2010 Silverado Parts Diagram Overview
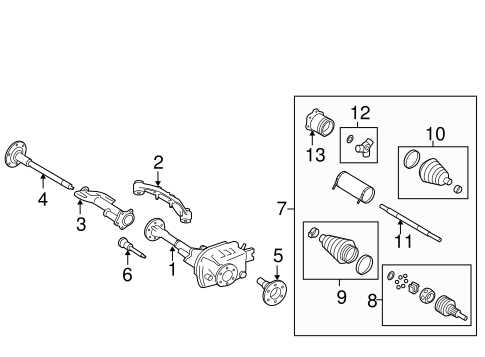
The intricate design of modern vehicles necessitates a comprehensive understanding of their individual components and how they interact with one another. This knowledge is essential not only for maintenance and repair but also for enhancing performance and ensuring safety on the road. Each vehicle model features a unique arrangement of elements, tailored to optimize functionality and efficiency.
In this discussion, we will explore a specific model from a well-known manufacturer, focusing on the arrangement and classification of various elements within its structure. By delving into this schematic representation, enthusiasts and mechanics alike can gain valuable insights into the workings of their vehicles.
Whether you are a seasoned professional or a novice owner, familiarity with the layout of these components can greatly aid in troubleshooting issues and planning upgrades. With a clear visualization, understanding the relationships and functions of each part becomes more accessible, leading to informed decisions when it comes to repairs or enhancements.
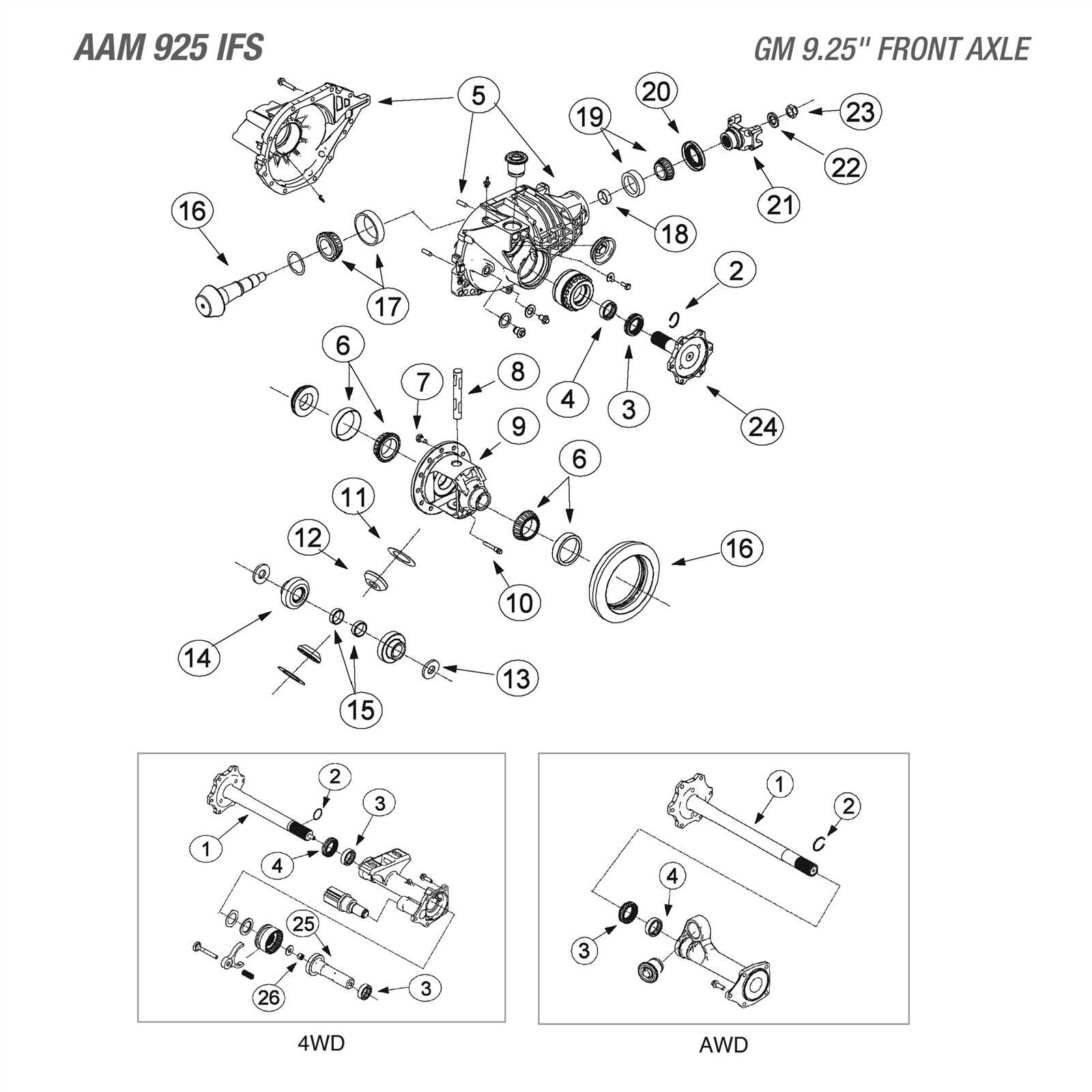
Overview of 2010 Silverado Components
This section provides a comprehensive look at the essential elements that make up a specific model of a popular truck. Understanding these components is crucial for maintenance, repair, and enhancement of the vehicle’s performance and reliability. Each segment plays a vital role in ensuring a smooth and efficient driving experience.
