Understanding the Anatomy of the Human Nose
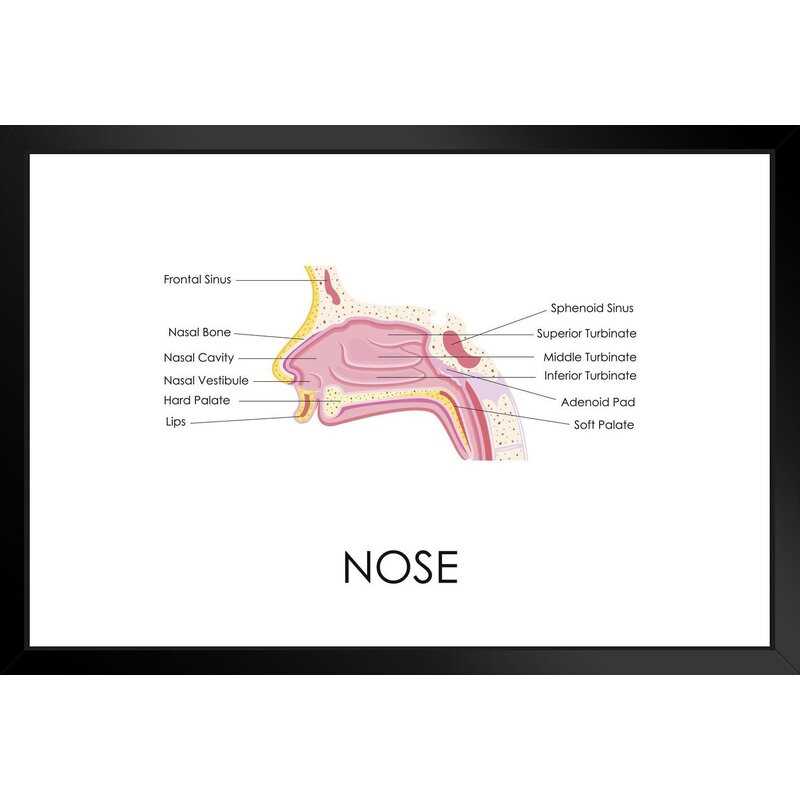
The structure we often take for granted plays a vital role in our daily experiences. It is intricately designed to fulfill essential functions, from aiding in respiration to enhancing our sense of smell. This section delves into the various components that contribute to its remarkable capabilities, offering insights into their unique roles and significance.
Each segment of this complex organ is essential for maintaining overall functionality. From the outermost features that provide protection to the inner areas responsible for sensory perception, every element collaborates seamlessly. By exploring these intricacies, we can gain a deeper appreciation for how this vital system operates.
As we embark on this exploration, we will uncover the relationships between each component, shedding light on how they interact to support not only our physical health but also our emotional well-being. Understanding this fascinating structure opens doors to a broader comprehension of our sensory experiences and their impact on our lives.
Understanding the Anatomy of the Nose
The structure of the olfactory organ plays a crucial role in various physiological processes, influencing our ability to breathe, taste, and interact with our environment. By exploring its intricate design, we can gain insights into how this essential feature contributes to overall health and sensory perception.
Key components of this structure include:
- External features: The visible section that defines facial aesthetics and facilitates airflow.
- Internal cavities: Complex passageways that filter, warm, and humidify inhaled air.
- Olfactory receptors: Specialized cells that detect and transmit scent information to the brain.
- Supporting structures: Cartilage and bone that provide stability and shape.
Understanding these elements helps in recognizing how they work together to perform vital functions. Each component has its own role, contributing to the overall efficacy of the respiratory system and the sensory experience.
To appreciate the complexity of this organ, one can consider the following aspects:
- Functionality: How each part contributes to breathing and olfaction.
- Health implications: The impact of disorders or injuries on overall function.
- Evolutionary perspective: The adaptations that have occurred over time for improved efficiency.
A comprehensive understanding of this anatomical marvel fosters greater awareness of its significance in daily life and health maintenance.
