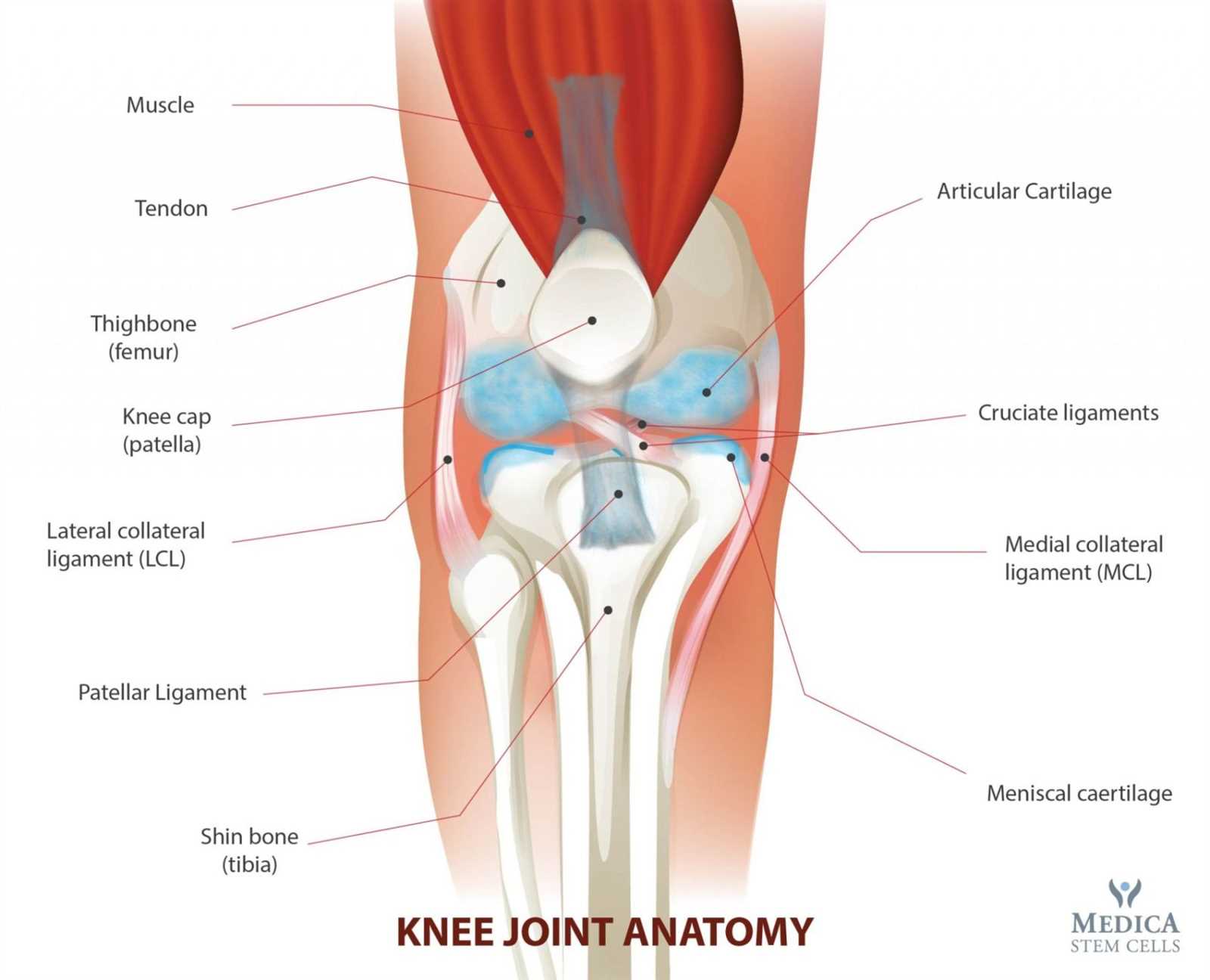
Understanding the Components of the Knee
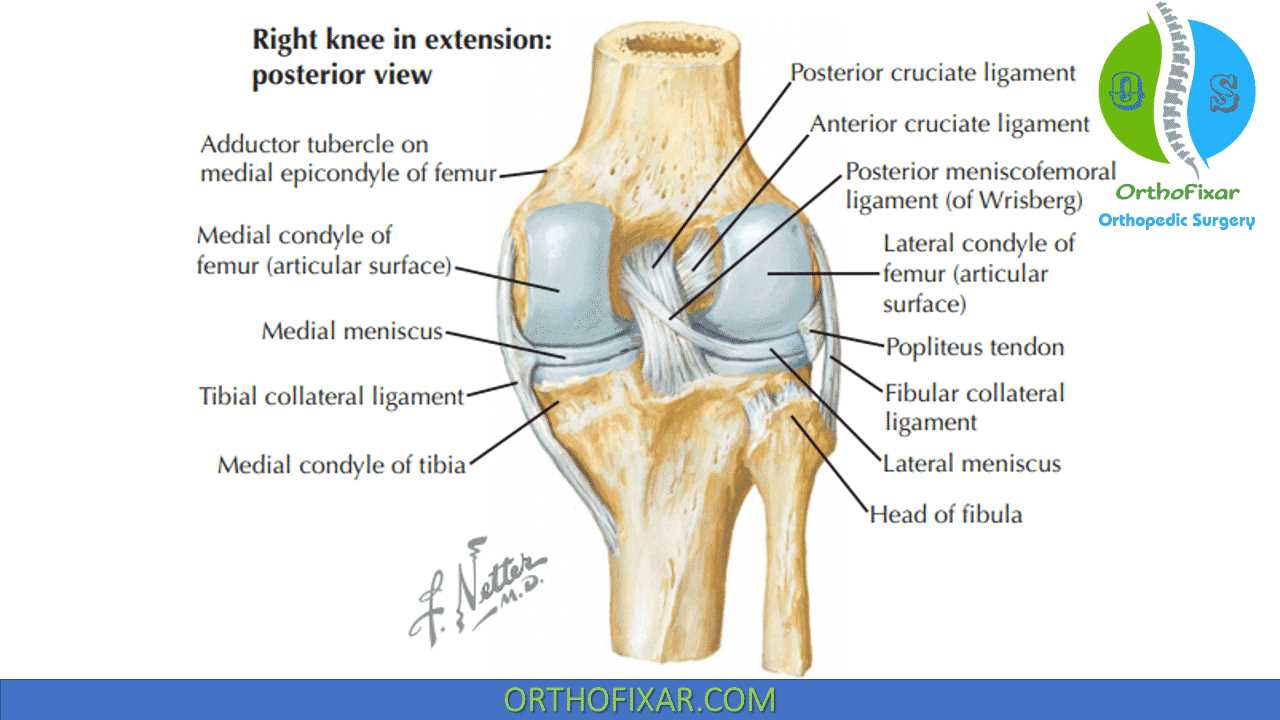
The intricate design of the joint in question plays a vital role in human movement and stability. It comprises various components that work together seamlessly to allow for flexibility and strength during activities such as walking, running, and jumping. Gaining insight into this anatomical region can enhance our understanding of mobility and the mechanics involved.
Exploring the various elements involved in this essential joint reveals a complex interplay of bones, ligaments, tendons, and cartilage. Each of these structures contributes uniquely to the overall function and health of the joint. By examining their relationships and roles, one can appreciate the importance of maintaining proper care and awareness of any potential issues that may arise.
