Understanding the Air Compressor Parts Diagram for Efficient Maintenance
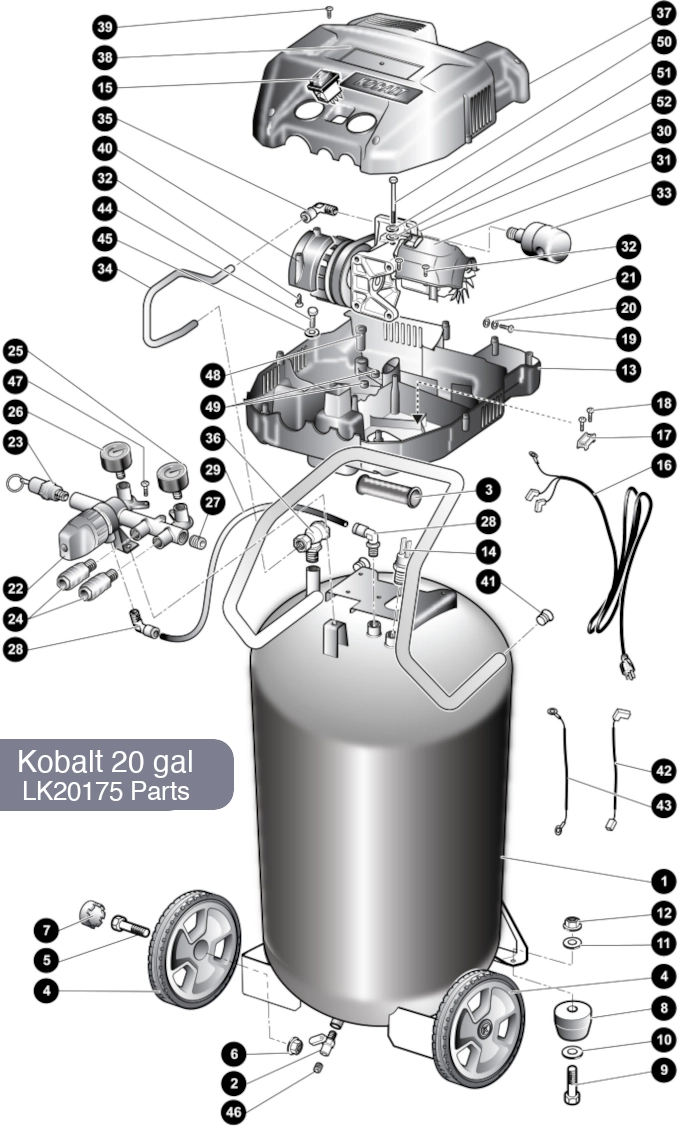
The functionality of a pressure unit relies on a well-coordinated system of various elements working together to achieve optimal performance. Each component plays a vital role, contributing to the overall efficiency and effectiveness of the equipment. Gaining insights into these individual elements can enhance your understanding and ability to troubleshoot issues as they arise.
Identifying the relationships and interactions among these elements is essential for anyone involved in maintenance or operation. Recognizing how each segment contributes to the whole will not only improve operational knowledge but also facilitate better decision-making during repairs or upgrades. Whether for industrial applications or DIY projects, this knowledge is invaluable.
In the following sections, we will explore the different components in detail, offering a clear and structured overview. By breaking down the complexity of the system, we aim to provide a comprehensive guide that will empower you to navigate the intricacies of your equipment with confidence and precision.
Understanding Air Compressor Components
Grasping the various elements of a pressure-generating system is essential for effective operation and maintenance. Each component plays a pivotal role, contributing to the overall efficiency and functionality of the unit. By familiarizing oneself with these elements, users can ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Core Elements
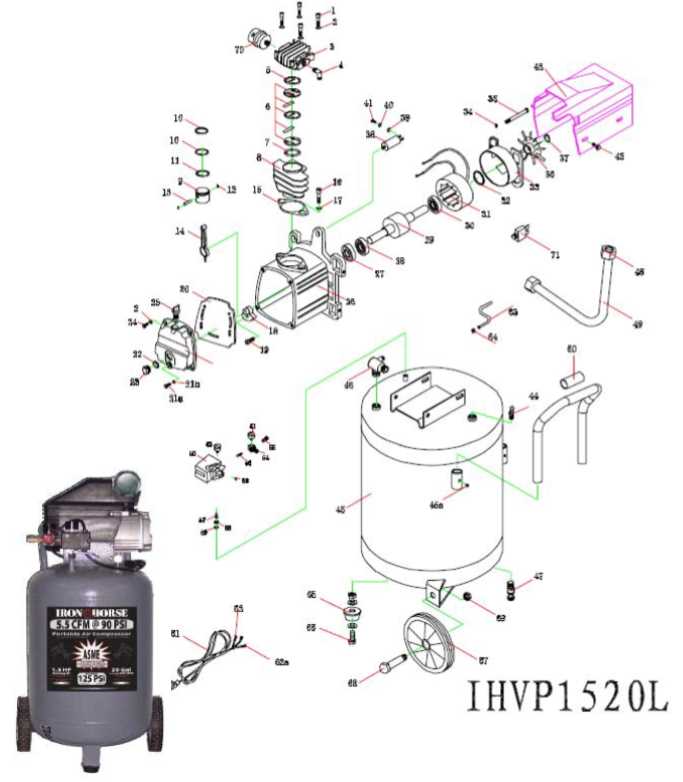
At the heart of any pressure system lies the mechanism responsible for the compression process. This central component works in tandem with auxiliary features to facilitate the intake and release of air, creating the necessary pressure for diverse applications. Additionally, components like the reservoir and cooling system help maintain stability and prevent overheating, ensuring smooth functionality.
