Understanding Briggs Stratton Parts Diagram for Efficient Maintenance
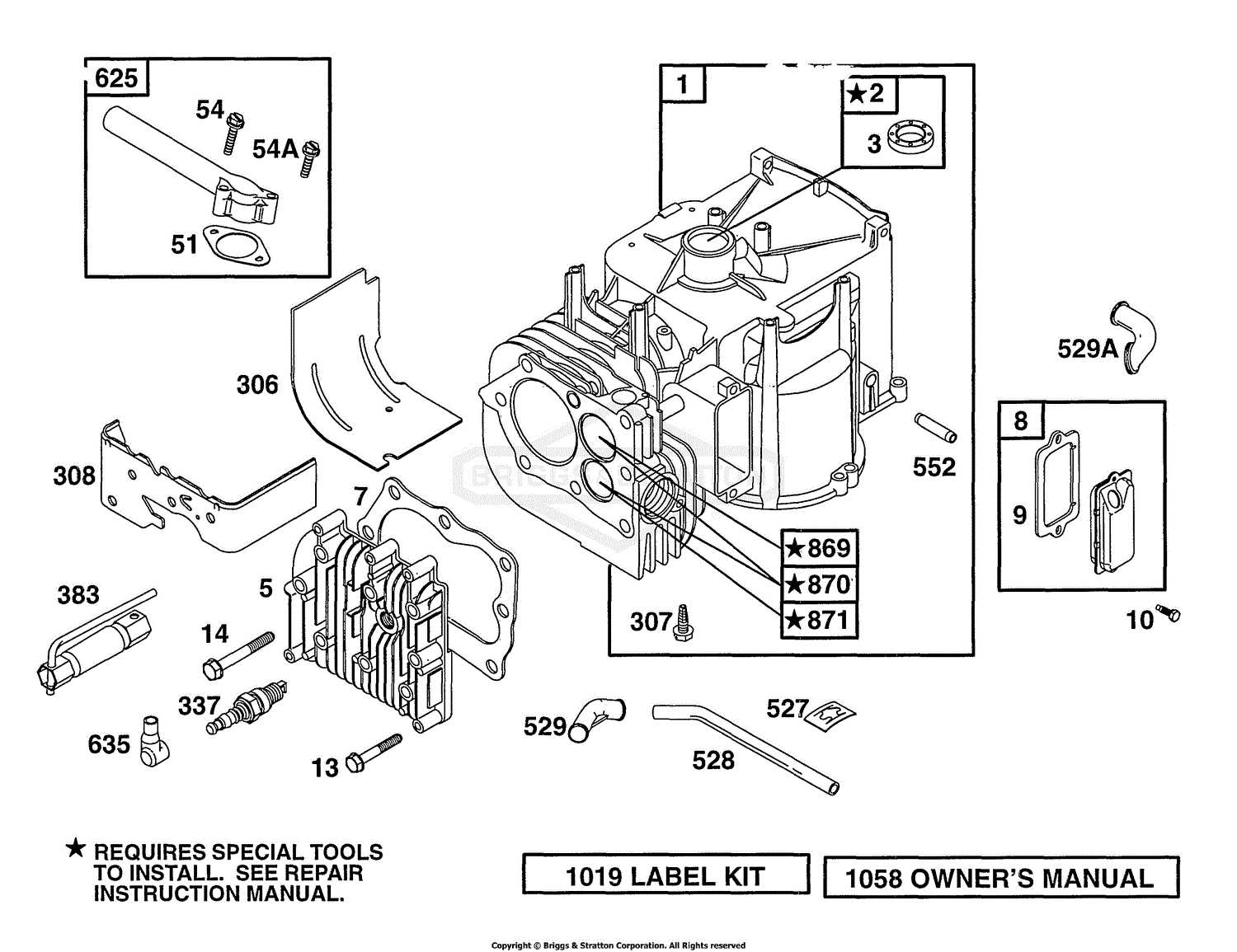
Understanding the internal structure of engine systems can greatly enhance your ability to maintain and repair mechanical equipment. Each part plays a critical role in ensuring that the machine runs smoothly and efficiently. By familiarizing yourself with the placement and function of these elements, you can diagnose issues and perform regular upkeep with confidence.
Whether you’re working on small engines or larger machines, having a clear view of how the components are arranged helps streamline the repair process. Knowing where everything fits and how each piece interacts with others can reduce downtime and prevent costly mistakes.
