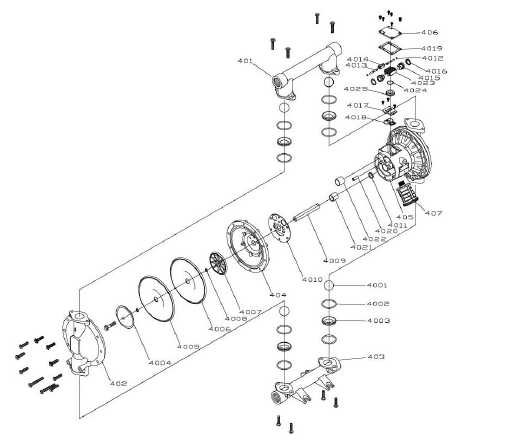
Aro Pump Parts Diagram Explained
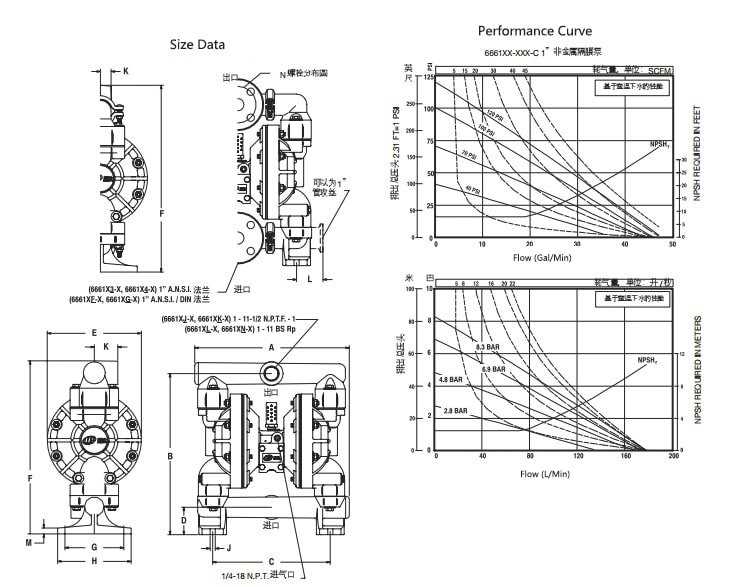
In the realm of fluid handling mechanisms, a comprehensive grasp of the individual elements that contribute to operational efficiency is crucial. Each component plays a specific role, working in harmony to facilitate the seamless movement of liquids and gases. A clear visual representation can greatly enhance one’s ability to comprehend the intricate interactions between these parts.
By examining a detailed schematic, one can identify not only the structure but also the function of each section. This understanding empowers users to maintain, troubleshoot, and optimize their systems effectively. A well-organized illustration serves as a valuable reference, simplifying the complex relationships within the assembly.
Moreover, a focused study of these components encourages informed decision-making regarding repairs and upgrades. Whether you are an industry professional or a DIY enthusiast, familiarizing yourself with the various elements involved can significantly improve your overall experience and outcomes in fluid management tasks.
Aro Pump Components Overview
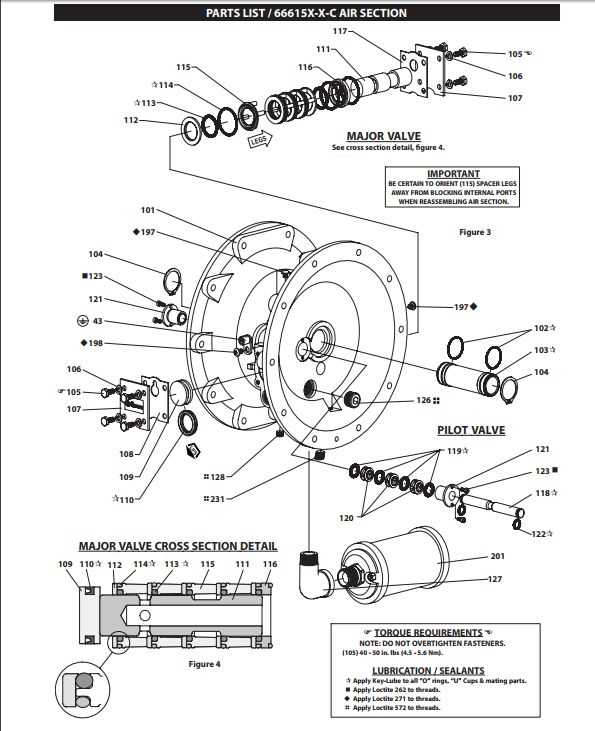
This section provides a comprehensive look at the essential elements that make up these industrial devices. Understanding each component’s role is crucial for effective operation and maintenance, ensuring longevity and reliability in various applications.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Housing | Serves as the protective outer shell, enclosing internal mechanisms and providing structural integrity. |
| Diaphragm | Facilitates the movement of fluids through expansion and contraction, critical for the device’s functionality. |
| Check Valve | Prevents backflow, ensuring that the flow direction remains consistent and efficient. |
| Drive Mechanism | Converts energy into motion, enabling the operational process that moves the medium. |
| Seals | Prevent leaks and protect internal components from contaminants, maintaining operational efficiency. |
Familiarity with these elements aids in troubleshooting and optimizing performance, making it easier to address any issues that may arise during usage.