Key Mechanical Elements
Among the primary mechanical elements are the engine, transmission, and suspension systems. The engine serves as the powerhouse, converting fuel into motion, while the transmission facilitates the transfer of power to the wheels, allowing for variable speeds and torque. Additionally, the suspension system ensures a comfortable ride by absorbing shocks and maintaining tire contact with the road.
Electrical and Safety Features
The electrical components, including the battery and alternator, are crucial for starting the vehicle and powering various systems. Safety features, such as airbags and anti-lock braking systems, enhance driver and passenger protection. Understanding these elements allows for better troubleshooting and upgrades, ensuring the vehicle remains in optimal condition.
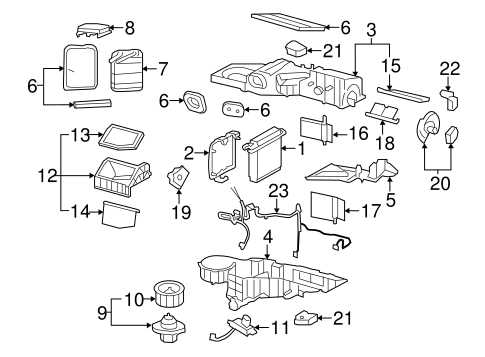
Exploring the Engine Bay Layout
The engine compartment serves as a crucial hub for various components that power a vehicle. Understanding its organization allows for more effective maintenance and troubleshooting. Each element within this area plays a specific role in the overall functionality, making familiarity with their locations and interactions essential for any enthusiast.
At the heart of the bay lies the engine itself, flanked by vital systems such as the cooling mechanism and electrical wiring. These components are meticulously arranged to optimize space and efficiency, ensuring that every part can be accessed easily for repairs or upgrades. Recognizing how these elements interact helps in identifying potential issues before they escalate.
Additionally, fluid reservoirs, including those for oil and coolant, are strategically positioned to facilitate quick checks and top-ups. Accessibility is key; thus, the layout reflects both practicality and design, encouraging regular maintenance practices that contribute to a vehicle’s longevity and performance.
Understanding the Suspension and Steering System
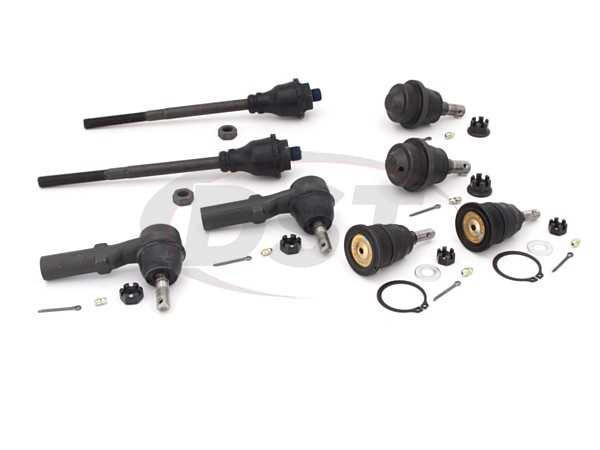
The suspension and steering mechanism plays a crucial role in vehicle dynamics, influencing both ride quality and handling characteristics. This system is responsible for connecting the vehicle’s chassis to its wheels, ensuring stability and comfort while navigating various terrains. A well-engineered assembly enhances control, minimizes vibrations, and improves safety on the road.
Key components of the suspension and steering assembly include springs, shock absorbers, control arms, and steering links. Each element works together to absorb shocks from uneven surfaces and allow precise maneuvering. Understanding how these parts interact is essential for maintenance and performance enhancement.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Springs | Support vehicle weight and absorb impacts from the road. |
| Shock Absorbers | Dampen vibrations and maintain stability during movement. |
| Control Arms | Connect the chassis to the wheels, allowing controlled wheel movement. |
| Steering Links | Transmit driver input from the steering wheel to the wheels. |
Regular inspection and maintenance of these components are vital to ensure optimal performance. Wear and tear can lead to diminished handling capabilities and safety risks. By understanding the suspension and steering system, vehicle owners can make informed decisions regarding repairs and upgrades.