Supportive Mechanisms
Support structures, such as valves and filters, are crucial for regulating flow and maintaining air quality. Valves control the direction and pressure of the air, while filters remove impurities, safeguarding the entire system from damage. Regular inspection and maintenance of these supportive mechanisms are vital for achieving peak performance and avoiding costly repairs.
Essential Parts of Air Compressors
Understanding the fundamental components of these machines is crucial for effective operation and maintenance. Each element plays a vital role in ensuring the overall functionality and efficiency of the system.
- Motor: The driving force behind the operation, converting electrical energy into mechanical energy.
- Piston: A critical component that compresses the gas, increasing its pressure and density.
- Tank: Stores the compressed gas, providing a reserve for various applications.
- Regulator: Controls the pressure output, ensuring it meets the required specifications for different tools and machinery.
- Valves: Manage the flow of gas in and out, preventing backflow and ensuring safety.
- Filter: Removes impurities from the gas, protecting the internal components from damage and maintaining efficiency.
- Cooling System: Maintains optimal operating temperatures, preventing overheating and extending the lifespan of the unit.
Each of these elements works together harmoniously, contributing to the reliable performance of the machine. Regular maintenance and understanding of these components can significantly enhance operational efficiency and longevity.
Functionality of Each Component
Understanding the roles of various elements within a system is crucial for effective operation and maintenance. Each component contributes uniquely to the overall efficiency and performance, ensuring that the entire mechanism functions harmoniously.
Key Elements and Their Functions
- Intake Valve: Responsible for allowing the entry of ambient gas into the system, this element regulates the flow to ensure optimal performance.
- Piston: This moving part compresses the gas, increasing its pressure. Its motion is vital for the system’s operation.
- Crankshaft: This component converts rotary motion into linear motion, driving the piston and facilitating compression.
- Exhaust Valve: This valve releases the compressed gas, allowing it to exit the mechanism when necessary.
- Cooling System: Essential for maintaining optimal temperatures, this system prevents overheating, ensuring longevity and efficiency.
Supporting Components
- Filter: Cleans the incoming gas, removing impurities that could damage internal components.
- Reservoir: Stores the compressed gas, ensuring a steady supply during operation.
- Pressure Regulator: Maintains consistent pressure levels, providing stability during use.
- Safety Valve: Prevents over-pressurization, protecting the system from potential hazards.
Each of these components plays a pivotal role in enhancing the overall functionality of the system, contributing to its reliability and effectiveness in various applications.
Types of Air Compressors Explained
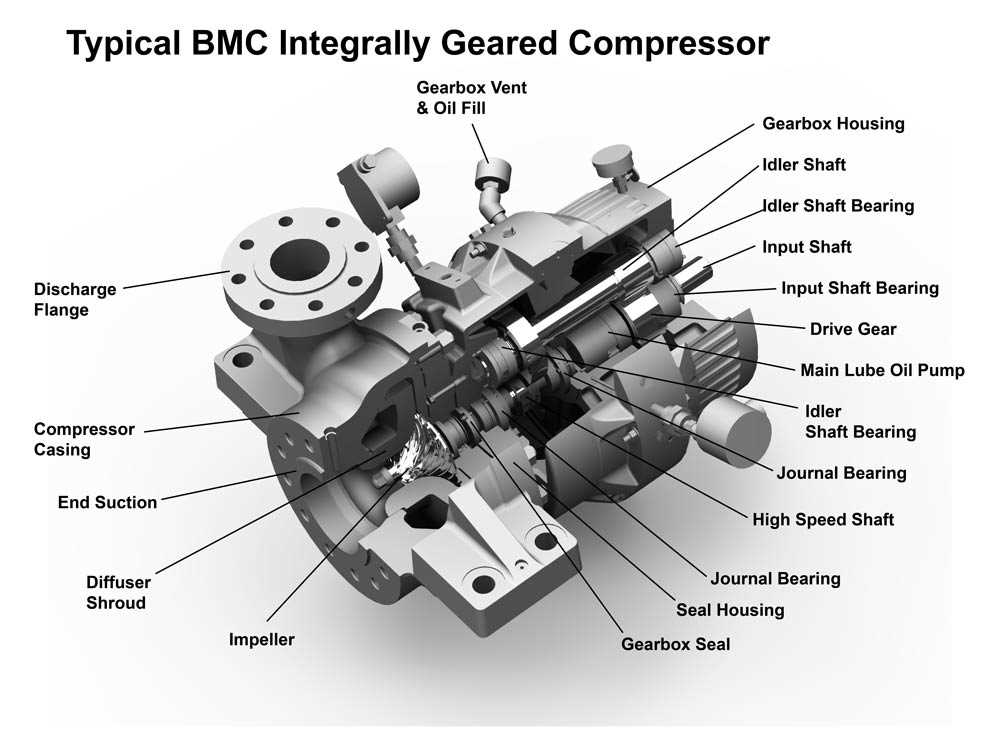
Understanding the various categories of pressurized gas systems is essential for choosing the right model for specific applications. Each type has its own characteristics and advantages, making it suitable for different tasks, from industrial uses to home projects.