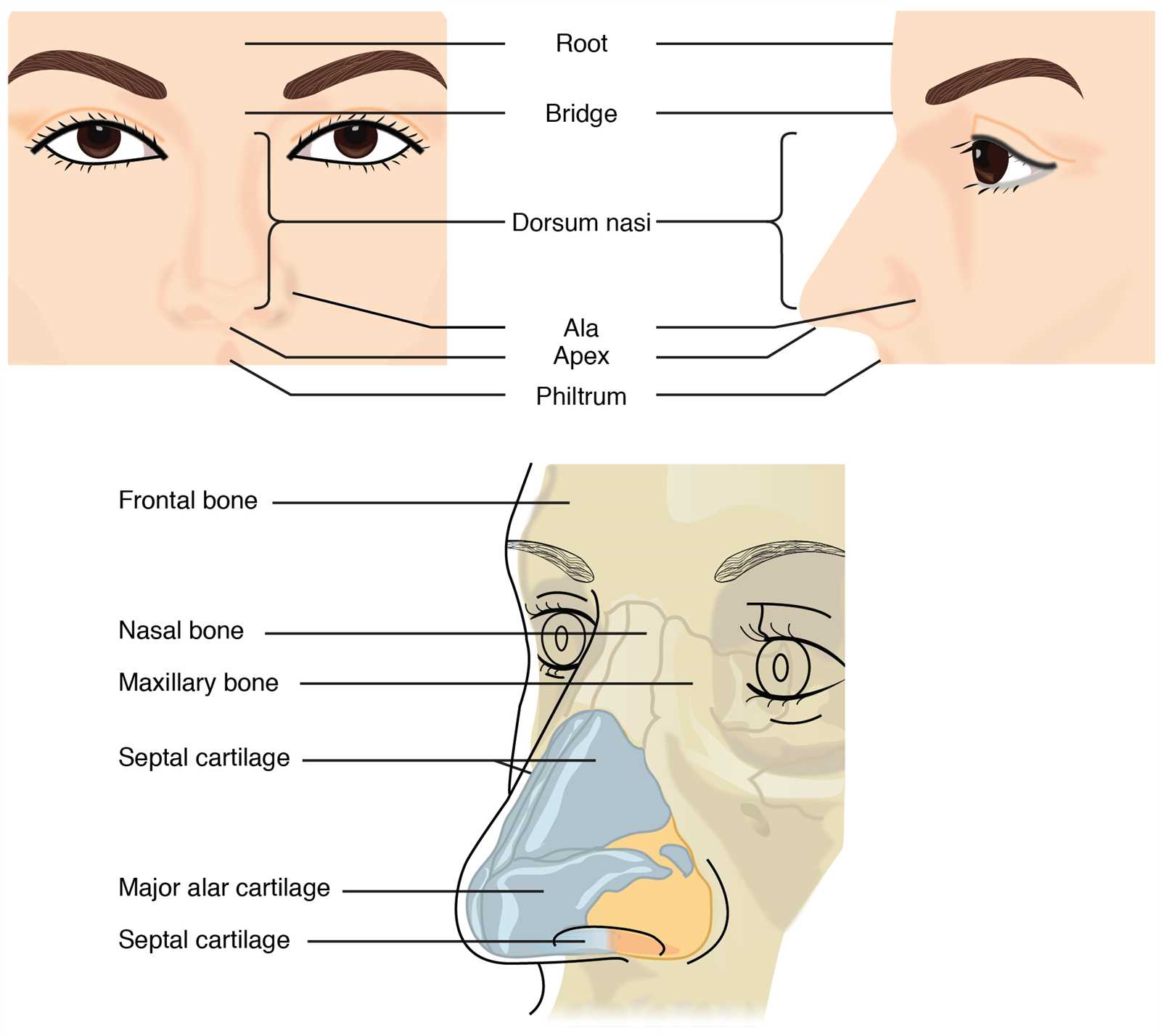
Main Components of the Nasal Structure

The intricate design of the nasal area plays a crucial role in various physiological functions. Understanding its essential elements helps in comprehending how this structure contributes to processes like respiration and olfaction.
External Features
At the forefront, the visible attributes create the entrance to the respiratory system. These elements not only define aesthetic appearance but also serve functional purposes, such as filtering and humidifying incoming air. The outer framework provides support while enhancing airflow efficiency.
