Understanding Key Railroad Track Parts with Diagram

In the intricate world of railway systems, various elements work harmoniously to ensure safe and efficient transportation. This segment delves into the essential components that form the backbone of this network, illustrating how each piece contributes to the overall functionality. Grasping these vital elements is crucial for both enthusiasts and professionals alike, as they play a significant role in daily operations.
From the robust support structures to the intricate connections, every component is designed with precision to withstand the rigors of daily use. Understanding their arrangement and interaction offers valuable insights into the engineering marvels that facilitate seamless journeys. This exploration not only highlights their importance but also emphasizes the innovative designs that enhance durability and performance.
As we navigate through this discussion, we will examine the various elements in detail, uncovering their individual functions and how they collectively contribute to the safe movement of trains. The knowledge gained here will deepen your appreciation for the engineering expertise that underpins railway operations, showcasing the commitment to safety and reliability in this critical industry.
Understanding Railroad Track Components
In transportation infrastructure, the arrangement of metal beams and support structures plays a critical role in ensuring stability, safety, and smooth operation. This interconnected system is designed to distribute weight efficiently, absorb vibrations, and guide vehicles along designated routes with precision.
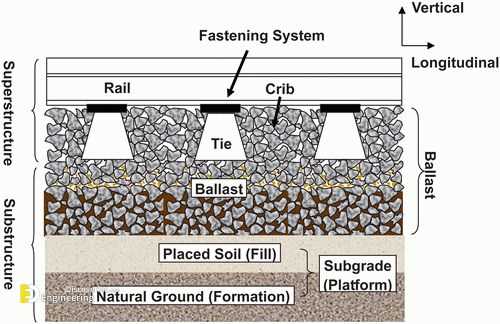
Metal Rails are the main guiding elements, responsible for supporting the load of passing vehicles. They must be durable enough to withstand repeated stress and wear over time. These elements are typically secured to supportive platforms through specially designed fasteners.
Supportive platforms, often made from wooden or concrete materials, provide a stable base for
Types of Railroad Track Sections
There are several variations in how transportation paths are designed, each serving specific purposes and environments. These sections differ based on their construction, support systems, and materials used. Understanding the distinctions between these layouts is crucial for ensuring both durability and efficiency in transport systems.
Ballasted Sections are commonly used in various terrains due to their flexibility in load distribution. The foundation consists of a bed of crushed stone that helps in stabilizing the structure and reducing vibration.
Slab Sections utilize concrete surfaces for more rigid and long-lasting support. These designs are typically used in urban areas where space is limited, and maintenance needs to be minimized.
Elevated Sections are constructed on bridges or
Function of Rails in Track Systems
The rails play a critical role in guiding and supporting the movement of vehicles along designated pathways. Their primary function is to provide a smooth and consistent surface that ensures stability and efficient motion. Properly aligned and maintained, they form the backbone of any transport system, allowing for seamless operation and safety.
Structural Integrity and Load Distribution
The rails are designed to withstand significant pressure, distributing the weight of passing vehicles evenly across the supporting infrastructure. This helps prevent wear and tear on individual components and reduces the need for frequent maintenance.
Guidance and Direction
Another key function is to maintain the correct path for vehicles
Importance of Ties in Railroads
Ties play a crucial role in supporting and stabilizing the system of steel rails. They are responsible for maintaining the proper spacing and alignment of the components, ensuring smooth and efficient operation. Without these foundational elements, the entire infrastructure would be susceptible to damage and misalignment, leading to operational challenges.
Structural Integrity and Load Distribution
The primary function of ties is to distribute the weight of passing vehicles across a wide area, preventing excessive stress on any single point. This helps in preserving the longevity of the entire network and ensuring the safety of both cargo and passengers. Their material and design significantly impact how well they perform in absorbing loads and reducing vibrations.

Fasteners play a critical role in securing steel beams and other foundational elements of transportation infrastructure. They ensure stability, durability, and proper alignment, making them indispensable in maintaining the structural integrity of various systems. Understanding these components and their functions is essential for maintaining safe and efficient transit pathways.
Types of Fasteners
There are several key types of fasteners, each designed for specific purposes. Spikes and bolts are among the most common, providing robust attachment points for structural elements. Plates and clips add additional support, ensuring alignment and reducing movement that could lead to wear and tear over time.
Materials and Durability
Switches and Their Role in Railways
Switches are essential components in the operation of rail systems, enabling trains to change paths and move between different routes. By guiding vehicles along various lines, switches enhance the flexibility and efficiency of the entire network. Their precise construction and maintenance are crucial to ensure smooth transitions and safety.