Positive Displacement Systems
These mechanisms work by trapping a specific volume of gas and forcing it into a smaller space, increasing the pressure. They are typically used in applications requiring consistent flow rates.
- Reciprocating Units: Utilize pistons to compress the gas, ideal for high-pressure tasks.
- Rotary Screw Models: Employ two interlocking screws for continuous operation, great for large-scale industries.
Dynamic Compressors
This category relies on the kinetic energy generated by rotating components to increase gas pressure. These systems are known for their efficiency and are often used in high-demand environments.
- Centrifugal Types: Use a rotating disk to impart velocity to the gas, suitable for large volumes at moderate pressures.
- Axial Flow Units: Move gas in a linear path through rotating blades, typically used in aircraft and power generation.
Choosing the right type depends on factors such as required pressure, volume, and intended use, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency.
Common Issues with Compressor Parts
Many individuals encounter frequent challenges with various components in their systems. Understanding these common issues can help in identifying problems early and ensuring optimal performance. From wear and tear to improper installation, several factors can lead to malfunctioning elements.
One prevalent issue is leakage, which can result from deteriorating seals or loose connections. Such leaks not only reduce efficiency but can also lead to increased operational costs. Regular inspections are essential to catch these issues before they escalate.
Another common concern is overheating, often caused by inadequate cooling or excessive workload. High temperatures can damage internal mechanisms and lead to premature failure, highlighting the importance of proper maintenance and monitoring.
Furthermore, accumulation of dirt and debris can hinder performance, affecting airflow and pressure levels. Routine cleaning and servicing are vital to maintain the functionality and longevity of these essential components.
Lastly, electrical failures may arise from faulty wiring or components, which can disrupt operation entirely. Ensuring that all electrical connections are secure and free from corrosion can prevent such issues and promote reliable performance.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
Proper upkeep is essential for ensuring the durability and efficiency of your equipment. By following a few simple guidelines, you can significantly extend its lifespan and maintain optimal performance. Regular attention to maintenance not only prevents costly repairs but also enhances overall functionality.
First, routinely check for any signs of wear or damage. Inspect components for leaks, cracks, or other issues that could lead to operational failures. Promptly addressing these problems will help avoid more extensive repairs down the line.
Next, keep the environment clean and free from dust and debris. Accumulation of dirt can hinder performance and lead to overheating. Regularly cleaning surfaces and ensuring adequate ventilation will promote efficient operation.
Additionally, adhere to the recommended lubrication schedule. Using the correct type and amount of lubricant is crucial for reducing friction and wear. Regularly lubricating moving parts helps maintain smooth operation and prevents unnecessary damage.
Lastly, always refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines for maintenance schedules and procedures. Following these recommendations ensures that you are performing necessary tasks at appropriate intervals, which contributes to the longevity of your machinery.