In this guide, we’ll walk through the most important areas of engine construction, focusing on the different sections and their purposes. This will serve as a valuable resource for anyone looking to improve their understanding of mechanical layouts and ensure long-term performance.
Briggs Stratton Engine Component Overview
The internal structure of small engines is comprised of various essential elements that work together to ensure smooth operation and optimal performance. Understanding how these components interact can help with maintenance and troubleshooting, ensuring the machine functions efficiently over time.
Main Internal Elements
At the core of the motor lies the piston, which moves within the cylinder to convert fuel into mechanical power. Another vital part is the crankshaft, which transforms the piston’s motion into rotational energy that drives the external equipment. Additionally, the valves manage the intake of air and fuel while regulating the exhaust gases.
Supporting Mechanisms
Other key systems include the cooling mechanism, which prevents overheating, and the lubrication system that reduces friction between moving parts, prolonging the engine’s lifespan. Together, these elements create a reliable and powerful machine when properly maintained.
Identifying Key Parts of the Engine
Understanding the main components of an internal combustion engine is crucial for proper maintenance and troubleshooting. Each element plays a specific role in ensuring the machine operates efficiently and reliably.
Main Components
The engine is composed of several essential parts, including the cylinder, piston, and valve system. These components work together to control the flow of air and fuel, which powers the motor.
Other Essential Elements
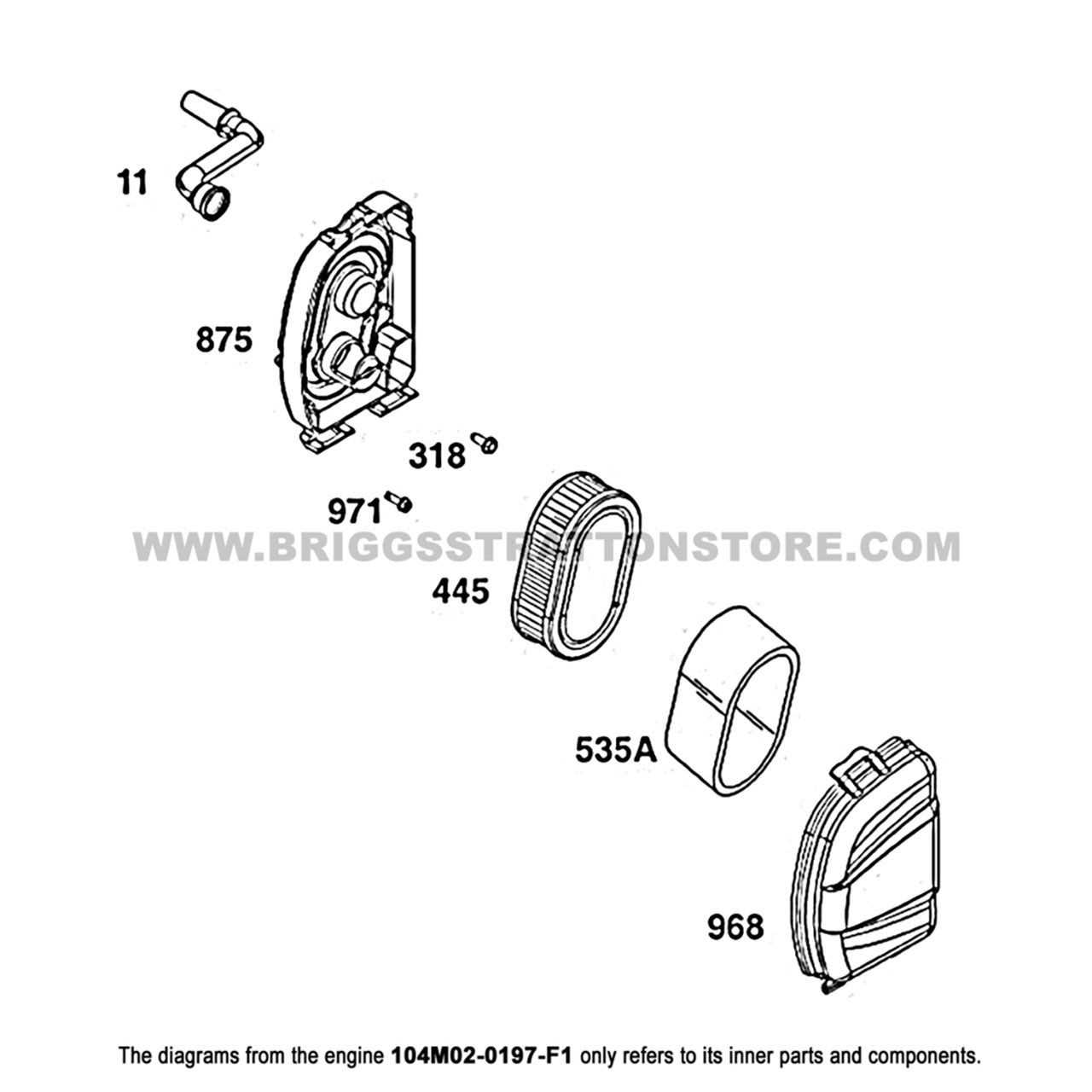
Additional critical parts include the crankshaft and camshaft, which convert the linear motion of the piston into rotational energy, powering other systems connected to the engine.
