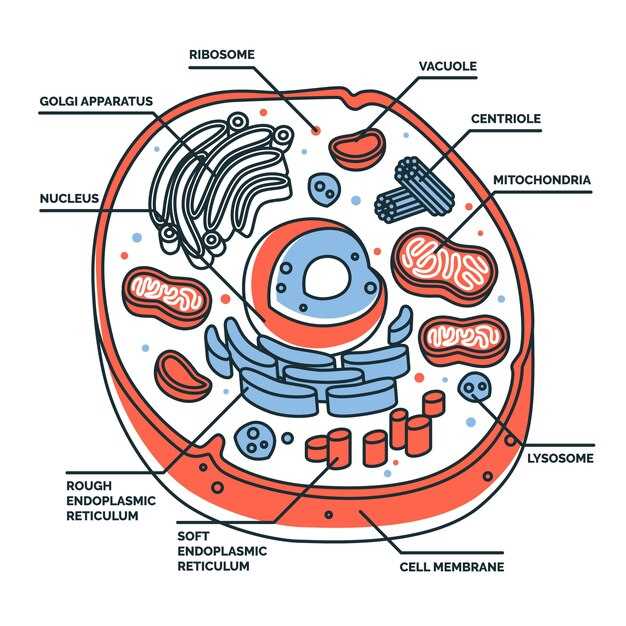
Exploring the Essential Parts of an Animal Cell Diagram
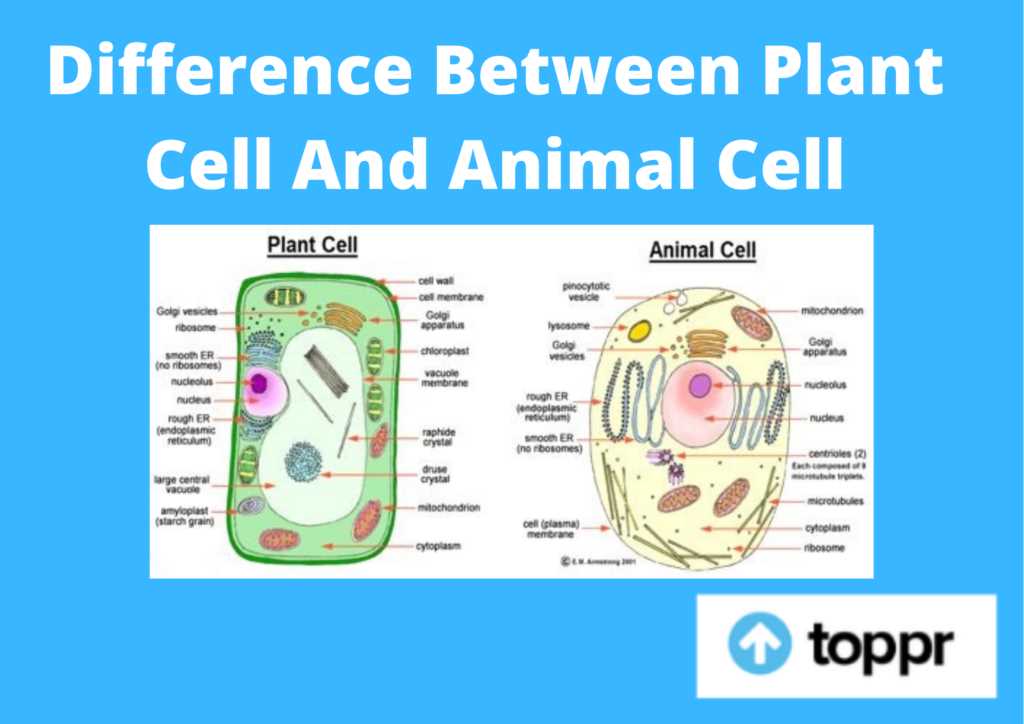
Exploring the intricate world of living entities reveals a fascinating landscape of microscopic structures, each playing a vital role in sustaining life. These essential components work in harmony, contributing to the overall functionality and health of the organism. By examining these building blocks, we can better appreciate the complexity of life.