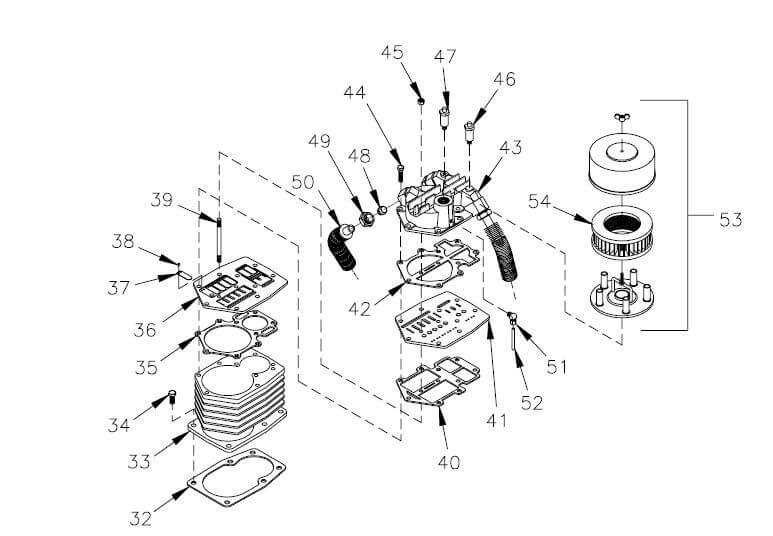
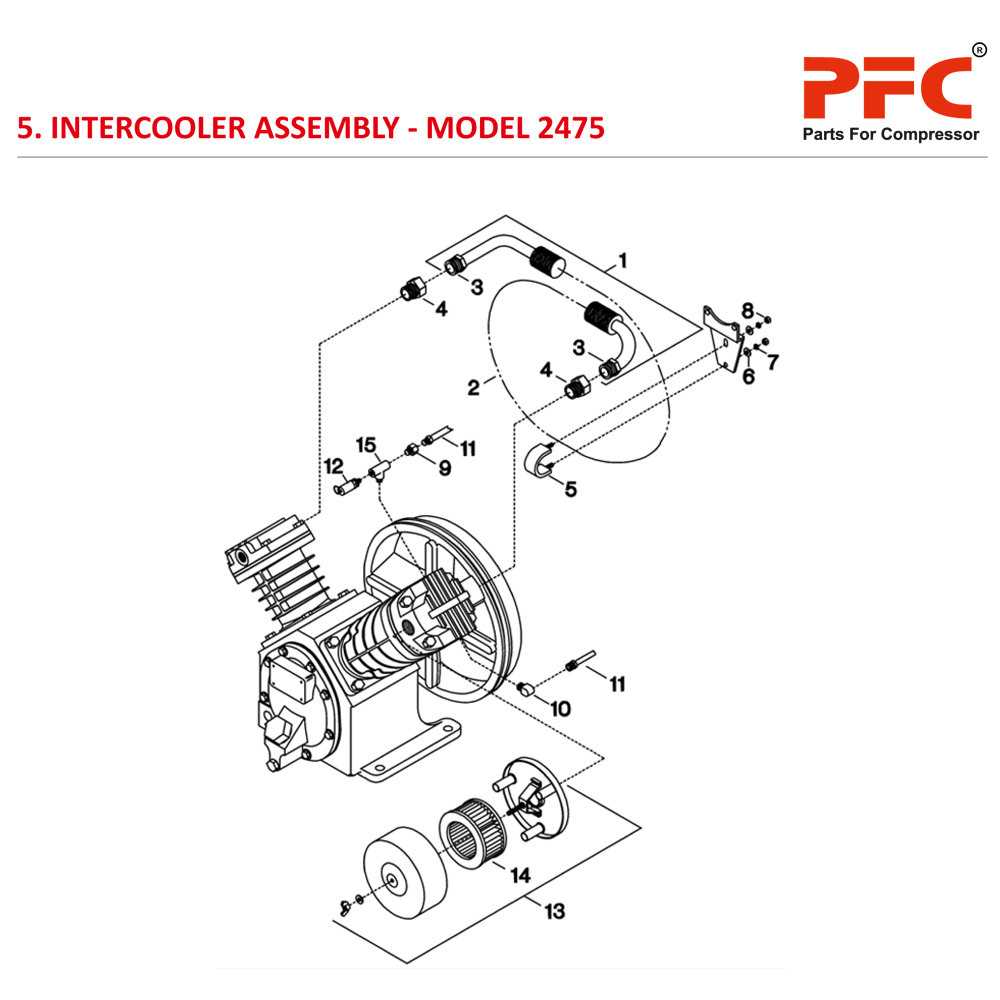
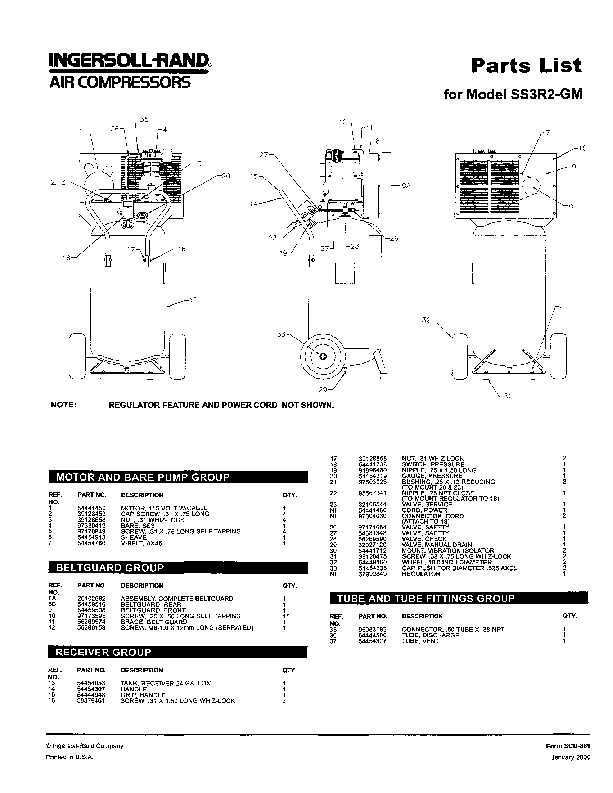
How to Read a Parts Diagram
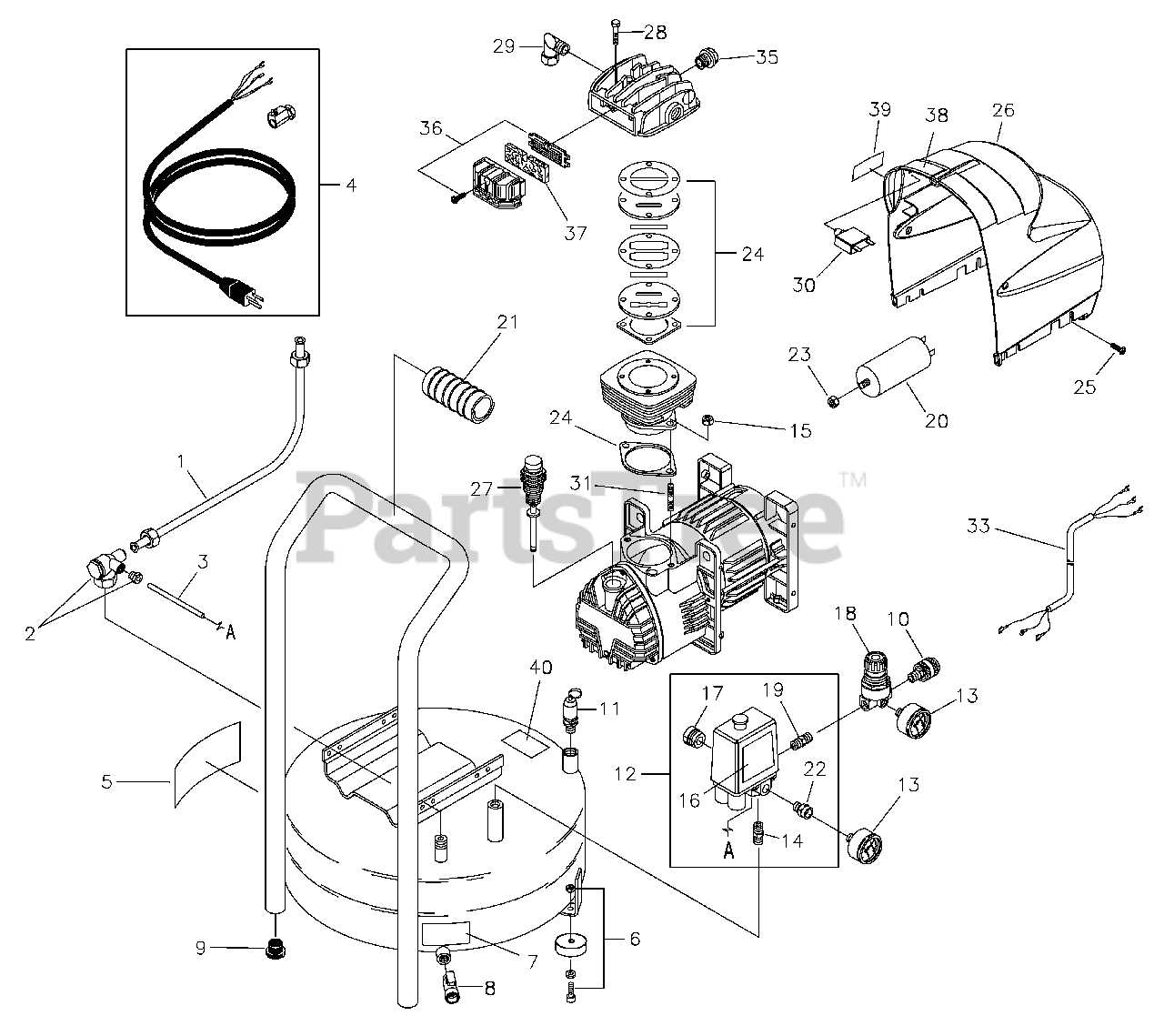
Understanding a technical illustration is crucial for effective maintenance and repair tasks. These visual representations serve as a guide, showcasing components and their relationships. By familiarizing yourself with the symbols and layout, you can streamline your approach to troubleshooting and assembly.