Common Issues with Briggs Stratton Engines
Many small engines face recurring problems that can impact their performance and reliability. Understanding these typical malfunctions can help users identify and resolve issues before they become major setbacks.
- Starting Problems: One of the most frequent complaints is difficulty getting the engine to start. This can be caused by a variety of factors, including a clogged fuel filter or dirty spark plug.
- Overheating: Prolonged use or insufficient ventilation can lead to engines overheating, potentially damaging internal components if not addressed promptly.
- Poor Fuel Efficiency: Engines may consume more fuel than usual due to issues with the carburetor or improper air-fuel mixture.
- Unusual Noises: Grinding or knocking sounds could indicate loose or worn parts inside the engine, requiring immediate attention.
- Loss of Power: If the engine struggles to maintain power or suddenly shuts off, this could point to blockages in the exhaust or air filter.
Addressing these problems early can significantly extend the lifespan of small engines and ensure smooth, efficient operation.
Fuel System Breakdown for Efficient Maintenance
The fuel system is a crucial component that ensures the smooth functioning of the engine by providing the necessary energy. Proper understanding of its layout and regular upkeep can prevent common issues, leading to more reliable performance and prolonged engine life. This section will outline key elements of the fuel delivery process and suggest best practices for maintaining them efficiently.
- Fuel Tank: Responsible for storing the fuel, it’s important to inspect for leaks or debris that could contaminate the supply.
- Fuel Line: Transports fuel from the tank to the engine. Ensure that the lines are free from cracks or blockages to avoid interruptions in fuel flow.
- Carburetor: Regulates the fuel-air mixture. Regular cleaning of this component is essential to avoid build-up that could impair engine efficiency.
- Fuel Filter: Removes impurities from the fuel. Replacing this filter periodically will keep the fuel clean and protect the engine from contaminants.
By following these steps, you can ensure a well-maintained fuel system, leading to improved engine performance and fewer breakdowns.
Understanding the Ignition System Functionality
The ignition system plays a crucial role in starting and operating an engine by creating the spark needed to ignite the air-fuel mixture. This process ensures that the engine runs smoothly and efficiently. Without a proper ignition sequence, combustion wouldn’t take place, making engine operation impossible.
To gain a deeper insight into how this mechanism works, let’s explore its main components and their functions:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Spark Plug | Generates the spark that ignites the fuel-air mixture in the combustion chamber. |
| Ignition Coil | Converts the low voltage from the battery into the high voltage needed to create a spark. |
| Flywheel | Works with the magneto to generate the electric charge for the ignition system. |
| Magneto | Produces the electrical energy that powers the spark plug, ensuring the engine starts and runs. |
These key
Air Filters: Importance and Replacement Tips
Air filtration systems play a crucial role in ensuring optimal performance and longevity of engines. These components prevent contaminants from entering the machinery, which can lead to damage and reduced efficiency. Regular maintenance of these filters is essential for maintaining the health of your equipment.
Why Air Filters Matter
Proper air circulation is vital for the combustion process in engines. Clean air filters facilitate efficient airflow, enhancing power output and fuel efficiency. When these filters become clogged with dirt and debris, they restrict airflow, resulting in poor performance and increased emissions.
Replacement Guidelines
To ensure your machinery runs smoothly, follow these replacement guidelines:
| Indicator for Replacement | Recommended Frequency |
|---|---|
| Visible dirt or discoloration | Every 25 hours of use |
| Decrease in engine performance | As needed |
| Annual maintenance check | At least once a year |
Regularly inspecting and replacing air filters ensures that your engine operates efficiently and reliably, ultimately prolonging its lifespan.
