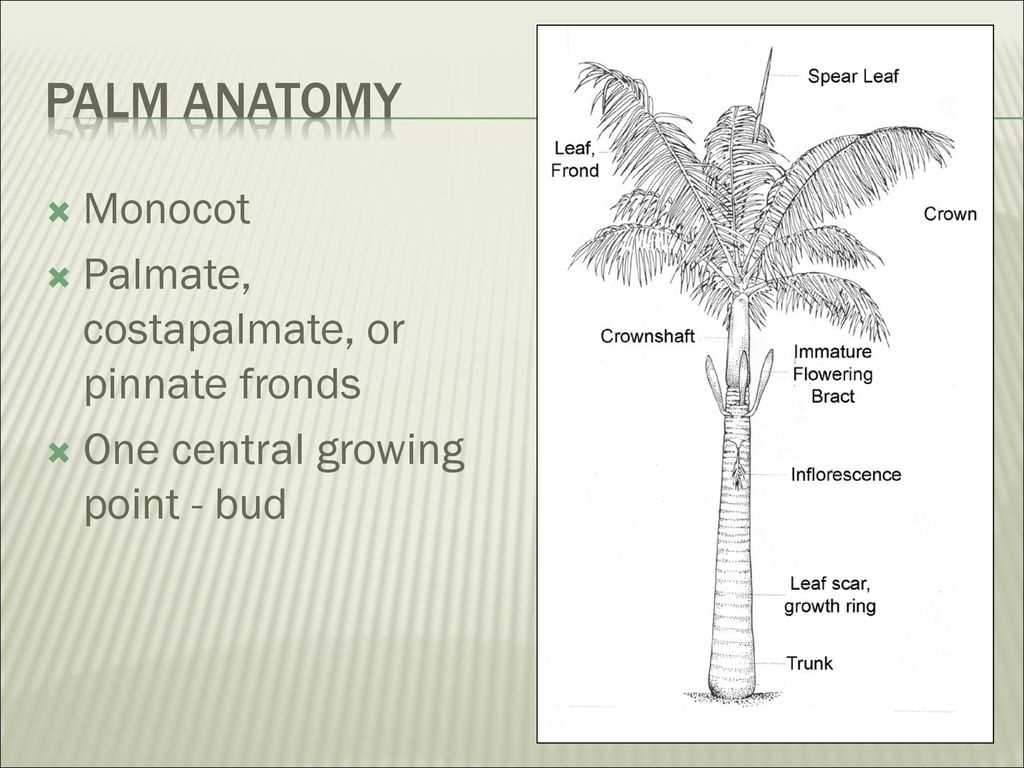
Understanding the Anatomy of a Palm Tree

Exploring the intricate composition of certain exotic vegetation reveals a fascinating array of components that contribute to their unique characteristics. These elements work in harmony, allowing the species to thrive in diverse environments while exhibiting remarkable resilience.
In this section, we will delve into the various segments that make up these lush organisms. By examining each feature, we can uncover the ultimate secrets behind their growth patterns and ecological significance.
Furthermore, understanding the roles of these components not only enhances our appreciation of their beauty but also highlights their importance within their ecosystems. Each segment plays a crucial role, and recognizing this interdependence deepens our connection to the natural world.
Palm Tree Structure Overview
This section provides a comprehensive look at the various elements that contribute to the overall design and functionality of these iconic plants. Understanding the distinct components helps appreciate their adaptability and significance in diverse ecosystems.
The primary component is the towering trunk, which serves as a vital support structure, allowing for impressive height and access to sunlight. Surrounding this central pillar are leafy fronds that emerge from the top, playing a crucial role in photosynthesis and providing shade. At the base, a network of roots anchors the organism, ensuring stability and nutrient absorption.
Each of these elements collaborates seamlessly, illustrating the ultimate adaptation of these species to their environment. By examining their anatomy, one can delve deeper into their ecological roles and the beauty they bring to landscapes.
Key Components of Palm Trees
Understanding the essential elements of these unique flora can enhance appreciation for their beauty and ecological significance. Each component plays a crucial role in their growth, survival, and overall function within their environment.
- Fronds: The large, fan-like leaves are vital for photosynthesis, capturing sunlight to produce energy.