Familiarizing with Symbols
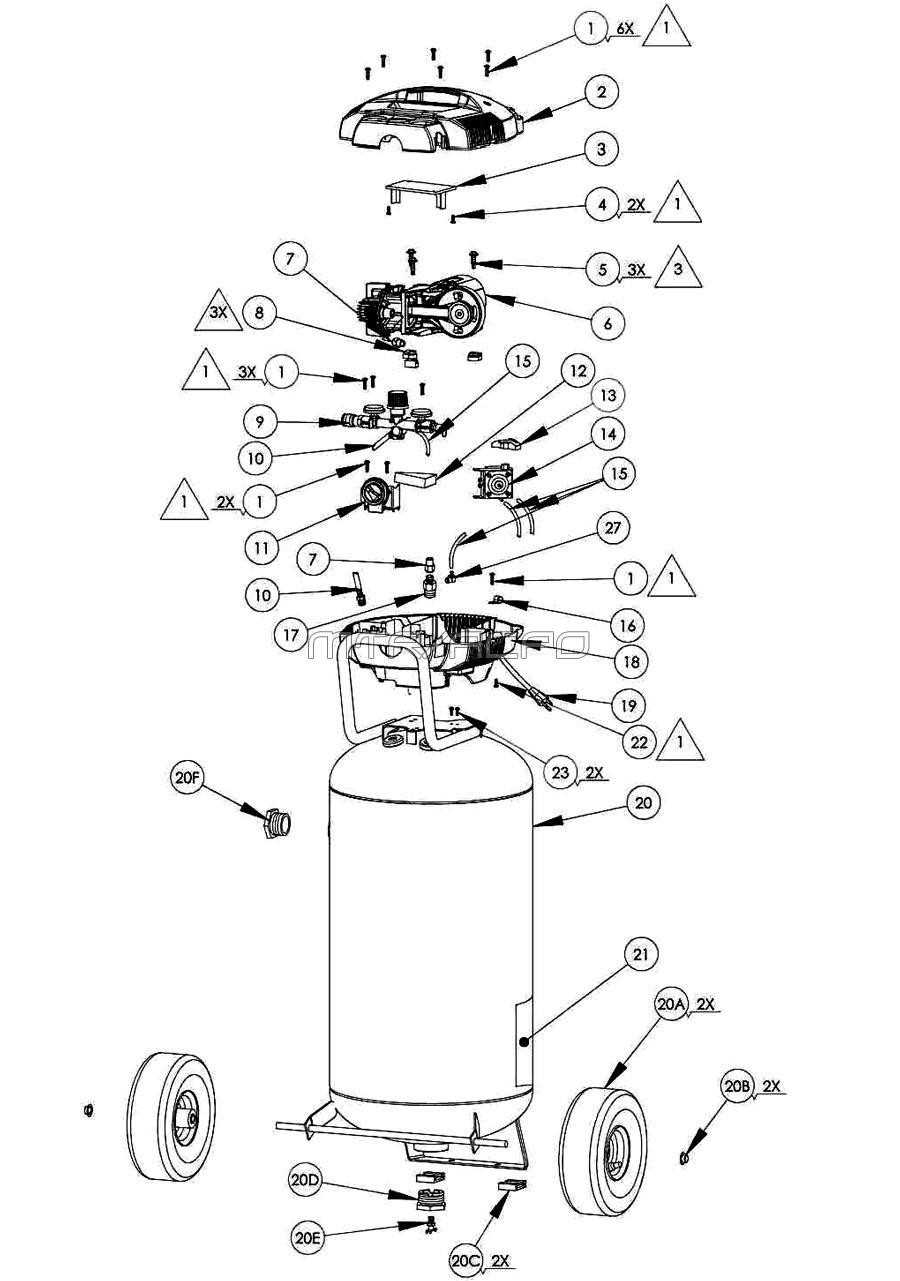
Each illustration employs specific icons and markings to denote various elements. Take time to study the legend or key, which explains these symbols. Recognizing these will enable you to identify each part’s function swiftly. For instance, circles might represent connectors, while rectangles could indicate different units.
Understanding Layout and Groupings
Components are typically organized in a logical manner, reflecting their assembly sequence. Pay attention to how parts are grouped; this often reveals functional relationships. Note any arrows or lines that indicate movement or connection points, as these are vital for grasping how everything fits together.