In addition, knowledge of the specific locations and functions of these elements can assist in identifying injuries and developing effective treatment strategies. A comprehensive understanding of this area promotes better health outcomes and improves athletic performance, making it crucial for both medical professionals and individuals seeking to enhance their physical capabilities.
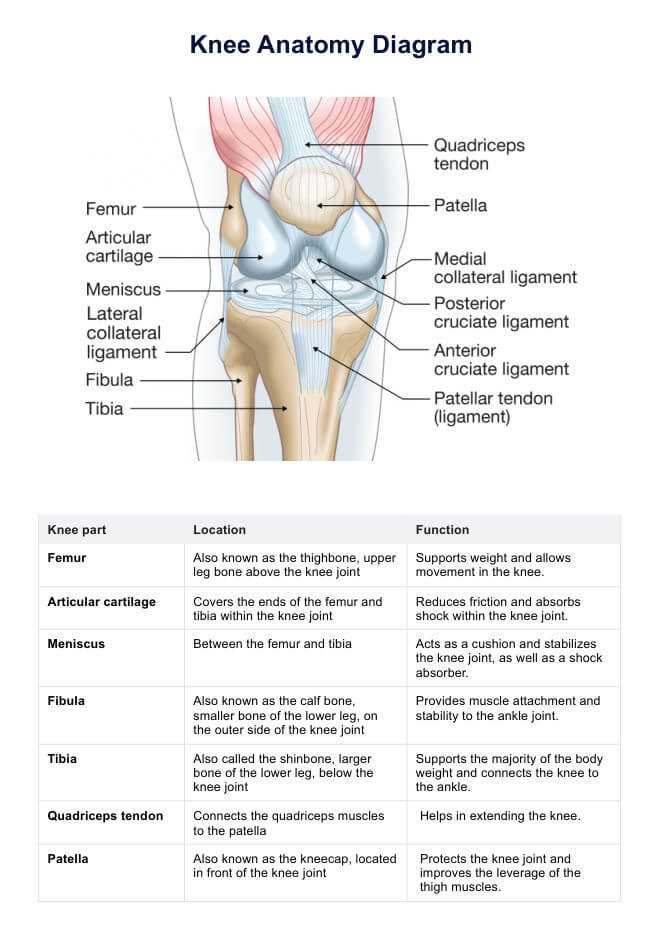
Knee Parts Diagram
This section provides a visual representation of the components that constitute a specific joint in the human body. Understanding the various elements involved is essential for grasping how this joint functions and the importance of each component in facilitating movement and stability.