- Stipe: This elongated stem provides structural support and elevates the fronds, allowing them to access more light.
- Root System: The network below the surface stabilizes the organism and absorbs water and nutrients from the soil.
- Flowers: These reproductive structures attract pollinators and are essential for the production of seeds.
- Fruits: The mature ovaries develop into seeds, facilitating reproduction and the continuation of the species.
Each of these components contributes to the overall health and sustainability of the organism, making it a remarkable example of adaptation in diverse environments.
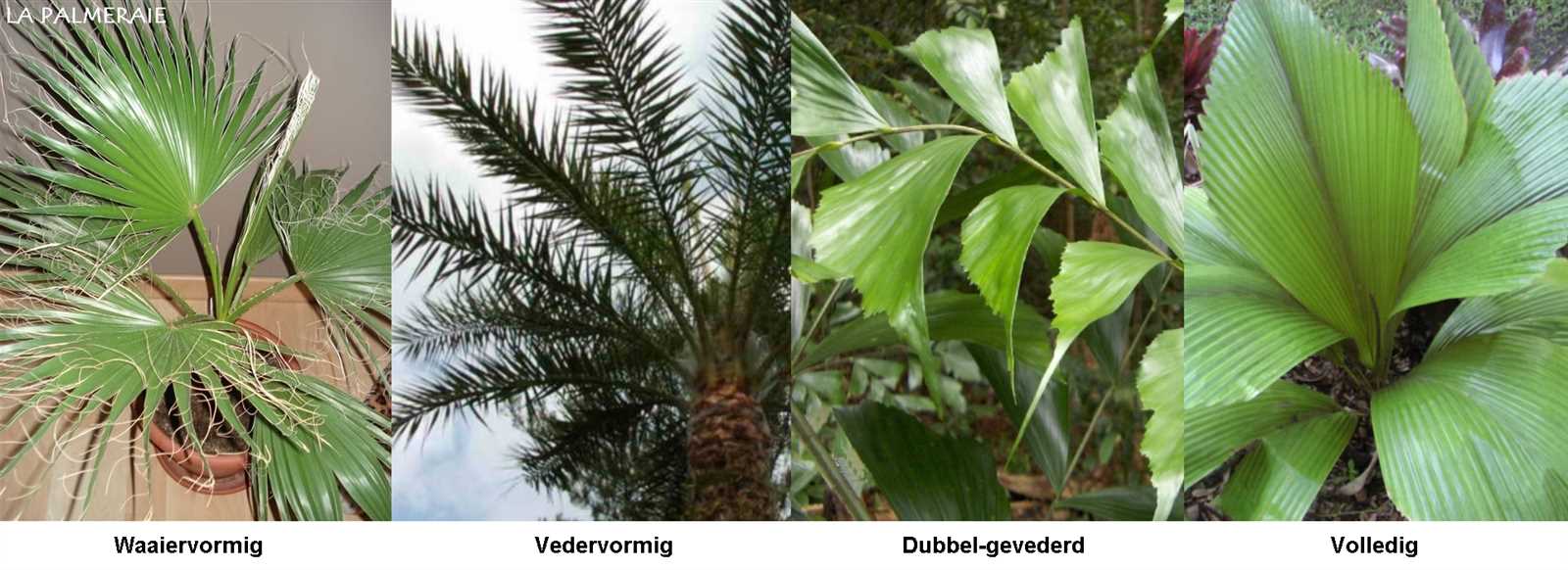
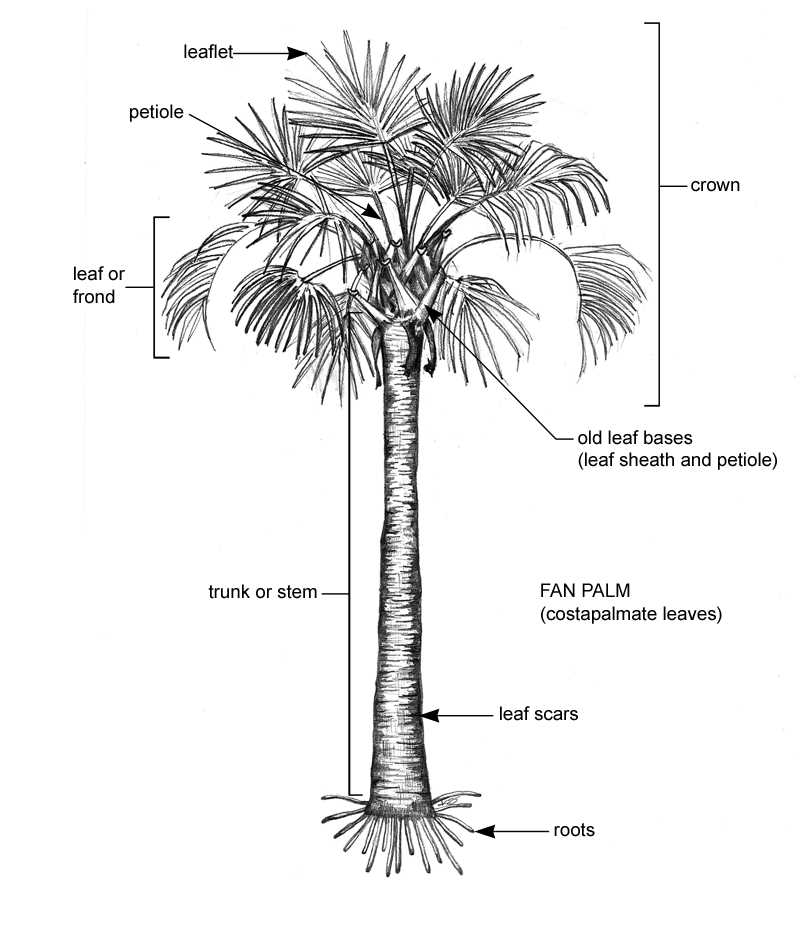
Leaf Types and Functions
Foliage structures play a crucial role in the overall functionality of plants, showcasing a variety of forms and purposes that contribute to their survival and growth. Understanding the different categories of these structures helps to appreciate their unique contributions to the ecosystem.
- Compound Leaves: These consist of multiple leaflets, enhancing surface area for photosynthesis.
- Serrated Leaves: Featuring jagged edges, they often aid in water drainage and pest deterrence.
- Heart-Shaped Leaves: Common in certain species, they can help in capturing sunlight efficiently.
- Fan-Shaped Leaves: These structures are effective in maximizing light exposure while minimizing water loss.
Each type exhibits distinct characteristics that serve essential functions such as photosynthesis, transpiration, and protection against environmental stressors.