Internal Cavities

Within lies a complex network of passages that further process inhaled air. This region is lined with specialized tissue that aids in trapping particles and pathogens, ensuring that only clean air reaches the lungs. Additionally, the presence of olfactory receptors here is vital for the sense of smell, connecting the respiratory system to sensory experiences.
The Role of Nasal Cartilage
Nasal cartilage plays a crucial part in the overall structure and function of the respiratory system. This flexible connective tissue provides support while allowing for the necessary mobility and shape retention that facilitates breathing and airflow. Its unique properties contribute to both aesthetic and functional aspects of the face.
Support and Flexibility
One of the primary functions of this connective tissue is to maintain the framework of the external structure. Its resilient nature allows for slight movements without compromising integrity, ensuring that the airway remains open. This balance of support and flexibility is vital for proper respiratory mechanics.
Contribution to Sensory Function
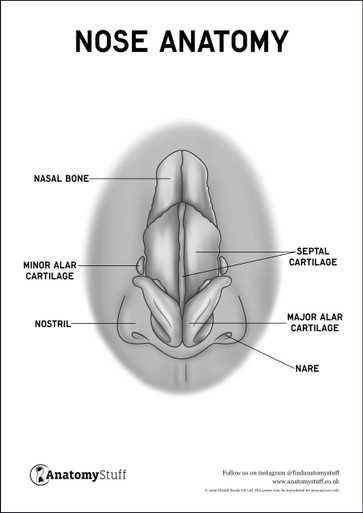
In addition to providing structural support, nasal cartilage is integral to the sensory capabilities of the olfactory system. The shape it helps form can influence airflow patterns, which are essential for the detection of odors. By shaping the external profile, it enhances the efficiency of the sensory receptors located within the nasal passages.
In summary, the role of this connective tissue extends beyond mere support; it is essential for maintaining functionality, sensory perception, and overall facial aesthetics.
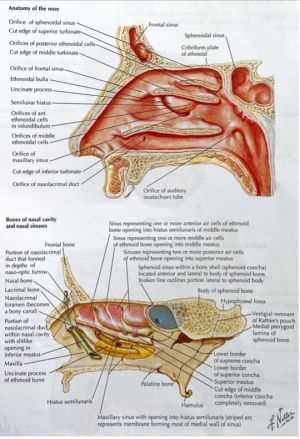
Sinuses and Their Functions
These air-filled cavities play a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being. Their unique structure not only contributes to respiratory processes but also influences various physiological functions. Understanding their significance can shed light on how they impact daily life.
Primarily, these cavities help to humidify and warm inhaled air, making the respiratory process more efficient. By adding moisture, they reduce irritation in the airways, which is essential for comfort and functionality. Additionally, they assist in filtering out dust and other particles, acting as a natural barrier against environmental pollutants.
Another key function involves sound resonance. The presence of these spaces enhances vocal quality, contributing to the richness of speech. Furthermore, they help alleviate the weight of the skull, making it easier for individuals to maintain head posture without excessive strain.
Finally, these cavities play a role in the immune system. By producing mucus, they trap pathogens and foreign substances, facilitating their removal from the body. This protective mechanism is vital for preventing infections and ensuring a healthier respiratory environment.
