Bicycle Hub Parts Diagram Explained
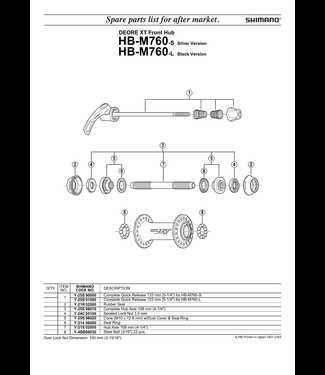
The intricate mechanisms that allow for smooth rotation are essential to the functionality of any two-wheeled transport. A closer examination reveals a variety of interconnected elements that work in harmony, each contributing to overall performance and efficiency. Grasping these components enhances appreciation for engineering excellence in modern mobility solutions.
From the central structure that serves as a rotation axis to the various elements that secure and support, every piece plays a critical role. Understanding how these elements interact provides valuable insights into both maintenance and enhancement of performance. Each component, whether visible or hidden, ensures durability and reliability on any journey.
In this exploration, we will delve into the specifics of these essential components, highlighting their functions and relationships. By unraveling the complexity of the assembly, enthusiasts and casual users alike can gain a better understanding of what makes a well-crafted system truly exceptional.
Bicycle Hub Parts Diagram Overview
This section provides an insightful look into the essential components that make up the core structure of a wheel assembly. Understanding these elements is crucial for both maintenance and performance optimization. Each piece plays a significant role in ensuring smooth operation and stability during rides.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Shell | The outer casing that encases the internal mechanisms and provides structural integrity. |
| Axle | The central rod that supports the wheel and allows it to rotate freely. |
| Bearings | Small spherical elements that reduce friction between moving parts, facilitating smooth rotation. |
| Flange | Protrusions that provide a mounting point for spokes, connecting the rim to the assembly. |
| Seal | A protective covering that prevents dirt and moisture from entering the inner workings. |
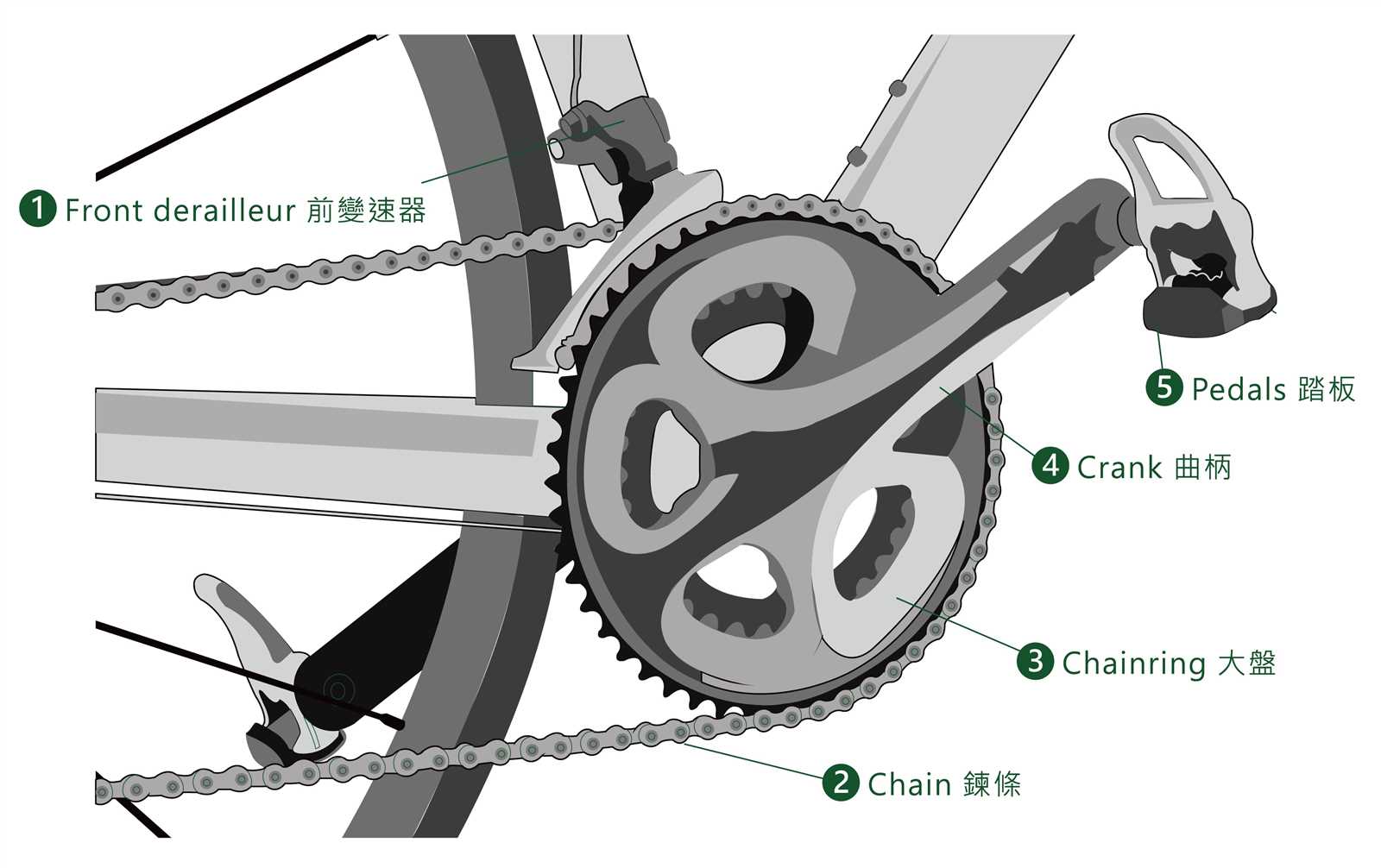
Understanding Bicycle Hub Functionality