Understanding the Trunk Anatomy

The central column of certain species plays a crucial role in their overall structure and health. This segment serves as the backbone, supporting the upper foliage while facilitating nutrient transport from the ground to the leaves. Exploring its composition reveals a fascinating interplay of layers and tissues, each contributing to the organism’s vitality.
Key Components
- Fibrous Layers: These provide strength and flexibility, enabling the structure to withstand environmental stresses.
- Vascular Tissues: Comprising xylem and phloem, these tissues are vital for the movement of water, nutrients, and sugars.
- Cortex: The outer layer that protects internal structures and plays a role in storage.
- Heartwood and Sapwood: The innermost sections, with heartwood offering stability while sapwood is active in nutrient transport.
Functions and Benefits
- Structural Support: The robust design allows for the growth of tall and expansive foliage.
- Nutrient Distribution: Efficient transport systems ensure that all parts receive essential sustenance.
- Water Retention: Specialized tissues help in maintaining moisture levels, crucial for survival in arid environments.
Understanding this anatomy enhances appreciation for the resilience and adaptability of these remarkable organisms in diverse ecosystems.
Root Systems of Palm Trees
The underground structure of these tropical species plays a vital role in their overall health and stability. Understanding how these systems function can provide insights into their growth patterns and adaptability to different environments.