Within this realm, a variety of specialized elements can be found, each with distinct duties that support growth, energy production, and communication. These elements interact dynamically, ensuring that the organism operates smoothly and efficiently. Delving into their specific roles can unveil the ultimate secrets behind cellular organization.
In the following sections, we will uncover the various components that make up these vital structures, highlighting their functions and significance. Understanding these aspects not only enhances our knowledge of biology but also fosters a deeper appreciation for the wonders of nature.
Understanding Animal Cell Structure
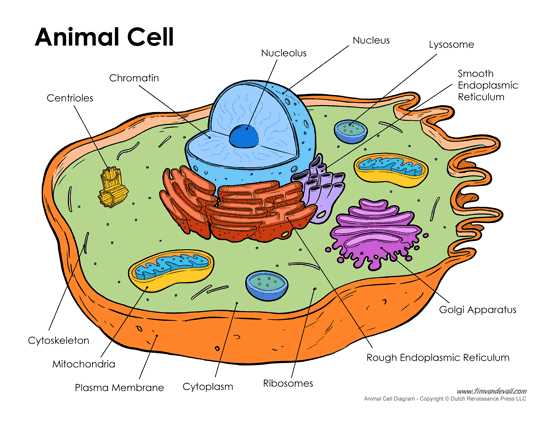
The intricate architecture of living organisms is a marvel of nature, showcasing a harmonious interplay of various components that work together to sustain life. Each unit within this biological framework plays a critical role, contributing to the overall functionality and efficiency of the organism.
At the core of this system are specialized structures, each with unique responsibilities that ensure the proper operation of vital processes. These elements are surrounded by a protective barrier, regulating the movement of substances in and out, thereby maintaining an optimal internal environment.
Energy production is facilitated by distinct entities that harness nutrients and convert them into usable forms, powering various activities. Meanwhile, genetic material is meticulously organized, safeguarding the instructions necessary for growth, development, and reproduction.
Communication between these components is essential for coordination, allowing for responses to internal and external stimuli. This complex network not only supports life but also exemplifies the beauty of biological diversity, reflecting the adaptability and resilience of living systems.