How Switches Operate
The mechanism behind a switch involves moving a section of the running surface, directing the vehicles to continue along one of the possible routes. Controlled either manually or electronically, switches adjust the alignment of the steel surfaces to facilitate seamless transitions. These mechanisms are carefully timed to avoid conflicts and maintain the flow of transportation.
The Importance of Switch Maintenance
Proper upkeep of these devices is essential to the reliability of the system. Over time, wear and external factors such as weather
Ballast: Foundation of Track Stability
The ballast serves as a critical foundation for maintaining the integrity of the entire system. It supports the upper structure, ensuring durability and resistance to shifting forces. Its ability to absorb pressure and redistribute loads plays a key role in enhancing performance and longevity.
Composition and Structure: Typically composed of crushed stone or gravel, the ballast provides an ideal balance between strength and flexibility. Its angular fragments interlock, creating a firm base that also allows for drainage, preventing water accumulation which could weaken the underlying foundation.
Functions: Apart from offering mechanical support, the ballast layer prevents vegetation growth, which could disrupt stability. Its design also helps mitigate vibrations caused by heavy loads, contributing to a
Significance of Rail Joints
The role of joints in a rail system is vital for maintaining continuous and efficient operation. These connecting points enable the smooth movement of vehicles over long distances, ensuring stability and alignment. Joints also allow for thermal expansion and contraction, reducing the likelihood of structural damage.
Types of Rail Joints
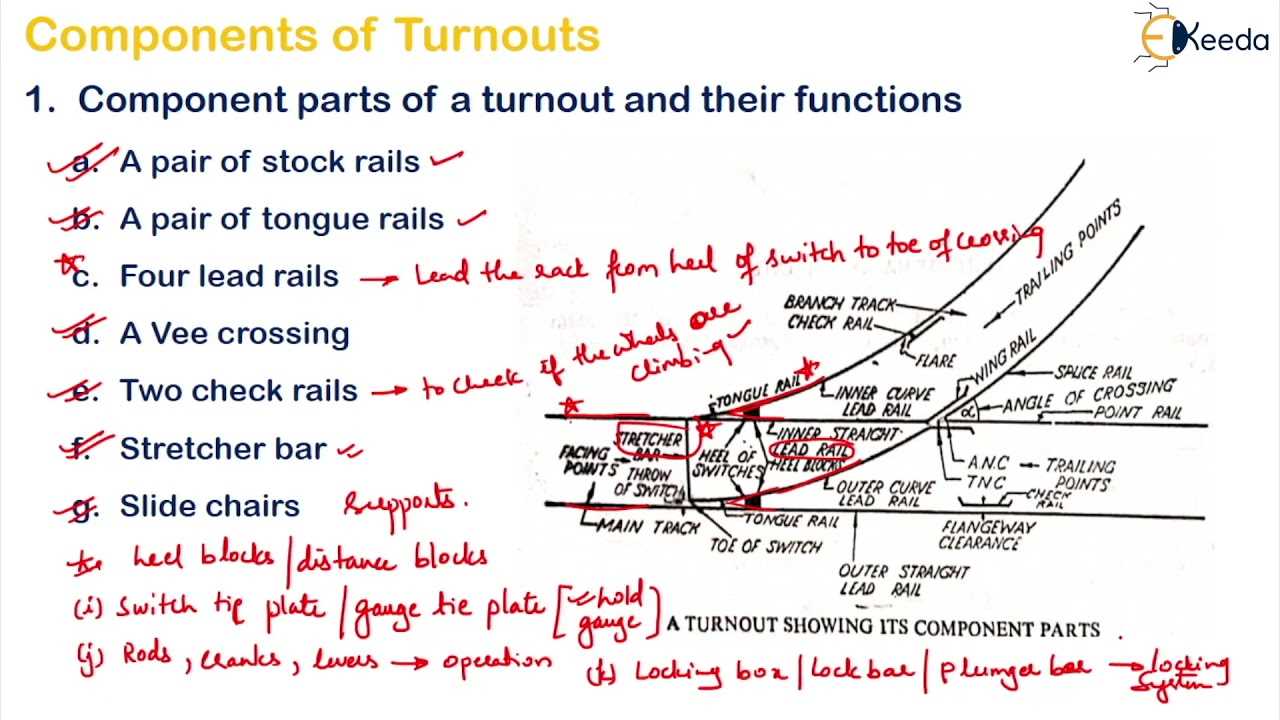
There are several types of joints used depending on the needs of the infrastructure. Each type is designed to handle specific mechanical stresses and environmental conditions, ensuring durability and performance.
| Joint Type | Characteristics |
|---|---|