according to their needs. Additionally, door bins can be useful for storing frequently accessed items, ensuring they remain easily reachable. Thermometers are crucial for monitoring temperature, while lock kits offer added security for the contents. Moreover, specialized organizers help maintain order, preventing clutter and making it easier to locate items.
Investing in these enhancements can significantly improve the performance and user satisfaction of compact cooling devices, making them more suitable for a variety of environments, from dorm rooms to small kitchens.
Maintenance Tips for Mini Fridge Parts
Ensuring the longevity and efficiency of compact cooling appliances requires regular attention to various components. Proper upkeep not only enhances performance but also prevents costly repairs and energy wastage. Below are some practical strategies to maintain these vital elements.
Regular Cleaning
Keeping surfaces clean is essential for optimal function. Dust and grime can accumulate on the exterior and interior, affecting airflow and temperature regulation. Use a soft cloth and mild detergent to wipe down surfaces, and pay particular attention to the coils at the back or underneath. Cleaning these areas every few months can significantly improve efficiency.
Temperature Settings
Maintaining the correct temperature is crucial for the effective operation of your appliance. Regularly check the temperature settings to ensure they are within the recommended range. Adjust as necessary, as excessively low or high temperatures can lead to increased energy consumption and strain on the cooling system.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting Tips
When dealing with compact cooling appliances, various complications may arise, impacting their efficiency and performance. Understanding these common challenges and how to address them is essential for ensuring optimal functionality. This section outlines frequent problems encountered with these devices and provides practical solutions to resolve them effectively.
Identifying Frequent Problems
Users often experience specific malfunctions that can disrupt the operation of their cooling units. Below are some typical issues along with their potential causes:
| Issue | Possible Causes | Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Insufficient Cooling | Blocked vents, low refrigerant levels | Clear obstructions, check refrigerant levels |
| Unusual Noises | Loose components, fan problems | Secure loose parts, inspect the fan |
| Ineffective Temperature Control | Faulty thermostat, door seals | Replace the thermostat, inspect seals for gaps |
| Power Issues | Tripped circuit, faulty plug | Reset the circuit breaker, check the plug |
Preventive Measures
Taking proactive steps can help prevent many common issues from arising. Regular maintenance, such as cleaning the appliance, checking seals, and ensuring proper ventilation, can significantly extend the lifespan of the device and enhance its efficiency.