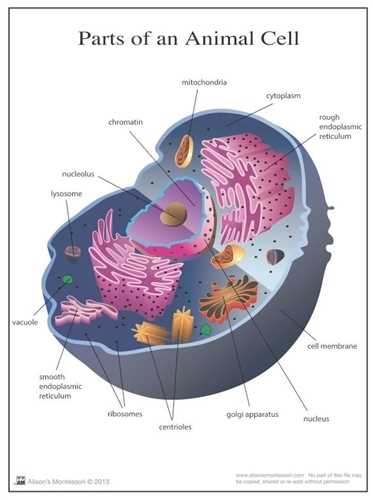
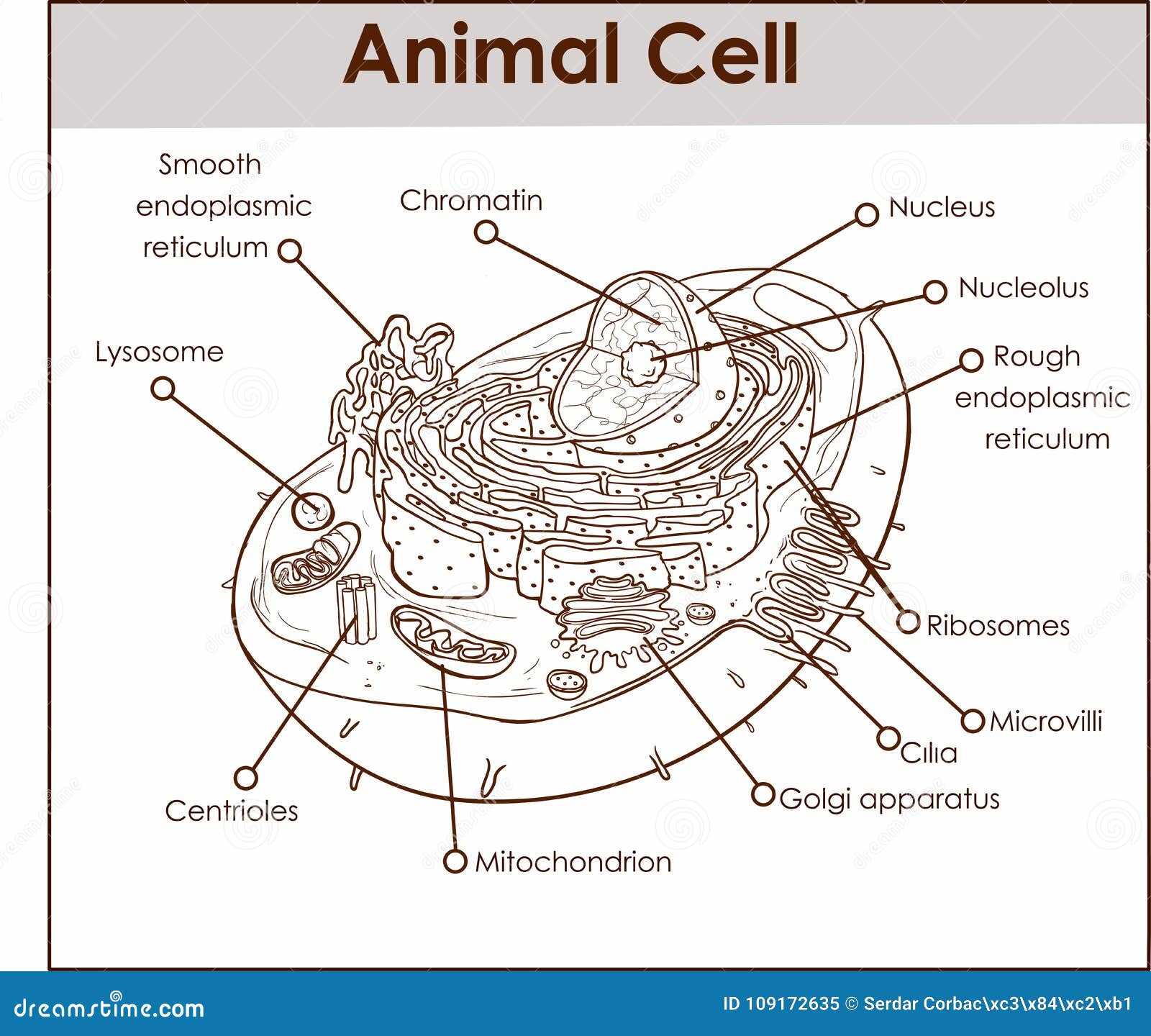
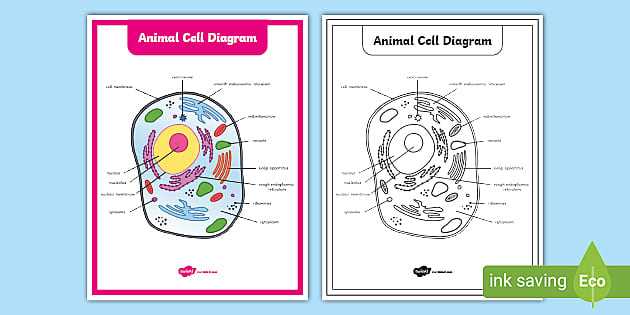
Key Components of Animal Cells
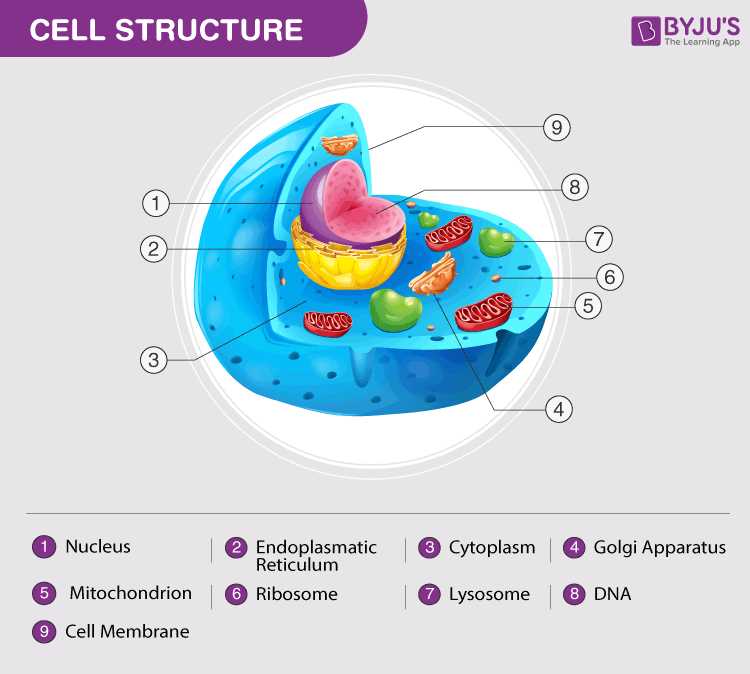
Understanding the fundamental elements that constitute living organisms is crucial for appreciating their complex functions. These essential structures play vital roles in maintaining the overall health and efficiency of the organism. Each component collaborates to ensure that processes like energy production, communication, and waste management occur seamlessly.
Nucleus serves as the control center, housing genetic material that dictates cellular activities and growth. It regulates gene expression and coordinates various functions, ensuring that the organism responds appropriately to its environment.
Mitochondria are known as the powerhouses, generating adenosine triphosphate (ATP) through the process of respiration. This energy currency fuels numerous biochemical reactions necessary for survival and functionality.
Ribosomes are critical for protein synthesis, translating genetic information into functional proteins that facilitate a wide range of processes, from enzymatic activities to structural support.
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER), both rough and smooth, plays a role in synthesizing and processing proteins and lipids. The rough ER is studded with ribosomes, while the smooth variant is involved in lipid synthesis and detoxification.
Golgi apparatus acts as a shipping and receiving center, modifying, sorting, and packaging proteins and lipids for secretion or delivery to various destinations within the organism.
Plasma membrane forms a selective barrier, regulating the movement of substances in and out of the cellular environment. This dynamic interface is crucial for maintaining homeostasis and facilitating communication with neighboring structures.