Carburetor Parts and Cleaning Procedures
The carburetor is a vital component in internal combustion engines, responsible for mixing air and fuel to facilitate combustion. Proper maintenance and cleaning of this assembly ensure optimal performance and longevity. Understanding its structure and function is crucial for effective upkeep.
Components of the Carburetor
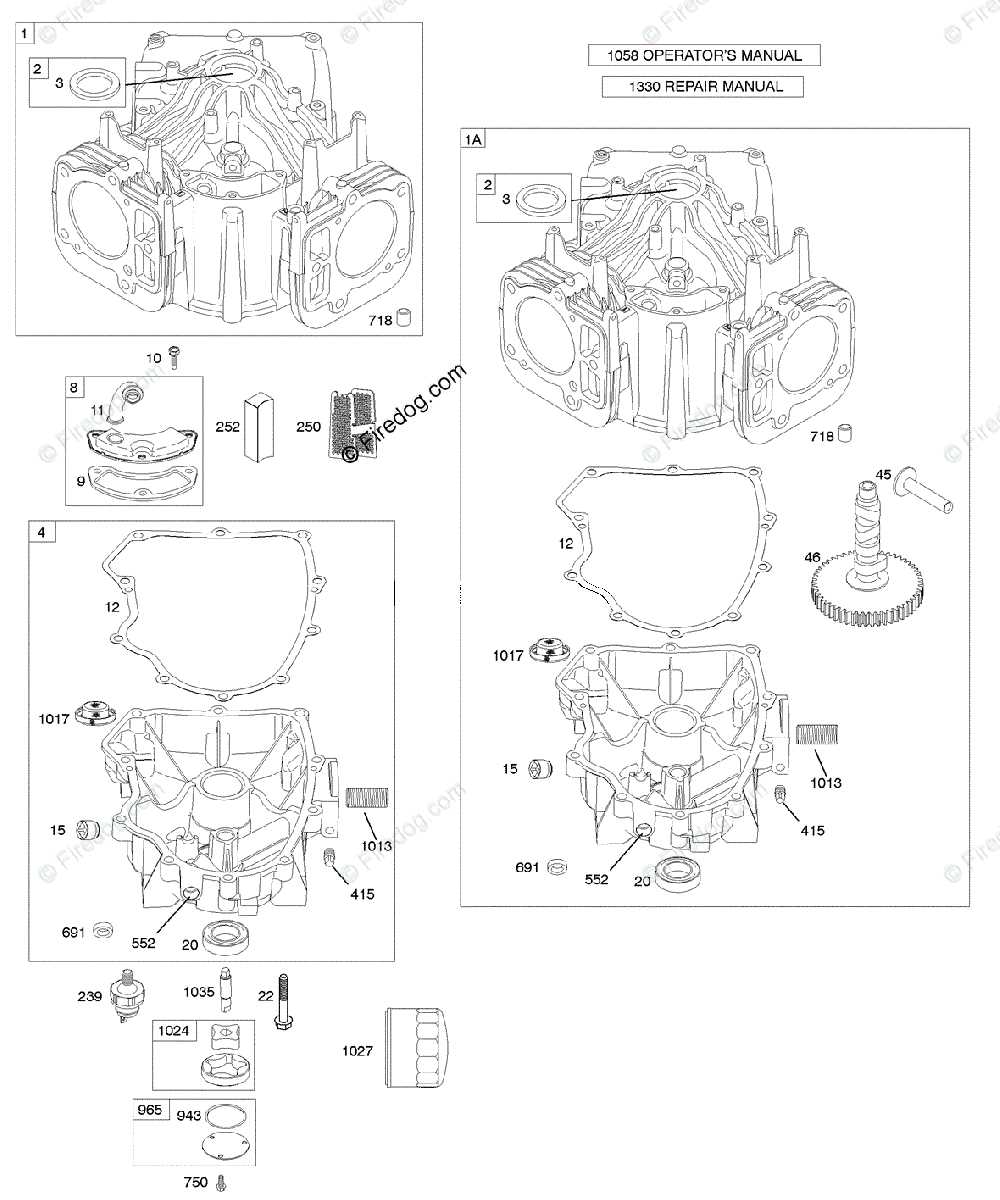
Various elements contribute to the functionality of the carburetor. Each component plays a specific role in regulating the air-fuel mixture. Familiarity with these parts aids in troubleshooting and maintenance tasks.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Float | Regulates the fuel level within the bowl, ensuring a consistent supply. |
| Jet | Controls the amount of fuel that enters the air stream, impacting performance. |
| Throttle Valve | Regulates the flow of air and fuel mixture into the engine. |
| Choke | Aids in starting the engine by restricting airflow and enriching the mixture. |
Cleaning Procedures
Regular cleaning of the carburetor is essential for preventing buildup that can hinder performance. Begin by removing the carburetor from the engine, ensuring all connections are properly detached. Utilize a suitable cleaning solution to remove residue, focusing on the jets and passages. Rinse thoroughly and allow it to dry before reassembling and reinstalling it on the engine.