Characteristics of the Root Structure
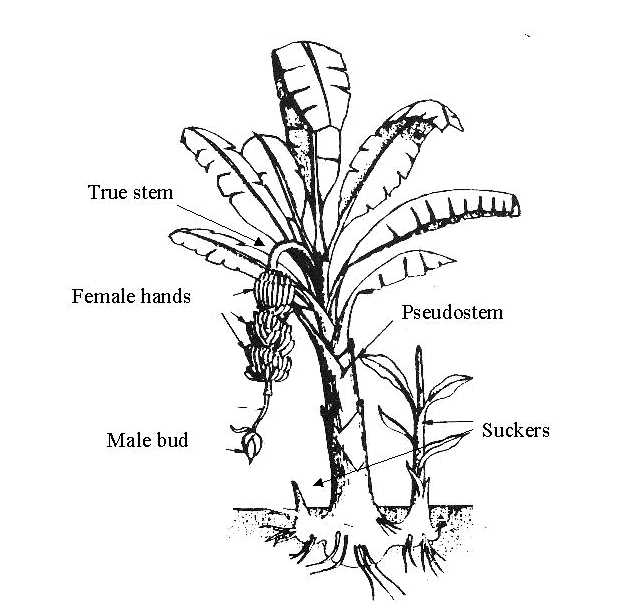
- Typically shallow and fibrous, allowing for rapid nutrient absorption.
- Extensive lateral growth, which helps in anchoring the plant securely.
- Capable of forming symbiotic relationships with soil organisms to enhance nutrient uptake.
Adaptations to Environmental Conditions
- In sandy soils, roots spread wide to maximize water and nutrient collection.
- In wetter regions, they may develop specialized structures to cope with excess moisture.
- In arid climates, they can reach deeper layers to access groundwater.
Overall, the root systems are crucial for survival, enabling these plants to thrive in a variety of ecological niches while providing stability and resilience against external stresses.
Flowering Parts of Palms

The reproductive features of these remarkable plants play a crucial role in their lifecycle and contribute to their overall beauty. Understanding these structures reveals their significance in the propagation and diversity of various species.
Structure of Flowers
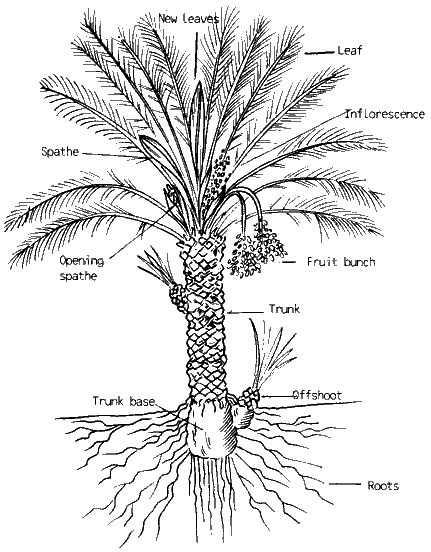
The floral composition consists of several essential elements, including bracts, sepals, petals, stamens, and carpels. Each component contributes uniquely to the plant’s reproductive success, attracting pollinators and facilitating fertilization.
Pollination Mechanisms
Many species rely on specific mechanisms for pollination, including wind and insect activity. This interplay between floral structures and pollinators enhances genetic variation and adaptation.
| Floral Structure | Function |
|---|---|
| Bracts | Protect developing flowers |
| Sepals | Support and shield the petals |
| Petals | Attract pollinators |
| Stamens | Produce pollen |
| Carpels | House ovules and facilitate fertilization |
Fruit Development and Characteristics
The process of maturation and unique features of certain tropical flora are fascinating topics that reveal the intricate relationships between biology and environment. Understanding these aspects allows for a deeper appreciation of their ecological roles and agricultural significance.
Initially, the reproductive structures undergo a series of transformations, leading to the formation of distinct edible items. These transformations are influenced by various factors, including climate, soil quality, and pollination methods. As the structures develop, they showcase a range of textures, colors, and flavors, each contributing to the overall diversity of the ecosystem.
Mature specimens exhibit a spectrum of shapes and sizes, often characterized by a tough outer layer that protects the nutrient-rich interior. The nutritional content varies significantly, with some being rich in vitamins and others providing essential fatty acids. This variability not only supports wildlife but also plays a crucial role in human diets across the globe.