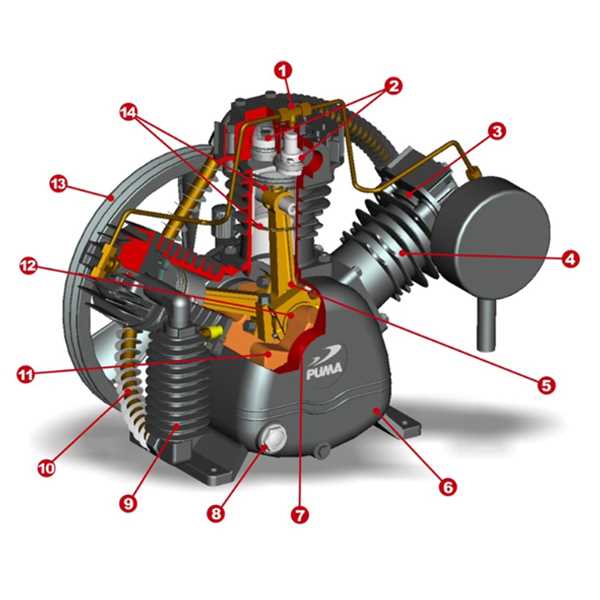
Identifying Faulty Components Easily

Recognizing malfunctioning elements within a system is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and preventing further issues. By understanding the typical signs of wear and tear, users can swiftly address concerns and extend the lifespan of their equipment.
Common Indicators of Defective Elements
- Unusual Noises: Grinding, rattling, or hissing sounds often signal underlying problems.
- Performance Drops: Noticeable declines in efficiency can indicate that components are failing.
- Leakage: Any signs of fluid escaping are red flags for potential issues.
- Excessive Heat: Components running hotter than normal may be under stress or damaged.
Steps for Identification
- Conduct regular visual inspections to check for signs of damage or wear.
- Listen for irregular sounds during operation, documenting any anomalies.
- Monitor performance metrics closely for any deviations from expected levels.
- Utilize diagnostic tools to assess the health of critical components.
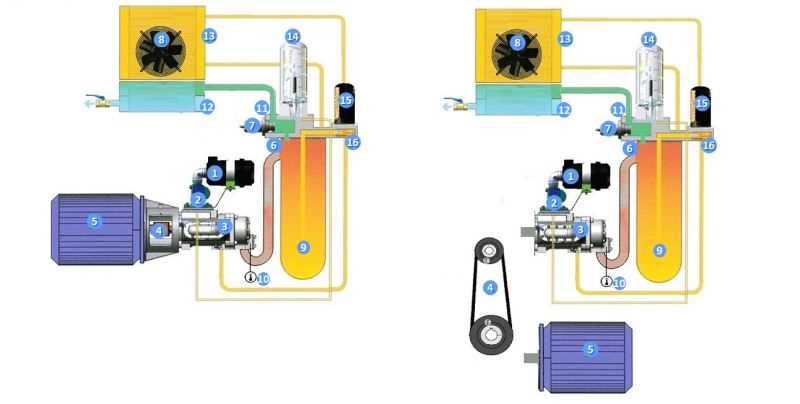
Replacement Parts: When and Why
Understanding when and why to substitute components in your equipment is essential for maintaining optimal performance and longevity. Over time, various elements can wear out or become less effective due to usage, environmental factors, or inherent material fatigue. Timely replacements can prevent more significant issues and ensure that machinery operates smoothly.
Indicators for Replacement
Recognizing the signs that a component needs to be replaced can save time and resources. Common indicators include unusual noises, reduced efficiency, and visible wear. Regular inspections play a crucial role in identifying these issues early.
Benefits of Timely Substitution
Replacing worn or damaged elements not only enhances functionality but also extends the life of your equipment. It can lead to improved efficiency, reduced energy consumption, and lower maintenance costs in the long run.
| Indicator | Recommended Action |
|---|---|
| Unusual Noises | Inspect and consider replacement |
| Decreased Performance | Evaluate for possible substitution |
| Visible Wear | Replace affected components |
| Frequent Breakdowns | Assess overall condition and replace |
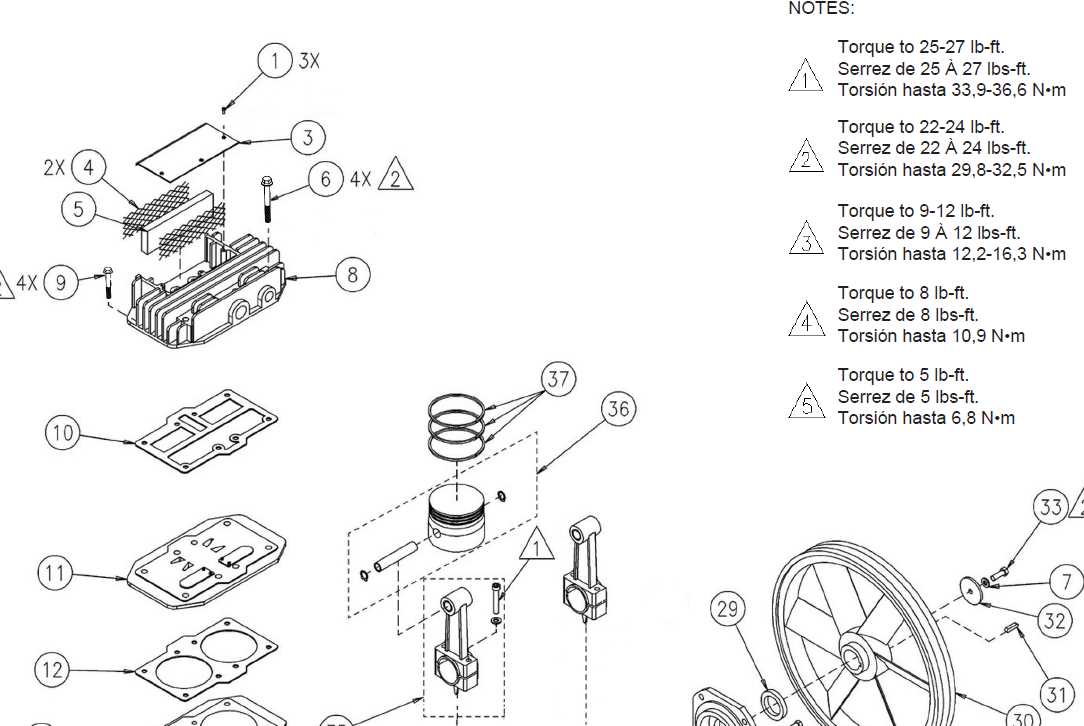
Tools Needed for Repair Work
When undertaking maintenance or fixing mechanical devices, having the right instruments is essential for efficient and effective results. Proper tools not only facilitate the repair process but also ensure safety and precision, helping to avoid potential damage to the equipment.
Commonly required instruments include wrenches and screwdrivers for loosening and tightening components, pliers for gripping and bending, and specialized devices like torque wrenches for applying precise force. Additionally, having measuring tools, such as calipers or rulers, is crucial for ensuring correct dimensions during repairs.
Safety gear, including gloves and goggles, should not be overlooked, as they protect the technician from potential hazards. By assembling the appropriate toolkit, one can significantly enhance the repair experience and achieve satisfactory outcomes.
Safety Precautions During Maintenance
Ensuring safety during the upkeep of machinery is crucial to prevent accidents and injuries. Proper precautions help maintain a secure working environment and protect both personnel and equipment. Adhering to established safety guidelines significantly reduces risks and enhances operational efficiency.