Troubleshooting Electrical Components in Briggs Engines
Diagnosing issues with electrical systems in small engines can be challenging yet essential for optimal performance. A methodical approach helps identify and resolve problems effectively, ensuring that the machinery operates smoothly. Below are key steps and considerations to assist in troubleshooting electrical components.
Common Electrical Issues

- Battery failure: Check for corrosion or loose connections.
- Faulty ignition system: Inspect spark plugs and ignition coils for damage.
- Wiring problems: Look for frayed wires or poor connections that may disrupt power flow.
- Starter motor issues: Test the starter for proper function and connection.
Diagnostic Steps
- Begin by checking the battery charge and connections.
- Inspect the ignition components to ensure they are functioning correctly.
- Examine all wiring for any visible damage or wear.
- Test the starter motor to confirm it engages properly.
- Utilize a multimeter to measure voltage and continuity in the electrical system.
Oil and Lubrication System Explored
The efficiency and longevity of small engines greatly depend on the effectiveness of their lubrication systems. Proper oil management is essential to minimize friction, reduce wear, and enhance overall performance. This section delves into the various components and functions of the lubrication system, emphasizing its crucial role in maintaining engine health.
Key Components of the Lubrication System
The lubrication system comprises several critical elements that work together to ensure optimal engine function. These include the oil pump, oil filter, and various oil passages. Each component plays a specific role in circulating and filtering oil to maintain a clean and efficient operation.
Importance of Regular Maintenance
Routine checks and maintenance of the lubrication system are vital for sustaining engine performance. Regular oil changes, inspections of filters, and monitoring of oil levels can prevent potential issues and prolong the life of the engine. Neglecting these aspects can lead to increased friction, overheating, and ultimately, engine failure.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Oil Pump | Circulates oil throughout the engine. |
| Oil Filter | Removes impurities and contaminants from the oil. |
| Oil Passages | Channels through which oil flows to various engine parts. |
Signs of Wear in Moving Parts
Understanding the indicators of deterioration in mechanical components is essential for maintaining optimal performance. Various factors can lead to wear, resulting in reduced efficiency and potential failures. Recognizing these signs early can help prevent more significant issues and extend the lifespan of the machinery.
Visual Indicators
One of the primary ways to detect wear is through visual inspection. Look for scratches, cracks, or discoloration on surfaces that experience friction. Any abnormal changes in color or texture may suggest that components are degrading and may require attention.
Auditory Signs
Listening for unusual noises can also provide valuable insights into the condition of moving components. Grinding, clattering, or any irregular sounds during operation may indicate misalignment or excessive wear. Addressing these auditory signs promptly can prevent further damage and maintain the integrity of the system.
Maintaining Cooling Systems for Longevity
Ensuring the efficiency of cooling mechanisms is crucial for the prolonged performance of machinery. Regular maintenance not only enhances functionality but also extends the lifespan of essential components. Adopting systematic care practices can lead to significant improvements in performance and reliability.
To achieve optimal results, consider the following essential maintenance practices:
- Regular Inspections: Conduct thorough checks to identify wear and tear or any potential issues before they escalate.
- Cleaning Components: Remove dirt, debris, and buildup from cooling fins and air passages to ensure proper airflow.
- Fluid Checks: Monitor coolant levels and quality, replacing fluids as necessary to prevent overheating.
- Thermostat Functionality: Ensure that the thermostat operates correctly, as it regulates the temperature effectively.
- Belts and Hoses: Inspect belts and hoses for cracks or signs of deterioration, replacing them when needed.
By implementing these strategies, operators can significantly enhance the efficiency and reliability of cooling systems, leading to a longer service life and improved performance.