Electrical System Parts and Wiring Diagram
The electrical system in a vehicle is crucial for its overall functionality, ensuring that all electronic components operate seamlessly. Understanding the various elements involved can significantly aid in troubleshooting and repairs, enhancing the performance and reliability of the automobile.
Key components of the electrical system include:
- Battery
- Alternator
- Starter motor
- Fuses and relays
- Wiring harnesses
- ECU (Electronic Control Unit)
- Sensors and actuators
When examining the wiring layout, it’s essential to identify the following:
- Power supply paths
- Ground connections
- Connector locations
- Signal transmission routes
- Component interconnections
Proper comprehension of these elements not only aids in maintaining the vehicle but also assists in making informed decisions during modifications or upgrades. Each component plays a vital role in the overall system, and understanding their relationships is fundamental for effective vehicle management.
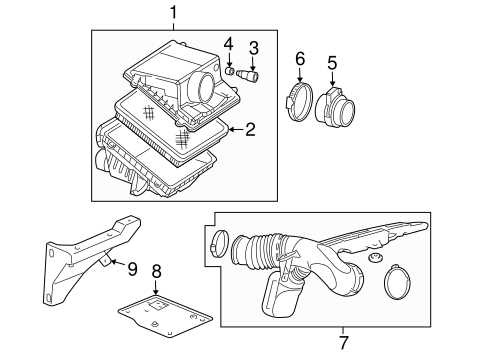
Cooling System Elements and Their Functions
The cooling system in a vehicle plays a vital role in maintaining optimal engine temperature, ensuring efficient performance and longevity. This system comprises various components, each designed to work harmoniously to prevent overheating and promote proper functioning of the engine.
Key Components

Central to the cooling system is the radiator, which dissipates heat from the coolant. The water pump circulates this coolant throughout the engine and back to the radiator, maintaining a consistent flow. Thermostats regulate the coolant temperature, allowing for efficient operation under varying conditions.
Additional Elements
Hoses transport the coolant to and from the engine and radiator, while the cooling fan aids in air circulation to enhance the radiator’s efficiency. The expansion tank serves as a reservoir for excess coolant, preventing pressure build-up and ensuring a steady supply throughout the system.
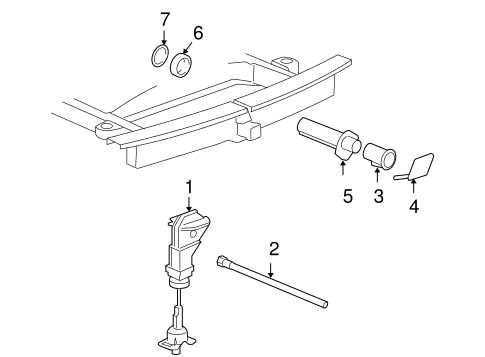
Brake Components and Replacement Tips
Understanding the key elements of a vehicle’s braking system is essential for maintaining safety and performance. Proper knowledge helps in timely replacements and ensures optimal functionality.
- Brake Pads: These are crucial for generating friction. Regular inspection is necessary to prevent damage to rotors.
- Brake Rotors: These components experience wear over time. Look for signs of warping or scoring.
- Calipers: Functionality can be affected by rust or leakage. Regular checks can prevent costly repairs.
- Brake Lines: Inspect for cracks or corrosion, as compromised lines can lead to brake failure.
Here are some tips for effective replacements:
- Always use high-quality components to ensure longevity.
- Follow manufacturer guidelines for installation to maintain performance.
- Bleed the brake system after replacing components to remove air bubbles.
- Check brake fluid levels and replace fluid periodically for optimal performance.
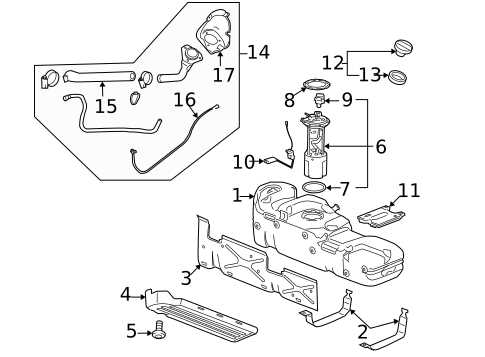
Fuel System Overview and Key Parts
The fuel system plays a crucial role in the operation of any vehicle, ensuring that the engine receives the appropriate amount of fuel for optimal performance. This system is designed to deliver fuel from the tank to the engine efficiently, while also maintaining the right pressure and ensuring cleanliness to prevent damage to internal components.