Anatomical Elements
The structure consists of several key features that work together harmoniously. These include the supportive ligaments, the cushioning cartilage, and the connecting bones. Each feature plays a vital role in maintaining the overall integrity and functionality of the joint.
The interaction between these components is crucial for mobility and support during activities. Proper functioning of this joint is essential for everyday movements such as walking, running, and climbing stairs. Understanding these elements aids in identifying potential issues and implementing effective treatments.
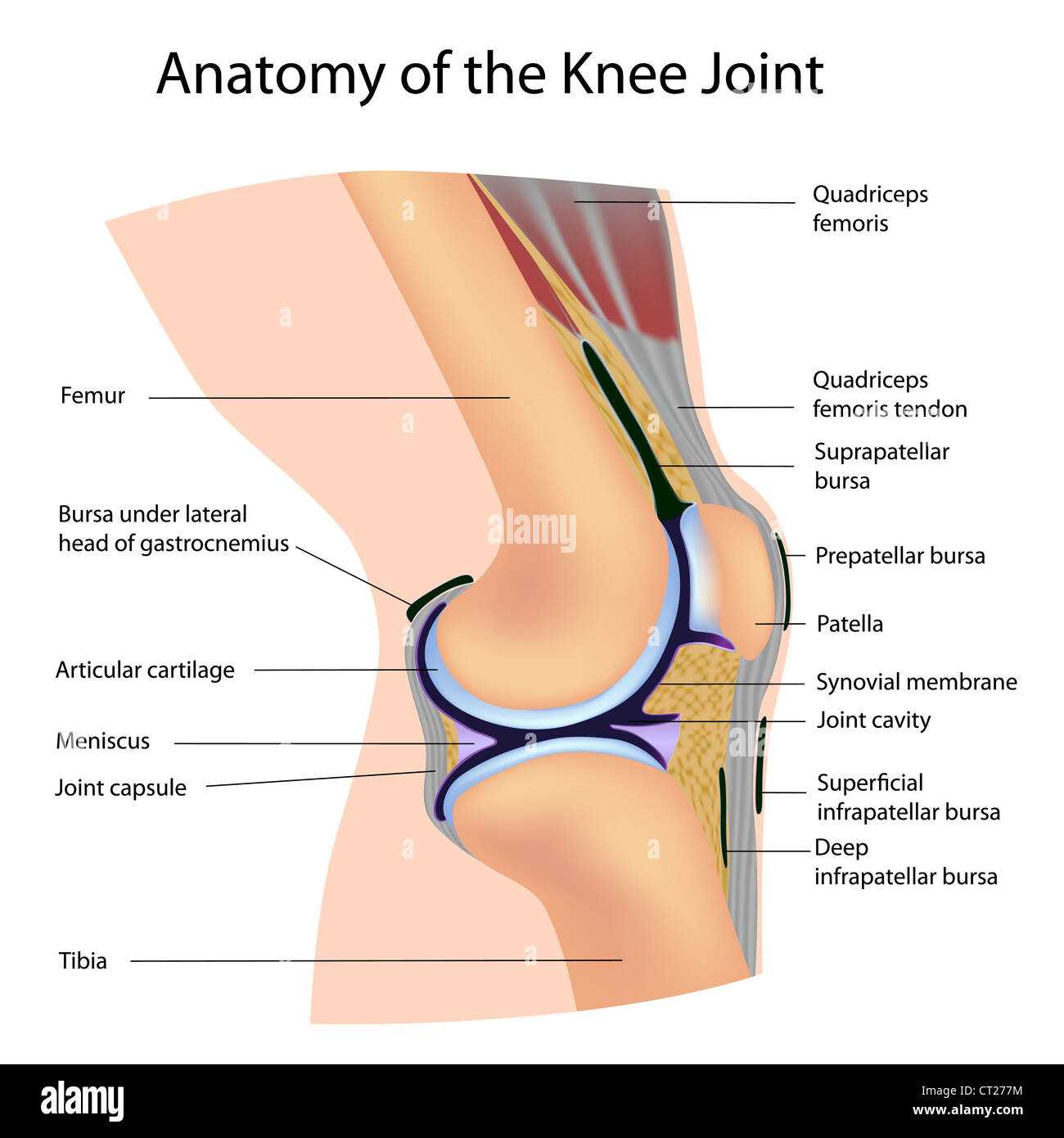
Anatomy of the Knee Joint
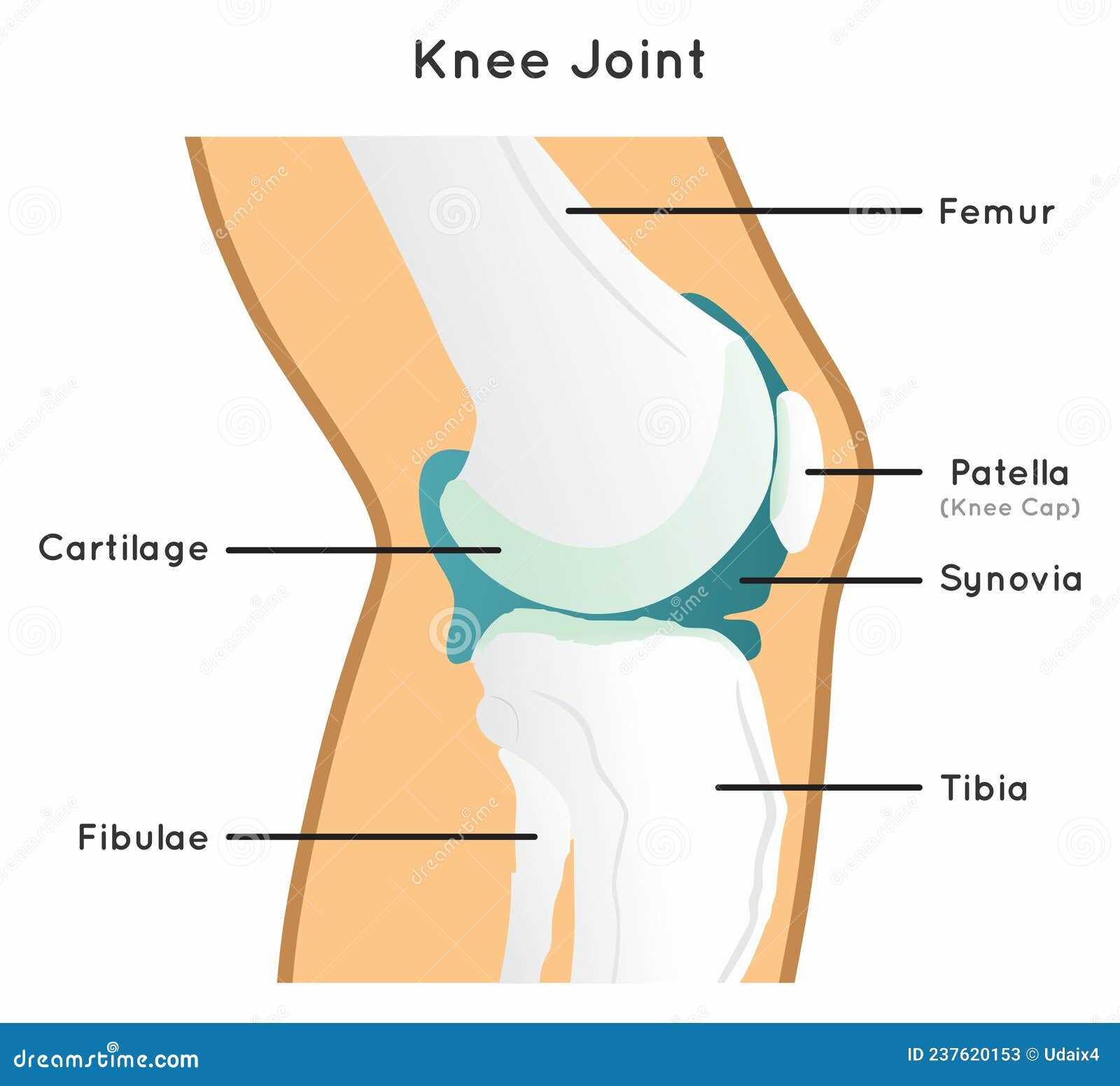
The complex structure that facilitates movement and support in the lower limb is essential for various activities, from walking to running. Understanding this intricate system helps in appreciating its function and the potential issues that may arise due to injury or wear.