Each of these components is integral to the intricate web of life, working together to ensure that organisms function efficiently and adapt to their surroundings. The study of these structures offers insights into the remarkable complexity of life itself.
Function of Cell Membrane
The outer layer of a living structure plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity and functionality of the organism. It serves as a selective barrier, regulating the exchange of substances between the internal environment and the outside world. This selective permeability is essential for sustaining life processes and responding to environmental changes.
Key Functions
This boundary has several vital functions that contribute to the overall homeostasis of the organism. Some of these functions include:
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Protection | It acts as a shield, safeguarding the internal components from external hazards. |
| Transport | Facilitates the movement of essential molecules in and out, ensuring nutrient uptake and waste removal. |
| Communication | Contains receptors that allow interactions with signaling molecules, enabling responses to stimuli. |
| Adhesion | Provides structural support and enables connections with neighboring structures, maintaining tissue integrity. |
Conclusion
Understanding the multifaceted roles of this outer layer is fundamental to appreciating how living organisms maintain balance and interact with their environment. Its functions are interdependent, working in harmony to sustain life.
Role of Nucleus in Cells
The nucleus serves as a central hub for various vital processes within a biological entity. It orchestrates the activities necessary for growth, reproduction, and overall functionality, ensuring that genetic information is managed and expressed appropriately.