Understanding Aro Pump Functionality
Comprehending the operation of fluid transfer devices is crucial for effective maintenance and optimal performance. These mechanisms are designed to move liquids efficiently, relying on various components that work in harmony. A clear understanding of how each element contributes to the overall functionality can enhance both troubleshooting and efficiency.
The basic operation of these systems involves a cycle of suction and discharge, facilitated by the movement of specific elements. When one section is activated, it creates a pressure differential that allows for the intake of liquid, which is then expelled through another pathway. This cyclical process is key to ensuring continuous flow and reliability.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Diaphragm | Creates a seal and facilitates movement for fluid intake and discharge. |
| Valves | Control the direction of flow and prevent backflow. |
| Air Supply | Provides the necessary energy to drive the movement of the diaphragm. |
| Fluid Chamber | Holds the liquid during the suction and discharge phases. |
By recognizing the specific roles of these components, operators can better understand the entire system’s dynamics. This knowledge is essential for troubleshooting issues and ensuring longevity and efficiency in liquid transfer operations.
Key Parts of Aro Pumps
Understanding the essential components of fluid transfer equipment is crucial for effective operation and maintenance. Each element plays a significant role in ensuring optimal performance and reliability. Below are the primary components commonly found in such machinery.
- Displacement Chamber: This is the area where the fluid is collected and moved, crucial for the system’s efficiency.
- Drive Mechanism: Often responsible for initiating the movement, this component ensures smooth operation.
- Seals: Vital for preventing leaks, these elements protect the integrity of the system.
- Valves: Essential for controlling the flow, these devices help direct the movement of fluids as needed.
- Connectors: These components facilitate the attachment of hoses and other fittings, ensuring a secure link to external systems.
- Frame: The structure that supports and houses all other components, providing stability and durability.
By familiarizing yourself with these key elements, you can better appreciate their function and importance in the overall operation of fluid handling systems.
Importance of Diagrams in Maintenance
Visual representations play a crucial role in the upkeep and servicing of machinery. They provide a clear overview of components and their interrelations, facilitating a more effective approach to repairs and inspections. Understanding these illustrations can significantly reduce downtime and enhance the efficiency of maintenance tasks.
Enhanced Understanding
Having access to detailed visuals allows technicians to quickly grasp the layout and function of various elements. This leads to more informed decision-making and a streamlined repair process, minimizing errors that could arise from misinterpretation.
Facilitating Training
Diagrams serve as excellent educational tools for new staff. They help convey complex information in a simplified manner, making it easier for trainees to understand how systems operate. This foundational knowledge is essential for maintaining optimal performance.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Clarity | Offers a visual guide to intricate systems. |
| Efficiency | Reduces time spent troubleshooting by providing quick references. |
| Safety | Helps identify potential hazards in the system layout. |
| Standardization | Ensures consistent practices among maintenance personnel. |
Common Aro Pump Issues
In the realm of fluid transfer equipment, various complications may arise, impacting efficiency and functionality. Understanding these frequent challenges is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and prolonging service life. Below, we explore some prevalent concerns encountered by users.