Components Involved
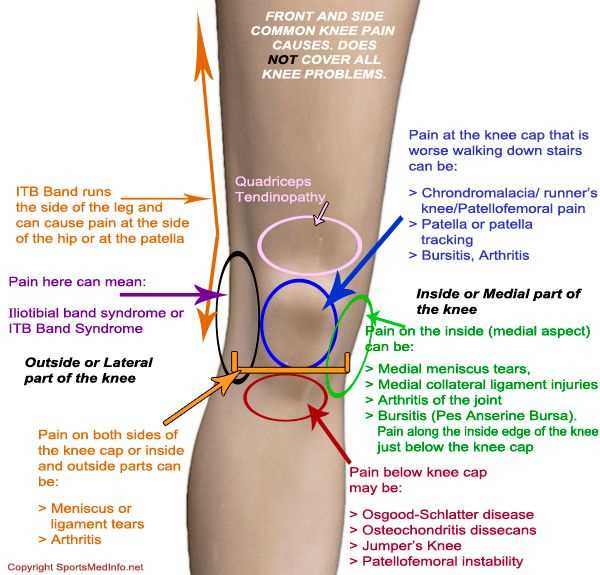
This region comprises several crucial elements, including bones, cartilage, ligaments, and tendons. Each component plays a vital role in maintaining stability and enabling motion.
Functional Importance
The arrangement of these components allows for flexibility and strength, which are necessary for daily activities and athletic performance. Proper functioning relies on the harmonious interaction of all parts.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Femur | Supports body weight and enables motion |
| Tibia | Transmits weight from the body to the foot |
| Patella | Protects the joint and improves leverage of the thigh muscles |
| Cartilage | Absorbs shock and reduces friction |
| Ligaments | Stabilize and support the structure |
| Tendons | Connect muscles to bones for movement |
Major Components of the Knee
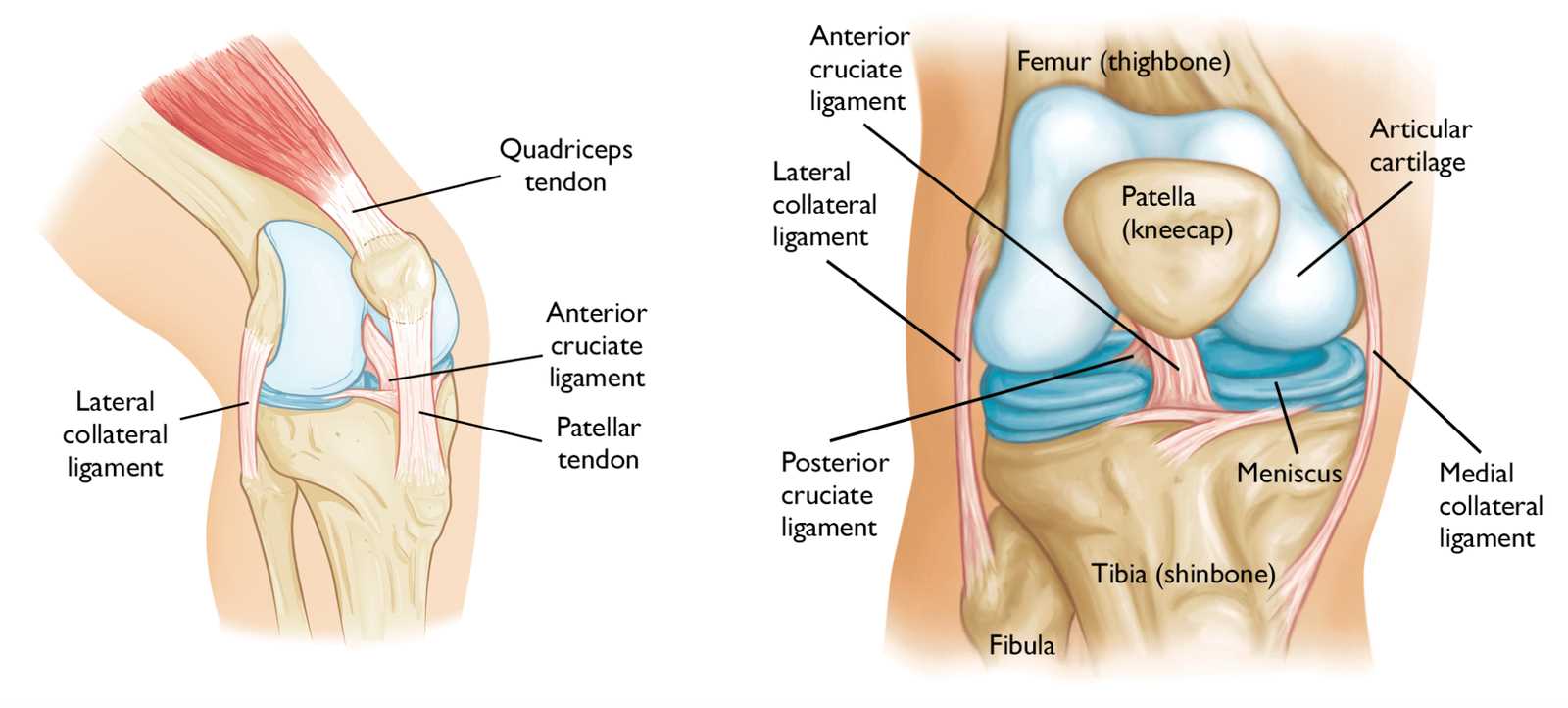
The complex structure of this joint includes several essential elements that work together to provide stability and mobility. Each component plays a vital role in ensuring smooth movement while supporting weight during various activities.
Articular Cartilage covers the ends of the bones, creating a smooth surface that reduces friction and absorbs shock. This protective layer is crucial for maintaining joint health and preventing damage during motion.
Ligaments connect the bones and provide stability, preventing excessive movement that could lead to injury. The key ligaments include the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL), which help maintain the joint’s integrity.
Tendons attach muscles to the bones and are vital for movement. The quadriceps tendon and patellar tendon are essential for extending the leg and facilitating various activities, from walking to jumping.
Menisci are two crescent-shaped pieces of cartilage that act as shock absorbers and stabilizers within the joint. They help distribute weight evenly and reduce the risk of injury during physical activities.
Understanding these key elements contributes to a greater appreciation of the joint’s function and the importance of maintaining its health through proper care and exercise.
Understanding Knee Ligaments