Photosynthesis in Palm Leaves
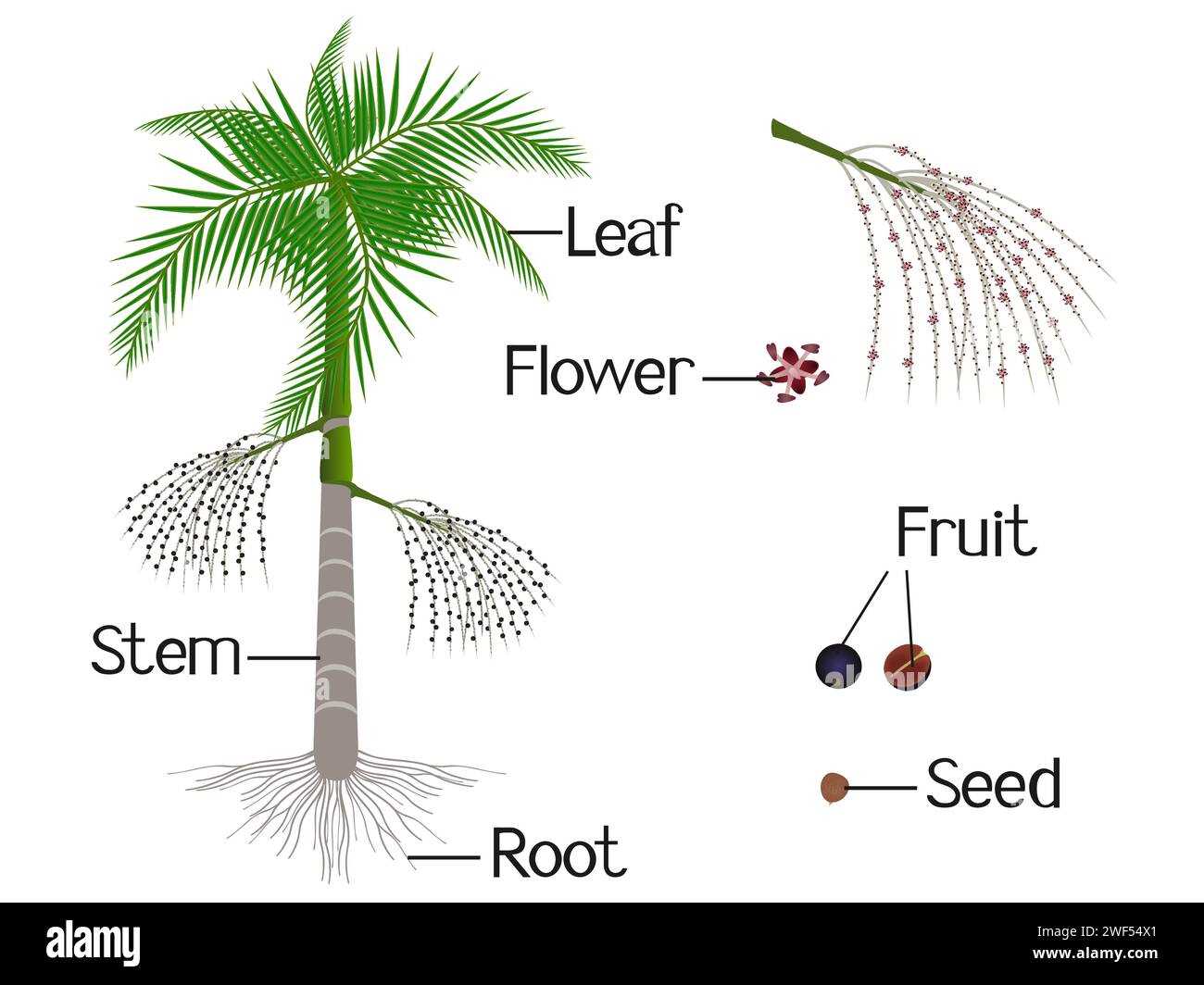
This section explores the intricate process of converting light energy into chemical energy within the green foliage of certain tropical species. Through a series of complex reactions, these plants harness sunlight to produce essential nutrients, playing a vital role in their growth and overall health.
Mechanism of Light Absorption
The green structures contain chlorophyll, which captures sunlight. This absorption initiates a sequence of reactions that ultimately transform carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen, showcasing nature’s efficiency.