Functions of the Nucleus
This essential structure has multiple roles, including:
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Genetic Information Storage | Houses DNA, which contains the instructions for organismal development and function. |
| Regulation of Gene Expression | Controls the timing and rate of gene transcription, influencing cellular behavior. |
| Ribosome Production | Site of ribosomal RNA synthesis and assembly, crucial for protein synthesis. |
Significance in Cellular Function
The nucleus is critical for maintaining the integrity of genetic material and facilitating communication between different cellular components. Its role is ultimately indispensable for the proper functioning of living organisms.
Mitochondria and Energy Production
Mitochondria are often referred to as the powerhouses of organisms, playing a crucial role in converting nutrients into energy. This transformation is essential for various biological processes, ensuring that living entities function optimally and thrive in their environments.
The Role of Mitochondria
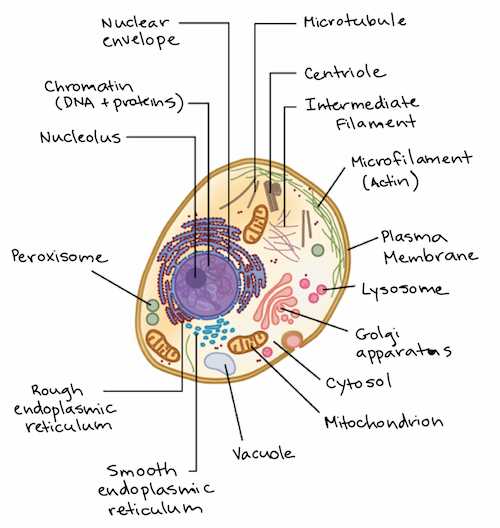
These organelles are responsible for producing adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy currency. Through a process known as cellular respiration, they harness the energy stored in food molecules, enabling vital functions like movement, growth, and repair.
Importance of Efficient Energy Production
Efficient energy generation is vital for maintaining metabolic balance. Any dysfunction in mitochondrial activities can lead to various health issues, underscoring their ultimate importance in overall well-being and vitality.
Importance of Ribosomes in Synthesis
Ribosomes play a crucial role in the intricate process of creating proteins, which are essential for various functions within living organisms. These molecular machines facilitate the translation of genetic information into functional molecules, thus acting as a bridge between the genetic code and the resulting proteins. Without them, the entire framework of biological activity would be compromised.
Mechanism of Protein Production
The primary function of ribosomes involves reading messenger RNA (mRNA) sequences and assembling amino acids in the correct order to form proteins. This process, known as translation, is vital for producing enzymes, structural components, and signaling molecules that maintain cellular integrity and function. The efficiency of ribosomes directly influences the speed and accuracy of protein synthesis, highlighting their significance in cellular operations.
Impact on Cellular Health
Deficiencies or malfunctions in ribosomal activity can lead to various health issues, as proteins are integral to nearly every biological process. When synthesis is disrupted, it can result in diseases, developmental disorders, and metabolic dysfunctions. Therefore, understanding the importance of these structures not only sheds light on fundamental biological mechanisms but also opens avenues for medical research and therapeutic interventions.
Endoplasmic Reticulum: Smooth vs Rough
The endoplasmic reticulum serves as a crucial network within a biological structure, facilitating various essential processes. This intricate system is divided into two distinct forms, each contributing uniquely to the overall function and efficiency of the organism’s internal activities.
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) is characterized by its lack of ribosomes, resulting in a smooth appearance. It plays a significant role in lipid synthesis, detoxification, and calcium ion storage. By producing essential fats and metabolizing harmful substances, SER ensures cellular health and balance.
In contrast, rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) is studded with ribosomes, giving it a rough texture. This structure is primarily involved in the synthesis and processing of proteins destined for secretion or membrane incorporation. The ribosomes attached to RER translate messenger RNA into polypeptide chains, which are then folded and modified within this specialized network.
Both forms of the endoplasmic reticulum work in concert, supporting the intricate machinery of life. Their distinct functions highlight the complexity of biological systems and the necessity of specialized structures to maintain homeostasis and facilitate growth.