The stability of the joint relies significantly on a network of strong connective tissues. These structures play a crucial role in maintaining proper alignment and function, allowing for a range of movements while providing support during physical activities. A thorough comprehension of these elements is essential for recognizing their importance in overall mobility and the prevention of injuries.
These fibrous tissues can be categorized into different groups based on their location and function. Each group serves distinct purposes, contributing to the dynamic functionality of the joint. Below is a table summarizing the main types of these structures along with their roles:
| Type | Function |
|---|---|
| Anteromedial | Prevents excessive backward movement |
| Posterolateral | Stabilizes during rotational movements |
| Central | Facilitates smooth articulation |
| Lateral | Ensures stability during lateral movements |
Role of Knee Cartilage
Cartilage plays a crucial role in maintaining the overall function and health of the joint. It acts as a cushion, absorbing shock and reducing friction between bones during movement. This smooth surface is essential for allowing easy motion and supporting the weight of the body, contributing to mobility and stability.
Types of Cartilage
There are different types of cartilage found in the joint, each serving unique functions:
| Type of Cartilage | Description |
|---|---|
| Hyaline Cartilage | This is the most common type, providing a smooth surface for articulation and supporting the structure of the joint. |
| Fibrocartilage | This type offers greater tensile strength and is found in areas requiring more support, such as the menisci. |
Importance of Cartilage Health
Maintaining the integrity of cartilage is vital for preventing discomfort and ensuring long-term functionality. Damage or degradation can lead to conditions that impair movement and cause pain, highlighting the necessity of protective measures and regular care.
Knee Bones and Their Functions
The structure of the joint comprises several critical elements that work together to facilitate movement and provide stability. Understanding the various components and their roles is essential for appreciating how this complex mechanism operates effectively.