The central component of a two-wheeled vehicle plays a crucial role in ensuring smooth motion and efficient energy transfer. This element facilitates the connection between the frame and the wheels, allowing for seamless rotation while supporting the rider’s weight and delivering power from the pedals. By grasping the mechanics behind this essential unit, one can appreciate its significance in overall performance and handling.
At its core, this component consists of several key elements that work in unison to create a reliable system. Below is a table summarizing these essential features:
| Element | Function |
|---|---|
| Shell | Houses internal components and connects to the wheel structure. |
| Axle | Serves as the main shaft that supports the wheel assembly. |
| Bearings | Reduce friction between moving parts, enabling smooth rotation. |
| Freehub | Allows for the engagement and disengagement of the drivetrain when coasting. |
| Locknut | Secures components in place, maintaining stability during operation. |
Each of these components contributes to the overall functionality, affecting how energy is transmitted and how effectively the vehicle can maneuver. Understanding their interplay can enhance one’s insight into maintenance and performance optimization.
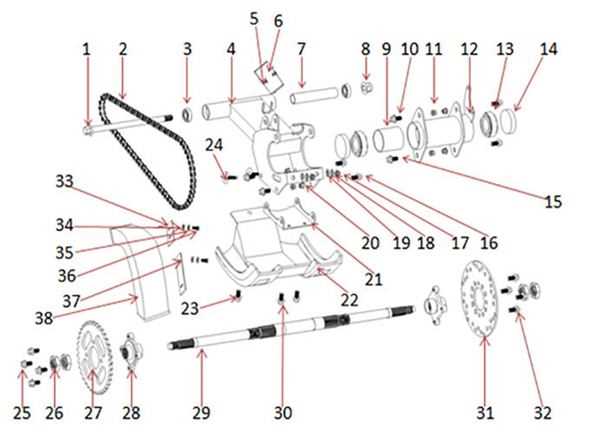
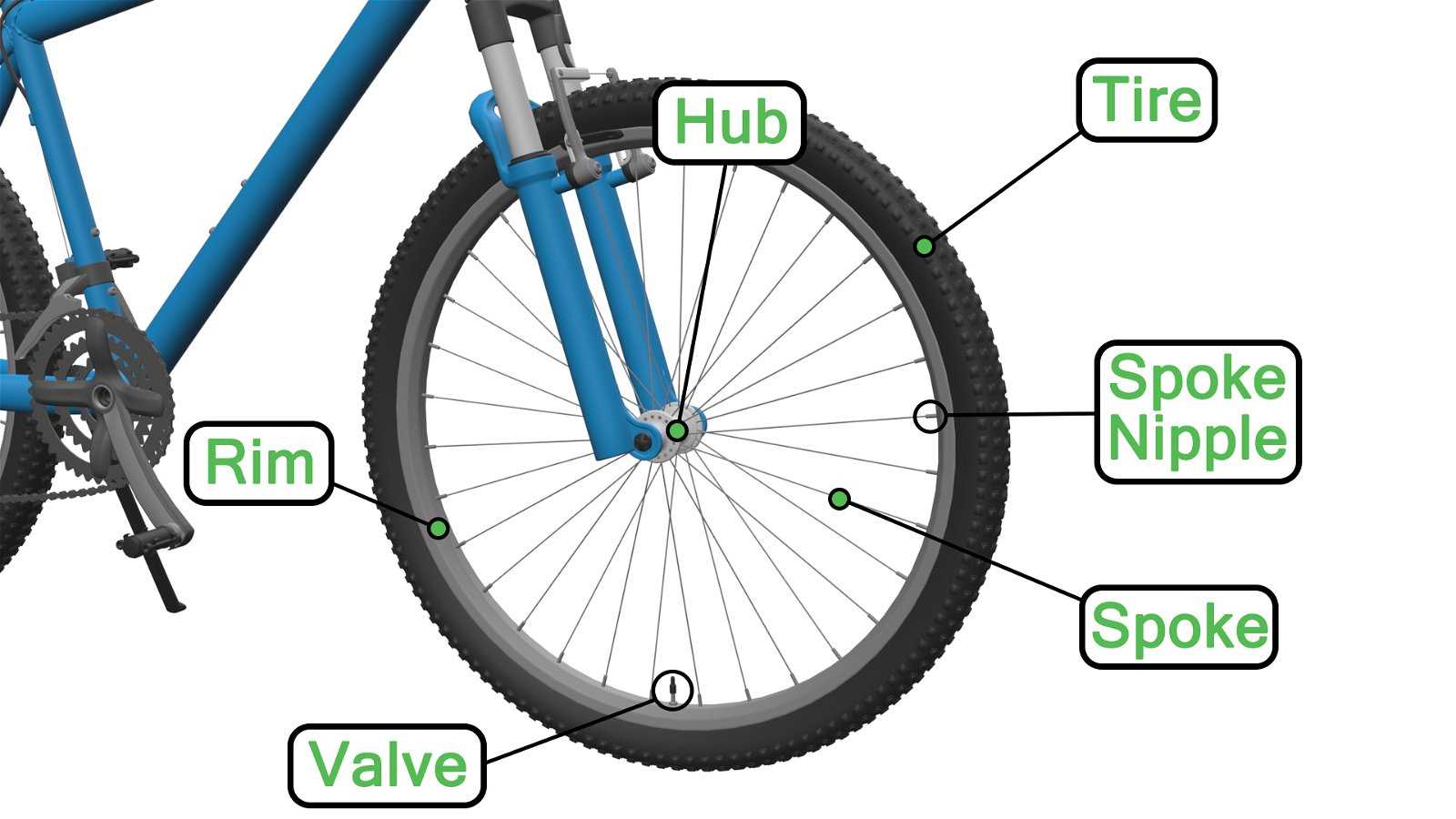
Main Components of a Bicycle Hub
The essential structure of a wheel assembly includes several key elements that work together to ensure smooth operation and stability. Understanding these components is crucial for anyone looking to maintain or enhance their riding experience.
Axle serves as the central shaft around which everything rotates. It provides the foundation for the entire assembly, connecting the wheel to the frame and allowing for effective power transfer from the rider.
Bearings facilitate the rotation of the wheel, reducing friction between moving parts. These small yet vital components can significantly impact performance and longevity, making regular inspection important for maintaining optimal function.