Essential Components
- Fuel Tank: The primary reservoir that stores the fuel until it is needed by the engine.
- Fuel Pump: A vital component that transports fuel from the tank to the engine, often electric or mechanical in nature.
- Fuel Filter: This element cleans the fuel, removing impurities and debris to protect the engine from damage.
- Fuel Injectors: Precision devices that atomize fuel and deliver it into the combustion chamber for efficient burning.
- Fuel Lines: Hoses or tubes that transport fuel between the tank, pump, filter, and injectors.
Functionality and Maintenance
Regular maintenance of the fuel system is essential to ensure reliability and efficiency. Key aspects include:
- Routine inspection of the fuel filter to prevent clogs.
- Checking fuel lines for leaks or damage.
- Monitoring the fuel pump’s operation to ensure proper pressure.
- Cleaning or replacing injectors to maintain optimal fuel atomization.
By understanding these components and their functions, vehicle owners can better appreciate the importance of the fuel system and take proactive steps to maintain it.
Interior Components and Control Modules
The interior of a vehicle is equipped with various elements that enhance comfort, convenience, and functionality. These components work together to create an inviting atmosphere while ensuring the driver has full control over the vehicle’s features. Understanding these components and their arrangement is essential for both maintenance and upgrades.
Key Interior Elements

Central to the cabin experience are the seating arrangements, dashboard, and control interfaces. Each seat is designed for optimal comfort, often featuring adjustable settings. The dashboard houses crucial instruments, including speedometers and fuel gauges, providing vital information at a glance. Control interfaces, such as touchscreens and buttons, allow users to navigate through entertainment, climate control, and navigation systems seamlessly.
Control Modules and Their Functions
Control modules are the brains behind many of the vehicle’s electronic systems. They manage everything from lighting and infotainment to climate settings. Each module communicates with others, ensuring that adjustments made by the user are executed promptly. Understanding the layout and function of these modules is important for troubleshooting and ensuring optimal performance.
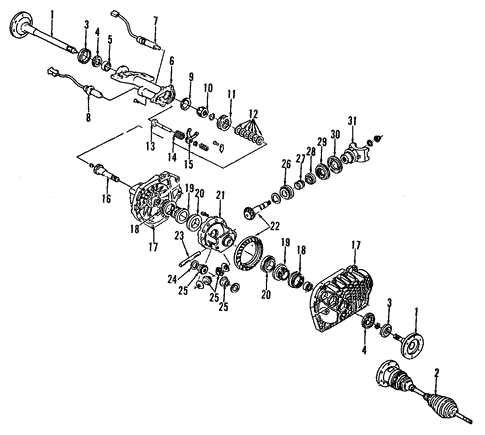
Transmission Diagram with Key Connections
This section explores the intricate layout of the transmission system, highlighting essential linkages and components that ensure seamless operation. Understanding these connections is crucial for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Transmission Control Module | Manages shifting and performance of the transmission |
| Gear Selector | Allows the driver to select the desired gear |
| Shift Linkage | Connects the gear selector to the transmission |
| Torque Converter | Transfers power from the engine to the transmission |
| Transmission Fluid Cooler | Regulates temperature to maintain optimal fluid conditions |
Exhaust System Layout and Common Issues
The exhaust assembly plays a crucial role in managing engine emissions and maintaining optimal performance. Understanding its configuration and potential problems can aid in timely maintenance and repairs.
Key components of the exhaust system include:
- Exhaust manifold
- Catalytic converter
- Muffler
- Exhaust pipes
- Oxygen sensors
Common issues that may arise within this system are:
- Leaks: Often caused by rust or damaged seals, leading to decreased efficiency.
- Clogs: Accumulation of carbon deposits can restrict flow, impacting performance.
- Rattling noises: These may indicate loose components or internal damage.
- Check engine light: Triggered by sensor malfunctions or emission failures.
Regular inspection and maintenance are essential to ensure the longevity and functionality of the exhaust assembly.
Body Panels and Exterior Attachments

The integrity and aesthetic appeal of any vehicle greatly depend on its outer shell and components. These elements not only contribute to the overall design but also serve functional purposes, such as protecting the internal mechanics and ensuring aerodynamics. Understanding the various components involved can enhance maintenance and customization efforts.
Key Components
Outer surfaces consist of essential elements like fenders, hoods, and doors, which are crucial for both safety and style. Fenders shield the wheels, while hoods provide access to the engine compartment. The doors, of course, are vital for entry and exit, blending functionality with the vehicle’s visual identity.
Attachment Methods
Exterior components are typically secured using a variety of fasteners and clips. Understanding these attachment techniques is important for anyone looking to replace or upgrade parts. Using the correct tools and methods ensures a secure fit, contributing to the vehicle’s longevity and performance.