Femur serves as the upper bone, connecting to the lower leg and forming a pivotal point for mobility. Its rounded end interacts with the next component, allowing for smooth articulation.
Tibia, the larger bone in the lower leg, supports the weight of the body and contributes to the overall stability of the joint. It plays a crucial role in absorbing impact during activities such as walking or running.
Patella, commonly known as the kneecap, acts as a protective shield for the joint. It also aids in the movement of the femur by enhancing leverage during physical activity.
Each of these bones collaborates with ligaments and tendons to ensure a balanced range of motion while maintaining structural integrity. This coordination is vital for performing daily tasks and engaging in sports.
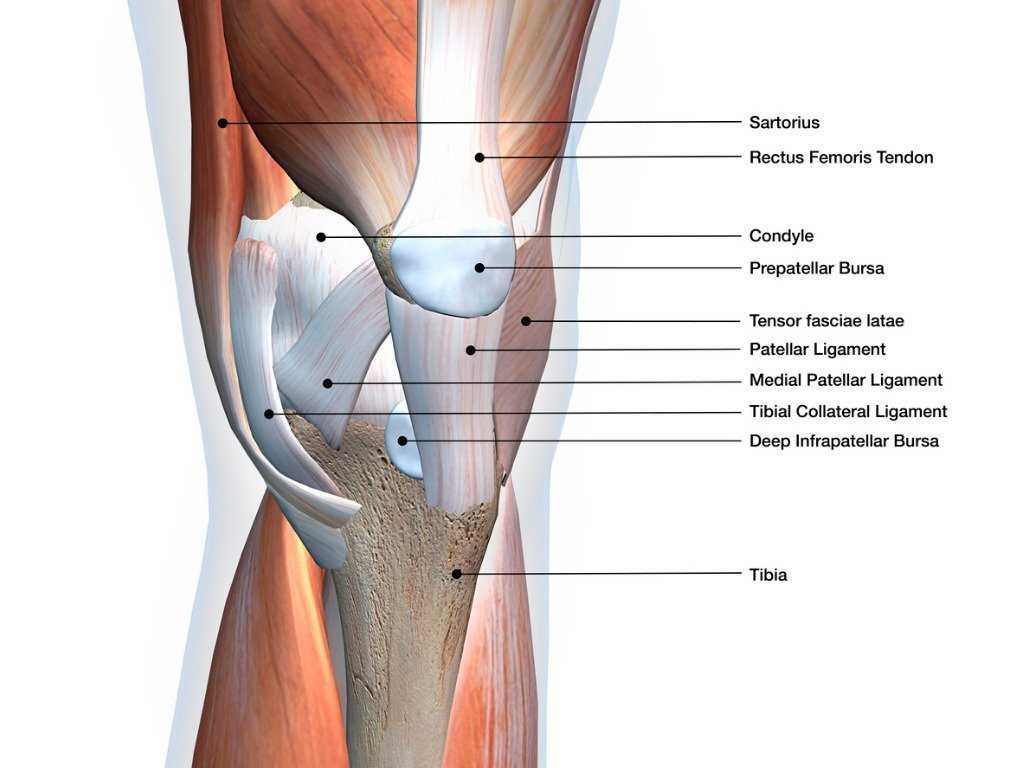
Muscles Surrounding the Knee
The area around the joint is supported by a complex network of muscles that play crucial roles in movement and stability. These muscles work together to facilitate various actions, such as bending, straightening, and rotation. Understanding these muscle groups is essential for grasping how they contribute to overall mobility and function.
Major Muscle Groups
- Quadriceps: This large muscle group located at the front of the thigh is responsible for extending the leg.
- Hamstrings: Situated at the back of the thigh, these muscles assist in flexing the leg and are vital for running and jumping.
- Gastrocnemius: This calf muscle crosses the joint and plays a role in bending the leg and stabilizing the lower limb.
- Sartorius: The longest muscle in the human body, it aids in flexion, abduction, and outward rotation.
Function and Importance
The coordination between these muscle groups is essential for efficient movement patterns. They not only allow for physical activities but also provide protection to the joint by absorbing impact and reducing stress on surrounding structures. Strengthening these muscles can enhance performance and prevent injuries.
Common Knee Injuries Explained
Understanding the frequent ailments that affect the joint in the leg is essential for prevention and recovery. Various factors can contribute to these injuries, ranging from physical activity to underlying health conditions. This section highlights some of the most prevalent issues faced by individuals, outlining their causes and symptoms.