Shell acts as the outer casing, housing the internal components securely. Its design can vary, influencing both aesthetic appeal and structural integrity, which can affect overall riding efficiency.
Freehub or freewheel mechanism is responsible for enabling the rider to coast without pedaling, allowing for greater control during various riding conditions. This feature is crucial for improving handling and comfort on diverse terrains.
Spokes, though often overlooked, play a significant role in maintaining the wheel’s shape and strength. They connect the rim to the central structure, distributing weight evenly and ensuring a stable ride.
Understanding these fundamental components is vital for enhancing performance and ensuring longevity, making them indispensable for any enthusiast or casual rider alike.
Types of Bicycle Hubs Explained
Understanding the various types of wheel centers is crucial for any cycling enthusiast. Each design serves a distinct purpose and caters to specific riding styles and terrains. By examining the key variations, riders can make informed choices that enhance their performance and experience.
| Type | Description | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Standard | Commonly found in everyday models, offering a balance of durability and weight. | Leisure riding and commuting |
| Disc | Designed for use with disc brakes, providing improved stopping power and heat dissipation. | Off-road cycling and mountainous terrain |
| Freewheel | Features a mechanism that allows for coasting without pedaling, commonly used in single-speed setups. | Urban riding and casual use |
| Through-axle | Utilizes a larger axle for added strength and rigidity, ensuring stability under heavy loads. | Performance cycling and competitive racing |
| Fixed | Offers direct connection between pedals and wheel, allowing for unique riding styles. | Track racing and city riding |
By considering the characteristics and intended uses of each type, cyclists can select the most suitable option for their needs, ultimately improving their riding experience.