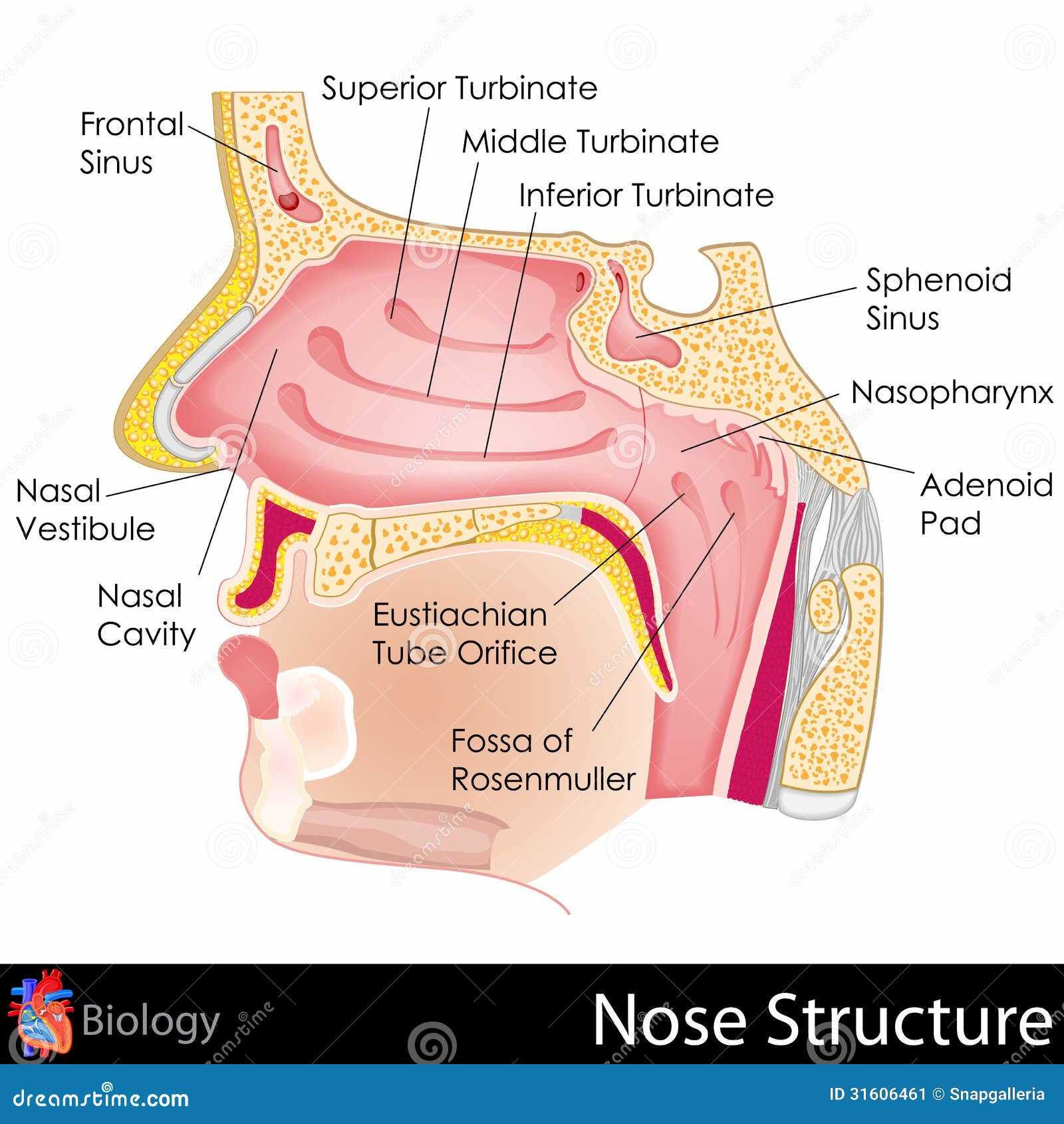
Nasal Cavity: An Overview
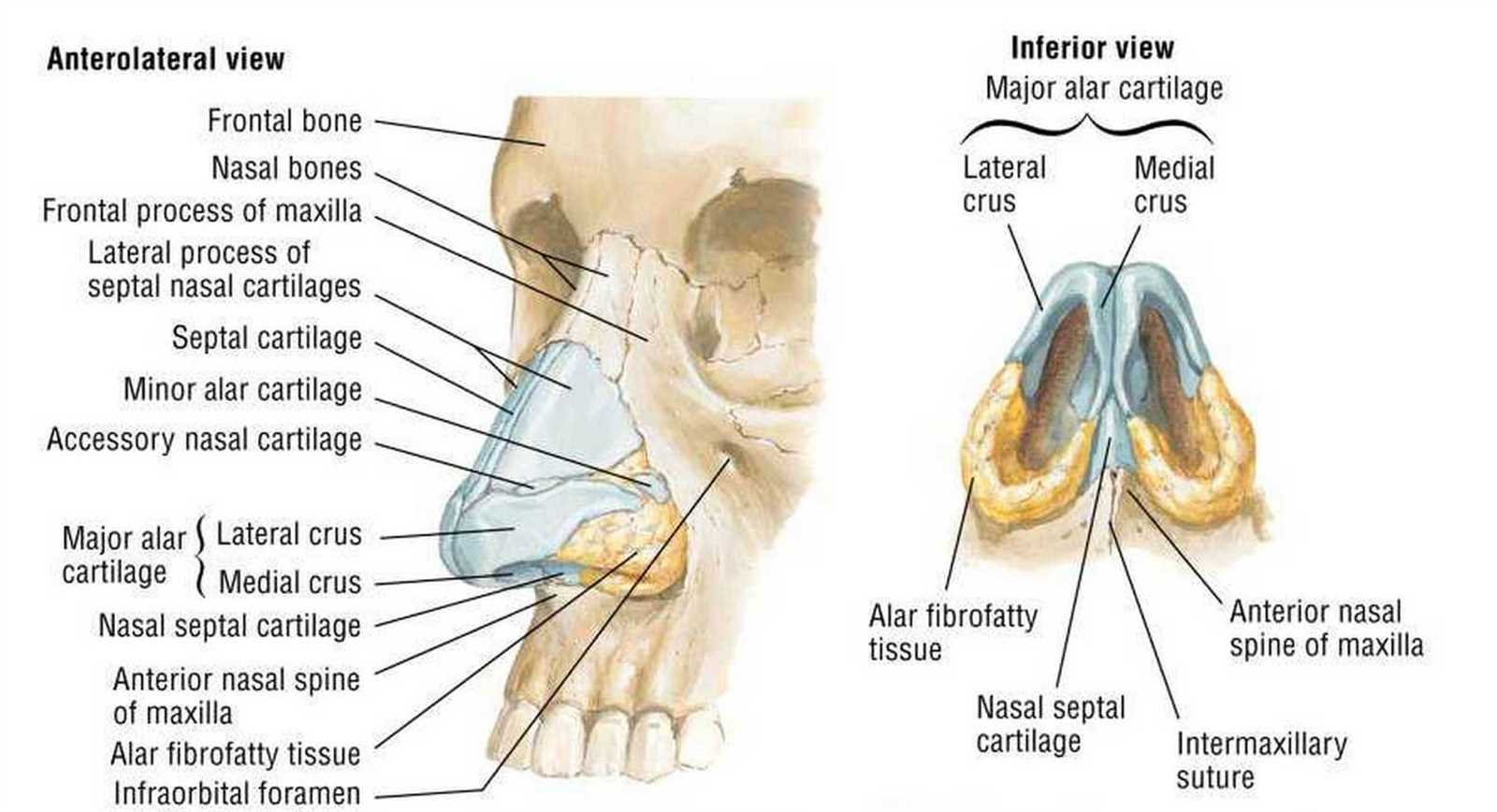
The nasal cavity serves as a crucial component of the respiratory system, playing a significant role in various essential functions. This space is not only responsible for air passage but also engages in filtering, humidifying, and warming the air before it reaches the lungs.
Structure and Function
The anatomy of this cavity is intricate, consisting of several key features that contribute to its overall functionality:
- Sinuses: Air-filled spaces that reduce the weight of the skull and enhance resonance during speech.
- Mucosa: Lining that traps particles and pathogens, keeping the respiratory tract clear.
- Olfactory region: Area responsible for the sense of smell, which is vital for taste and environmental awareness.
Importance in Health
Maintaining the health of this area is vital for overall well-being. Common issues that can arise include:
- Allergies, leading to inflammation and discomfort.
- Infections, such as sinusitis, which can cause pain and pressure.
- Structural abnormalities that may hinder airflow.
By understanding the significance of this region, individuals can better appreciate its role in respiratory health and overall functioning.
Importance of Nasal Mucosa
The mucosal lining of the nasal cavity plays a vital role in maintaining overall health and well-being. It serves multiple functions that are essential for respiratory efficiency, protection against pathogens, and the enhancement of olfactory capabilities. Understanding the significance of this tissue can shed light on various physiological processes and their implications for human health.