Frequent Problems
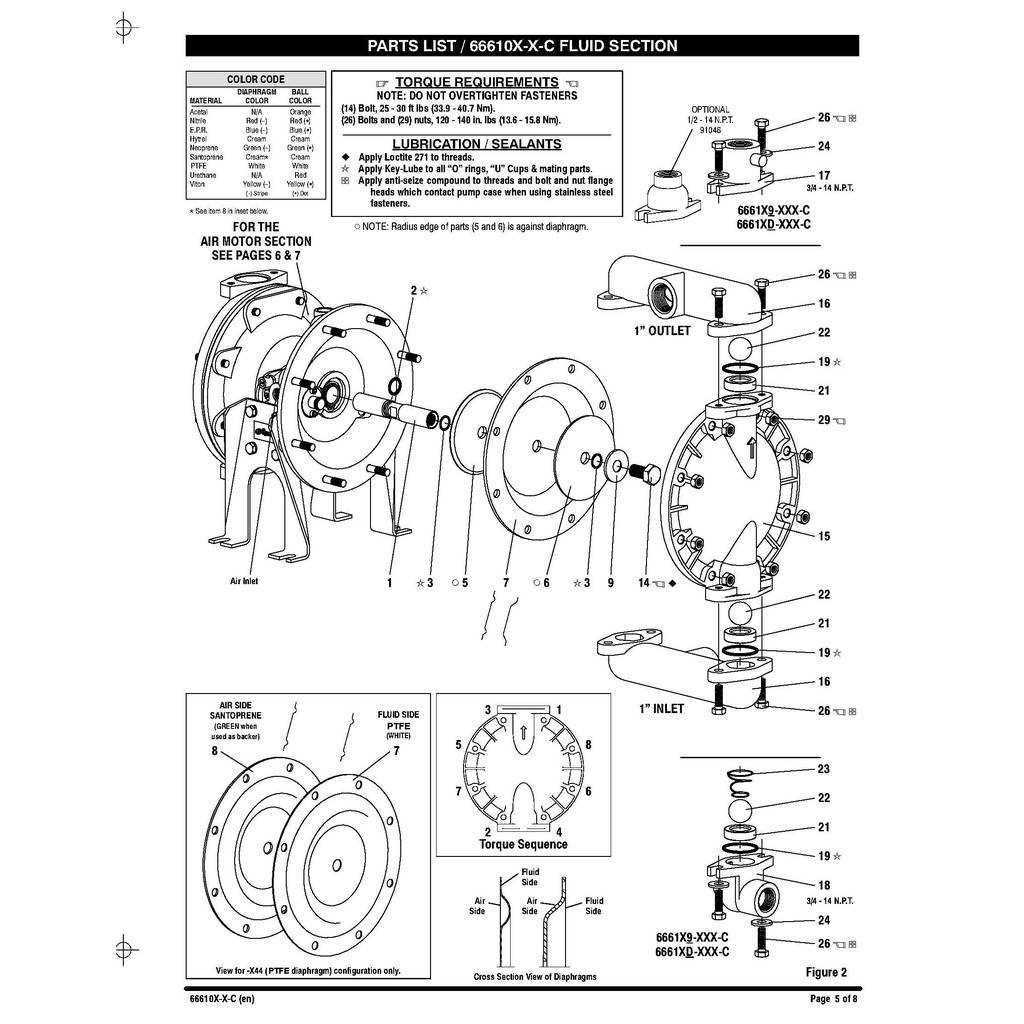
| Issue | Description | Possible Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Leakage | Unwanted fluid escape from seals or fittings. | Check seals for wear; tighten fittings or replace components. |
| Noisy Operation | Excessive noise during functioning. | Inspect for loose parts; lubricate moving components. |
| Reduced Flow Rate | Lower than expected fluid movement. | Clear any blockages; check for damaged hoses or valves. |
| Overheating | Excessive temperature during operation. | Ensure proper cooling; reduce load or inspect for friction. |
Maintenance Tips

Regular inspection and maintenance can prevent many of the issues listed above. Implementing a routine checkup schedule will help identify wear and tear early, enabling timely repairs and minimizing downtime.