Hub Bearings: Types and Benefits
In the realm of cycling mechanics, the smooth operation of rotating components is crucial for performance and durability. One key element that contributes to this functionality is the bearing system. Understanding the various types of these components and their advantages can greatly enhance the experience of riding and maintenance.
Types of Bearings
There are primarily two types of bearings commonly used in wheel assemblies: ball bearings and cartridge bearings. Ball bearings consist of small spheres that reduce friction and allow for smoother rotation. They are widely appreciated for their affordability and ease of replacement. Cartridge bearings, on the other hand, come pre-sealed and offer a more robust solution against dirt and moisture. Their design ensures less maintenance and longer lifespan, making them a popular choice among serious riders.
Benefits of Quality Bearings
Investing in high-quality bearing systems leads to several benefits. Firstly, they significantly enhance efficiency by minimizing resistance, which can translate into faster speeds and improved energy conservation during rides. Secondly, durable bearings are less susceptible to wear and tear, thus reducing the frequency of replacements and overall maintenance costs. Finally, well-functioning components contribute to a more enjoyable and smoother ride, allowing enthusiasts to focus on the journey rather than mechanical issues.
Importance of Hub Shell Material
The material composition of the outer casing plays a crucial role in determining the performance and longevity of the entire assembly. Different materials offer unique benefits, influencing factors such as weight, durability, and resistance to environmental elements. Understanding these characteristics helps enthusiasts make informed choices when selecting components for their ride.
Weight Considerations
Choosing a lightweight material can significantly reduce overall weight, enhancing speed and maneuverability. This is particularly important for competitive users who require efficiency. However, lighter options must also ensure adequate strength to withstand the stresses encountered during use.
Durability and Maintenance
The choice of material directly impacts how well the casing resists wear and tear over time. Robust materials provide longevity, minimizing the need for frequent replacements or repairs. Additionally, some compositions offer better resistance to corrosion, making them suitable for various weather conditions and prolonging the lifespan of the assembly.
Wheel Alignment and Hub Impact
Proper alignment of wheels plays a crucial role in the overall performance and longevity of a two-wheeled vehicle. Misalignment can lead to uneven wear, affecting not just the tires, but also various components that contribute to a smooth ride. Understanding how the positioning of wheels interacts with the central mechanism can help in maintaining optimal functionality.
Factors influencing wheel alignment include:
- Terrain type
- Riding habits
- Environmental conditions
- Wear and tear of tires
Effects of poor alignment may manifest as:
- Increased resistance while pedaling
- Uneven tire degradation
- Impaired handling and stability
- Heightened stress on the vehicle’s structure
Regular inspections and adjustments are essential to ensure that wheels remain correctly aligned. By doing so, riders can enhance safety, efficiency, and overall enjoyment of their experience.
Brake Systems and Hub Interaction
The relationship between braking mechanisms and the central rotating component is crucial for overall performance and safety. Understanding how these systems work together allows for improved efficiency and reliability during operation. The interaction affects not only stopping power but also the wear and longevity of various elements involved.
Braking systems generally fall into two categories: mechanical and hydraulic. Each type has distinct advantages and operational characteristics that influence the interaction with the central rotating component.
| Brake Type | Interaction Characteristics | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical | Direct force transmission through cables | Simplicity and ease of maintenance |
| Hydraulic | Fluid pressure for force distribution | Increased stopping power and modulation |
The effectiveness of either system can be impacted by the alignment and condition of the central component. Regular maintenance ensures optimal contact and function, reducing the risk of malfunction and enhancing overall user experience.
Hub Maintenance: Tips and Tricks
Proper upkeep of essential components is crucial for optimal performance and longevity. Regular attention ensures smooth operation and can prevent costly repairs. Here are some effective strategies to keep everything in top shape.
Routine Inspection
Performing regular checks is vital. Look for signs of wear, rust, or misalignment. Catching issues early can save time and resources. Make it a habit to inspect the crucial elements during your maintenance routine.
Lubrication and Cleaning
Maintaining cleanliness and applying the right lubricants can greatly enhance functionality. Use appropriate cleaning solutions to remove dirt and grime. Select a suitable lubricant that prevents corrosion and reduces friction.
| Task | Frequency | Tools Needed |
|---|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Every month | Wrench, flashlight |
| Cleaning | Every 3 months | Brush, cleaning solution |
| Lubrication | Every 6 months | Grease, applicator |
Identifying Hub Problems Easily
Understanding common issues within the wheel mechanism is essential for maintaining optimal performance. By recognizing early signs of trouble, riders can prevent more significant complications and ensure a smoother experience. This section outlines key indicators that signal potential malfunctions, making it easier to diagnose and address them promptly.