One of the most widespread concerns is the strain or tear of ligaments, which often results from sudden movements or impact during sports. These injuries can lead to instability and discomfort, significantly affecting mobility.
Another common condition is cartilage damage, which can occur due to wear and tear over time or from traumatic events. This damage may lead to pain and swelling, hindering regular activities and physical exertion.
Additionally, tendinitis is a frequent issue, characterized by inflammation of the tendons around the joint. This condition is often seen in athletes who engage in repetitive motions, causing discomfort and reducing overall functionality.
Lastly, bursitis, an inflammation of the small sacs of fluid that cushion the joint, can cause pain and swelling. This ailment is typically the result of prolonged pressure or overuse, making it important to recognize and address early.
Diagnostic Methods for Knee Issues
Identifying complications in the joint area often necessitates a systematic approach utilizing various assessment techniques. Understanding these methodologies is crucial for accurate evaluation and treatment planning. Medical professionals employ several strategies to investigate discomfort, instability, or mobility restrictions.
Common Evaluation Techniques
Initial assessments typically include a comprehensive medical history review, physical examinations, and imaging studies. Each technique provides unique insights that aid in understanding the underlying conditions affecting joint functionality.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Medical History | Collecting information about symptoms, previous injuries, and overall health status. |
| Physical Examination | Assessing range of motion, strength, and pain response during movement. |
| X-rays | Using radiography to detect fractures, bone spurs, or joint space narrowing. |
| MRI | Employing magnetic resonance imaging to visualize soft tissue structures. |
Advanced Diagnostic Approaches
For persistent issues, specialists may recommend advanced techniques such as ultrasound or arthroscopy. These methods offer deeper insights into the condition of soft tissues and ligaments, facilitating precise diagnoses and tailored treatment strategies.
Rehabilitation Exercises for Knee Health
Maintaining optimal function of the joint is crucial for overall mobility and well-being. A well-structured exercise regimen can significantly enhance strength, flexibility, and stability. Incorporating specific movements can aid in recovery and prevent future complications, promoting a healthier lifestyle.
Strengthening Movements
Targeted strengthening exercises play a vital role in enhancing the support structures around the joint. Activities such as leg raises, squats, and step-ups can effectively build muscle endurance. Performing these exercises regularly can contribute to improved stability and functionality, allowing for better performance in daily activities.
Flexibility and Stretching Techniques
Incorporating stretching into the routine is essential for maintaining a healthy range of motion. Techniques such as hamstring stretches, quadriceps stretches, and calf stretches help alleviate tightness and improve overall flexibility. Regular practice can enhance mobility, reduce stiffness, and contribute to long-term joint health.
Importance of Knee Stability
Maintaining joint stability is crucial for overall mobility and performance. A well-functioning support system allows for efficient movement, reduces the risk of injuries, and enhances physical activities. Without proper stability, individuals may experience discomfort and diminished functionality in their daily routines.
Role in Injury Prevention
Strength and flexibility are key components that contribute to joint stability. When these attributes are well-balanced, they help prevent strains and tears, allowing individuals to engage in various activities with confidence. A stable joint can absorb shocks and resist excessive forces, minimizing the likelihood of traumatic injuries.
Impact on Physical Performance
Optimal joint support not only promotes safety but also enhances athletic performance. Athletes and active individuals benefit from improved coordination and balance, which are vital for executing movements effectively. When stability is prioritized, it allows for greater power output and endurance, leading to better outcomes in sports and physical endeavors.
Preventive Measures for Knee Injuries
Taking proactive steps can significantly reduce the risk of damage to the joint structures. Engaging in regular strength training and flexibility exercises helps support the surrounding musculature, enhancing stability and function. Additionally, incorporating proper warm-up and cool-down routines into physical activities promotes overall joint health.
Proper Footwear: Selecting appropriate shoes tailored for specific activities provides essential support and cushioning. Well-fitted footwear minimizes excessive stress on the joints, contributing to better alignment and balance during movement.
Technique and Training: Learning correct movement patterns and techniques during sports and exercises is crucial. Engaging a coach or trainer can ensure proper form, reducing the likelihood of injury during high-impact activities.
Rest and Recovery: Allowing adequate time for recovery is vital. Overuse can lead to fatigue and increase the risk of injury, so incorporating rest days into training regimens is essential for maintaining long-term health.