Importance of Temperature and Water
Optimal conditions, including suitable temperatures and adequate moisture, significantly enhance the efficiency of this energy conversion. These elements ensure that the photosynthetic process remains robust, allowing for sustained growth.
| Factor | Impact on Photosynthesis |
|---|---|
| Light Intensity | Increased rates of energy absorption |
| Temperature | Affects reaction speed |
| Water Availability | Essential for chemical reactions |
Importance of Bark Layers
The outer covering of certain plants plays a crucial role in their overall health and survival. This protective layer not only shields the inner structures from external threats but also facilitates essential processes that sustain life. Understanding its significance can reveal insights into the adaptability and resilience of these organisms.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Protection | Acts as a barrier against pests and diseases. |
| Water Retention | Helps in retaining moisture within the organism. |
| Growth Support | Provides structural integrity during growth cycles. |
| Insulation | Regulates temperature and protects against extreme conditions. |
Variations Among Different Species
The diversity among various species within this family is remarkable, showcasing a wide range of characteristics that adapt to different environments. These differences can be seen in foliage shape, trunk structure, and reproductive features, each tailored to specific ecological niches.
Foliage Differences
Leaves vary significantly; some exhibit large, fan-like forms, while others present elongated, feather-like shapes. This diversity not only adds aesthetic value but also influences photosynthetic efficiency and water retention strategies.
Reproductive Features

Reproductive structures are equally varied, with some species producing clusters of fruits that are small and edible, while others bear larger, inedible seeds. This variation plays a crucial role in the survival and distribution of species across different habitats.
Common Diseases Affecting Palm Parts
Understanding the ailments that can impact various elements of these tropical giants is essential for maintaining their health and vitality. Numerous pathogens and environmental factors can lead to significant challenges, affecting not only the overall appearance but also the longevity of these cherished species.
Fungal Infections

One of the most prevalent issues stems from fungal infections, which can lead to decay and discoloration. Symptoms may include wilting fronds and lesions on the foliage. Botryosphaeria and Thielaviopsis are common culprits that thrive in humid conditions, often resulting in severe damage if not managed promptly.
Pest Infestations

Another significant threat comes from pest infestations. Insects such as scale and aphids can weaken the structure, causing stunted growth and yellowing of leaves. Regular monitoring and appropriate treatment are vital to prevent these nuisances from causing extensive harm.
Environmental Adaptations of Palm Trees
The ability of certain tropical and subtropical species to thrive in diverse environments showcases their remarkable adaptations. These organisms have evolved unique traits that enable them to survive and flourish under varying climatic conditions, soil types, and water availability.
Key Adaptations
- Leaf Structure: The wide, fan-like leaves assist in maximizing sunlight absorption while minimizing water loss.
- Root System: Deep and extensive roots allow for stability and efficient water uptake, essential in sandy or loose soils.
- Water Storage: Specialized tissues in the stem can store moisture during dry periods, providing a vital resource for survival.
Habitat Versatility
These organisms exhibit a remarkable capacity to occupy various habitats, from coastal regions to arid zones. Their adaptability is evident in the following ways:
- Salt Tolerance: Certain species can thrive in saline conditions, making them suitable for coastal environments.
- Heat Resistance: Many varieties withstand high temperatures, which is crucial for survival in sun-drenched areas.
- Wind Resistance: The flexible structure allows them to bend without breaking during storms, ensuring longevity in windy regions.
Ecological Role of Palm Trees
The significance of these towering plants extends beyond their aesthetic appeal. They play a crucial role in their ecosystems, contributing to the balance and health of their environments. From providing shelter to various species to influencing soil quality, their presence is vital for biodiversity.
Key ecological functions include:
- Habitat Creation: These organisms offer nesting sites and living spaces for numerous animals, including birds, insects, and mammals.
- Carbon Sequestration: They absorb carbon dioxide, helping to mitigate climate change effects and improve air quality.
- Soil Protection: Their extensive root systems prevent soil erosion, maintaining land stability and promoting nutrient retention.
- Water Regulation: They assist in maintaining the water cycle by aiding in groundwater recharge and reducing runoff.
Additionally, these flora contribute to human well-being by providing resources such as food, shelter materials, and medicinal products. Their versatility makes them invaluable in both natural and urban settings.
Overall, the ecological contributions of these majestic species are indispensable for maintaining healthy and sustainable environments.