Common Symptoms to Watch For
Listen for unusual noises while pedaling; grinding or clicking sounds may indicate wear or misalignment. Additionally, observe for any wobbling or excessive play in the wheel, as these can suggest that components are not functioning correctly. Regular visual inspections can also reveal cracks or damage that might compromise integrity.
Steps for Troubleshooting
Begin by checking the tightness of the axle and associated fasteners. If they are loose, tightening them might resolve the issue. If noises persist, disassembly for cleaning and lubrication of moving parts is advisable. In cases of severe damage or persistent problems, consulting a professional mechanic may be necessary to ensure safety and performance.
Choosing the Right Hub for You
Selecting the ideal central component for your ride is crucial for both performance and comfort. This decision affects your overall experience, impacting everything from speed to maneuverability. Understanding your riding style and preferences is essential in making an informed choice.
Consider the terrain you frequently navigate. If you enjoy rugged trails, a robust design may be necessary for enhanced durability. Conversely, if you prefer smooth pavements, a lighter option could improve efficiency. Additionally, pay attention to the axle type and the gear ratio, as these factors influence the smoothness and responsiveness of your experience.
Don’t overlook compatibility with your existing setup. Ensuring that your selected component aligns with your frame and wheel dimensions will prevent any installation issues. Take the time to explore various brands and models, as well as user reviews, to find a reliable option that meets your specific needs.
Lastly, budget plays a significant role in your decision-making process. High-quality options are available across a range of prices, so it’s important to balance cost with performance. Investing in a reliable component can significantly enhance your enjoyment and efficiency on the road or trail.
Upgrading Your Bicycle Hub: What to Consider
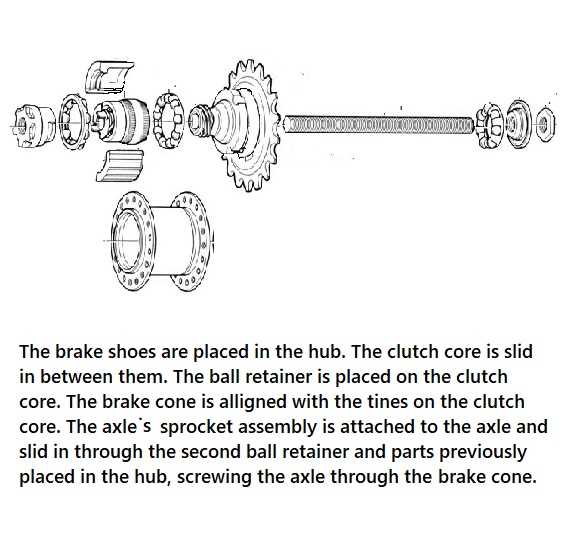
Enhancing your wheel assembly can significantly impact your riding experience. Whether you seek improved performance, better durability, or a lighter setup, there are several key factors to keep in mind during the upgrade process.
Here are essential considerations to guide your decision:
- Type of Riding: Determine the primary use of your setup–whether for commuting, racing, or off-road adventures. This will influence your choice of components.
- Weight: Lighter components can enhance speed and agility, but may compromise durability. Balance is key.
- Durability: Assess the materials used. Some options may offer better longevity, especially under harsh conditions.
- Compatibility: Ensure new elements are compatible with your existing setup. Check dimensions and attachment methods.
- Maintenance: Consider how easy it is to service or replace components. Simplicity can save time and effort in the long run.
Each of these factors can shape your riding experience. Carefully evaluate your needs to select the right enhancements for your setup.
DIY Hub Repair: A Step-by-Step Guide
Repairing the rotational mechanism of your two-wheeled vehicle can seem daunting, but with the right tools and a bit of patience, you can restore its functionality. This guide will walk you through each step, ensuring you can tackle the project confidently and effectively.
Gathering Your Tools and Materials
Before you begin, it’s essential to have the necessary tools at hand. You’ll need a variety of items such as a wrench, grease, and possibly replacement components. Make sure to set up a clean workspace where you can focus without distractions.
Step-by-Step Repair Process
Start by disassembling the mechanism carefully, taking note of how each piece fits together. Once disassembled, clean all components thoroughly to remove any dirt or grime. Inspect each element for wear and damage; replace any parts that show significant signs of deterioration. After cleaning and replacing, apply a suitable lubricant to ensure smooth operation. Finally, reassemble the mechanism, ensuring everything is aligned correctly and securely tightened.
Remember, taking your time during each step is crucial for achieving the best results. With practice, you’ll be able to maintain and repair this critical aspect of your ride efficiently.