Repairing Aro Pump Components
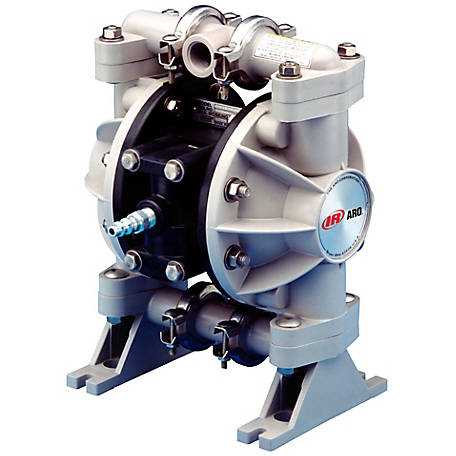

Understanding the intricacies of mechanical systems is essential for effective maintenance and restoration. Addressing issues within these units requires a methodical approach to ensure longevity and optimal performance. This section will explore key strategies for diagnosing and resolving common complications encountered in such systems.
Identifying Common Issues
When dealing with mechanical failures, the first step is to recognize the symptoms that indicate a malfunction. Typical problems may include irregular vibrations, unusual noises, or decreased efficiency. Conducting a thorough examination of the assembly can reveal wear and tear or misalignments that may be affecting functionality. Regular inspections can help detect these issues early, allowing for timely interventions.
Effective Repair Techniques
Once issues are identified, appropriate repair methods can be implemented. For minor damages, replacing seals and gaskets can restore functionality without extensive disassembly. In cases of significant wear, components may need to be completely replaced. Utilizing high-quality replacement elements is crucial for maintaining performance standards. Additionally, following manufacturer guidelines for reassembly is vital to ensure that all parts function harmoniously.
Regular maintenance routines, including cleaning and lubrication, will help prolong the lifespan of these systems. By understanding the underlying mechanics and being proactive about repairs, users can effectively manage the performance of their equipment.
Choosing Quality Aro Parts
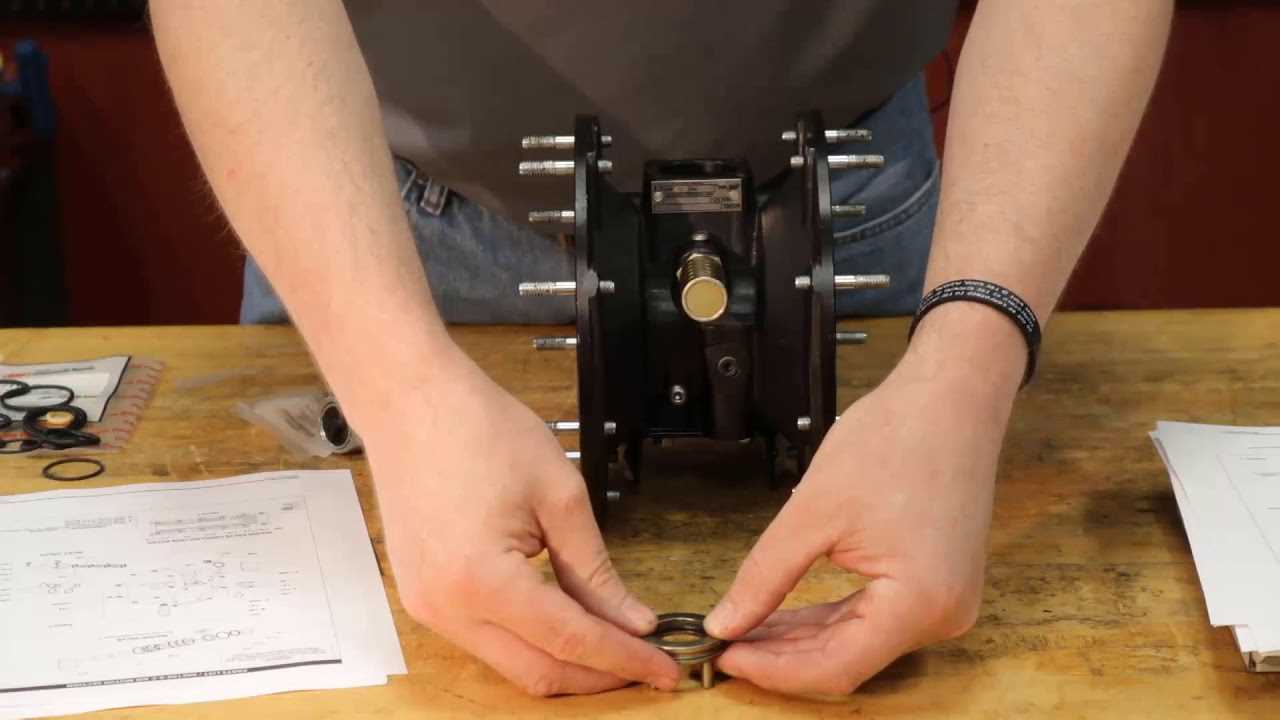

When selecting components for your equipment, the focus should be on durability and performance. High-quality elements ensure that your machinery operates efficiently and reliably, reducing the likelihood of malfunctions. Investing in top-notch materials not only enhances functionality but also extends the lifespan of your system, ultimately leading to cost savings in maintenance and repairs.