Functions of the Mucosal Lining
This specialized tissue performs several crucial tasks:
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Moisturization | Helps maintain humidity in the air we breathe, preventing dryness in the respiratory tract. |
| Filtration | Catches dust, allergens, and other particles, reducing the risk of infection. |
| Immune Defense | Contains immune cells that respond to pathogens, offering a first line of defense. |
| Olfaction | Facilitates the detection of scents by housing olfactory receptors, enhancing the sense of smell. |
Impact on Overall Health
The integrity of the mucosal barrier is crucial for preventing respiratory conditions and infections. Damage to this lining can lead to increased susceptibility to diseases, highlighting the need for its protection and maintenance. Understanding its role can guide better healthcare practices and promote respiratory wellness.
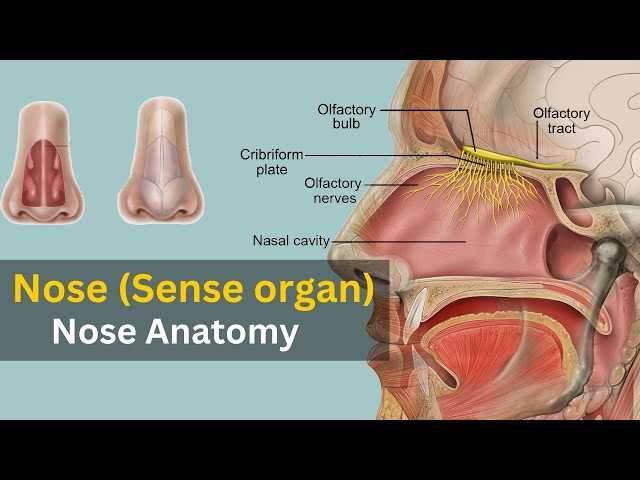
Function of Olfactory Receptors
Olfactory receptors play a crucial role in the sensory experience, enabling individuals to detect and differentiate various scents in their environment. These specialized proteins are embedded in the sensory epithelium, where they interact with airborne molecules, initiating a cascade of neural signals that contribute to the perception of smell.
Mechanism of Action
The process begins when odorant molecules bind to specific receptors, triggering a series of biochemical events:
- Odorant binding: Molecules attach to receptors on the surface of sensory cells.
- Signal transduction: This binding activates G-proteins, leading to the generation of secondary messengers.
- Neural response: The resulting changes in ion concentrations produce an electrical signal that travels to the brain.
Importance in Daily Life
The functionality of olfactory receptors is essential for various aspects of life:
- Identification of food: Scents guide choices and enhance flavors.
- Detection of hazards: Smells can indicate danger, such as smoke or spoiled food.
- Social interactions: Scent influences emotional connections and memories.
Overall, these receptors are vital for navigating the world through the sense of smell, enriching experiences and ensuring safety. Their intricate operation highlights the complexity of sensory perception and its impact on daily activities.
How the Nose Filters Air
The respiratory system plays a crucial role in maintaining health by purifying the air we breathe. A well-designed mechanism ensures that incoming air is cleansed of harmful particles, allowing only the cleanest air to reach the lungs.
This filtering process involves several key features:
- Mucous Membranes: These sticky surfaces trap dust, pollen, and other impurities.
- Cilia: Tiny hair-like structures move in unison to push trapped particles towards the throat for swallowing or expulsion.
- Humidity Regulation: The air is moistened to prevent dryness in the respiratory tract.
- Temperature Control: Incoming air is warmed to match body temperature, ensuring comfort and efficiency.
This intricate system not only protects vital organs but also enhances the overall quality of the air we inhale. By filtering out contaminants, it contributes significantly to respiratory health and well-being.
Connecting the Nose and Throat
The intricate relationship between the respiratory system and the vocal tract plays a vital role in our daily functions, encompassing everything from breathing to speaking. This connection serves not only for the passage of air but also for the exchange of sensory information, contributing significantly to our overall well-being.
Physiological Significance

The interplay between these two regions facilitates various critical processes. It allows for the humidification and filtration of incoming air, protecting the lower respiratory pathways while enhancing our ability to perceive different scents. Additionally, this connection aids in producing sounds, making communication possible.