Personal Protective Equipment
Wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) is essential. Always use safety goggles to shield your eyes from debris, and wear gloves to protect your hands from sharp edges and hazardous materials. Additionally, ear protection should be utilized when working in noisy conditions to prevent hearing damage.
Equipment Lockout Procedures

Implementing lockout/tagout procedures is vital for ensuring that machinery remains inoperable during maintenance. This involves disabling energy sources and clearly marking equipment to indicate that it should not be operated. Such practices help prevent accidental activation, safeguarding maintenance personnel from potential harm.
Benefits of Understanding Your System
Having a comprehensive grasp of your equipment can lead to significant advantages. When you know how each component functions together, you enhance your ability to maintain efficiency and reliability.
Improved Performance: Familiarity with your machinery allows for optimized operation. By understanding the roles of various elements, you can make informed adjustments to improve overall functionality.
Cost Efficiency: Knowledge of your system helps in identifying issues early, which can prevent costly repairs. Regular maintenance becomes more straightforward, leading to savings in both time and resources.
Enhanced Safety: Recognizing potential hazards associated with different components can significantly reduce risks. A well-informed operator is better equipped to manage safety protocols effectively.
Informed Upgrades: Understanding your system empowers you to make strategic decisions regarding enhancements or replacements. You can select the most suitable upgrades based on your specific needs and goals.
In summary, a thorough understanding of your equipment not only fosters better performance but also promotes safety, cost savings, and informed decision-making.
Resources for Further Learning
Expanding your knowledge in the field of mechanical systems can significantly enhance your understanding and skills. Numerous resources are available to help you delve deeper into various components, their functionalities, and applications. Engaging with these materials can provide valuable insights and practical information for both beginners and experienced individuals alike.
Books: Consider exploring comprehensive texts that cover the fundamentals of machinery and their mechanisms. These can serve as excellent references, offering both theoretical knowledge and practical examples.
Online Courses: Numerous platforms offer structured courses focusing on industrial equipment. These courses often include video lectures, quizzes, and forums for discussion, making it easier to grasp complex concepts.
Webinars and Workshops: Attending live sessions conducted by industry experts can be beneficial. These interactive events provide opportunities to ask questions and engage directly with professionals.
Technical Forums: Participating in online communities can foster peer-to-peer learning. Sharing experiences and troubleshooting techniques with others can deepen your understanding and provide diverse perspectives.
Manufacturer Resources: Many manufacturers provide detailed documentation, including manuals and specifications. These resources can help you familiarize yourself with specific technologies and innovations.
Utilizing a combination of these resources can enhance your expertise and keep you updated on the latest advancements in the field.