Key Factors to Consider
Before making a purchase, evaluate several crucial aspects. First, look for reputable manufacturers known for their commitment to excellence. This often includes certifications or industry standards that validate their products’ reliability. Additionally, consider the materials used; high-grade materials typically offer better resistance to wear and environmental factors.
Benefits of Quality Components
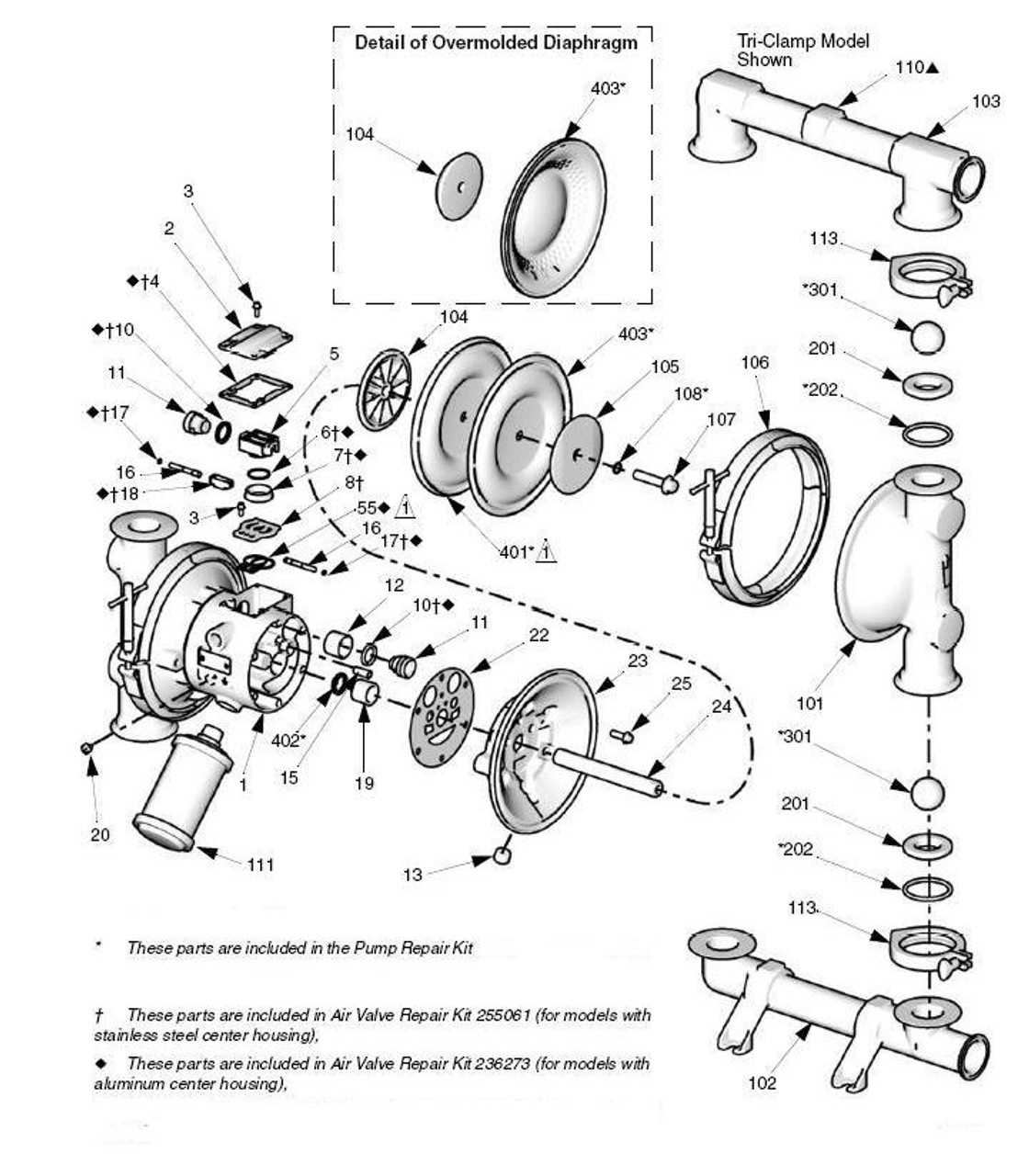
Choosing superior elements can significantly improve the overall performance of your machinery. Enhanced efficiency leads to reduced energy consumption, while greater reliability minimizes downtime. Furthermore, high-quality components can lead to improved safety, reducing risks associated with equipment failure. In the long run, prioritizing quality over cost can yield substantial benefits.