Anatomical Overview
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Nasopharynx | The upper part of the throat located behind the nasal cavity, playing a key role in airflow. |
| Eustachian Tube | A canal that links the middle ear to the nasopharynx, equalizing pressure and draining fluids. |
| Soft Palate | The back portion of the roof of the mouth, essential for proper speech and swallowing. |
| Tonsils | Lymphoid tissues that provide immune function, situated in the throat region. |
Blood Supply to the Nasal Region
The vascular network serving the area of the olfactory system is essential for maintaining its health and functionality. This intricate supply ensures that various tissues receive the necessary nutrients and oxygen, while also facilitating the removal of waste products. The effective distribution of blood not only supports physiological processes but also plays a crucial role in the overall immunity of the region.
| Vessel | Origin | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Sphenopalatine artery | Maxillary artery | Supplies the posterior part of the nasal cavity |
| Anterior ethmoidal artery | Ophthalmic artery | Supplies the anterior part of the nasal cavity |
| Posterior ethmoidal artery | Ophthalmic artery | Supplies the superior nasal concha |
| Nasal branches of the facial artery | Facial artery | Supplies the external aspects and anterior part of the nasal passage |
This vascular architecture highlights the complexity and significance of blood flow in this critical area. By ensuring an adequate supply, these vessels contribute to the overall well-being and function of the olfactory system, allowing for the effective processing of sensory information.
Common Nasal Disorders Explained
Nasal issues can affect individuals of all ages, often leading to discomfort and a variety of symptoms. Understanding these conditions is essential for effective management and treatment. This section provides insights into frequently encountered disorders that can impact the upper respiratory system.
| Disorder | Symptoms | Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Allergic Rhinitis | Sneezing, itching, runny or stuffy passages | Avoid allergens, antihistamines, nasal sprays |
| Sinusitis | Facial pain, pressure, nasal congestion, thick discharge | Decongestants, nasal corticosteroids, antibiotics if bacterial |
| Deviated Septum | Difficulty breathing, frequent sinus infections, nosebleeds | Medications for symptoms, surgery in severe cases |
| Nasal Polyps | Blocked airways, loss of smell, chronic congestion | Nasal corticosteroids, surgery for large polyps |
| Chronic Rhinosinusitis | Persistent nasal congestion, facial pain, reduced sense of smell | Long-term medications, saline rinses, surgery if needed |
Recognizing the signs of these common conditions allows for prompt intervention, ultimately leading to improved quality of life and overall well-being. Consultation with healthcare professionals is advised for accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plans.
Visualizing the Nose Through Diagrams
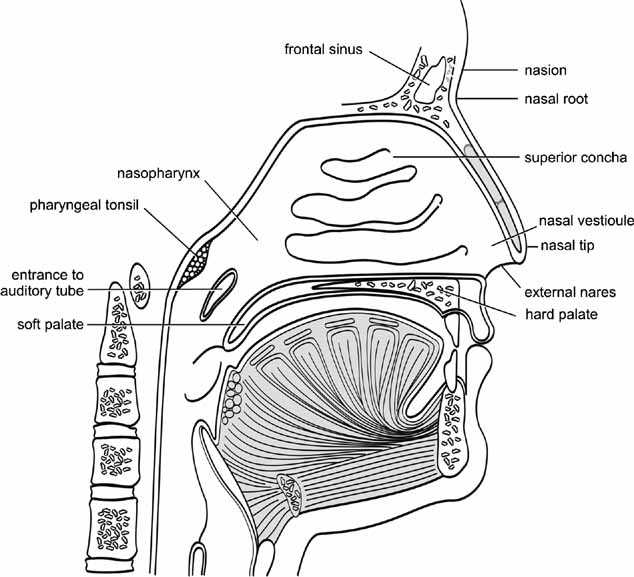
Understanding the structure of the facial feature requires more than mere observation; it benefits from a detailed visual representation. By utilizing illustrations, we can gain insights into the complexity and functionality of this prominent facial attribute. Visual aids serve to clarify relationships and enhance comprehension of intricate systems.
Diagrams can be particularly effective in highlighting key elements, including:
- External contours and symmetry
- Internal anatomy and airflow pathways
- Supporting structures and their roles
- Associated tissues and their functions
Employing such visuals enables learners to:
- Identify critical components more easily
- Understand the interconnections between various elements
- Visualize how changes may impact overall functionality
By incorporating these illustrative methods, we can foster a deeper appreciation for the intricate design and purpose of this essential feature.