Golgi Apparatus: Processing and Shipping

The Golgi apparatus plays a crucial role in the modification, sorting, and distribution of biomolecules within organisms. This essential organelle ensures that proteins and lipids are properly processed before they reach their final destinations, ultimately maintaining cellular function and integrity.
Structure and Function
Composed of stacked, flattened membranes, the Golgi apparatus functions like a postal service for the organism. It receives vesicles containing newly synthesized molecules from the endoplasmic reticulum, processes them through enzymatic reactions, and prepares them for transport. This ensures that each substance is accurately modified and packaged for delivery.
Significance in Cellular Operations
By managing the distribution of vital components, the Golgi apparatus contributes significantly to overall cellular health. Its ability to modify carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins highlights its role in creating functional molecules necessary for various physiological processes. Disruptions in its function can lead to a range of cellular dysfunctions and diseases.
Lysosomes and Cellular Digestion
Lysosomes play a crucial role in the breakdown and recycling of various biomolecules within organisms. These specialized organelles contain enzymes that facilitate the digestion of complex substances, ensuring the maintenance of cellular health and function.
Functionality of Lysosomes
Equipped with hydrolytic enzymes, lysosomes are essential for decomposing waste materials and cellular debris. This process not only removes potentially harmful substances but also allows the recycling of valuable components, contributing to the overall efficiency of biological systems.
Importance in Homeostasis
The activity of these organelles is vital for maintaining homeostasis. By regulating the turnover of cellular constituents, they help sustain an optimal internal environment. In cases of dysfunction, the consequences can lead to various diseases, highlighting their ultimate importance in cellular integrity.
Cytoplasm: The Cell’s Matrix
The fluid-filled environment within a biological unit serves as a vital medium where numerous essential processes unfold. This gel-like substance not only supports various structures but also facilitates the movement of organelles and molecules, enabling communication and interaction among cellular components.
Functionally rich, this matrix plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis, providing a stable environment that allows biochemical reactions to occur efficiently. It acts as a cushion, protecting delicate structures from mechanical stress while ensuring that nutrients and waste products can be effectively transported throughout the interior.
Within this dynamic space, a complex network of proteins and other molecules forms a supportive scaffold. This cytoskeleton not only contributes to the cell’s shape but also plays a key role in intracellular transport and signaling, making it indispensable for overall functionality.
Overall, the matrix represents a highly organized yet fluid environment, integral to the life of the unit, ensuring that various processes operate smoothly and in concert.
Centrioles and Cell Division
Centrioles play a crucial role in the intricate process of cellular replication. Their primary function involves facilitating the organization of structures necessary for dividing the genetic material, ensuring that each new entity receives the correct amount of information. This mechanism is vital for maintaining the integrity of organisms and their growth.
Structure and Function
Each centriole consists of a cylindrical arrangement of microtubules, which provides the framework for their activity. During division, these structures help to form the spindle apparatus, which is essential for separating chromosomes. This coordination allows for a smooth transition from one phase of replication to another, highlighting their importance in sustaining life.
Role in Disease
Abnormalities in centriole function can lead to significant issues, including cancer and developmental disorders. When the mechanisms governing their behavior are disrupted, the fidelity of genetic transmission can be compromised, ultimately affecting organismal health. Understanding these complexities can lead to breakthroughs in medical science.
Vesicles: Transport within the Cell
Within the intricate landscape of biological structures, vesicles play a crucial role in the movement and distribution of materials. These small, membrane-bound entities facilitate the efficient transport of various substances, ensuring that essential components reach their destinations seamlessly.
| Type of Vesicle | Function |
|---|---|
| Transport Vesicles | Carry proteins and lipids from one organelle to another. |
| Secretory Vesicles | Release substances outside the structure through exocytosis. |
| Endocytic Vesicles | Engulf extracellular material for internal processing. |
Understanding the mechanisms by which these entities operate provides insight into their ultimate importance in maintaining cellular homeostasis and functionality.