Assembly Process of Aro Pumps
The assembly of these fluid transfer devices is a crucial step in ensuring their efficiency and reliability. This process involves several systematic phases that contribute to the overall functionality of the system.
Initially, it is important to gather all necessary components, which typically include:
- Housing elements
- Seals and gaskets
- Valves and actuators
- Pistons and cylinders
- Fasteners and brackets
The following steps outline the assembly procedure:
- Preparation: Clean all components to remove any debris or contaminants that could affect performance.
- Installation of Seals: Carefully place seals and gaskets to ensure a proper fit, preventing leaks.
- Assembly of Housing: Join the housing parts together, securing them with fasteners to create a robust structure.
- Incorporation of Internal Components: Insert pistons and cylinders, ensuring they move freely and smoothly.
- Valve Integration: Install valves and actuators, verifying their alignment and function within the assembly.
- Final Checks: Conduct thorough inspections of all connections and seals, tightening fasteners as necessary.
Upon completion, testing the assembled unit under various conditions is vital to confirm its operational integrity and performance metrics. This meticulous approach ensures that the final product meets industry standards and customer expectations.
Safety Considerations with Aro Equipment
When working with fluid transfer machinery, it is crucial to prioritize safety to prevent accidents and ensure the longevity of the equipment. Understanding potential hazards and implementing proper safety measures can significantly reduce risks associated with operation and maintenance.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
- Always wear appropriate gear such as gloves, goggles, and protective clothing.
- Ensure that the footwear is suitable for slippery surfaces.
- Training and Competence:
- Operators should be well-trained in the functioning and handling of the machinery.
- Regular refresher courses can help maintain skill levels and awareness of safety protocols.
- Regular Inspections:
- Conduct routine checks for wear and tear or any signs of malfunction.
- Inspect hoses and connections to prevent leaks and pressure buildup.
- Emergency Procedures:
- Establish clear protocols for emergencies, including leaks or equipment failure.
- Ensure that all personnel are aware of evacuation routes and emergency contact numbers.
- Environment Control:
- Maintain a clean and organized workspace to minimize hazards.
- Implement measures to control spills and ensure proper drainage in the area.
By adhering to these safety considerations, users can enhance their operational efficiency while safeguarding themselves and their environment. Regular evaluation and updates to safety practices are essential for ongoing protection and effective management of fluid handling systems.
Upgrading Your Aro Pump System
Enhancing your fluid transfer system can lead to improved efficiency and performance. By investing in the latest components and technologies, you can optimize operations and extend the lifespan of your equipment. This process often involves assessing current configurations and identifying areas where upgrades can yield significant benefits.
When considering enhancements, focus on high-quality replacements and modern features that align with your specific needs. Researching compatible enhancements can lead to better flow rates, reduced energy consumption, and improved reliability. Additionally, integrating smart technology can provide real-time monitoring, ensuring your system operates at peak performance.
Don’t overlook the importance of maintenance during this transition. Regular checks and timely replacements can prevent unforeseen issues and maintain optimal functionality. By proactively addressing wear and tear, you ensure that your upgraded system continues to meet demands efficiently.